Abstract
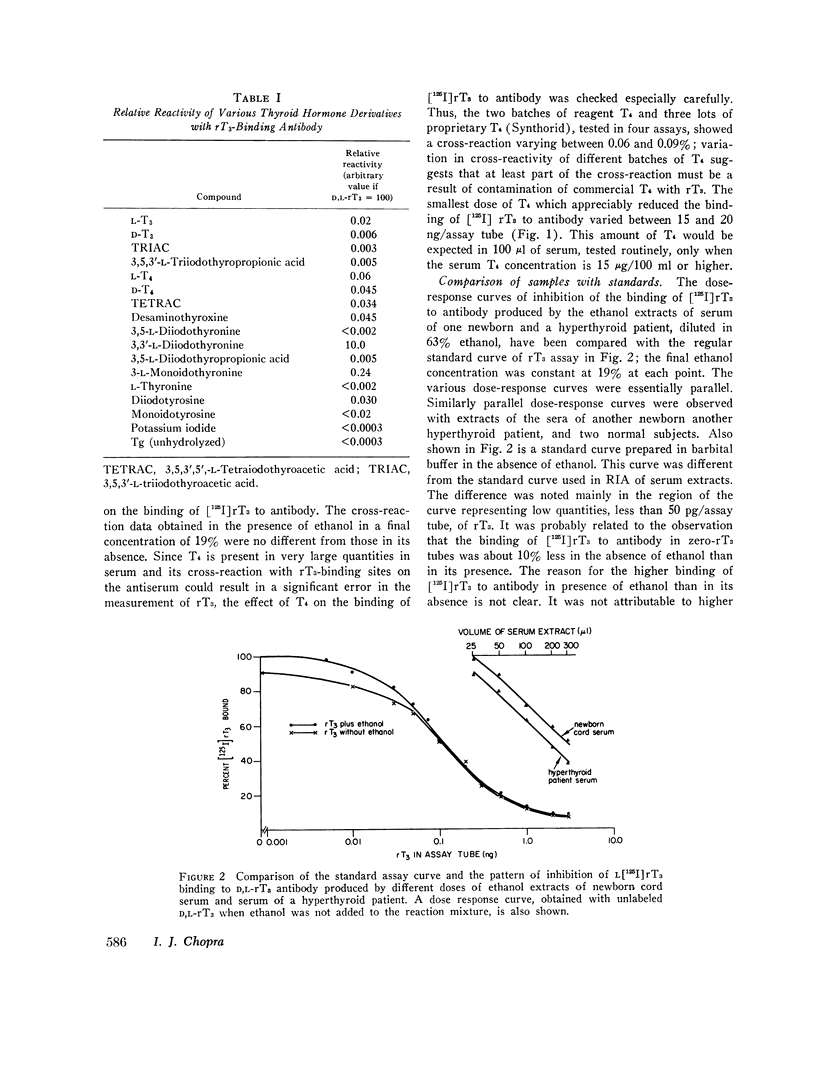
A highly specific antiserum to 3,3′,5′-triiodothyronine (reverse T3, rT3) was prepared by immunization of rabbits with D,L-rT3-human serum albumin conjugate. Of the various thyroid hormone derivatives tested, only 3,3′-diiodothyronine (3,3′-T2) cross-reacted significantly (10%) with rT3-binding sites on the antiserum, while thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) cross-reacted by less than 0.1%. The antiserum was used in a simple, sensitive, precise, and reproducible radioimmunoassay (RIA) for measurement of rT3 in ethanolic extracts of serum. The dose-response curves of inhibition of the binding of [125I]rT3 to antibody obtained by serial dilutions of serum extracts were essentially parallel to the standard assay curve. Recovery of nonradioactive rT3 added to serum before extraction averaged 93%.
