Abstract
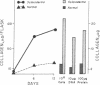
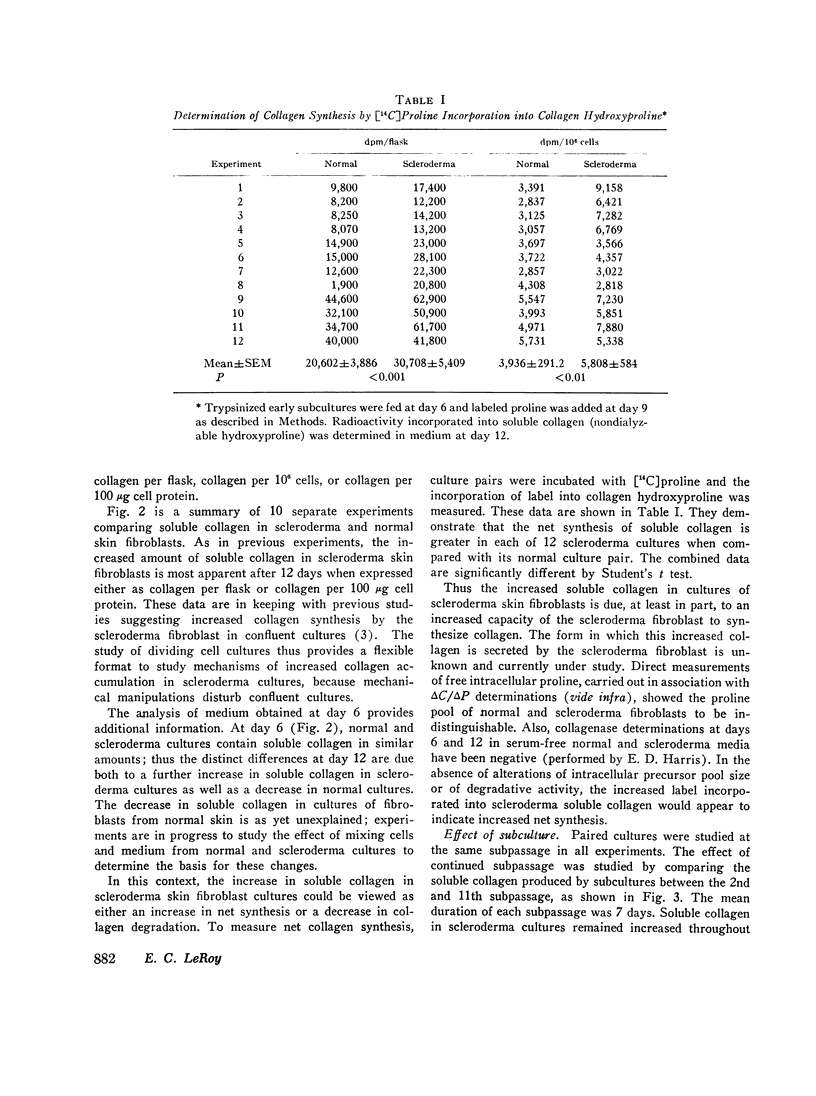
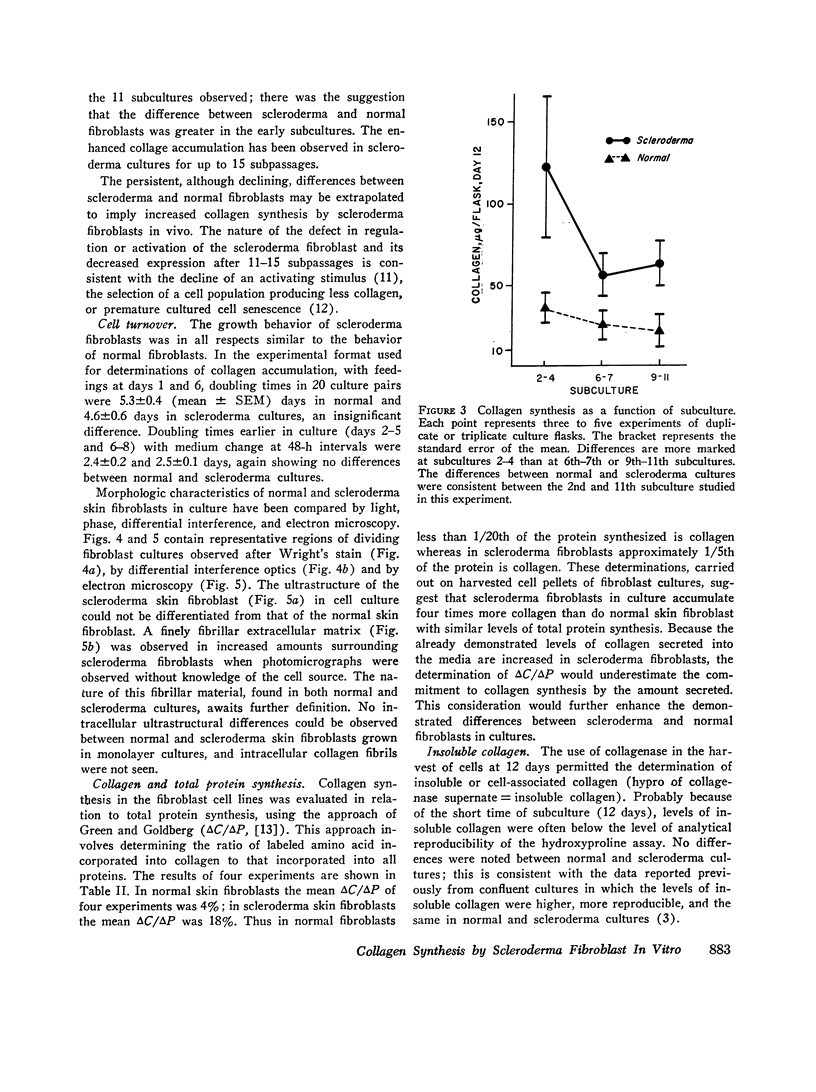
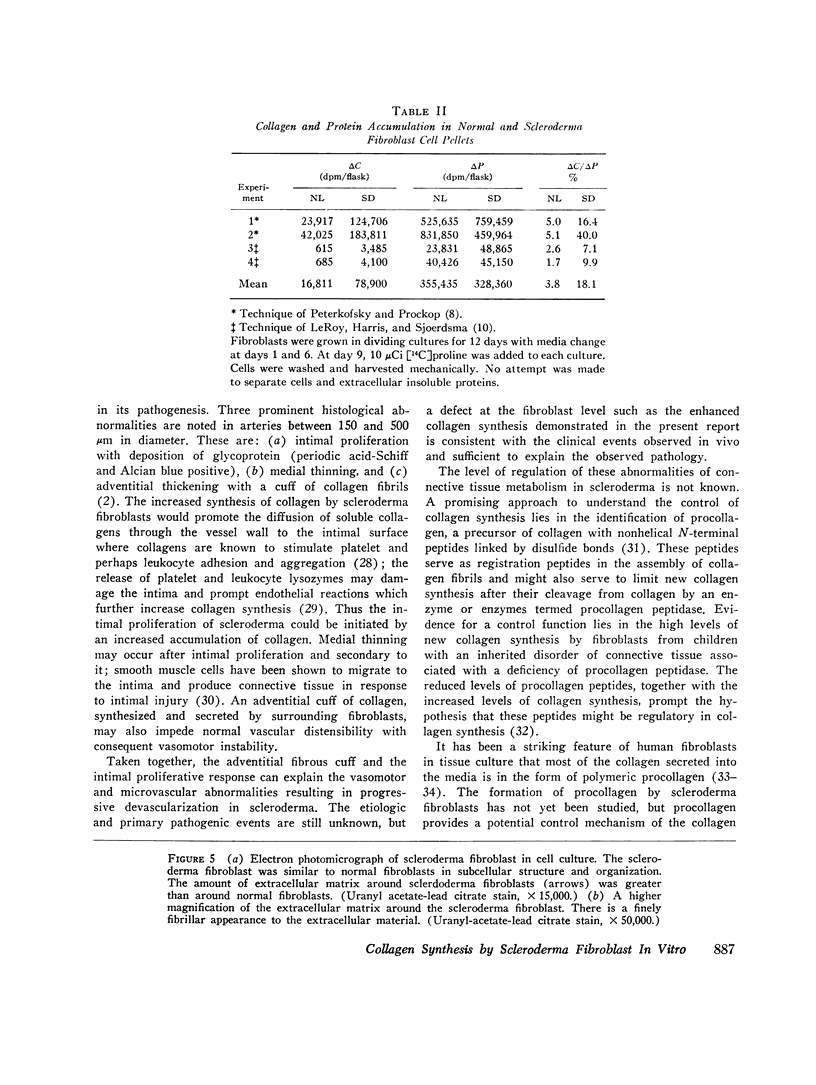
Cultures of dividing skin fibroblasts from normal and sclerodermatous human skin have permitted estimations of soluble collagen concentration, net collagen accumulation, cell-doubling times, and the comparison of morphologic and ultrastructural characteristics. In vitro, the scleroderma fibroblast produces more soluble collagen, synthesizes collagen more rapidly, and fourfold more of its protein synthetic activity is directed to collagen production than in the normal skin fibroblast. Cell-doubling times and morphologic and ultrastructural observations of cells in culture have not provided clues to the nature of the biologic defect in the regulation or activation of collagen synthesis by the scleroderma fibroblast.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bellamy G., Bornstein P. Evidence for procollagen, a biosynthetic precursors of collagen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1138–1142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon P. J., Hassar M., Case D. B., Casarella W. J., Sommers S. C., LeRoy E. C. The relationship of hypertension and renal failure in scleroderma (progressive systemic sclerosis) to structural and functional abnormalities of the renal cortical circulation. Medicine (Baltimore) 1974 Jan;53(1):1–46. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197401000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castor C. W. Connective tissue activation. VI. The effects of cylic nucleotides on human synovial cells in vitro. J Lab Clin Med. 1974 Jan;83(1):47–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLEISCHMAJER R. THE COLLAGEN IN SCLERODERMA. Arch Dermatol. 1964 Mar;89:437–441. doi: 10.1001/archderm.1964.01590270123028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischmajer R., Damiano V., Nedwich A. Alteration of subcutaneous tissue in systemic scleroderma. Arch Dermatol. 1972 Jan;105(1):59–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischmajer R., Damiano V., Nedwich A. Scleroderma and the subcutaneous tissue. Science. 