Abstract
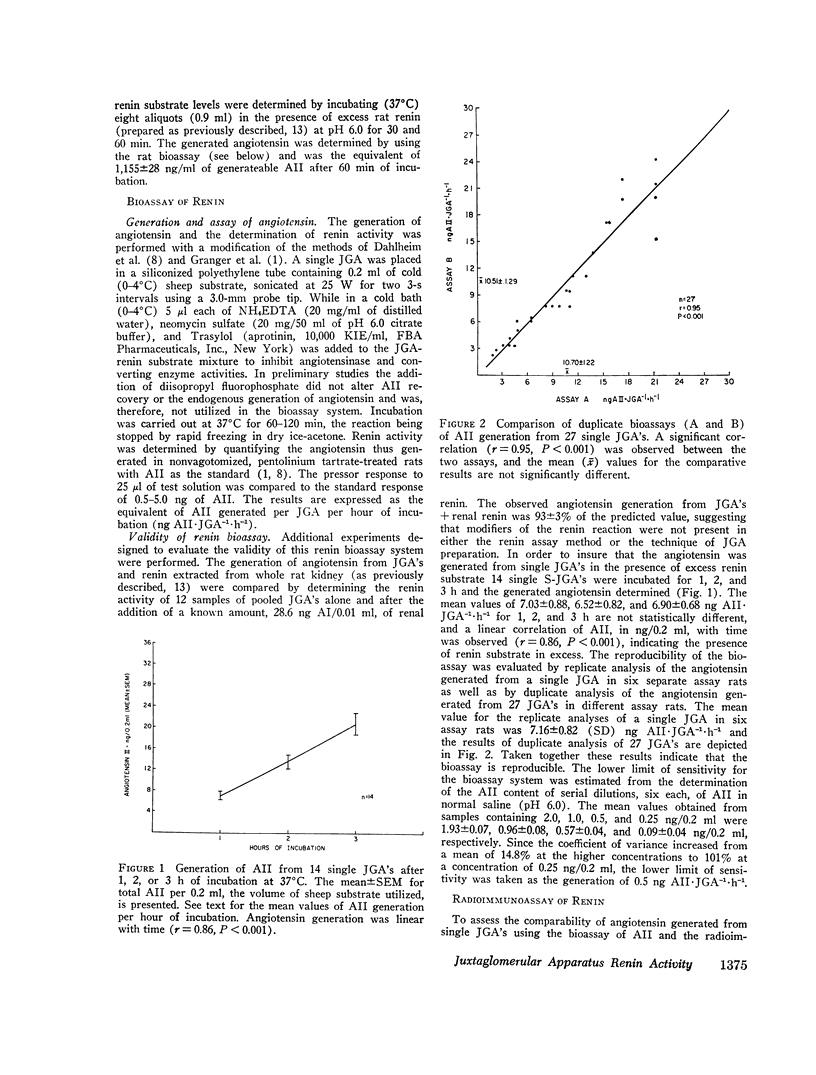
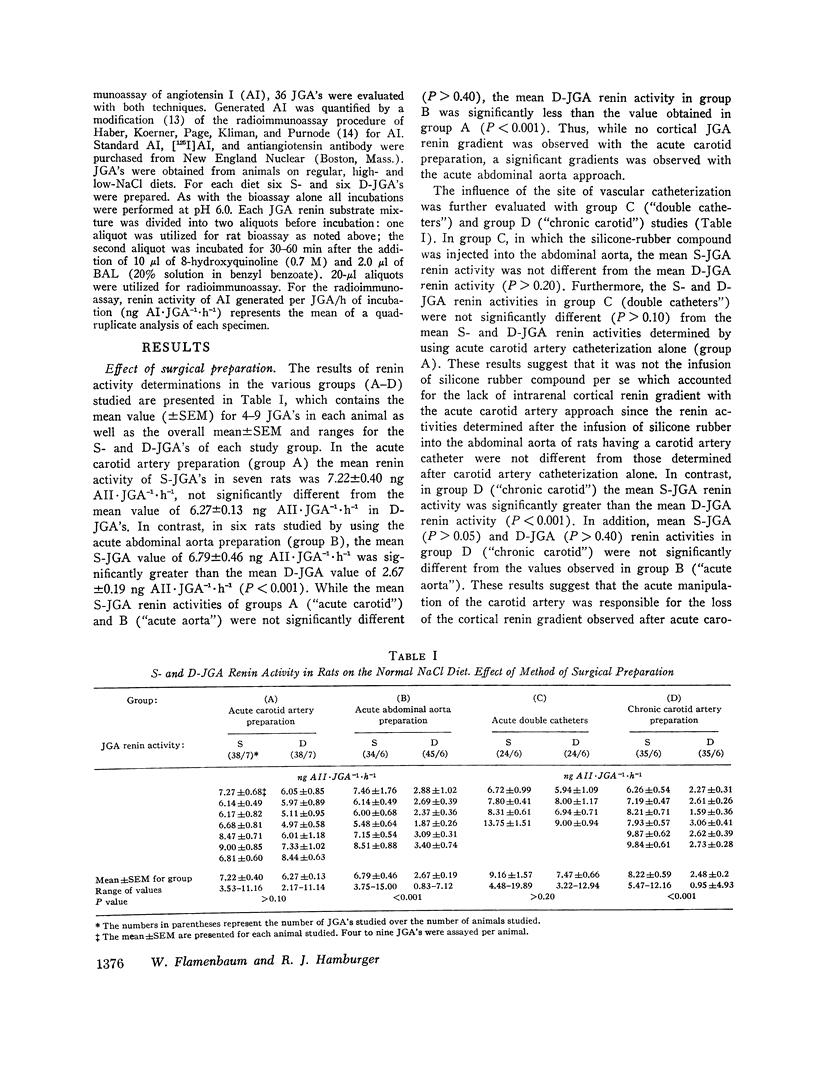
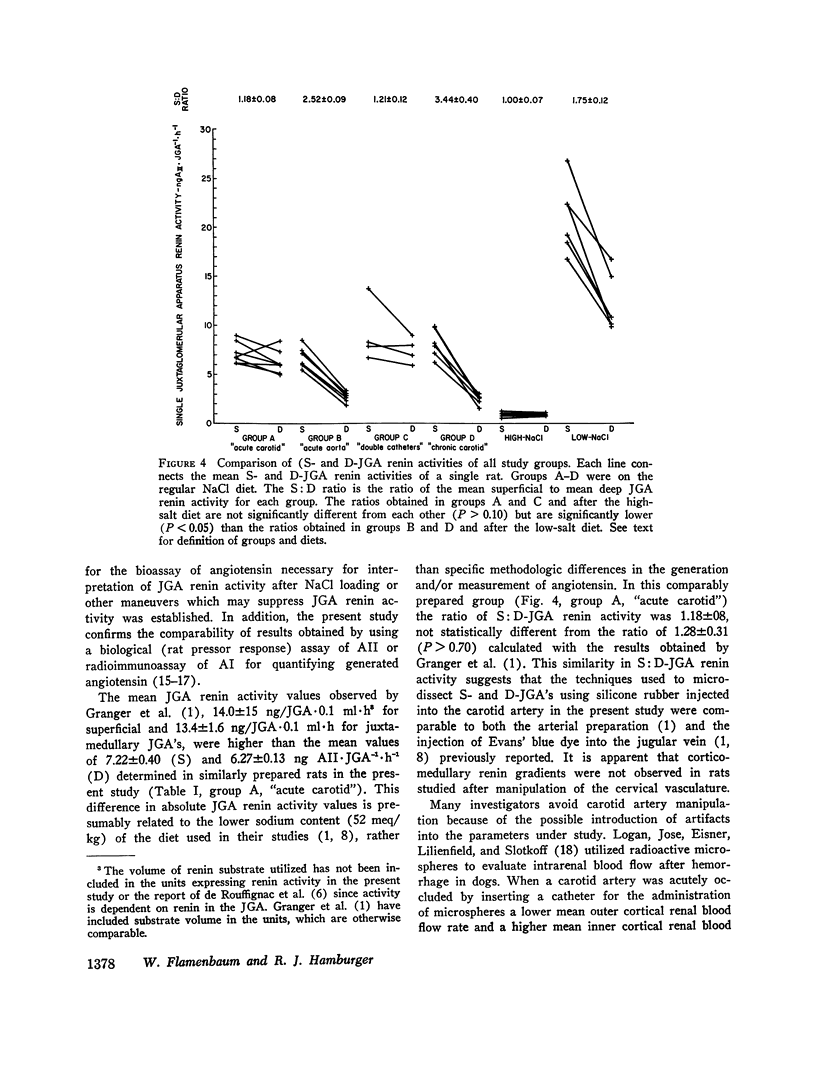
The intrarenal gradient of renin activity was determined in rats by using superficial (S) and deep (D) cortical juxtaglomerular apparatuses (JGA's), identified and microdissected after silicone-rubber compound injection. Angiotensin generated from single JGA's using partially purified sheep renin substrate was quantified by rat bioassay. When, in rats on a normal NaCl diet, silicone-rubber was injected into a carotid artery, alone or with abdominal aorta catheterization, S:D renin activity ratios were 1.18±0.08 (SEM) and 1.21±0.12, respectively. The S:D renin activity ratios obtained when silicone-rubber was injected into the abdominal aorta (2.52±0.09) or a chronic carotid artery catheter (3.44±0.40) were significantly higher (P < 0.001). The lower S:D renin activity ratios after carotid artery manipulation were due to significantly higher D-JGA renin activities. This increased D-JGA renin activity and the lack of a renin gradient appear to be related to acute carotid artery manipulation.
