Abstract
Purpose
To study the role of drug transporters in central nervous system (CNS) penetration and cellular accumulation of erlotinib and its metabolite, OSI-420.
Experimental Design
After oral erlotinib administration to wild-type and ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter-knockout mice (Mdr1a/b−/−, Abcg2−/−, Mdr1a/b−/−Abcg2−/−, and Abcc4−/−), plasma was collected and brain extracellular fluid (ECF) was sampled using intracerebral microdialysis. A pharmacokinetic model was fit to erlotinib and OSI-420 concentration-time data and brain penetration (PBrain) was estimated by the ratio of ECF-to-unbound plasma area under concentration-time curves. Intracellular accumulation of erlotinib was assessed in cells overexpressing human ABC transporters or SLC22A solute carriers.
Results
PBrain in wild-type mice was 0.27±0.11 and 0.07±0.02 (mean ± SD) for erlotinib and OSI-420, respectively. Erlotinib and OSI-420 PBrain in Abcg2−/− and Mdr1a/b−/−Abcg2−/− mice were significantly higher than in wild-type mice. Mdr1a/b−/− mice showed similar brain ECF penetration as wild-type mice (0.49±0.37 and 0.04±0.02 for erlotinib and OSI-420, respectively). In vitro, erlotinib and OSI-420 accumulation was significantly lower in cells overexpressing BCRP than control cells. Only OSI-420, not erlotinib, showed lower accumulation in cells overexpressing P-gp than control cells. The P-gp/BCRP inhibitor, elacridar, increased erlotinib and OSI-420 accumulation in BCRP-overexpressing cells. Erlotinib uptake was higher in OAT3 and OCT2-transfected cells as compared to empty vector control cells.
Conclusion
Abcg2 is the main efflux transporter preventing erlotinib and OSI-420 penetration in mouse brain. Erlotinib and OSI-420 are substrates for SLC22A family members OAT3 and OCT2. Our findings provide a mechanistic basis for erlotinib CNS penetration, cellular uptake, and efflux mechanisms.
Keywords: erlotinib, OSI-420, pharmacokinetics, CNS penetration, microdialysis
Introduction
Erlotinib (Tarceva™) is an orally administered epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitor approved for certain types of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and pancreatic cancer (1). In humans, erlotinib is extensively metabolized primarily by hepatic CYP3A4 and CYP3A5 with some metabolism by CYP1A2 and CYP2C8 (2). The metabolite, OSI-420, retains EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitory activity as well as in vivo tumor growth inhibitory activity (3). Clinical trials have evaluated the safety and activity of erlotinib in patients with primary and secondary central nervous system (CNS) tumors with frequent EGFR alterations, such as high-grade glioma and brain metastases of NSCLC (4, 5). In most of these studies, erlotinib failed to show clinically significant activity (1, 4, 6). A potential explanation for this lack of efficacy is that the blood brain barrier (BBB) prevents the accumulation of effective erlotinib concentrations in the tumor (7, 8). This is supported by evidence from clinical studies showing low erlotinib and OSI-420 accumulation in high-grade glioma (9).
One mechanism by which the blood brain barrier (BBB) limits erlotinib CNS penetration is the expression of efflux proteins of the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter family at the brain endothelial cells (10). ABC transporters likely to impede erlotinib CNS distribution include P-glycoprotein (P-gp/MDR1/ABCB1; Mdr1a/b in mice), breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP/ABCG2; Bcrp1/Abcg2 in mice), and the multidrug resistance-associated protein 4 (MRP4/ABCC4; Mrp4/Abcc4 in mice) (11, 12). Expression of efflux transporters on tumor cell membranes would be an additional mechanism of drug resistance preventing the intracellular penetration of anti-cancer drugs (13).
In addition to ABC transporters, uptake transporters located at the BBB or at the blood-tumor barrier could also regulate drug delivery to the CNS and brain tumors (14). Several uptake transporters of the SLC22A family are localized at the BBB or at the blood cerebrospinal fluid barrier (BCSFB) where they affect the disposition of their substrates (15-18). The expression of some uptake transporters is detected in vessels of high-grade glioma where they may affect drug accumulation inside the tumor (19). However, the affinity of these transporters towards many anti-cancer agents, including erlotinib, has not been studied.
Erlotinib concentrations in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of patients with brain tumors have been previously reported as 8% of the total plasma concentration (20, 21). However, several studies in animals have demonstrated differential (usually increased) drug distribution in the CSF as compared to the brain parenchyma extracellular fluid (ECF) (22-24), emphasizing the limitations of using CSF sampling, or whole brain homogenates, to examine CNS drug penetration.
In the present study, we used intracerebral microdialysis sampling to assess the role of murine ABC transporters Bcrp1, P-gp, and Mrp4 in CNS penetration of erlotinib and OSI-420. Furthermore, we used a panel of cell lines expressing human efflux or uptake transporters to investigate transport processes involved in CNS penetration and intracellular accumulation of erlotinib and OSI-420.
Materials and Methods
Animals
Animals used were wild-type FVB, Abcg2−/−, Mdr1a/b−/−, Abcc4−/−, and Mdr1a/b−/−Abcg2−/− mice. All mice were on a FVB genetic background, 3-4 month old, females, and provided by Taconic (Hudson, NY; except Abcc4−/−, obtained at SJCRH). All animal studies were conducted using protocols and conditions approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee.