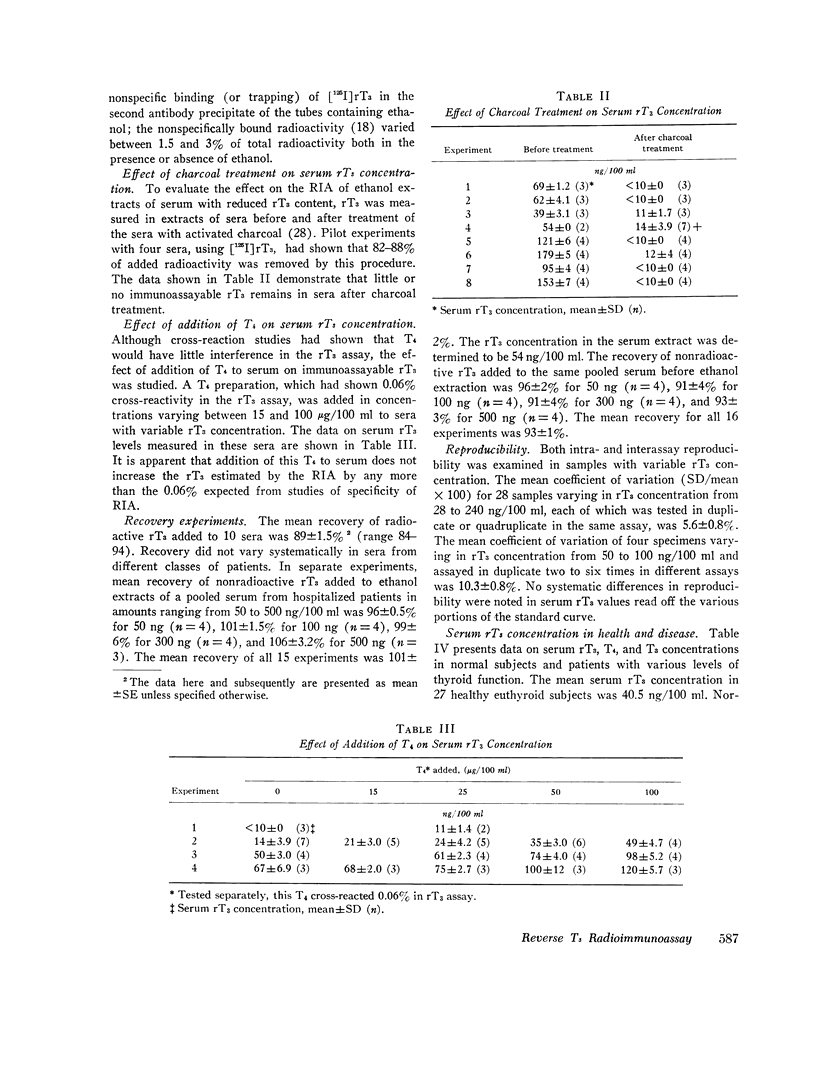
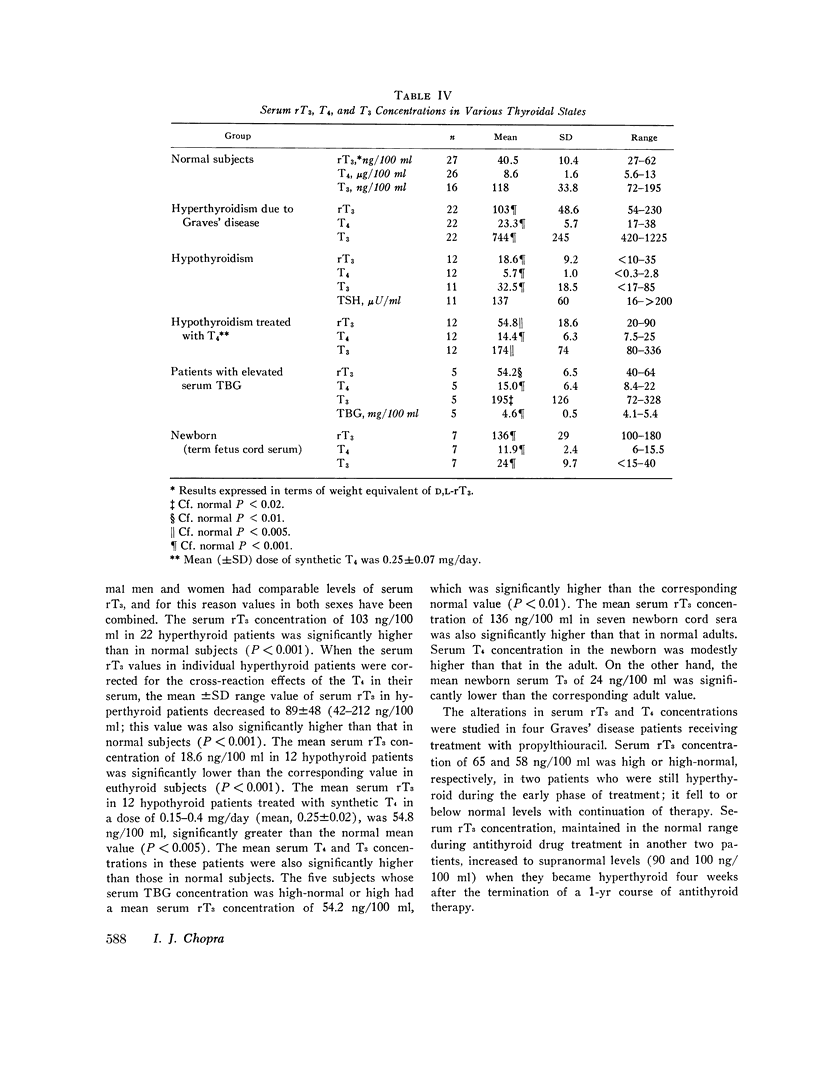
Serum rT3 concentrations were found to be (mean±SD) 41±10 ng/100 ml in 27 normal subjects, 103±49 ng/100 ml in 22 hyperthyroid patients, 19±9 ng/100 ml in 12 hypothyroid patients, and 54±7 ng/100 ml in five subjects with elevated serum thyroxine-binding globulin: the values in each of the latter three groups of individuals were significantly different from normal. Reverse T3 was detected regularly in normal or supranormal concentrations in serum of 12 hypothyroid patients rendered euthyroid or mildly hyperthyroid by treatment with synthetic T4. It is suggested that serum rT3 values noted here should be taken to reflect the relative changes in serum rT3 rather than its absolute values in health and thyroid disease. True serum rT3 may be somewhat different because: (a) D.L-rT3 employed in the standard curve and L-rT3 present in human serum may react differently with anti-D,L-rT2. (b) Even though 3,3′-T2, which cross-reacted 10% in rT3 RIA, has been considered unlikely to be present in human serum, it may circulate in low levels. (c) Cross-reaction of T4 in rT3 RIA of 0.06% although small, could contribute to RIA estimates of rT2; the effect of T4 would be particularly important in case of serum of hyperthyroid patients. Thus, serum rT3 concentration in hyperthyroid patients averaged 89±48 μg/100 ml after correction for cross-reaction effects of T4: this value was about 14% lower than that before correction (see above).
