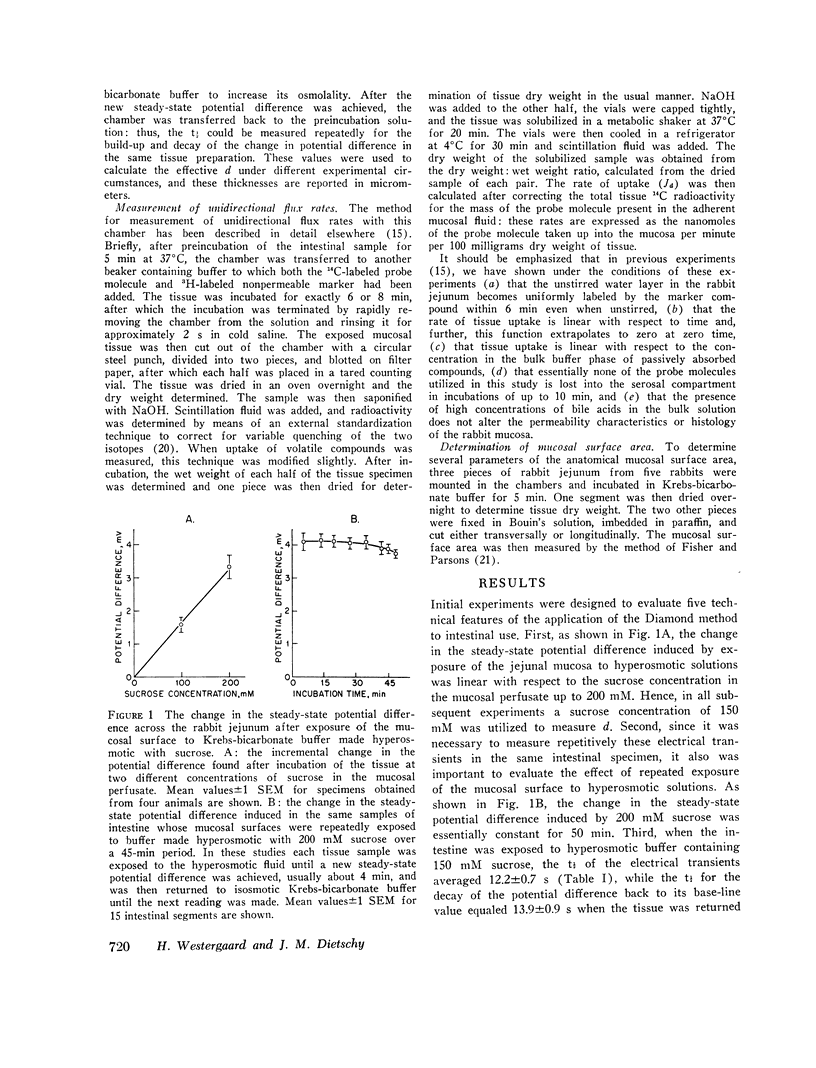
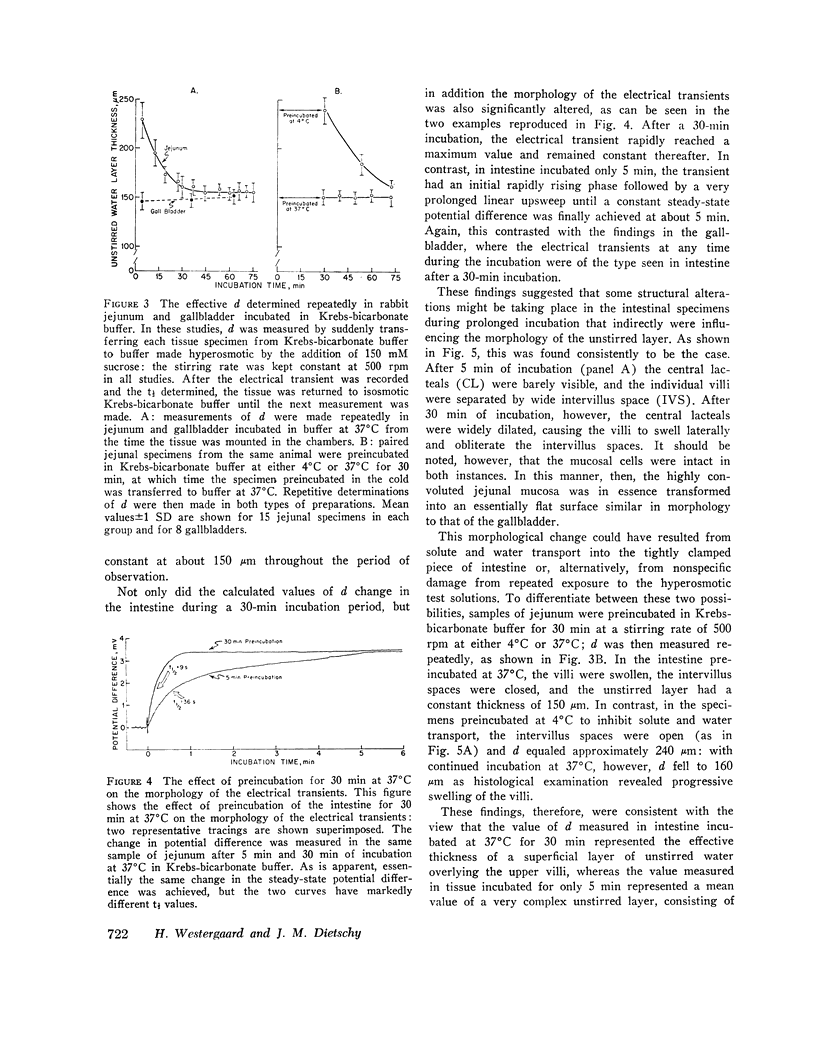
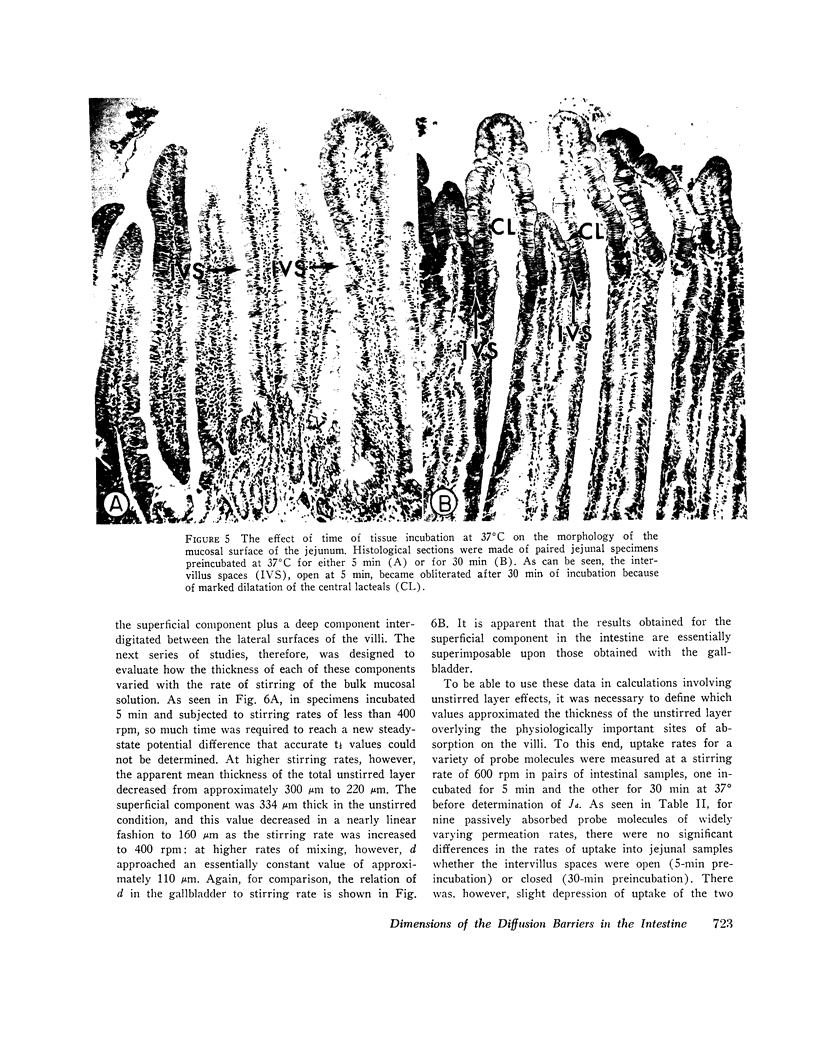
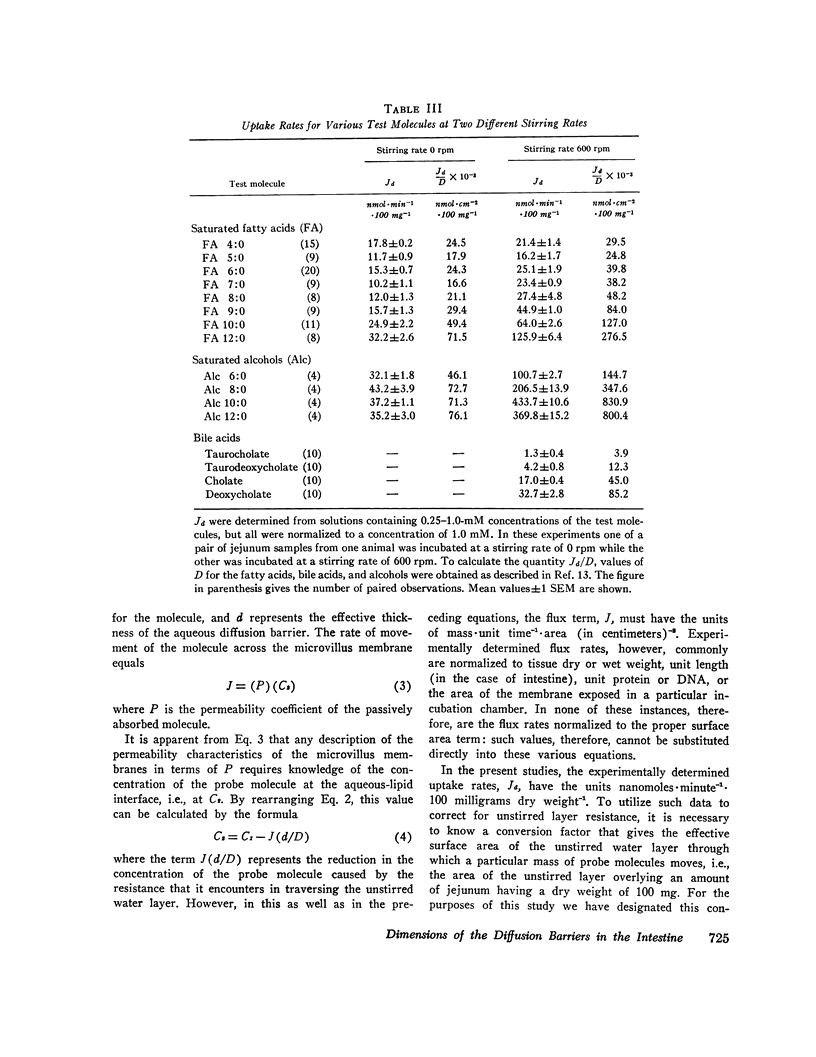
Abstract
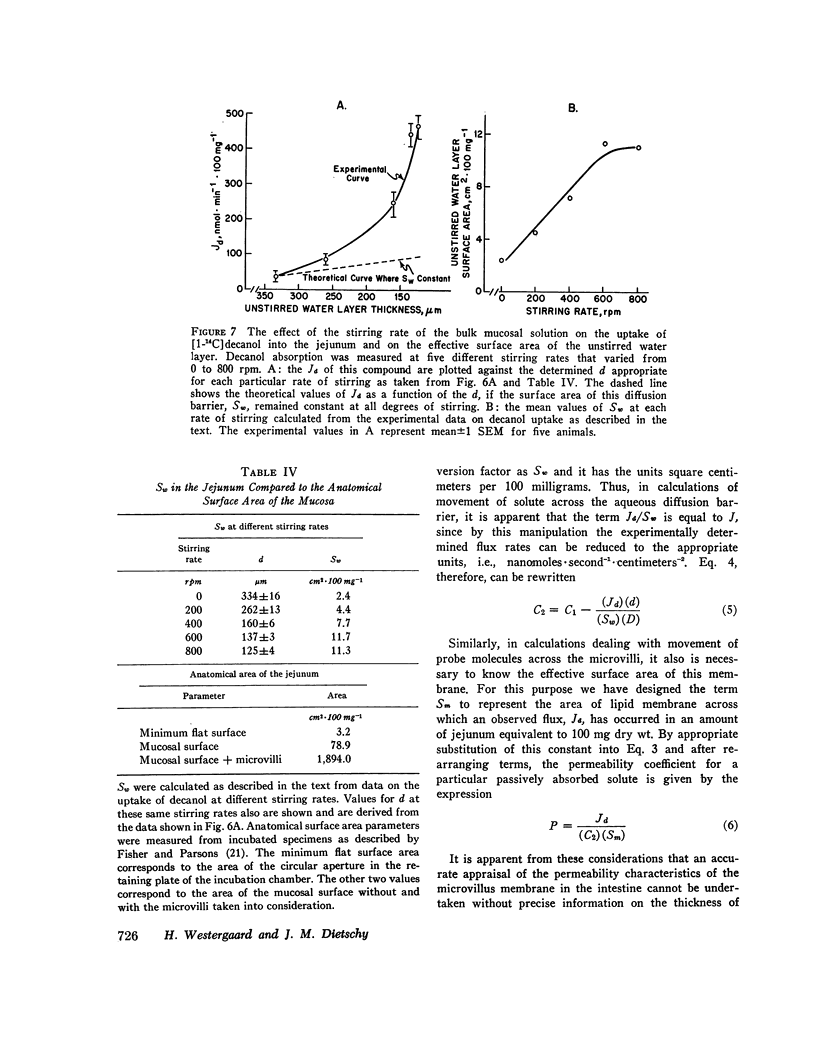
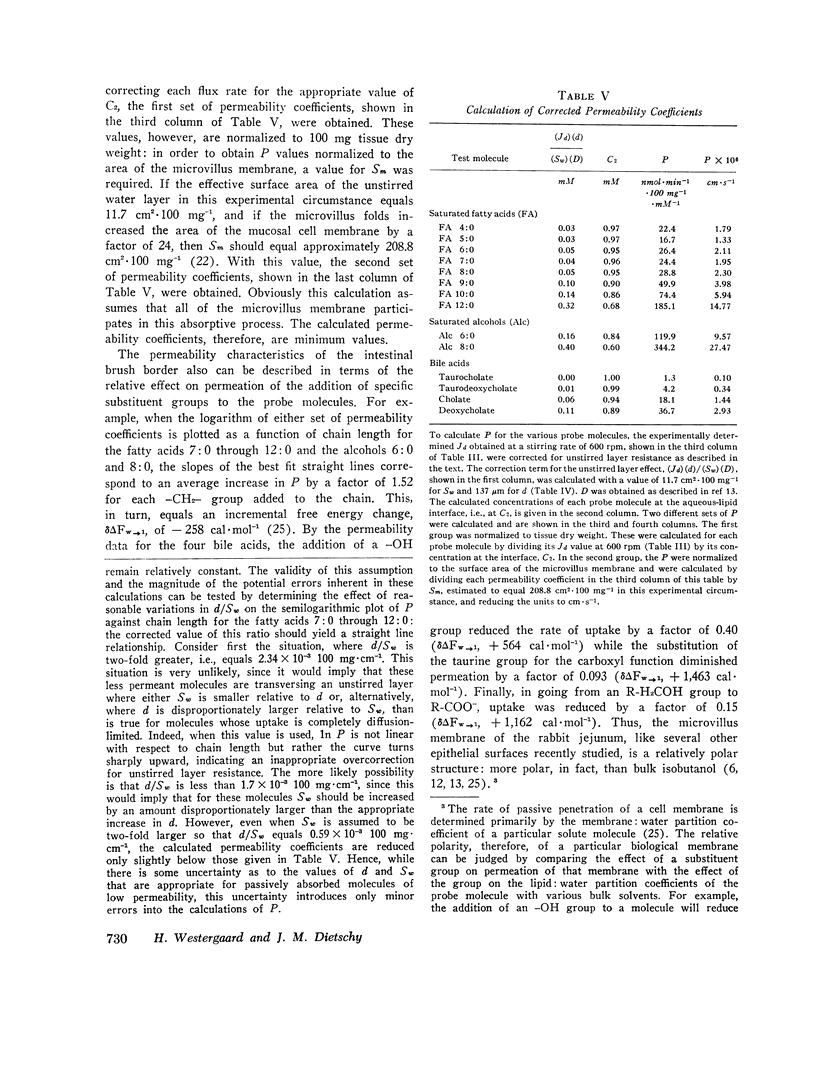
The rate of passive absorption into the intestinal mucosal cell is determined by at least two major diffusion barriers: an unstirred water layer and the cell membrane. This study defines the morphology and permeability characteristics of these two limiting structures. The unstirred water layer was resolved into two compartments: one behaves like a layer of water overlying the upper villi while the other probably consists of solution between villi. The superficial layer is physiologically most important during uptake of highly permeant compounds and varies in thickness from 115 to 334 μm as the rate of mixing of the bulk mucosal solution is varied. From data derived from a probe molecule whose uptake was limited by the unstirred layer, the effective surface area of this diffusion barrier also was determined to vary with stirring rate and equaled only 2.4 cm2·100 mg-1 in the unstirred condition but increased to 11.3 cm2·100 mg-1 with vigorous mixing. This latter value, however, was still only 1/170 of the anatomical area of the microvillus membrane. With these values, uptake rates for a number of passively absorbed probe molecules were corrected for unstirred layer resistance, and these data were used to calculate the incremental free energy changes