1971 Mar 12;171(3975):1019–1021. doi: 10.1126/science.171.3975.1019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischmajer R., Krol S. Chemical synthesis of the dermis in scleroderma. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Oct;126(1):252–256. doi: 10.3181/00379727-126-32415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischmajer R., Perlish J. S. Glycosaminoglycans in scleroderma and scleredema. J Invest Dermatol. 1972 Mar;58(3):129–132. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12538919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILES K. W., MYERS A. THE ROLE OF NUCLEIC ACIDS IN THE GROWTH OF THE HYPOCOTYL OF LUPINUS ALBUS UNDER VARYING LIGHT AND DARK REGIMES. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Jul 22;87:460–477. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(64)90118-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN H., GOLDBERG B. COLLAGEN SYNTHESIS BY HUMAN FIBROBLAST STRAINS. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Oct;117:258–261. doi: 10.3181/00379727-117-29551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg B., Epstein E. H., Jr, Sherr C. J. Precursors of collagen secreted by cultured human fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3655–3659. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes R. L., Rodnan G. P. The ultrastructure of skin in progressive systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). I. Dermal collagen fibers. Am J Pathol. 1971 Jun;63(3):433–442. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayflick L. The longevity of cultured human cells. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1974 Jan;22(1):1–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.1974.tb02152.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keiser H. R., Sjoerdsma A. Direct measurement of the rate of collagen synthesis in skin. Clin Chim Acta. 1969 Feb;23(2):341–346. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(69)90050-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keiser H. R., Stein H. D., Sjoerdsma A. Increased protocollagen proline hydroxylase activity in sclerodermatous skin. Arch Dermatol. 