Abstract
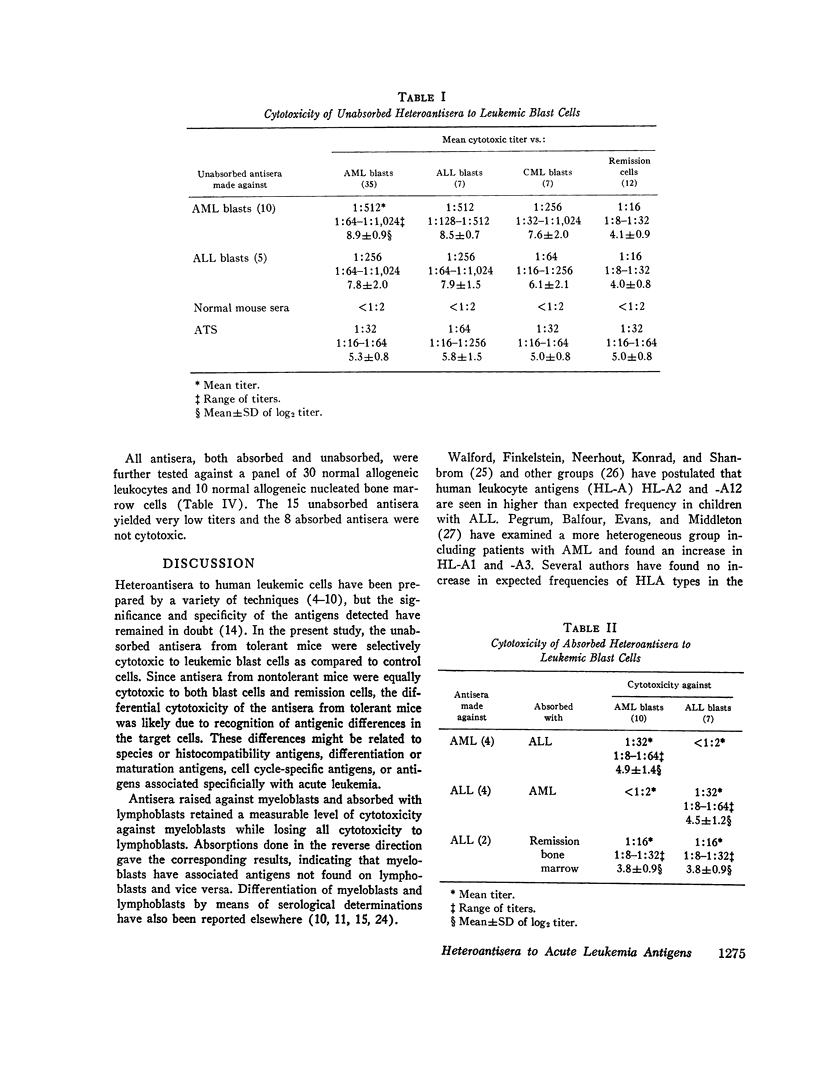
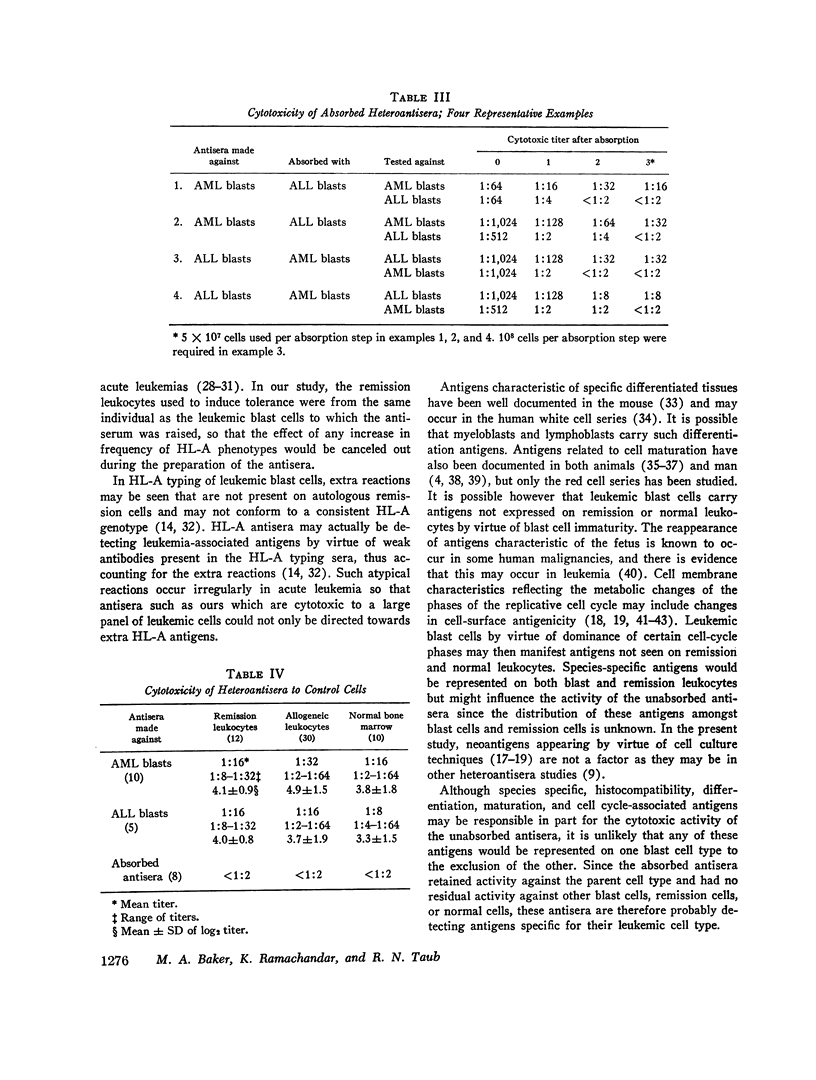
Antisera have been raised to human leukemic blast cells from individual patients in mice rendered tolerant with cyclophosphamide to remission leukocytes from the same individual. 10 antisera were raised against acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) cells and 5 antisera were raised against acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) cells. Antisera to AML cells were absorbed with ALL cells, and antisera to ALL cells were absorbed with AML cells. Unabsorbed and absorbed antisera as well as antisera raised in nontolerant mice were tested for cytotoxicity against various cells of a panel containing myeloblasts from 35 patients with AML, lymphoblasts from 7 patients with ALL, myeloblasts from 7 patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) in blast crisis, peripheral blood leukocytes from 12 patients with acute leukemia in remission and 30 nonleukemic patients, and nucleated bone marrow cells from 10 nonleukemic patients. Unabsorbed antisera to AML or ALL cells raised in tolerant mice were highly cytotoxic to leukemic blasts cells but significantly less cytotoxic to remission and control cells. Antisera to AML cells absorbed with ALL cells retained measurable cytotoxicity against AML cells but were not cytotoxic to ALL cells or control cells. Similarly, antisera to ALL cells absorbed with AML cells retained significant cytotoxicity only to ALL cells. Control antisera raised in nontolerant mice were cytotoxic to all cells tested. Although species specific, histocompatibility, differentiation, maturation, and cell cycle-associated antigens may be responsible in part for the cytotoxic activity of the unabsorbed antisera, the absorbed antisera are probably detecting antigens specific for their leukemic cell type.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker M. A., Taub R. N. Production of antiserum in mice to human leukaemia-associated antigens. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jan 17;241(107):93–94. doi: 10.1038/newbio241093a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bias W. B., Santos G. W., Burke P. J., Mullins G. M., Humphrey R. L. Cytotoxic antibody in normal human serums reactive with tumor cells from acute lymphocytic leukemia. Science. 1972 Oct 20;178(4058):304–306. doi: 10.1126/science.178.4058.304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borsook H., Ratner K., Tattrie B. Differential immune lysis of erythroblasts. Nature. 1969 Mar 29;221(5187):1261–1262. doi: 10.1038/2211261b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyse E. A., Stockert E., Old L. J. Modification of the antigenic structure of the cell membrane by thymus-leukemia (TL) antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Sep;58(3):954–957. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.3.954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cikes M. Variations in expression of surface antigens on cultured cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Jun 21;177:190–200. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb35046.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dick H. M., Steel C. M., Crichton W. B. HL-A typing of cultured peripheral lymphoblastoid cells. Tissue Antigens. 1972;2(2):85–93. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1972.tb00122.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas K. S., Perkins H. A., Cochrum K., Kountz S. L. Comparison of the HL-A phenotypes of lymphocytes and kidney cells determined by the fluorochromasia cytotoxicity assay. J Clin Invest. 