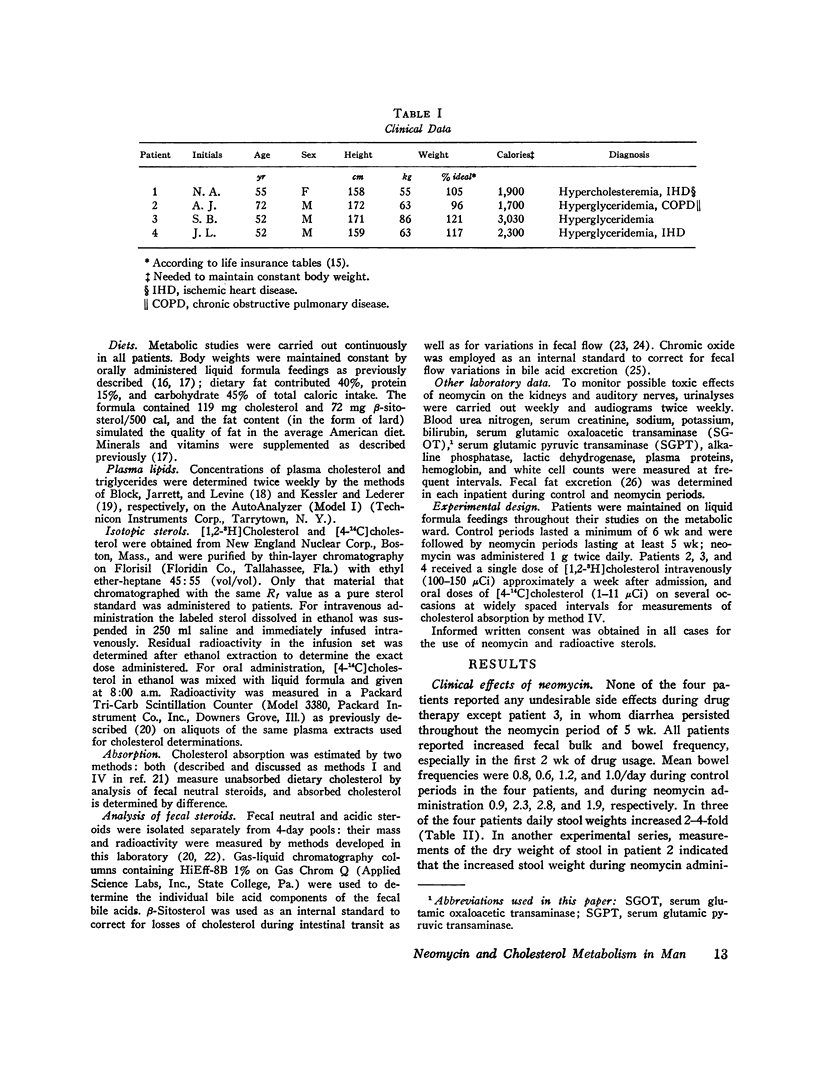
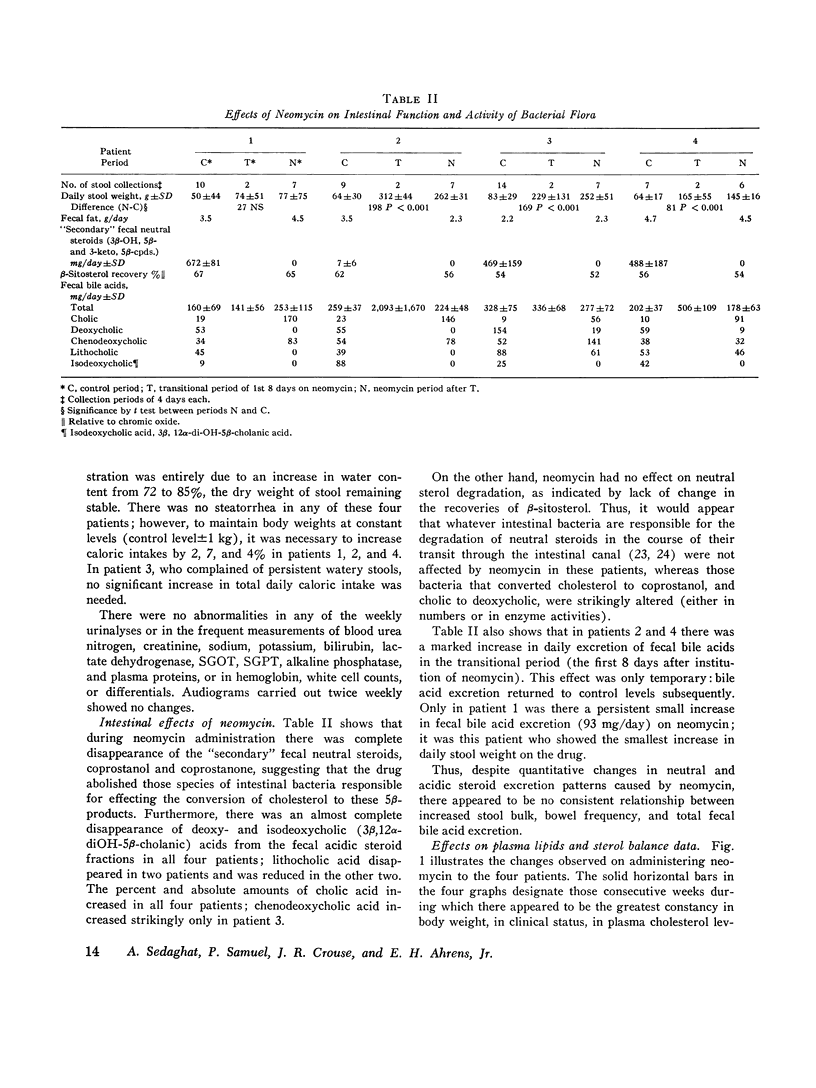
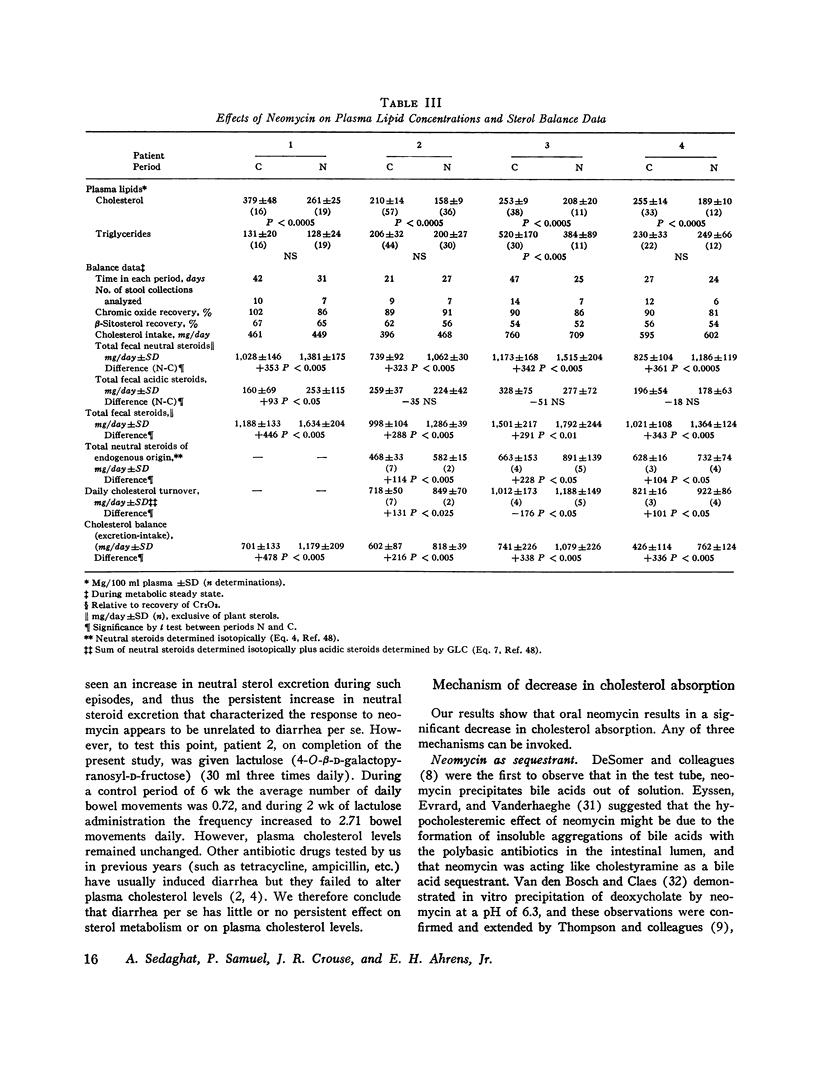
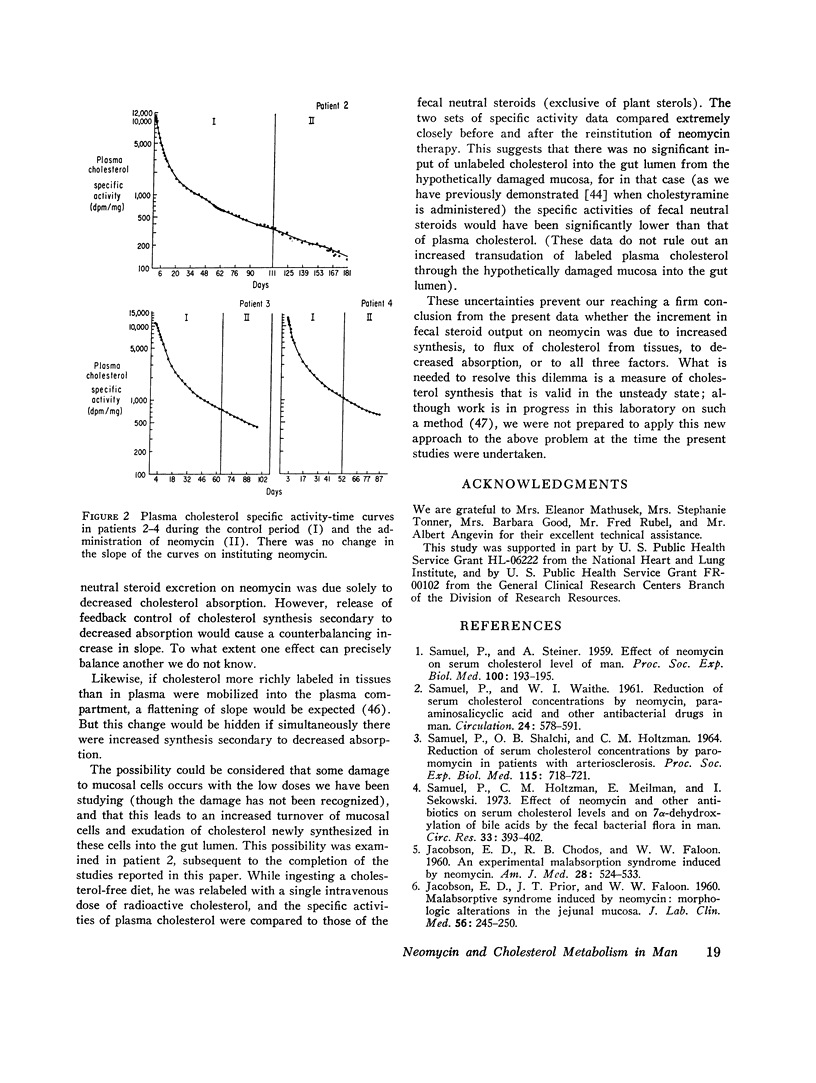
Abstract
The mode of action of the hypocholesteremic drug neomycin (2 g/day) was studied in four patients. All showed a significant reduction in plasma cholesterol concentrations (mean 25 percent, range 18-31 percent), and in one of three patients with hyperglyceridemia there was a decrease of plasma triglycerides of 26 percent. Cholesterol absorption was measured in three of four patients: there was a marked decrease. Sterol balance studies in four patients showed an unabating increase in fecal neutral steroid excretion (mean increase 345 mg/day, range 323-361) for 3-5 wk after plasma cholesterol levels had reached a new and lower plateau. Fecal acidic steroid excretion increased temporarily in two patients, with a sustained increase of 93 mg/day in only one. Daily stool weights increased significantly in three of four patients, though none had steatorrhea; there was a significant reduction in excretion of secondary bile acids; neutral sterol degradation rates were not affected by the drug. Slopes of plasma cholesterol-specific activity time curves did not change. These results fail to support the suggestion that neomycin acts as a bile acid precipitant. The finding of increased fecal neutral steroid excretion is consistent with decreased cholesterol absorption, but also with increased cholesterol absorption, but also with increased cholesterol synthesis (secondary to release of negative feedback control), with increased flux of cholesterol from tissues, or with a combination of all three actions.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AHRENS E. H., Jr, DOLE V. P., BLANKENHORN D. H. The use of orally-fed liquid formulas in metabolic studies. Am J Clin Nutr. 1954 Sep-Oct;2(5):336–342. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/2.5.336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DESOMER P., VANDERHAEGHE H., EYSSEN H. INFLUENCE OF BASIC ANTIBIOTICS ON SERUM- AND LIVER-CHOLESTEROL CONCENTRATIONS IN CHICKS. Nature. 