associated with uptake of the -CH2- (-258 cal·mol-1), -OH (+564), and taurine (+1,463) groups. These studies, then, have defined the thickness and area of the unstirred layer in the intestine and have shown that this barrier is rate-limiting for the mucosal uptake of compounds such as fatty acids and cholesterol; in addition, the lipid membrane of the microvillus surface has been shown to be a relatively polar structure.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreoli T. E., Troutman S. L. An analysis of unstirred layers in series with "tight" and "porous" lipid bilayer membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Apr;57(4):464–478. doi: 10.1085/jgp.57.4.464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond J. M. A rapid method for determining voltage-concentration relations across membranes. J Physiol. 1966 Mar;183(1):83–100. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond J. M., Wright E. M. Biological membranes: the physical basis of ion and nonelectrolyte selectivity. Annu Rev Physiol. 1969;31:581–646. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.31.030169.003053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond J. M., Wright E. M. Molecular forces governing non-electrolyte permeation through cell membranes. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1969 Mar 18;171(1028):273–316. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1969.0022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietschy J. M., Sallee V. L., Wilson F. A. Unstirred water layers and absorption across the intestinal mucosa. Gastroenterology. 1971 Dec;61(6):932–934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENEROTH P. THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY OF BILE ACIDS. J Lipid Res. 1963 Jan;4:11–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISHER R. B., PARSONS D. S. The gradient of mucosal surface area in the small intestine of the rat. J Anat. 1950 Jul;84(3):272–282. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frömter E., Diamond J. Route of passive ion permeation in epithelia. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jan 5;235(53):9–13. doi: 10.1038/newbio235009a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregg J. A. New solvent systems for thin-layer chromatography of bile acids. J Lipid Res. 1966 Jul;7(4):579–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutknecht J., Tosteson D. C. Diffusion of weak acids across lipid bilayer membranes: effects of chemical reactions in the unstirred layers. Science. 1973 Dec 21;182(4118):1258–1261. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4118.1258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hays R. M., Franki N., Soberman R. Activation energy for water diffusion across the toad bladder: evidence against the pore enlargement hypothesis. J Clin Invest. 