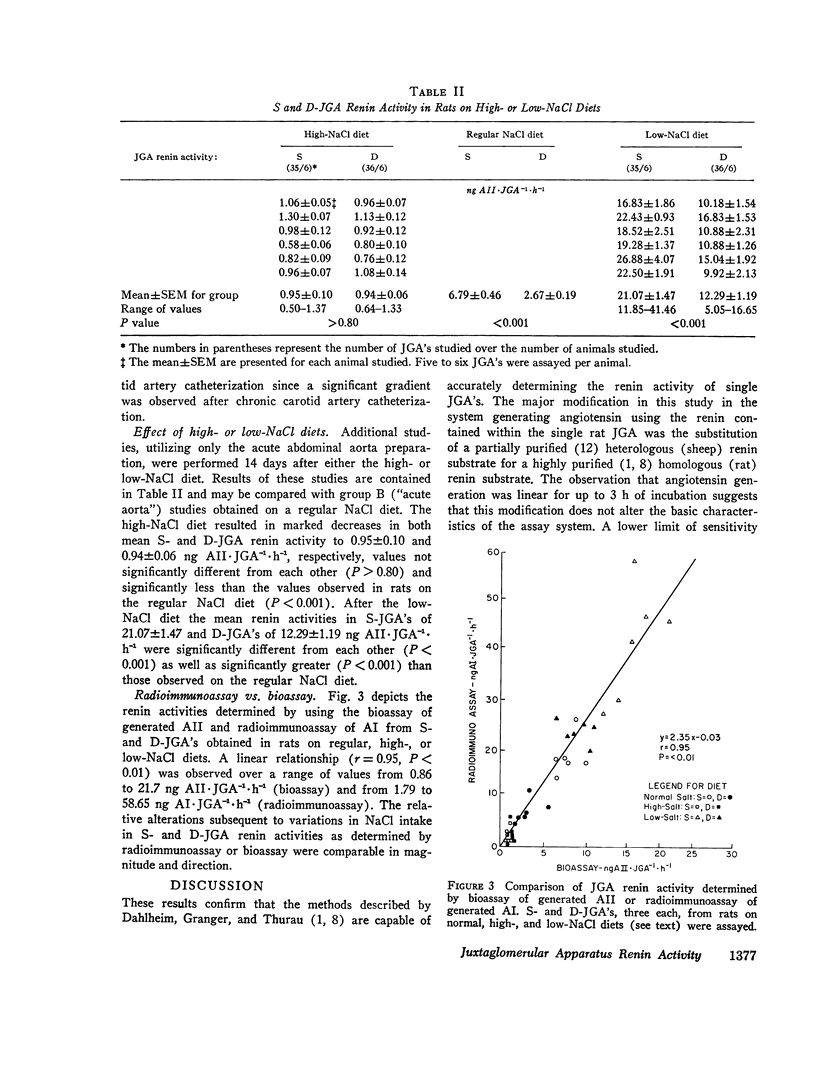
Alterations in JGA renin activity were examined relative to NaCl intake. 2 wk after high-NaCl diet the absolute net renin activity decreased (P < 0.001) more in S (5.84±0.11 ng AI·JGA-1·h-1) than D (1.73±0.06 ng AI·JGA-1·h-1) JGA's, and the intrarenal renin gradient was lost (S:D-JGA renin activity, 1.00±0.07), as compared to the regular NaCl diet. 2 wk of a low-NaCl diet resulted in a greater (P < 0.01) increase in S (14.28±1.47 ng AI·JGA-1·h-1) than D (9.62±1.19 ng AI·JGA-1·h-1) JGA renin activity and a renin gradient (S:D-JGA renin activity) of 1.75±0.12. These results demonstrate that NaCl intake clearly influences total JGA renin content and may also affect the relative intrarenal distribution of renin activity.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bunag R. D., Page I. H., McCubbin J. W. Neural stimulation of release of renin. Circ Res. 1966 Oct;19(4):851–858. doi: 10.1161/01.res.19.4.851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clement D. L., Pelletier C. L., Shepherd J. T. Role of vagal afferents in the control of renal sympathetic nerve activity in the rabbit. Circ Res. 1972 Dec;31(6):824–830. doi: 10.1161/01.res.31.6.824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen E. L., Grim C. E., Conn J. W., Blough W. M., Jr, Guyer R. B., Kem D. C., Lucas C. P. Accurate and rapid measurement of plasma renin activity by radioimmunoassay. Results in normal and hypertensive people. J Lab Clin Med. 1971 Jun;77(6):1025–1038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlheim H., Granger P., Thurau K. A sensitive method for determination of renin activity in the single juxtaglomerular apparatus of the rat kidney. Pflugers Arch. 1970;321(4):303–315. doi: 10.1007/BF00588645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. O. What signals the kidney to release renin? Circ Res. 1971 Mar;28(3):301–306. doi: 10.1161/01.res.28.3.301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDBERG E. C. THE DISTRIBUTION OF THE JUXTAGLOMERULAR GRANULES AND THE MACULA DENSA IN THE RENAL CORTEX OF THE MOUSE. Lab Invest. 1964 Sep;13:1003–1013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flamenbaum W., Kotchen T. A., Nagle R., McNeil J. S. Effect of potassium on the renin-angiotensin system and HgCl 2 -induced acute renal failure. Am J Physiol. 1973 Feb;224(2):305–311. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.224.2.305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flamenbaum W., Kotchen T. A., Oken D. E. Effect of renin immunization on mercuric chloride and glycerol-induced renal failure. Kidney Int. 1972 Jun;1(6):406–412. doi: 10.1038/ki.1972.53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILMORE J. P. CONTRIBUTION OF BARORECEPTORS TO THE CONTROL OF RENAL FUNCTION. Circ Res. 1964 Apr;14:301–317. doi: 10.1161/01.res.14.4.301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavras H., Brown J. J., Lever A. F., Robertson J. I. Changes of renin in individual glomeruli in response to variations of sodium intake in the rabbit. Clin Sci. 1970 Apr;38(4):409–414. doi: 10.1042/cs0380409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger P., Dahlheim H., Thurau K. Enzyme activities of the single juxtaglomerular apparatus in the rat kidney. Kidney Int. 1972 Feb;1(2):78–88. doi: 10.1038/ki.1972.