Abstract
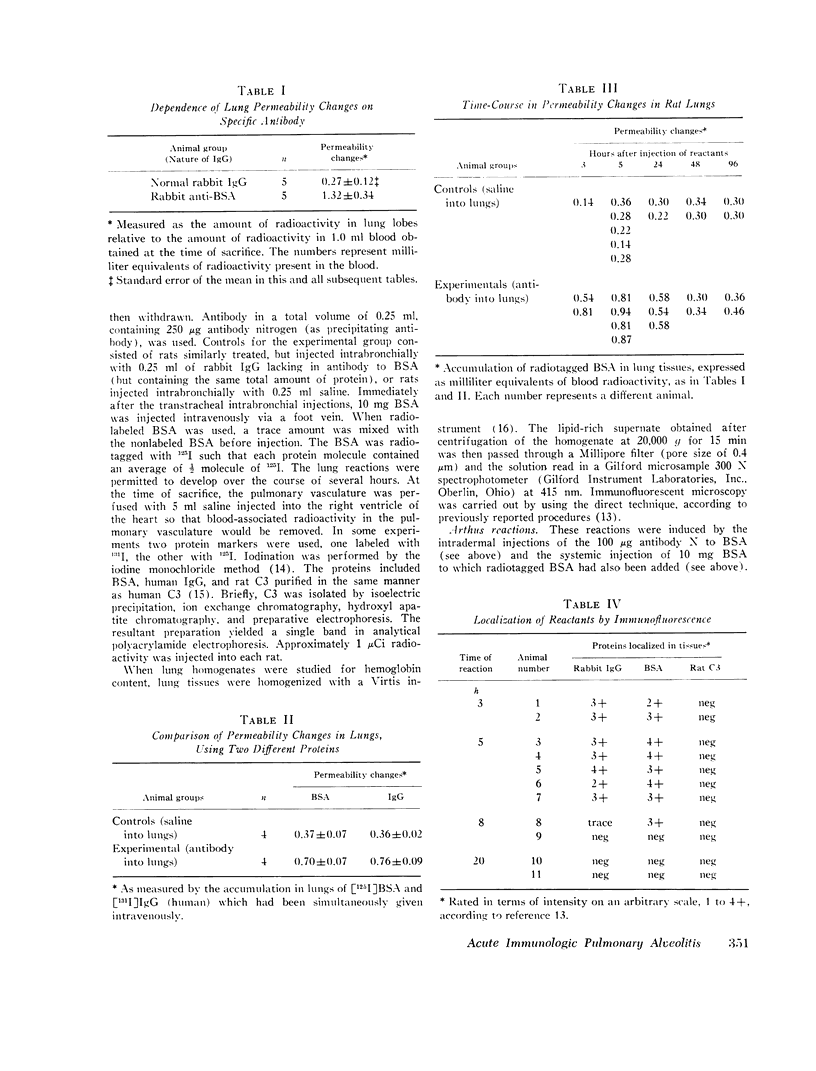
Acute immunologic injury of rat lung has been induced by the intrabronchial injection of heterologous antibody and the intravenous injection of radiolabeled antigen. Within 4 h an acute hemorrhagic neutrophil-rich exudate develops in alveolar and interstitial areas and then gradually fades. Lung injury in this model can be quantitated by measurements of increased vascular permeability and extractable hemoglobin. By the use of immunofluorescent techniques, alveolar and interstitial deposits of antigen and antibody have been demonstrated, but not the third component of complement (C3). Although not found in relation to immune complexes, C3 is nevertheless present in damaged lung as measured by accumulation of radiolabeled C3 from the circulation. Ablation experiments indicate the requirement for both circulating neutrophils and C3 for the development of lung injury. These studies provide definition for the development of lung damage induced by immune complexes.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballow M., Cochrane C. G. Two anticomplementary factors in cobra venom: hemolysis of guinea pig erythrocytes by one of them. J Immunol. 1969 Nov;103(5):944–952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COCHRANE C. G., UNANUE E. R., DIXON F. J. A ROLE OF POLYMORPHONUCLEAR LEUKOCYTES AND COMPLEMENT IN NEPHROTOXIC NEPHRITIS. J Exp Med. 1965 Jul 1;122:99–116. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.1.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COCHRANE C. G., WEIGLE W. O., DIXON F. J. The role of polymorphonuclear leukocytes in the initiation and cessation of the Arthus vasculitis. J Exp Med. 1959 Sep 1;110:481–494. doi: 10.1084/jem.110.3.481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon P. R., Walsh T. E., Marshall C. E. Acute local anaphylactic inflammation of the lungs. Am J Pathol. 1941 Sep;17(5):777–784.3. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eastham W. N., Muller H. K. Changes in guinea-pig lungs following the inhalation of powdered egg albumen. Pathology. 1972 Jul;4(3):235–241. doi: 10.3109/00313027209068946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HELMKAMP R. W., GOODLAND R. L., BALE W. F., SPAR I. L., MUTSCHLER L. E. High specific activity iodination of gamma-globulin with iodine-131 monochloride. ORINS Rep US At Energy Comm. 1960 Mar 31;UR-568:1–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagadorn J. E., Vazquez J. J., Kinney T. R. Immunopathologic studies of an experimental model resembling Goodpasture's syndrome. Am J Pathol. 1969 Oct;57(1):17–30. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill J. H., Ward P. A. C3 leukotactic factors produced by a tissue protease. J Exp Med. 1969 Sep 1;130(3):505–518. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.3.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill J. H., Ward P. A. The phlogistic role of C3 leukotactic fragments in myocardial infarcts of rats. J Exp Med. 1971 Apr 1;133(4):885–900. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.4.885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koffler D., Sandson J., Carr R., Kunkel H. G. Immunologic studies concerning the pulmonary lesions in Goodpasture's syndrome. Am J Pathol. 1969 Feb;54(2):293–305. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCombs R. P. Diseases due to immunologic reactions in the lungs (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1972 Jun 1;286(22):1186–1194. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197206012862205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKINNON G. E., ANDREWS E. C., Jr, HEPTINSTALL R. H., GERMUTH F. G., Jr An immunohistologic study on the occurrence of intravascular antigen-antibody precipitation and its role in anaphylaxis in the rabbit. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1957 Nov;101(5):258–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys J. Hypersensitivity diseases of the lungs due to fungi and organic dusts. Monogr Allergy. 1969;4:1–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richerson H. B., Cheng F. H., Bauserman S. C. Acute experimental hypersensitivity pneumonitis in rabbits. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1971 Oct;104(4):568–575. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1971.104.4.568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Dixon F. J. Experimental glomerulonephritis: immunological events and pathogenetic mechanisms. Adv Immunol. 1967;6:1–90. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60521-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARD P. A., COCHRANE C. G. BOUND COMPLEMENT AND IMMUNOLOGIC INJURY OF BLOOD VESSELS. J Exp Med. 1965 Feb 1;121:215–234. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.2.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willoughby W. F., Dixon F. J. Experimental hemorrhagic pneumonitis produced by heterologous anti-lung antibody. J Immunol. 1970 Jan;104(1):28–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