1971 May;50(5):1016–1018. doi: 10.1172/JCI106572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hingson D. J., Diamond J. M. Comparison of nonelectrolyte permeability patterns in several epithelia. J Membr Biol. 1972;10(2):93–135. doi: 10.1007/BF01867849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holz R., Finkelstein A. The water and nonelectrolyte permeability induced in thin lipid membranes by the polyene antibiotics nystatin and amphotericin B. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Jul;56(1):125–145. doi: 10.1085/jgp.56.1.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidder G. W., 3rd Unstirred layers in tissue respiration: application to studies of frog gastric mucosa. Am J Physiol. 1970 Dec;219(6):1789–1795. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.219.6.1789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PALAY S. L., KARLIN L. J. An electron microscopic study of the intestinal villus. II. The pathway of fat absorption. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1959 May 25;5(3):373–384. doi: 10.1083/jcb.5.3.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rey F., Drillet F., Schmitz J., Rey J. Influence of flow rate on the kinetics of the intestinal absorption of glucose and lysine in children. Gastroenterology. 1974 Jan;66(1):79–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sallee V. L., Dietschy J. M. Determinants of intestinal mucosal uptake of short- and medium-chain fatty acids and alcohols. J Lipid Res. 1973 Jul;14(4):475–484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sallee V. L., Wilson F. A., Dietschy J. M. Determination of unidirectional uptake rates for lipids across the intestinal brush border. J Lipid Res. 1972 Mar;13(2):184–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherrill B. C., Albright J. G., Dietschy J. M. Diffusion studies of bile acids, fatty acids and sucrose-NaCl-water systems at 37 degrees C by a modified capillary cell apparatus and their application to membrane transport studies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jun 22;311(2):261–271. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90273-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson F. A., Dietschy J. M. Characterization of bile acid absorption across the unstirred water layer and brush border of the rat jejunum. J Clin Invest. 1972 Dec;51(12):3015–3025. doi: 10.1172/JCI107129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson F. A., Sallee V. L., Dietschy J. M. Unstirred water layers in intestine: rate determinant of fatty acid absorption from micellar solutions. Science. 1971 Dec 3;174(4013):1031–1033. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4013.1031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winne D. Unstirred layer, source of biased Michaelis constant in membrane transport. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 27;298(1):27–31. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright E. M., Diamond J. M. Patterns of non-electrolyte permeability. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1969 Mar 18;171(1028):227–271. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1969.0021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




