Abstract
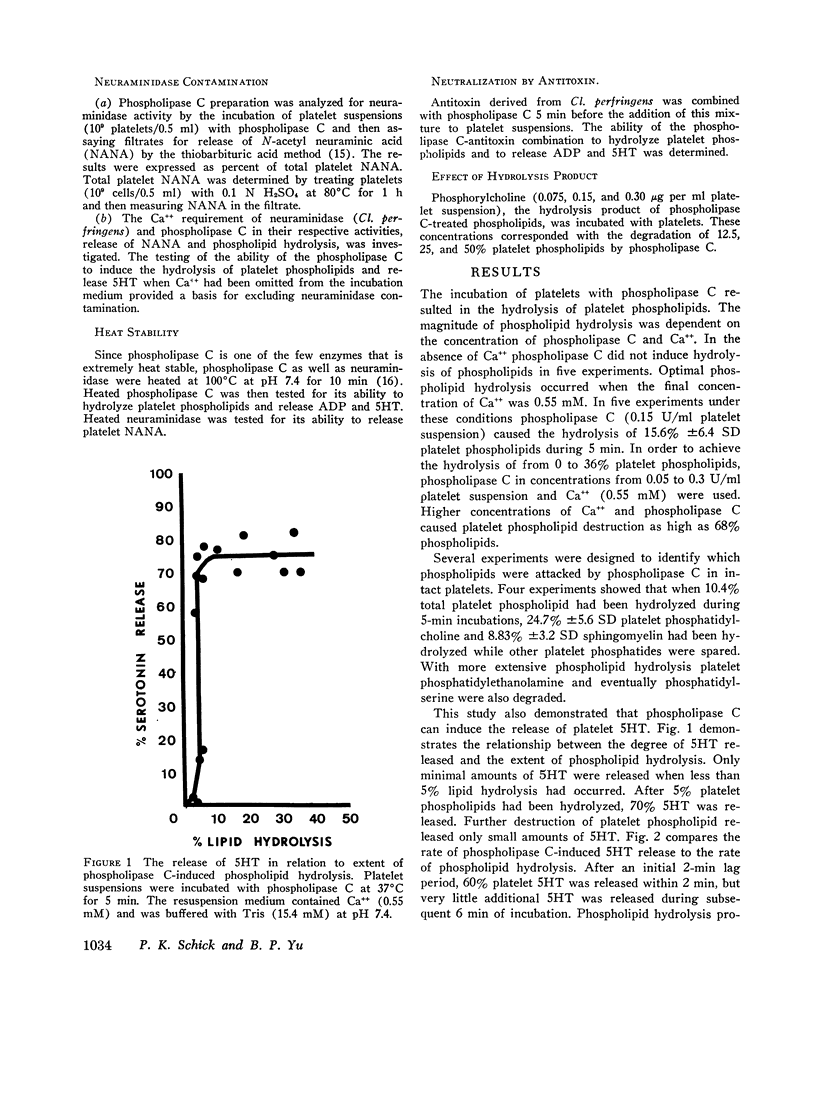
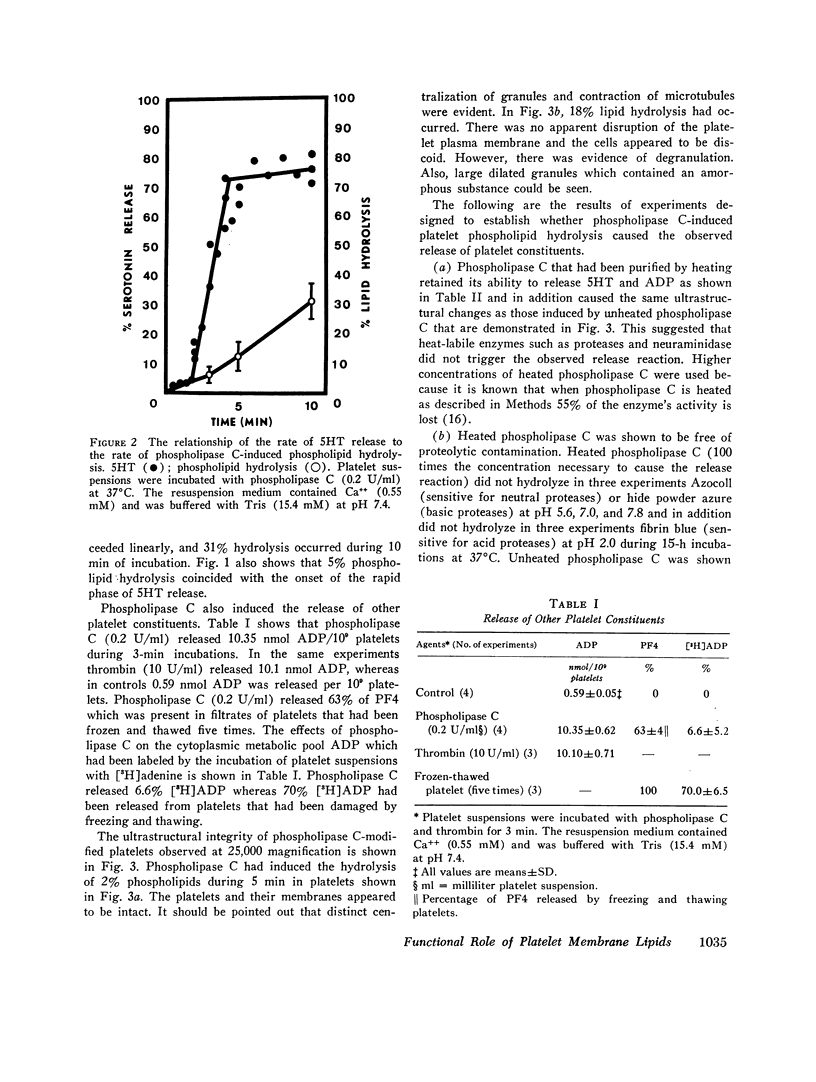
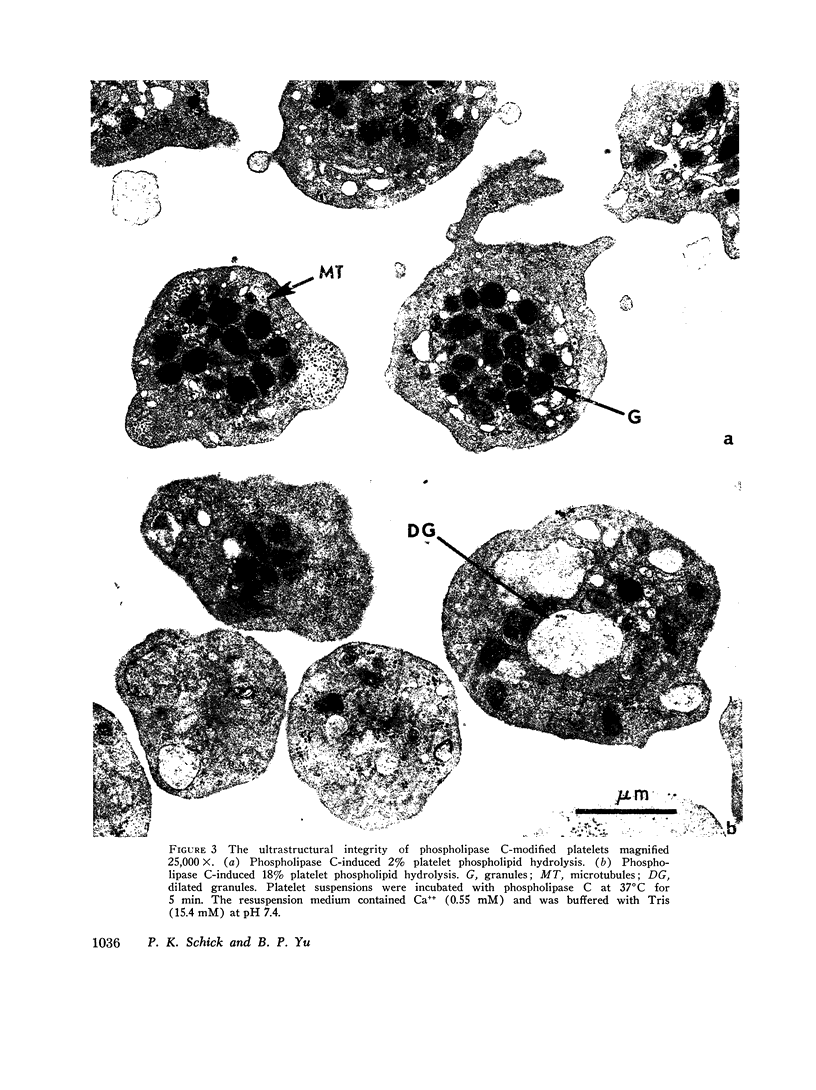
The structure and function of the platelet surface was probed by phospholipase C (Clostridium perfringens) which hydrolyzes membrane phospholipids, particularly phosphatidylcholine. Platelet phospholipids were susceptible to phospholipase C, and extent of hydrolysis was dependent on concentration of phospholipase C and Ca++. Phospholipase C (0.15 U/ml) with Ca++ (0.55 mM) hydrolyzed 15.6% phospholipids during 5 min. Phospholipase C released platelet serotonin (5HT), ADP, and platelet factor 4. Hydrolysis of 5% phospholipids resulted in release of 70% 5HT. Platelet 5HT release was rapid, occurring within 2 min. Phospholipase C (0.2 U/ml) with Ca++ (0.55 mM) also released 10.35 nmol sotrage pool ADP/109 platelets and 63% platelet factor 4 during 3 min. Phospholipase C did not cause leakage of cytoplasmic metabolic pool ADP, since only 6.6% [3H]ADP was released. Ultrastructural analysis of phospholipase C-modified platelets showed that platelets were intact. After 2% phospholipid hydrolysis, centralization of granules and contraction of microtubules were evident. After 18% phospholipid hydrolysis, there were morphological indications of degranulation. Phospholipase C-induced phospholipid hydrolysis caused the release of ADP and 5HT since: (a) Phospholipase C purified by heating was shown to be free of protease and neuraminidase activity and capable of inducing the platelet release reaction. (b) Antitoxin (Cl. perfringens) neutralized phospholipase C-induced 5HT release which rules out a contaminant. (c) Phosphorylcholine, the hydrolysis product, did not induce platelet 5HT release. This study demonstrates that minimal hydrolysis of platelet phospholipids triggers the release reaction. Our hypothesis is that phospholipids, presumably phosphatidylcholine, are situated at or near active site or “receptor” on the platelet surface and function as the modulator for the release reaction.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Born G. V. Uptake of adenosine and of adenosine diphosphate by human blood platelets. Nature. 