Abstract
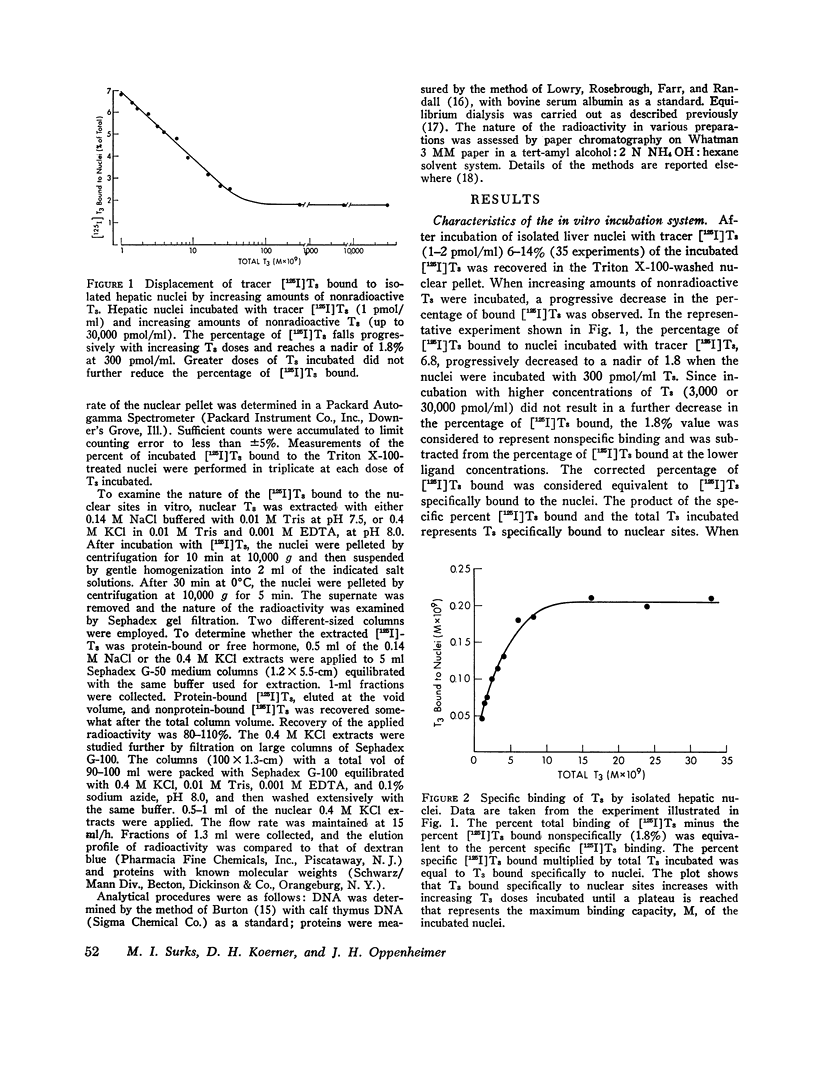
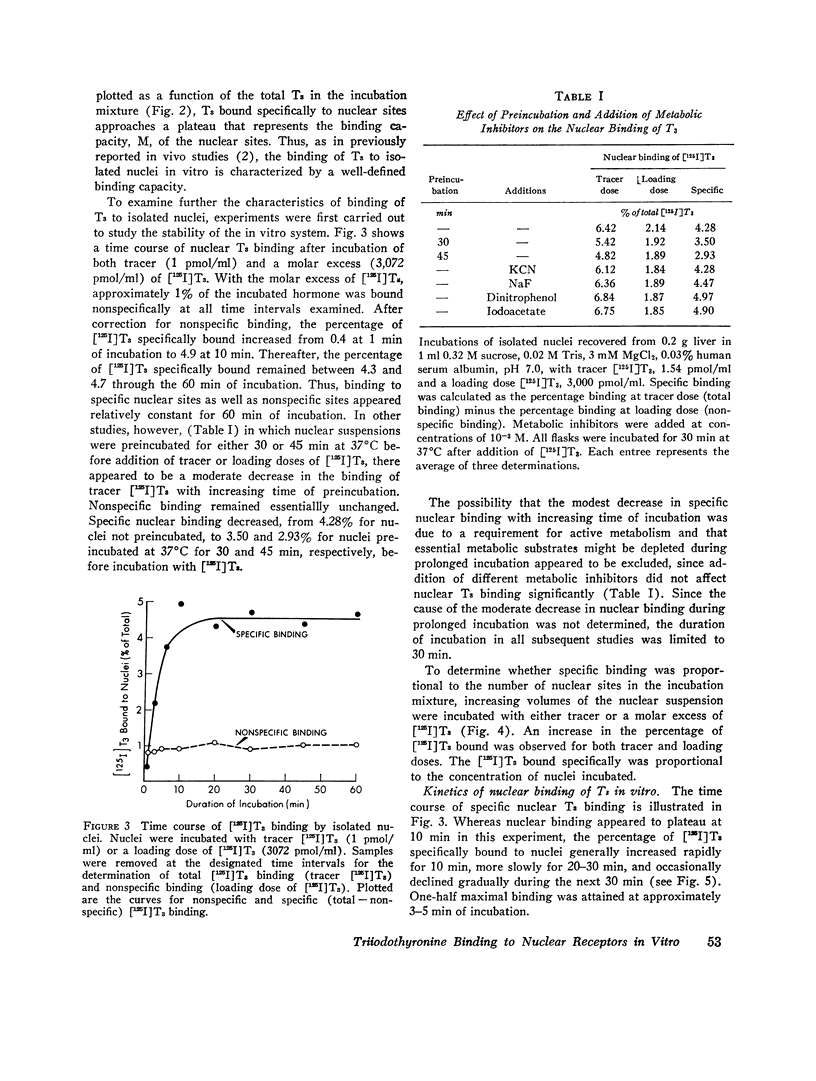
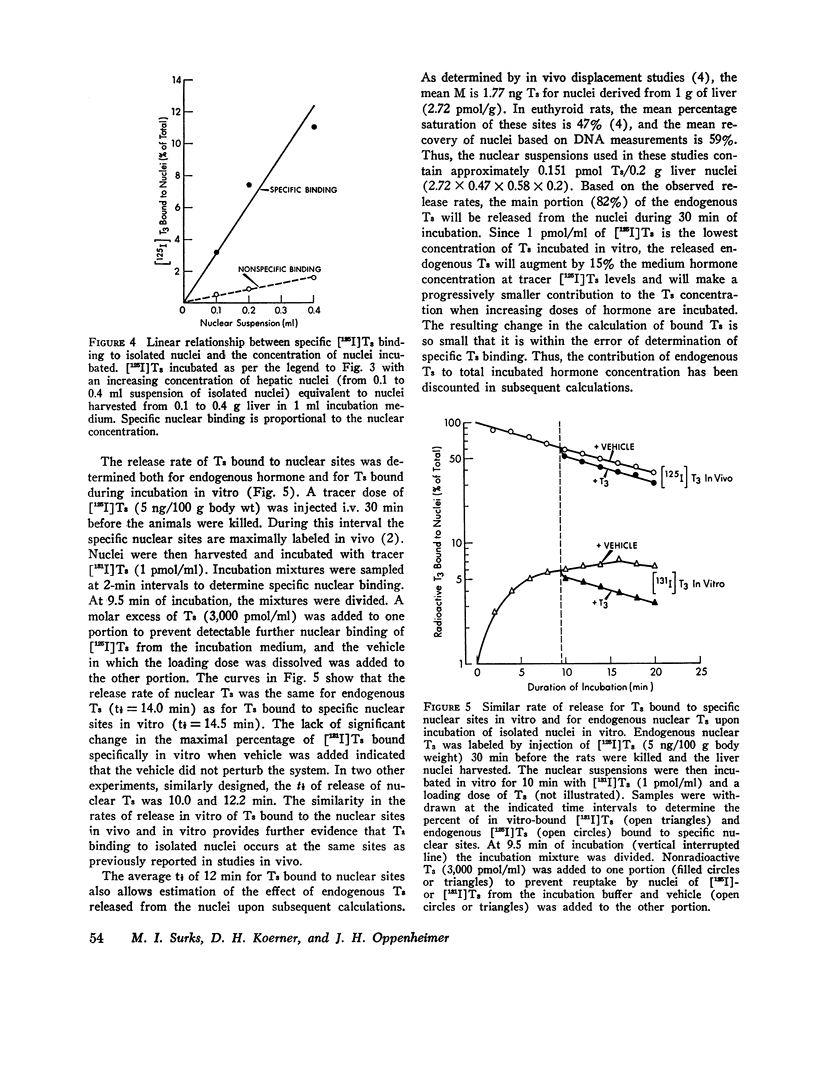
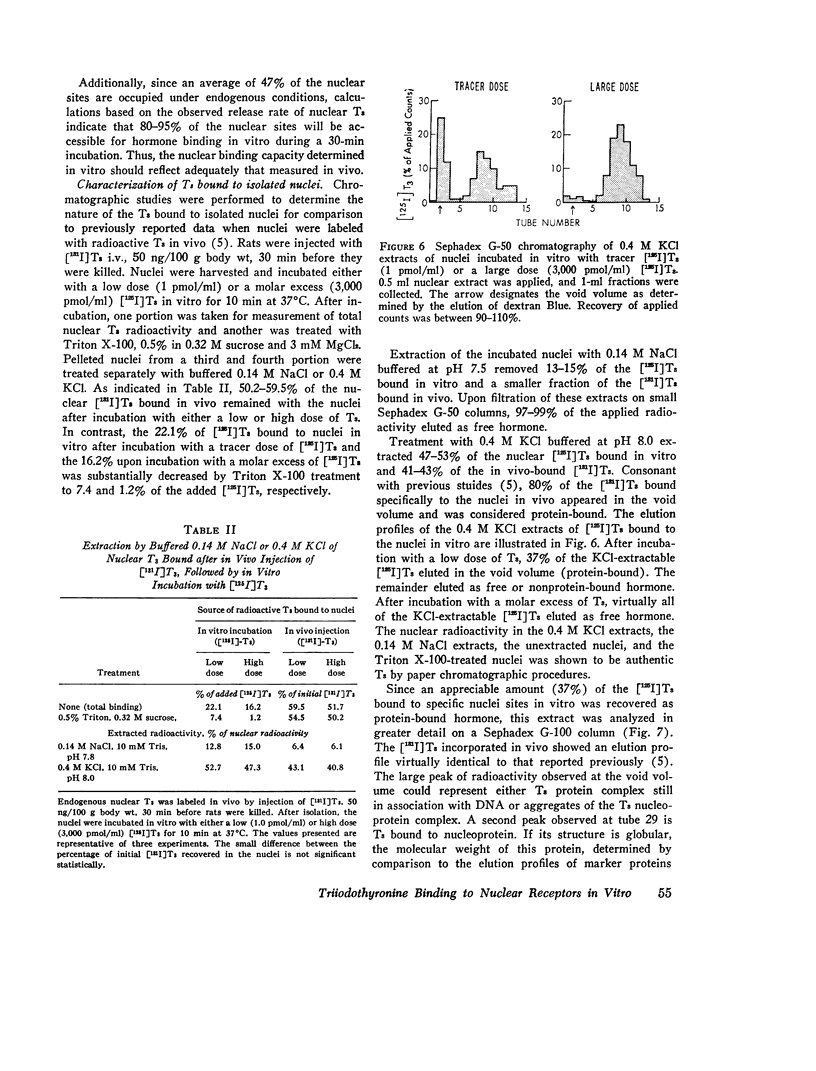
Isolated hepatic nuclei from euthyroid rats were incubated with tracer (125I)L-triiodothyronine (T3) and increasing doses of nonradioactive T3 for 30 min at 37degrees C. The T3 bound specifically to nuclear sites increased with increasing T3 doses to a plateau, which represented the nuclear binding capacity, M. Addition of 1 mM KCN, NaF, dinitrophenol, oriodoacetate did not affect nuclear binding, indicating that active metabolism was not required. Kinetic studies showed that the nuclear sites were equilibrated with T3 within 30 min of incubation (one-half maximal binding at 3 min) and that the rate of release of T3 in vitro (0.058 min-1) was the same for endogenous T3 or for T3 bound to nuclei in vitro. Nuclear T3 resisted extraction with 0.14 M NaC1 buffered at pH 7.5, but both endogenous hormone and T3 bound in vitro were readily extracted by 0.4 M KC1 at pH 8.0. The elution profiles of endogenous and in vitro-bound T3 from Sephadex G-100 columns showed a common protein peak with a molecular weight of 60-65,000, assuming a globular protein. Scatchard analysis of in vitro displacement studies showed a single class of binding sites. Mean M equals 0.23 times 10-9 M or 0.85 ng T3 for nuclei isolated from 1 g of liver. Mean M closely corresponded to that anticipated from reported in vivo studies. The apparent association constant Ka for the nuclear sites, 5.55 times 108 M-1, was lower than in studies in vivo, probably attributable to the different ionic milieu of nuclei in the incubation buffer and in the intact cell. Thus, the identity of the nuclear T3 binding sites studied in vitro to those reported for endogenous hormone is demonstrated by similar binding capacities, release rates, analogue binding affinities (previously reported), and localization to chromatin nonhistone