1964 Dec 26;204:1306–1306. doi: 10.1038/2041306a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davignon J., Simmonds W. J., Ahrens E. H. Usefulness of chromic oxide as an internal standard for balance studies in formula-fed patients and for assessment of colonic function. J Clin Invest. 1968 Jan;47(1):127–138. doi: 10.1172/JCI105703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDELMAN I. S., LEIBMAN J. Anatomy of body water and electrolytes. Am J Med. 1959 Aug;27:256–277. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(59)90346-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyssen H., Evrard E., Vanderhaeghe H. Cholesterol-lowering effects of N-methylated neomycin and basic antibiotics. J Lab Clin Med. 1966 Nov;68(5):753–768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faloon W. W., Paes I. C., Woolfolk D., Nankin H., Wallace K., Haro E. N. Effect of neomycin and kanamycin upon intestinal absortion. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jun 14;132(2):879–887. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb43008.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forman D. T., Garvin J. E., Forestner J. E., Taylor C. B. Increased excretion of fecal bile acids by an oral hydrophilic colloid. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Apr;127(4):1060–1063. doi: 10.3181/00379727-127-32870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDSMITH G. A., HAMILTON J. G., MILLER O. N. Lowering of serum lipid concentrations: mechanisms used by unsaturated fats, nicotinic acid, and neomycin: excretion of sterols and bile acids. Arch Intern Med. 1960;105:512–517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRUNDY S. M., AHRENS E. H., Jr, MIETTINEN T. A. QUANTITATIVE ISOLATION AND GAS--LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHIC ANALYSIS OF TOTAL FECAL BILE ACIDS. J Lipid Res. 1965 Jul;6:397–410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garvin J. E., Forman D. T., Eiseman W. R., Phillips C. R. Lowering of human serum cholesterol by an oral hydrophilic colloid. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Dec;120(3):744–746. doi: 10.3181/00379727-120-30643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundy S. M., Ahrens E. H., Jr, Davignon J. The interaction of cholesterol absorption and cholesterol synthesis in man. J Lipid Res. 1969 May;10(3):304–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundy S. M., Ahrens E. H., Jr Measurements of cholesterol turnover, synthesis, and absorption in man, carried out by isotope kinetic and sterol balance methods. J Lipid Res. 1969 Jan;10(1):91–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundy S. M., Ahrens E. H., Jr, Salen G. Dietary beta-sitosterol as an internal standard to correct for cholesterol losses in sterol balance studies. J Lipid Res. 1968 May;9(3):374–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundy S. M., Ahrens E. H., Jr, Salen G. Interruption of the enterohepatic circulation of bile acids in man: comparative effects of cholestyramine and ileal exclusion on cholesterol metabolism. J Lab Clin Med. 1971 Jul;78(1):94–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundy S. M., Ahrens E. H., Jr, Salen G., Schreibman P. H., Nestel P. J. Mechanisms of action of clofibrate on cholesterol metabolism in patients with hyperlipidemia. J Lipid Res. 1972 Jul;13(4):531–551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundy S. M., Ahrens E. H., Jr The effects of unsaturated dietary fats on absorption, excretion, synthesis, and distribution of cholesterol in man. J Clin Invest. 1970 Jun;49(6):1135–1152. doi: 10.1172/JCI106329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HVIDT S., KJELDSEN K. Malabsorption induced by small doses of neomycin sulphate. Acta Med Scand. 1963 Jun;173:699–705. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1963.tb17455.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardison W. G., Rosenberg I. H. The effect of neomycin on bile salt metabolism and fat digestion in man. J Lab Clin Med. 1969 Oct;74(4):564–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann A. F., Poley J. R. Role of bile acid malabsorption in pathogenesis of diarrhea and steatorrhea in patients with ileal resection. I. Response to cholestyramine or replacement of dietary long chain triglyceride by medium chain triglyceride. Gastroenterology. 1972 May;62(5):918–934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOBSON E. D., CHODOS R. B., FALOON W. W. An experimental malabsorption syndrome induced by neomycin. Am J Med. 1960 Apr;28:524–533. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(60)90146-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOBSON E. D., PRIOR J. T., FALOON W. W. Malabsorptive syndrome induced by neomyclin: morphologic alterations in the jejunal mucosa. J Lab Clin Med. 1960 Aug;56:245–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARMEN A., WHYTE M., GOODMAN D. S. FATTY ACID ESTERIFICATION AND CHYLOMICRON FORMATION DURING FAT ABSORPTION. 1. TRIGLYCERIDES AND CHOLESTEROL ESTERS. J Lipid Res. 1963 Jul;4:312–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVEILLE G. A., POWELL R. C., SAUBERLICH H. E., NUNES W. T. Effect of orally and parenterally administered neomycin on plasma lipids of human subjects. Am J Clin Nutr. 1963 Jun;12:421–426. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/12.6.421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIETTINEN T. A., AHRENS E. H., Jr, GRUNDY S. M. QUANTITATIVE ISOLATION AND GAS--LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHIC ANALYSIS OF TOTAL DIETARY AND FECAL NEUTRAL STEROIDS. J Lipid Res. 1965 Jul;6:411–424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meihoff W. E., Kern F., Jr Bile salt malabsorption in regional ileitis, ileal resection and mannitol-induced diarrhea. J Clin Invest. 1968 Feb;47(2):261–267. doi: 10.1172/JCI105722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POWELL R. C., NUNES W. T., HARDING R. S., VACCA J. B. The influence of nonabsorbable antibiotics on serum lipids and the excretion of neutral sterols and bile acids. Am J Clin Nutr. 1962 Aug;11:156–168. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/11.2.156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quintão E., Grundy S. M., Ahrens E. H., Jr An evaluation of four methods for measuring cholesterol absorption by the intestine in man. J Lipid Res. 1971 Mar;12(2):221–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Race T. F., Paes I. C., Faloon W. W. Intestinal malabsorption induced by oral colchicine. Comparison with neomycin and cathartic agents. Am J Med Sci. 1970 Jan;259(1):32–41. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197001000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAMUEL P., SHALCHI O. B., HOLTZMAN C. M. REDUCTION OF SERUM CHOLESTEROL CONCENTRATIONS BY PAROMOMYCIN IN PATIENTS WITH ARTERIOSCLEROSIS. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Mar;115:718–721. doi: 10.3181/00379727-115-29017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAMUEL P., STEINER A. Effect of neomycin on serum cholesterol level of man. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Jan;100(1):193–195. doi: 10.3181/00379727-100-24569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAMUEL P., WHITHE W. I. Reduction of serum cholesterol concentrations by neomycin, para-aminosalicylic acid, and other antibacterial drugs in man. Circulation. 1961 Sep;24:578–591. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.24.3.578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel P., Holtzman C. H., Meilman E., Perl W. Effect of neomycin on exchangeable pools of cholesterol in the steady state. J Clin Invest. 1968 Aug;47(8):1806–1818. doi: 10.1172/JCI105870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel P., Holtzman C. M., Meilman E., Sekowski I. Effect of neomycin and other antibiotics on serum cholesterol levels and on 7alpha-dehydroxylation of bile acids by the fecal bacterial flora in man. Circ Res. 1973 Oct;33(4):393–402. doi: 10.1161/01.res.33.4.393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel P., Meilman E. Dietary lipids and reduction of serum cholesterol levels by neomycin in man. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 Sep;70(3):471–479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodhi H. S., Kudchodkar B. J. Correlating metabolism of plasma and tissue cholesterol with that of plasma-lipoproteins. Lancet. 1973 Mar 10;1(7802):513–519. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)90329-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson G. R., Barrowman J., Gutierrez L., Dowling R. H. Action of neomycin on the intraluminal phase of lipid absorption. J Clin Invest. 1971 Feb;50(2):319–323. doi: 10.1172/JCI106497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson G. R., MacMahon M., Claes P. Precipitation by neomycin compounds of fatty acid and cholesterol from mixed micellar solutions. Eur J Clin Invest. 1970 Mar;1(1):40–47. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1970.tb00595.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


