Abstract
The mechanism of drug-induced displacement of bilirubin from the blood into tissues was studied. A model of simple, competitive binding of bilirubin and drug to one site on serum albumin was established. Variations of the free bilirubin concentration after addition of drugs were studied in vitro by measuring velocities of oxidation with hydrogen peroxide and horseradish peroxidase. In all cases, the results were in agreement with the model. The competitive effects of 20 drugs were measured and expressed quantitatively as binding constants to the bilirubin site on human serum albumin. Several drugs caused changes of the bilirubin-albumin light absorption spectrum, indicating simultaneous binding of both ligands, without an effect on the free bilirubin concentration. Noncompetitive site-to-site effects on bilirubin binding could not be demonstrated.
An equation is proposed for calculation of the maximal displacing effect of a drug from knowledge of its plasma concentration, the above-determined binding constant, and the degree of protein binding of the drug.
Comparison of these results with previous observations of bilirubin displacement in newborn humans and in experimental animals indicates a general agreement with a simple competitive mechanism of binding of bilirubin and drug to one site on the albumin molecule. Binding of drugs to other, noncompetitive sites is common.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSEN D. H., BLANC W. A., CROZIER D. N., SILVERMAN W. A. A difference in mortality rate and incidence of kernicterus among premature infants allotted to two prophylactic antibacterial regimens. Pediatrics. 1956 Oct;18(4):614–625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bratlid D., Langslet A. Displacement of albumin-bound bilirubin by injectable diazepam preparations in vitro. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1973 Sep;62(5):510–512. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1973.tb08146.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bratlid D. Reserve albumin binding capacity, salicylate saturation index, and red cell binding of bilirubin in neonatal jaundice. Arch Dis Child. 1973 May;48(5):393–397. doi: 10.1136/adc.48.5.393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bratlid D. The effect of antimicrobial agents on bilirubin binding by human erythrocytes. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1972 Nov;30(3):331–337. doi: 10.3109/00365517209084298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
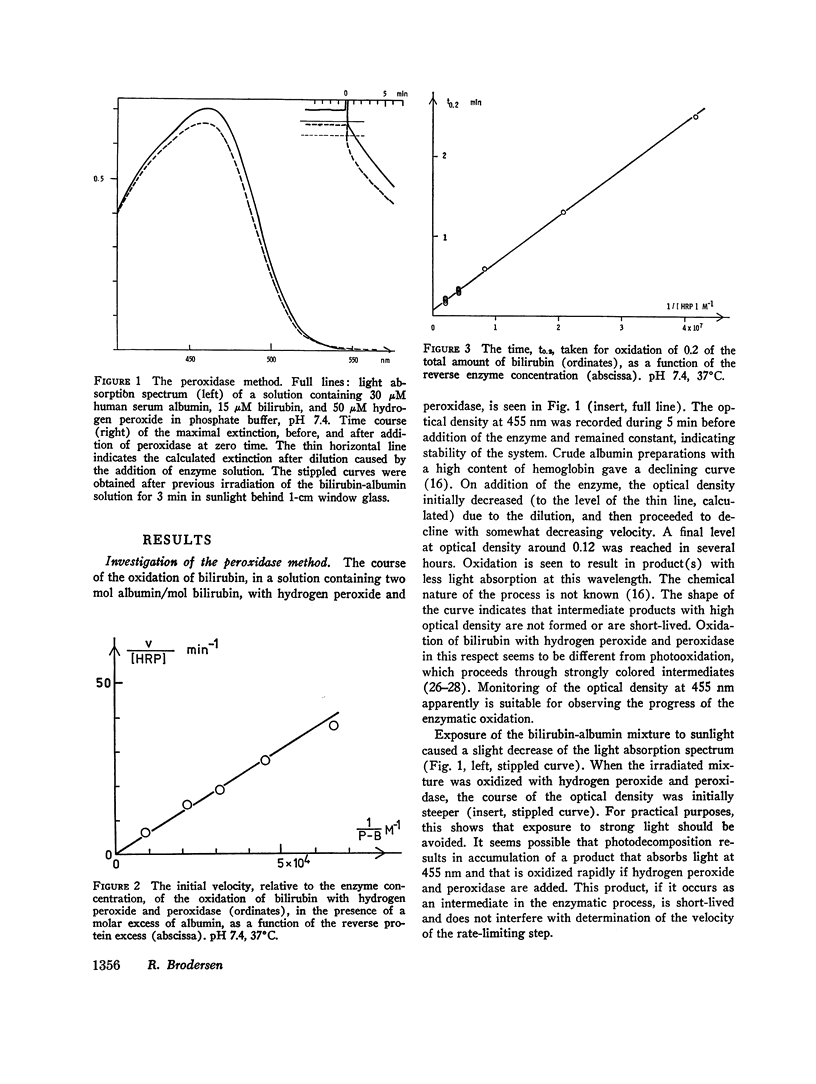
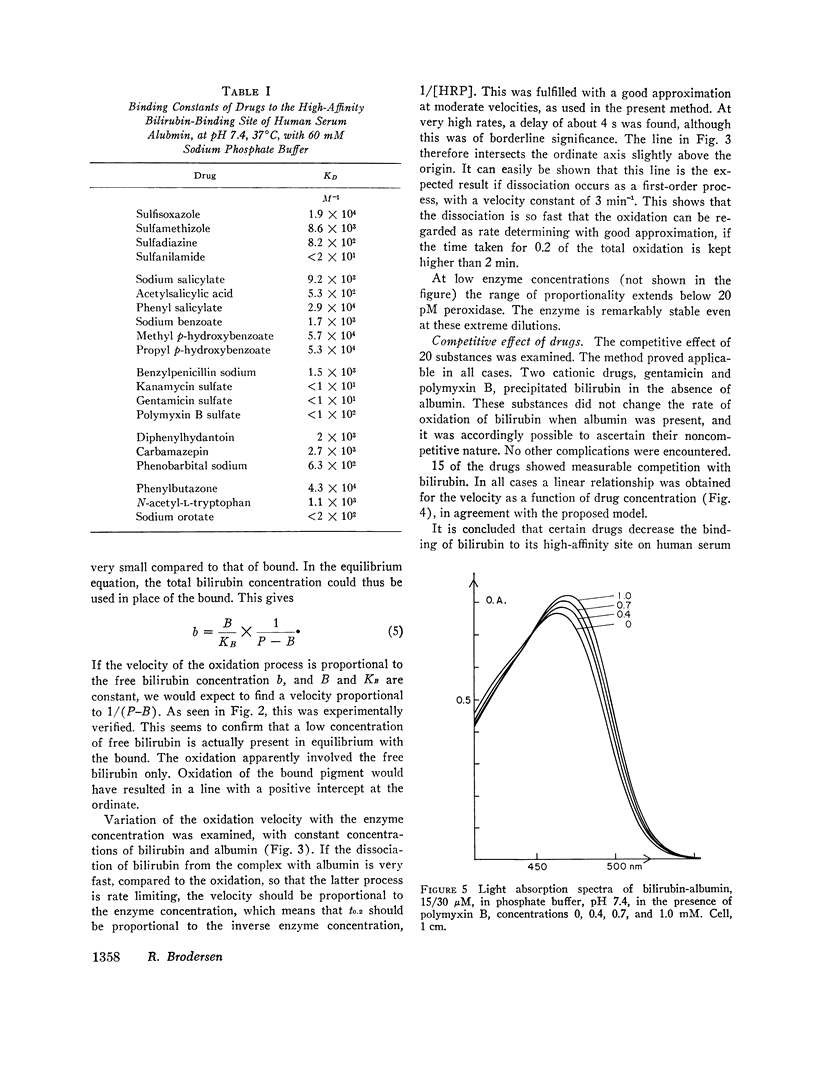