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haber E., Koerner T., Page L. B., Kliman B., Purnode A. Application of a radioimmunoassay for angiotensin I to the physiologic measurements of plasma renin activity in normal human subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1969 Oct;29(10):1349–1355. doi: 10.1210/jcem-29-10-1349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiuchi K., Tanaka H., Yamamoto K., Ueda J. Distribution of renin in the dog kidney. Life Sci I. 1971 Jul 1;10(13):727–734. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(71)90116-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horster M., Thurau K. Micropuncture studies on the filtration rate of single superficial and juxtamedullary glomeruli in the rat kidney. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1968;301(2):162–181. doi: 10.1007/BF00362733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iriuchijima J., Wilson M. F. Sympathetic vasoconstrictor activity to the kidney in carotid occlusion pressor reflex. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 May;131(1):189–192. doi: 10.3181/00379727-131-33836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. A., Davis J. O., Witty R. T. Effects of catecholamines and renal nerve stimulation on renin release in the nonfiltering kidney. Circ Res. 1971 Dec;29(6):646–653. doi: 10.1161/01.res.29.6.646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kezdi P., Geller E. Baroreceptor control of postganglionic sympathetic nerve discharge. Am J Physiol. 1968 Mar;214(3):427–435. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.214.3.427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Grange R. G., Sloop C. H., Schmid H. E. Selective stimulation of renal nerves in the anesthetized dog. Effect on renin release during controlled changes in renal hemodynamics. Circ Res. 1973 Dec;33(6):704–712. doi: 10.1161/01.res.33.6.704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljungqvist A., Wågermark J. The adrenergic innervation of intrarenal glomerular and extra-glomerular circulatory routes. Nephron. 1970;7(3):218–229. doi: 10.1159/000179824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan A., Jose P., Eisner G., Lilienfield L., Slotkoff L. Intracortical distribution of renal blood flow in hemorrhagic shock in dogs. Circ Res. 1971 Sep;29(3):257–266. doi: 10.1161/01.res.29.3.257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenna O. C., Angelakos E. T. Adrenergic innervation of the canine kidney. Circ Res. 1968 Mar;22(3):345–354. doi: 10.1161/01.res.22.3.345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menard J., Catt K. J. Measurement of renin activity, concentration and substrate in rat plasma by radioimmunoassay of angiotensin I. Endocrinology. 1972 Feb;90(2):422–430. doi: 10.1210/endo-90-2-422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogil R. A., Itskovitz H. D., Russell J. H., Murphy J. J. Renal innervation and renin activity in salt metabolism and hypertension. Am J Physiol. 1969 Apr;216(4):693–697. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.216.4.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninomiya I., Irisawa H. Summation of baroceptor reflex effects on sympathetic nerve activities. Am J Physiol. 1969 Jun;216(6):1330–1336. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.216.6.1330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninomiya I., Nisimaru N., Irisawa H. Sympathetic nerve activity to the spleen, kidney, and heart in response to baroceptor input. Am J Physiol. 1971 Nov;221(5):1346–1351. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.5.1346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomeranz B. H., Birtch A. G., Barger A. C. Neural contrfl of intrarenal blood flow. Am J Physiol. 1968 Nov;215(5):1067–1081. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.215.5.1067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROWN J. J., DAVIES D. L., LEVER A. F., PARKER R. A., ROBERTSON J. I. THE ASSAY OF RENIN IN SINGLE GLOMERULI IN THE NORMAL RABBIT AND THE APPEARANCE OF THE JUXTAGLOMERULAR APPARATUS. J Physiol. 1965 Feb;176:418–428. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojo-Ortega J. M., Genest J. Index de l'activité histochimique de la glucose-y-phosphate déhydrogénase dans la "macula densa" (IMD) et sa distribution dans le cortex rénal chez le rat. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1970 Jun-Jul;18(11):595–599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojo-Ortega J. M., Granger P., Boucher R., Genest J. Studies on the distribution of the JGI in the renal cortex of dogs and beavers. Nephron. 1970;7(1):61–66. doi: 10.1159/000179808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sealey J. E., Gerten-Banes J., Laragh J. H. The renin system: Variations in man measured by radioimmunoassay or bioassay. Kidney Int. 1972 Apr;1(4):240–253. doi: 10.1038/ki.1972.34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner S. L. Improved assay methods for renin "concentration" and "activity" in human plasma. Methods using selective denaturation of renin substrate. Circ Res. 1967 Apr;20(4):391–402. doi: 10.1161/01.res.20.4.391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thurau K. W., Dahlheim H., Grüner A., Mason J., Granger P. Activation of renin in the single juxtaglomerular apparatus by sodium chloride in the tubular fluid at the macula densa. Circ Res. 1972 Sep;31(9 Suppl):182–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VIKHERT A. M., SEREBROVSKAIA Iu A. [On the problem of localizing rennin in the kidneys of normal animals and men]. Kardiologiia. 1962 Jul-Aug;2:10–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vander A. J. Effect of catecholamines and the renal nerves on renin secretion in anesthetized dogs. Am J Physiol. 1965 Sep;209(3):659–662. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.209.3.659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallin J. D., Blantz R. C., Katz M. A., Andreucci V. E., Rector F. C., Jr, Seldin D. W. Effect of saline diuresis on intrarenal blood flow in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1971 Nov;221(5):1297–1304. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.5.1297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. F., Ninomiya I., Franz G. N., Judy W. V. Hypothalamic stimulation and baroceptor reflex interaction on renal nerve activity. Am J Physiol. 1971 Dec;221(6):1768–1773. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.6.1768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zehr J. E., Feigl E. O. Suppression of renin activity by hypothalamic stimulation. Circ Res. 1973 May 5;32(Suppl):17–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Rouffignac C., Bonvalet J. P., Menard J. Renin content in superficial and deep glomeruli of normal and salt-loaded rats. Am J Physiol. 1974 Jan;226(1):150–154. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.226.1.150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