proteins of comparable molecular weight. The role of cytosol protein in nuclear binding was assessed by comparing binding parameters for extensively washed nuclei and nuclei incubated either with contaminating or added cytosol. No difference in Ka or M was found. Moreover, it was unlikely that specific cytosol proteins were already present in nuclei and functioned during incubation as a shuttle for T3, since Ka and M for nuclei obtained from athyreotic rats were similar to Ka and M for nuclei from euthyroid animals. Thus, an initial interaction between T3 and specific cytosol proteins does not appear to be a prerequisite for translocation of T3 to nuclear sites.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeGroot L. J., Strausser J. L. Binding of T3 in rat liver nuclei. Endocrinology. 1974 Jul;95(1):74–83. doi: 10.1210/endo-95-1-74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillman W., Surks M. I., Oppenheimer J. H. Quantitative aspects of iodothyronine binding by cytosol proteins of rat liver and kidney. Endocrinology. 1974 Aug;95(2):492–498. doi: 10.1210/endo-95-2-492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmour R. S., Paul J. RNA transcribed from reconstituted nucleoprotein is similar to natural RNA. J Mol Biol. 1969 Feb 28;40(1):137–139. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90301-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada S., Torizuka K., Miyake T., Fukase M. Specific binding proteins of thyroxine and triiodothyronine in liver soluble proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Mar 24;201(3):479–492. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(70)90168-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koerner D., Surks M. I., Oppenheimer J. H. In vitro demonstration of specific triiodothyronine binding sites in rat liver nuclei. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 Apr;38(4):706–709. doi: 10.1210/jcem-38-4-706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OPPENHEIMER J. H., SQUEF R., SURKS M. I., HAUER H. BINDING OF THYROXINE BY SERUM PROTEINS EVALUATED BY EQUILIBRUM DIALYSIS AND ELECTROPHORETIC TECHNIQUES. ALTERATIONS IN NONTHYROIDAL ILLNESS. J Clin Invest. 1963 Nov;42:1769–1782. doi: 10.1172/JCI104862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer J. H., Koerner D., Schwartz H. L., Surks M. I. Specific nuclear triiodothyronine binding sites in rat liver and kidney. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1972 Aug;35(2):330–333. doi: 10.1210/jcem-35-2-330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer J. H., Schwartz H. L., Dillman W., Surks M. I. Effect of thyroid hormone analogues on the displacement of 125I-L-triiodothyronine from hepatic and heart nuclei in vivo: possible relationship to hormonal activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Dec 10;55(3):544–550. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91177-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer J. H., Schwartz H. L., Surks M. I. Tissue differences in the concentration of triiodothyronine nuclear binding sites in the rat: liver, kidney, pituitary, heart, brain, spleen, and testis. Endocrinology. 1974 Sep;95(3):897–903. doi: 10.1210/endo-95-3-897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuels H. H., Tsai J. S. Thyroid hormone action in cell culture: domonstration of nuclear receptors in intact cells and isolated nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3488–3492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuels H. H., Tsai J. S. Thyroid hormone action. Demonstration of similar receptors in isolated nuclei of rat liver and cultured GH1 cells. J Clin Invest. 1974 Feb;53(2):656–659. doi: 10.1172/JCI107601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz H. L., Surks M. I., Oppenheimer J. H. Quantitation of extrathyroidal conversion of L-thyroxine to 3,5,3'-triiodo-L-thyronine in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1971 May;50(5):1124–1130. doi: 10.1172/JCI106584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaulding S. W., Davis P. J. Thyroxine binding to soluble proteins in rat liver and its sex dependence. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jan 19;229(1):279–283. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90345-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterling K., Saldanha V. F., Brenner M. A., Milch P. O. Cytosol-binding protein of thyroxine and triiodothyronine in human and rat kidney tissue. Nature. 1974 Aug 23;250(5468):661–663. doi: 10.1038/250661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surks M. I., Koerner D., Dillman W., Oppenheimer J. H. Limited capacity binding sites for L-triiodothyronine in rat liver nuclei. Localization to the chromatin and partial characterization of the L-triiodothyronine-chromatin complex. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 25;248(20):7066–7072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surks M. I., Schadlow A. R., Oppenheimer J. H. A new radioimmunoassay for plasma L-triiodothyronine: measurements in thyroid disease and in patients maintained on hormonal replacement. J Clin Invest. 1972 Dec;51(12):3104–3113. doi: 10.1172/JCI107137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tata J. R., Widnell C. C. Ribonucleic acid synthesis during the early action of thyroid hormones. Biochem J. 1966 Feb;98(2):604–620. doi: 10.1042/bj0980604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai J. S., Samuels H. H. Thyroid hormone action: demonstration of putative nuclear receptors in human lymphocytes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 May;38(5):919–922. doi: 10.1210/jcem-38-5-919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widnell C. C., Tata J. R. A procedure for the isolation of enzymically active rat-liver nuclei. Biochem J. 1964 Aug;92(2):313–317. doi: 10.1042/bj0920313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