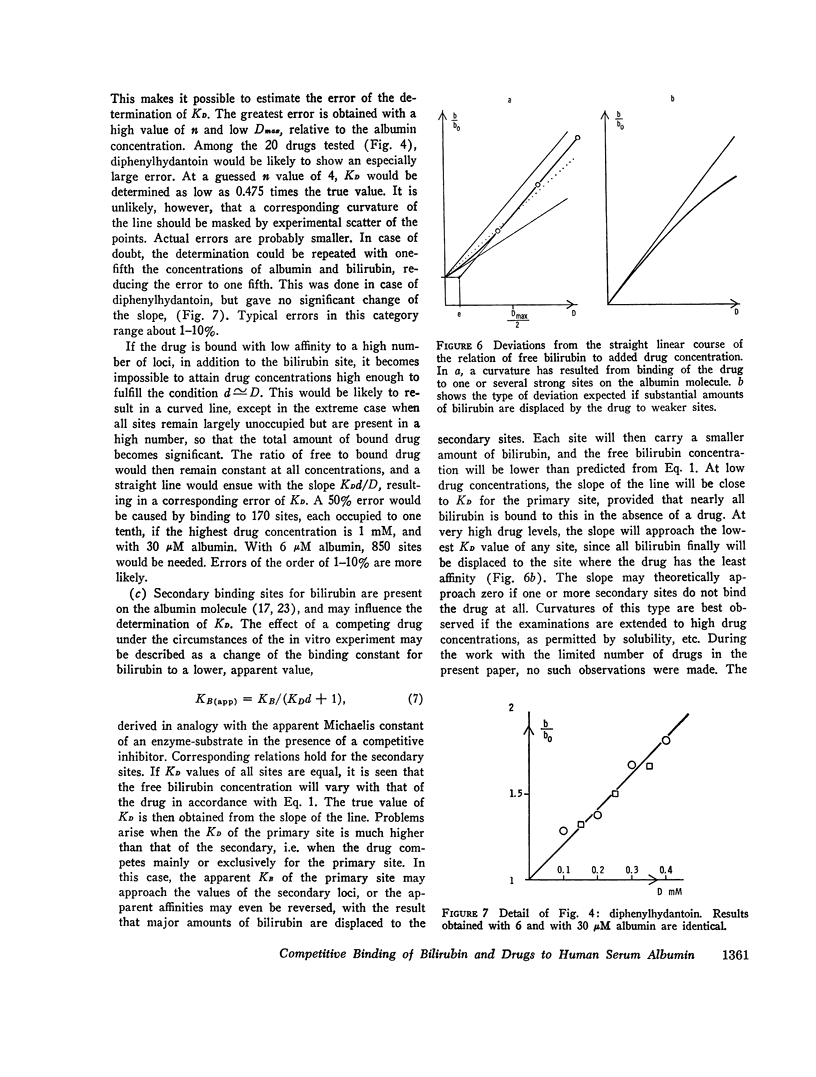
- Brodersen R., Bartels P. Enzymatic oxidation of bilirubin. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Oct;10(3):468–473. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00712.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodersen R., Theilgaard J. Bilirubin colloid formation in neutral aqueous solution. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1969 Dec;24(4):395–398. doi: 10.3109/00365516909080178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan G., Schiff D., Stern L. Competitive binding of free fatty acids and bilirubin to albumin: differences in HBABA dye versus sephadex G-25 interpretation of results. Clin Biochem. 1971 Oct;4(3):208–214. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9120(71)91551-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R. F. Removal of fatty acids from serum albumin by charcoal treatment. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jan 25;242(2):173–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarenburg R., Barnhart J. L. Interaction of serum albumin and bilirubin at low concentrations. Am J Physiol. 1973 Aug;225(2):493–496. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.225.2.493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOLE V. P. A relation between non-esterified fatty acids in plasma and the metabolism of glucose. J Clin Invest. 1956 Feb;35(2):150–154. doi: 10.1172/JCI103259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond I., Schmid R. Experimental bilirubin encephalopathy. The mode of entry of bilirubin-14C into the central nervous system. J Clin Invest. 1966 May;45(5):678–689. doi: 10.1172/JCI105383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garbagnati E., Manitto P. A new class of bilirubin photoderivatives obtained in vitro and their possible formation in jaundiced infants. J Pediatr. 1973 Jul;83(1):109–115. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80329-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRIS R. C., LUCEY J. F., MACLEAN J. R. Kernicterus in premature infants associated with low concentrations of bilirubin in the plasma. Pediatrics. 1958 Jun;21(6):875–884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins D., Pinckard R. N., Crawford I. P., Farr R. S. Structural changes in human serum albumin induced by ingestion of acetylsalicylic acid. J Clin Invest. 1969 Mar;48(3):536–542. doi: 10.1172/JCI106011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen C. Chemical modification of the high-affinity bilirubin-binding site of human-serum albumin. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jun 9;27(3):513–519. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01867.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen J. Binding of bilirubin to human serum albumin - determination of the dissociation constants. FEBS Lett. 1969 Oct 21;5(2):112–114. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(69)80307-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josephson B., Furst P. Sulfonamides competing with bilirubin for conjugation to albumin. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1966;18(1):51–63. doi: 10.3109/00365516609065606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KANTOR H. I., SUTHERLAND D. A., LEONARD J. T., KAMHOLZ J. H., FRY N. D., WHITE W. L. Effect on bilirubin metabolism in the newborn of sulfisoxazole administered to the mother. Obstet Gynecol. 1961 Apr;17:494–500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapitulnik J., Blondheim S. H., Grunfeld A., Kaufmann N. A. Photodecomposition of bilirubin: ultrafiltrable derivatives. Clin Chim Acta. 1973 Aug 30;47(2):159–166. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(73)90311-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King T. P., Spencer M. Structural studies and organic ligand-binding properties of bovine plasma albumin. J Biol Chem. 1970 Nov 25;245(22):6134–6148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMENAMY R. H., ONCLEY J. L. The specific binding of L-tryptophan to serum albumin. J Biol Chem. 1958 Dec;233(6):1436–1447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer M. C., Guttman D. E. The binding of drugs by plasma proteins. J Pharm Sci. 1968 Jun;57(6):895–918. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600570601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ODELL G. B. Studies in kernicterus. I. The protein binding of bilirubin. J Clin Invest. 1959 May;38(5):823–833. doi: 10.1172/JCI103864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ODELL G. B. The dissociation of bilirubin from albumin and its clinical implications. J Pediatr. 1959 Sep;55:268–279. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(59)80223-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odell G. B., Brown R. S., Holtzman N. A. Dye-sensitized photooxidation of albumin associated with a decreased capacity for protein-binding of bilirubin. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1970 Jun;6(2):31–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds J. A., Gallagher J. P., Steinhardt J. Effect of pH on the binding of N-alkyl sulfates to bovine serum albumin. Biochemistry. 