1971 Jul;104(1):57–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEROY E. C., KAPLAN A., UDENFRIEND S., SJOERDSMA A. A HYDROXYPROLINE-CONTAINING, COLLAGEN-LIKE PROTEIN IN PLASMA AND A PROCEDURE FOR ITS ASSAY. J Biol Chem. 1964 Oct;239:3350–3356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layman D. L., McGoodwin E. B., Martin G. R. The nature of the collagen synthesized by cultured human fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Feb;68(2):454–458. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.2.454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeRoy E. C., Harris E. D., Jr, Sjoerdsma A. A modified procedure for radioactive hydroxyproline assay in urine and tissues after labeled proline administration. Anal Biochem. 1966 Dec;17(3):377–382. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90173-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leroy E. C. Connective tissue synthesis by scleroderma skin fibroblasts in cell culture. J Exp Med. 1972 Jun 1;135(6):1351–1362. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.6.1351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenstein J. R., Martin G. R., Kohn L. D., Byers P. H., McKusick V. A. Defect in conversion of procollagen to collagen in a form of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Science. 1973 Oct 19;182(4109):298–300. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4109.298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONTGOMERY H., O'LEARY P. A., RAGSDALE W. E., Jr Dermatohistopathology of various types of scleroderma. AMA Arch Derm. 1957 Jan;75(1):78–87. doi: 10.1001/archderm.1957.01550130080008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neldner K. H., Jones J. D., Winkelmann R. K. Scleroderma: dermal amino acid composition with particular reference to hydroxyproline. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 May;122(1):39–41. doi: 10.3181/00379727-122-31044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OYAMA V. I., EAGLE H. Measurement of cell growth in tissue culture with a phenol reagent (folin-ciocalteau). Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1956 Feb;91(2):305–307. doi: 10.3181/00379727-91-22245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PETERKOFSKY B., PROCKOP D. J. A method for the simultaneous measurement of the radioactivity of proline-C14 and hydroxyproline-C14 in biological materials. Anal Biochem. 1962 Nov;4:400–406. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(62)90141-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PROCKOP D. J., UDENFRIEND S., LINDSTEDT S. A simple technique for measuring the specific activity of labeled hydroxyproline in biological materials. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1395–1398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puett D., Wasserman B. K., Ford J. D., Cunningham L. W. Collagen-mediated platelet aggregation. Effects of collagen modification involving the protein and carbohydrate moieties. J Clin Invest. 1973 Oct;52(10):2495–2506. doi: 10.1172/JCI107440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUPEC M., BRAUN-FALCO O. ELEKTRONENMIKROSKOPISCHE UNTERSUCHUNGEN UEBER DAS VERHALTEN DER KOLLAGENFIBRILLEN DER HAUT BEI SKLERODERMIE. Arch Klin Exp Dermatol. 1964 Aug 7;218:543–560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TROLL W., LINDSLEY J. A photometric method for the determination of proline. J Biol Chem. 1955 Aug;215(2):655–660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uitto J., Halme J., Hannuksela M., Peltokallio P., Kivirikko K. I. Protocollagen proline hydroxylase activity in the skin of normal human subjects and of patients with scleroderma. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1969 May;23(3):241–247. doi: 10.3109/00365516909077656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uitto J., Helin G., Helin P., Lorenzen I. Connective tissue in scleroderma. A biochemical study on the correlation of fractionated glycosaminoglycans and collagen in human skin. Acta Derm Venereol. 1971;51(6):401–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uitto J., Ohlenschläger K., Lorenzen I. Solubility of skin collagen in normal human subjects and in patients with generalised scleroderma. Clin Chim Acta. 1971 Jan;31(1):13–18. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(71)90356-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]