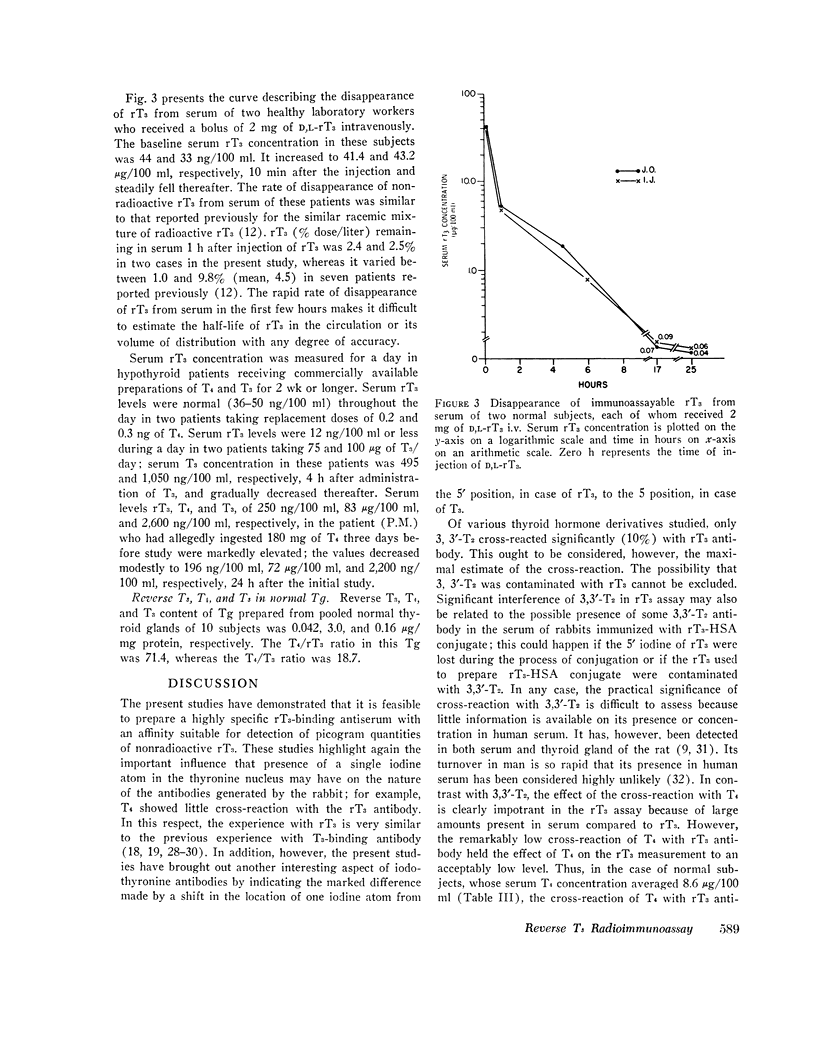
Serum rT3 concentration in cord sera of seven newborns averaged 136±19 ng/100 ml; it was clearly elevated and within the range of values seen in hyperthyroid patients. This was the case when the mean T4 concentration in the newborn cord sera was moderately higher than normal and about one-half that in hyperthyroid patients, whereas serum T3 was markedly below the normal adult level. A Pronase hydrolysate of thyroglobulin prepared from pooled normal thyroid glands contained 0.042, 3.0, and 0.16 μg/mg protein of rT3, T4, and T3, respectively. The various data suggest that: (a) rT3 is a normal component of human serum and thyroglobulin: (b) peripheral metabolism of T4 is an important source of the rT3 present in serum: (c) peripheral conversion of T4 to T3 and rT3 may not necessarily be a random process.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARKER S. B., PITTMAN C. S., PITTMAN J. A., Jr, HILL S. R., Jr Thyroxine antagonism by partially iodinated thyronines and analogues. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Apr 23;86:545–562. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb42828.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braverman L. E., Ingbar S. H., Sterling K. Conversion of thyroxine (T4) to triiodothyronine (T3) in athyreotic human subjects. J Clin Invest. 1970 May;49(5):855–864. doi: 10.1172/JCI106304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I. J. A radioimmunoassay for measurement of thyroxine in unextracted serum. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1972 Jun;34(6):938–947. doi: 10.1210/jcem-34-6-938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I. J., Fisher D. A., Solomon D. H., Beall G. N. Thyroxine and triiodothyronine in the human thyroid. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1973 Feb;36(2):311–316. doi: 10.1210/jcem-36-2-311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I. J., Ho R. S., Lam R. An improved radioimmunoassay of triiodothyronine in serum: its application to clinical and physiological studies. J Lab Clin Med. 1972 Nov;80(5):729–739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I. J., Nelson J. C., Solomon D. H., Beall G. N. Production of antibodies specifically binding triiodothyronine and thyroxine. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Mar;32(3):299–308. doi: 10.1210/jcem-32-3-299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I. J., Solomon D. H., Beall G. N. Radioimmunoassay for measurement of triiodothyronine in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1971 Oct;50(10):2033–2041. doi: 10.1172/JCI106696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I. J., Solomon D. H., Chua Teco G. N. Thyroxine: just a prohormone or a hormone too? J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1973 Jun;36(6):1050–1057. doi: 10.1210/jcem-36-6-1050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I. J., Solomon D. H., Ho R. S. A radioimmunoassay of thyroxine. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Nov;33(5):865–868. doi: 10.1210/jcem-33-5-865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I. J., Solomon D. H., Ho R. S. Competitive ligand-binding assay for measurement of thyronine-binding globulin (TBG). J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1972 Oct;35(4):565–573. doi: 10.1210/jcem-35-4-565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUNN J. T., STANBURY J. B. The metabolism of 3:3':5'-triiodothyronine in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1958 Jul;18(7):713–720. doi: 10.1210/jcem-18-7-713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca H. F. The kidney as an endocrine organ for the production of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D 3 , a calcium-mobilizing hormone. N Engl J Med. 1973 Aug 16;289(7):359–365. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197308162890710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ETLING N., MICHEL R., NUNEZ J., ROCHE J. Sur le métabolisme de la 3:3':5'-triiodothyronine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1956 Dec;22(3):550–557. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(56)90067-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher D. A., Chopra I. J., Dussault J. H. Extrathyroidal conversion of thyroxine to triiodothyronine in sheep. Endocrinology. 1972 Oct;91(4):1141–1144. doi: 10.1210/endo-91-4-1141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher D. A., Dussault J. H., Erenberg A., Lam R. W. Thyroxine and triiodothyronine metabolism in maternal and fetal sheep. Pediatr Res. 1972 Dec;6(12):894–899. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197212000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher D. A., Dussault J. H., Hobel C. J., Lam R. Serum and thyroid gland triiodothyronine in the human fetus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1973 Feb;36(2):397–400. doi: 10.1210/jcem-36-2-397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS J., PITT-RIVERS R., TROTTER W. R. Effect of 3:5:3'-L-triiodothyronine in myxoedema. Lancet. 1952 May 24;1(6717):1044–1045. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(52)90695-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gharib H., Ryan R. J., Mayberry W. E., Hockert T. Radioimmunoassay for triiodothyronine (T 3 ): I. Affinity and specificity of the antibody for T 3 . J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Sep;33(3):509–516. doi: 10.1210/jcem-33-3-509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue K., Taurog A. Digestion of 131I-labeled thyroid tissue with maximum recovery of 131I-iodothyronines. Endocrinology. 1967 Aug;81(2):319–332. doi: 10.1210/endo-81-2-319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen P. R. Direct immunoassay of triiodothyronine in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1972 Aug;51(8):1939–1949. doi: 10.1172/JCI107000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieblich J., Utiger R. D. Triiodothyronine radioimmunoassay. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jan;51(1):157–166. doi: 10.1172/JCI106786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORGAN C. R., SORENSON R. L., LAZAROW A. STUDIES OF AN INHIBITOR OF THE TWO ANTIBODY IMMUNOASSAY SYSTEM. Diabetes. 1964 Jan-Feb;13:1–5. doi: 10.2337/diab.13.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuma T., Nihei N., Gershengorn M. C., Hollander C. S. Serum triiodothyronine: measurements in human serum by radioimmunoassay with corroboration by gas-liquid chromatography. J Clin Invest. 1971 Dec;50(12):2679–2688. doi: 10.1172/JCI106769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odell W. D., Wilber J. F., Utiger R. D. Studies of thyrotropin physiology by means of radioimmunoassay. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1967;23:47–85. doi: 10.1016/b978-1-4831-9826-2.50005-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver G. C., Jr, Parker B. M., Brasfield D. L., Parker C. W. The measurement of digitoxin in human serum by radioimmunoassay. J Clin Invest. 1968 May;47(5):1035–1042. doi: 10.1172/JCI105793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omdahl J. L., DeLuca H. F. Regulation of vitamin D metabolism and function. Physiol Rev. 1973 Apr;53(2):327–372. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1973.53.2.327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer J. H., Schwartz H. L., Surks M. I. Propylthiouracil inhibits the conversion of L-thyroxine to L-triiodothyronine. An explanation of the antithyroxine effect of propylthiouracil and evidence supporting the concept that triiodothyronine is the active thyroid hormone. J Clin Invest. 1972 Sep;51(9):2493–2497. doi: 10.1172/JCI107063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PITMAN C. S., BARKER S. B. Inhibition of thyroxine action by 3,3',5'-triiodothyronine. Endocrinology. 1959 Mar;64(3):466–468. doi: 10.1210/endo-64-3-466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PITT-RIVERS R., STANBURY J. B., RAPP B. Conversion of thyroxine to 3-5-3'-triiodothyronine in vivo. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1955 May;15(5):616–620. doi: 10.1210/jcem-15-5-616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PITTMAN C. S., SHINOHARA M., THRASHER H., MCCRAW E. F. EFFECT OF THYROXINE ANALOGUES ON THE PERIPHERAL METABOLISM OF THYROXINE: THE HALF-LIFE AND PATTERN OF ELIMINATION. Endocrinology. 1964 Apr;74:611–616. doi: 10.1210/endo-74-4-611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PITTMAN J. A., BROWN R. W., REGISTER H. B., Jr Biological activity of 3,3',5'-triiodo-DL-thyronine. Endocrinology. 1962 Jan;70:79–83. doi: 10.1210/endo-70-1-79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel Y. C., Burger H. G. A simplified radioimmunoassay for triiodothyronine. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1973 Jan;36(1):187–190. doi: 10.1210/jcem-36-1-187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman C. S., Chambers J. B., Jr, Read V. H. The extrathyroidal conversion rate of thyroxine to triiodothyronine in normal man. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jun;50(6):1187–1196. doi: 10.1172/JCI106596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROCHE J., MICHEL R., NUNEZ J. Sur la présence de la 3:3':5'-triiodothyronine dans le sang de rat. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1956 May 28;150(1):20–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROCHE J., MICHEL R., WOLF W., NUNEZ J. Sur deux nouveaux constituants hormonaux du corps thyroïde, la 3:3' -diiodothyronine et la 3:3':5' -triiodothyronine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1956 Feb;19(2):308–317. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(56)90433-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubenstein H. A., Butler V. P., Jr, Werner S. C. Progressive decrease in serum triiodothyronine concentrations with human aging: radioimmunoassay following extraction of serum. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1973 Aug;37(2):247–253. doi: 10.1210/jcem-37-2-247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STANBURY J. B., MORRIS M. L. The metabolism of 3:3'-diiodothyronine in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1957 Nov;17(11):1324–1331. doi: 10.1210/jcem-17-11-1324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STASILLI N. R., KROC R. L., MELTZER R. I. Antigoitrogenic and calorigenic activities of thyroxine analogues in rats. Endocrinology. 1959 Jan;64(1):62–82. doi: 10.1210/endo-64-1-62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz H. L., Surks M. I., Oppenheimer J. H. Quantitation of extrathyroidal conversion of L-thyroxine to 3,5,3'-triiodo-L-thyronine in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1971 May;50(5):1124–1130. doi: 10.1172/JCI106584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterling K., Brenner M. A., Newman E. S. Conversion of thyroxine to triiodothyronine in normal human subjects. Science. 1970 Sep 11;169(3950):1099–1100. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3950.1099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surks M. I., Oppenheimer J. H. Metabolism of phenolic- and tyrosyl-ring labeled L-thyroxine in human beings and rats. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Oct;33(4):612–618. doi: 10.1210/jcem-33-4-612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surks M. I., Schadlow A. R., Stock J. M., Oppenheimer J. H. Determination of iodothyronine absorption and conversion of L-thyroxine (T 4 ) to L-triiodothyronine (T 3 ) using turnover rate techniques. J Clin Invest. 1973 Apr;52(4):805–811. doi: 10.1172/JCI107244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka Y., DeLuca H. F. Stimulation of 24,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 production by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Science. 1974 Mar;183(130):1198–1200. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4130.1198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