1965 Jun 12;206(989):1121–1122. doi: 10.1038/2061121a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradlow B. A., Marcus A. J. Action of snake venom phospholipase A on isolated platelet membranes. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Dec;123(3):889–893. doi: 10.3181/00379727-123-31632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deykin D., Snyder D. Effect of epinephrine on platelet lipid metabolism. J Lab Clin Med. 1973 Oct;82(4):554–559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donati M. B., Palester-Chlebowczyk M., De Gaetano G., Vermylen J. Platelet factor-4--methods of study. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1972;34:295–308. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3231-2_19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drum D. E., Li T. K., Vallee B. L. Considerations in evaluating the zinc content of horse liver alcohol dehydrogenase preparations. Biochemistry. 1969 Sep;8(9):3783–3791. doi: 10.1021/bi00837a044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganguly P. Isolation and properties of a thrombin-sensitive protein from human blood platelets. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jul 10;246(13):4286–4290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmsen H., Storm E., Day H. J. Determination of ATP and ADP in blood platelets: a modification of the firefly luciferase assay for plasma. Anal Biochem. 1972 Apr;46(2):489–501. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90323-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIRSCHMANN C., CONDREA E., MOAV N., ALOOF S., DEVRIES A. ACTION OF SNAKE VENOM ON HUMAN PLATELET PHOSPHOLIPIDS. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1964 Aug 1;150:372–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis N., Majerus P. W. Lipid metabolism in human platelets. II. De novo phospholipid synthesis and the effect of thrombin on the pattern of synthesis. J Clin Invest. 1969 Nov;48(11):2114–2123. doi: 10.1172/JCI106178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd J. V., Nishizawa E. E., Haldar J., Mustard J. F. Changes in 32 p-labelling of platelet phospholipids in response to ADP. Br J Haematol. 1972 Nov;23(5):571–585. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1972.tb07092.