1970 Mar 3;9(5):1232–1238. doi: 10.1021/bi00807a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudman D., Bixler T. J., 2nd, Del Rio A. E. Effect of free fatty acids on binding of drugs by bovine serum albumin, by human serum albumin and by rabbit serum. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1971 Feb;176(2):261–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan M. T. Influence of steroid binding on the tryptic hydrolysis of serum albumin. Biochemistry. 1973 Jun 5;12(12):2221–2230. doi: 10.1021/bi00736a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiff D., Chan G., Stern L. Fixed drug combinations and the displacement of bilirubin from albumin. Pediatrics. 1971 Jul;48(1):139–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid R., Diamond I., Hammaker L., Gundersen C. B. Interaction of bilirubin with albumin. Nature. 1965 Jun 5;206(988):1041–1043. doi: 10.1038/2061041b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schutta H. S., Johnson L. Electron microscopic observations on acute bilirubin encephalopathy in Gunn rats induced by sulfadimethoxine. Lab Invest. 1971 Jan;24(1):82–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starinsky R., Shafrir E. Displacement of albumin-bound bilirubin by free fatty acids. Implications for neonatal hyperbilirubinemia. Clin Chim Acta. 1970 Aug;29(2):311–318. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(70)90052-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern L. Drug interactions. II. Drugs, the newborn infant, and the binding of bilirubin to albumin. Pediatrics. 1972 Jun;49(6):916–918. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thaler M. M., Schmid R. Drugs and bilirubin. Pediatrics. 1971 May;47(5):807–810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiessen H., Jacobsen J., Brodersen R. Displacement of albumin-bound bilirubin by fatty acids. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1972 May;61(3):285–288. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1972.tb16100.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windorfer A., Jr, Mihailova K. Der Einfluss verschiedener Medikamente und pH-Werte auf die Albumin-Bilirubin-Bindung in vitro. Z Kinderheilkd. 1973 Jan 22;114(1):83–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamet P., Chunga F. Separation by gel filtration and microdetermination of unbound bilirubin. II. Study of sera in icteric newborn infants. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1971 Jan;60(1):33–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1971.tb06615.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