1971 Feb;50(2):274–281. doi: 10.1172/JCI106492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINK M. A., MALMGREN R. A., RAUSCHER F. J., ORR H. C., KARON M. APPLICATION OF IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE TO THE STUDY OF HUMAN LEUKEMIA. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1964 Sep;33:581–588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARB S., STEIN A. A., SIMS G. The production of anti-human leukemic serum in rabbits. J Immunol. 1962 Feb;88:142–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris R. Leukaemia antigens and immunity in man. Nature. 1973 Jan 12;241(5385):95–100. doi: 10.1038/241095a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris R., Viza D. HL-A, leukaemia, and leukaemia-associated antigens. Lancet. 1971 May 29;1(7709):1134–1135. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91876-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris R., Viza D., Todd R., Phillips J., Sugar R., Jennison R. F., Marriott G., Gleeson M. H. Detection of human leukaemia associated antigens in leukaemic serum and normal embryos. Nature. 1971 Oct 22;233(5321):556–557. doi: 10.1038/233556a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris R., Zervas J. D. Reticulocyte HL-A antigens. Nature. 1969 Mar 15;221(5185):1062–1063. doi: 10.1038/2211062a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyde R. M., Garb S., Bennett A. J. Demonstration by immunoelectrophoresis of antigen in human myelogenous leukemia. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1967 Jun;38(6):909–920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEIN E., KLEIN G. ANTIGENIC PROPERTIES OF LYMPHOMAS INDUCED BY THE MOLONEY AGENT. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1964 Mar;32:547–568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight S. C., Moore G. E., Clarkson B. D. Stimulation of autochthonous lymphocytes by cells from normal and leukaemic lines. Nat New Biol. 1971 Feb 10;229(6):185–187. doi: 10.1038/newbio229185a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krantz S. B., Moore W. H., Zaentz S. D. Studies on red cell aplasia. V. Presence of erythroblast cytotoxicity in G-globulin fraction of plasma. J Clin Invest. 1973 Feb;52(2):324–336. doi: 10.1172/JCI107188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawler S. D., Klouda P. T., Hardisty R. M., Till M. M. Histocompatibility and acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Lancet. 1971 Apr 3;1(7701):699–699. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)92704-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann D. L., Rogentine G. N., Halterman R., Leventhal B. Detection of an antigen associated with acute leukemia. Science. 1971 Dec 10;174(4014):1136–1137. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4014.1136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzgar R. S., Mohanakumar T., Miller D. S. Antigens specific for human lymphocytic and myeloid leukemia cells: detection by nonhuman primate antiserums. Science. 1972 Dec 1;178(4064):986–988. doi: 10.1126/science.178.4064.986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minio F., Howe C., Hsu K. C., Rifkind R. A. Antigen density on differentiating erythroid cells. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jun 7;237(75):187–188. doi: 10.1038/newbio237187a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell M. S., Mokyr M. B., Aspnes G. T., McIntosh S. Cytophilic antibodies in man. Ann Intern Med. 1973 Sep;79(3):333–339. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-79-3-333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohayon E., Ducos J., Goret P., Salmon H., Toma B. Cytotoxicity of A.L.S. and anti-HL-A antibodies in human leukaemia. Lancet. 1972 Jan 1;1(7740):39–40. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)90030-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacocke I., Amos B., Laszlo J. The detection of iso-antigens on leukemic cells using the cytotoxicity test. Blood. 1966 Nov;28(5):665–673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pegrum G. D., Balfour I. C., Evans C. A., Middleton V. L. HL-A antigens on leukaemic cells. Br J Haematol. 1970 Oct;19(4):493–498. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1970.tb06977.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pegrum G. D., Balfour I. C., Evans C. A., Middleton V. L. HL-A typing of "leukaemic" cells. Lancet. 1971 Apr 24;1(7704):852–853. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91511-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrino M. A., Ferrone S., Natali P. G., Pellegrino A., Reisfeld R. A. Expression of HL-A antigens in synchronized cultures of human lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1972 Feb;108(2):573–576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogentine G. N., Jr, Yankee R. A., Gart J. J., Nam J., Trapani R. J. HL-A antigens and disease. Acute lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin Invest. 1972 Sep;51(9):2420–2428. doi: 10.1172/JCI107055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld C., Doré J. F., Choquet C., Venuat A. M., Ajuria E., Marholev L., Wastiaux J. P. Variations in expression of cell membrane antigens by cultured cells. A study of antilymphocytic globulin binding by human lymphoblastoid cells before, during, and after their establishment as cell lines. Transplantation. 1973 Oct;16(4):279–286. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197310000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman H. M., Nelson R. A., Jr Antibody to rabbit reticulocytes. Nature. 1969 Aug 9;223(5206):623–624. doi: 10.1038/223623a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryckmans P., Delalieux G., Manaster J., Socquet M. The potentiality of out-of-cycle acute leukemic cells to synthesize DNA. Blood. 1970 Dec;36(6):697–703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takasugi M. An improved fluorochromatic cytotoxic test. Transplantation. 1971 Aug;12(2):148–151. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197108000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viza D., Davies D. A., Harris R. Solubilization and partial purification of human leukaemic specific antigens. Nature. 1970 Sep 19;227(5264):1249–1251. doi: 10.1038/2271249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walford R. L., Finkelstein S., Neerhout R., Konrad P., Shanbrom E. Acute childhood leukaemia in relation to the HL-A human transplantation genes. Nature. 1970 Jan 31;225(5231):461–462. doi: 10.1038/225461a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yata J., Klein G., Kobayashi N., Furukawa T., Yanagisawa M. Human thymus-lymphoid tissue antigen and its presence in leukaemia and lymphoma. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Dec;7(6):781–792. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Weerdt C. M., Lalezari P. P. Another example if isoimmune neonatal neutropenia due to anti-Na1. Vox Sang. 1972;22(5):438–446. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1972.tb03991.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