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macchia V., Pastan I. Action of phospholipase C on the thyroid. Abolition of the response to thyroid-stimulating hormone. J Biol Chem. 1967 Apr 25;242(8):1864–1869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macfarlane M. G., Knight B. C. The biochemistry of bacterial toxins: The lecithinase activity of Cl. welchii toxins. Biochem J. 1941 Sep;35(8-9):884–902. doi: 10.1042/bj0350884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus A. J., Ullman H. L., Safier L. B. Lipid composition of subcellular particles of human blood platelets. J Lipid Res. 1969 Jan;10(1):108–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NELSON W. L., CIACCIO E. I., HESS G. P. A rapid method for the quantitative assay of proteolytic enzymes. Anal Biochem. 1961 Feb;2:39–44. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(61)90037-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht H., Geokas M. C., Silverman P., Haverback B. J. A new ultrasensitive method for the determination of proteolytic activity. Clin Chim Acta. 1968 Aug;21(2):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(68)90127-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schick P. K., Spaet T. H., Jaffé E. R. The effects of phenazinemethosulfate and methylene blue on human platelet phospholipid synthesis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Oct;141(1):114–118. doi: 10.3181/00379727-141-36728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schick P. K., Yu B. P. Methylene blue-induced serotonin release in human platelets. J Lab Clin Med. 1973 Oct;82(4):546–553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WROBLEWSKI F., LADUE J. S. Lactic dehydrogenase activity in blood. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1955 Oct;90(1):210–213. doi: 10.3181/00379727-90-21985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G. Fine structural alterations induced in platelets by adenosine diphosphate. Blood. 1968 May;31(5):604–622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwaal R. F., Roelofsen B., Colley C. M. Localization of red cell membrane constituents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Sep 10;300(2):159–182. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(73)90003-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]