Chemicals and reagents
GF120918 was purchased from API (China). Erlotinib, OSI-420 analytical standards, and the internal standards for each compound used in the mass spectrometry assay were kindly provided by OSI pharmaceuticals (Uniondale, NY). 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (HPBCD) was purchased from CTD, Inc. (High Springs, FL).
Cell lines
The porcine kidney epithelial LLC-PK1 cell line and the L-MDR1 cell lines stably expressing human ABCB1 were cultured in DMEM, 10% fetal bovine serum, penicillin 100 U/ mL and streptomycin 100 μg/mL; all from Invitrogen (Carlsbad, CA). Saos2 cells containing pcDNA3.1 empty vector, ABCG2, or ABCC4 were maintained in DMEM containing 10% fetal bovine serum, penicillin (100 U/mL), streptomycin (100 μg/mL), and G418 sulfate (500 μg/mL; Invitrogen). HEK-293 cells stably transfected with OCT1, OCT2 (25), OAT1, OAT2, OAT3 (26), OCTN1, and OCTN2 (27), along with pcDNA vector–transfected controls were cultured in DMEM supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum and G418 sulfate (400-800 μg/mL).
Determination of erlotinib and OSI-420 protein binding in mouse plasma
Erlotinib and OSI-420 were added to mouse plasma (Hiltop, Scottdale, PA) to make final erlotinib and OSI-420 concentrations of 1, 2, and 4 μg/mL. 200 uL of plasma were added to each well of a 96-well equilibrium dialysis plate (Harvard Apparatus, MA) and incubated on a rotator at 37°C. Samples were collected from plasma and PBS buffer chambers at several time points after starting the experiment. Samples were analyzed using a validated liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry (LC/MS) method (28). Unbound fraction (fu) of either erlotinib or OSI-420 was calculated as follows:
where CPBS and CPlasma are the concentrations of erlotinib or OSI-420 in PBS and plasma, respectively. To compare the unbound fraction of erlotinib and OSI-420 in different strains, plasma was isolated from each strain and equilibrium dialysis was performed as previously described.
Erlotinib and OSI-420 plasma pharmacokinetics
A single erlotinib dose was administered to all five strains of mice (n = 8-13 mice per group). To administer erlotinib, Tarceva™ (OSI Pharmaceuticals, Uniondale, NY) tablets were pulverized and suspended in 0.2% carboxymethylcellulose and 0.05% Tween 20, for a final concentration of 5 mg/mL. The erlotinib suspension was administered at a dosage of 50 mg/kg by oral gavage. Plasma samples were taken by retro-orbital bleeding at 7 time points after drug administration (5 minutes, 0.5 hrs, 1, 2, 6, 12, and 24 hours). At least four different animals contributed to each time point. Blood samples were centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 3 minutes. Plasma samples were immediately stored at −80°C till further analysis using LC MS/MS (24, 28).
Development of pharmacokinetic limited sampling models for erlotinib and OSI-420
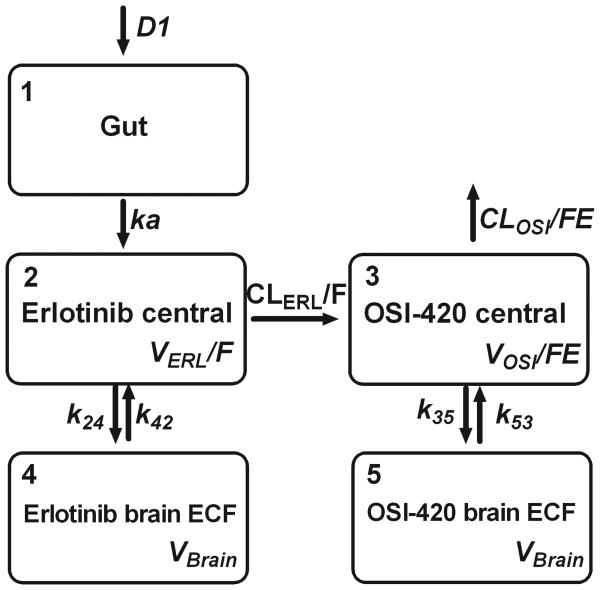
Data from the plasma pharmacokinetic experiment were analyzed with nonlinear mixed-effects modeling using the importance sampling EM algorithm in NONMEM VII (29). A model with one compartment for erlotinib and one compartment for OSI-420 and first-order conversion from erlotinib to OSI-420 and first-order elimination of OSI-420 was used to fit the plasma concentration-time data. Models with first-order absorption, zero-order absorption and sequential zero-order and first-order absorption were tested. The appropriate model was chosen based on objective function value (OFV) and inspection of goodness-of-fit plots. The estimated parameters included the duration of zero-order infusion (D1), first-order absorption rate constant (ka) apparent oral clearance of erlotinib (CLERL/F), apparent volume of distribution of erlotinib (VERL/F), apparent clearance of OSI-420 (CLOSI/FE), and apparent volume of distribution of OSI-420 (VOSI/FE), where F is the bioavailability and FE is the fraction of erlotinib converted to OSI-420. Inter-individual variability (IIV) terms were added to the CLERL/F, VERL/F, CLOSI/FE, and D1 parameters. IIV was modeled as a log-normal distribution and a proportional error model was used for residual variability. Data below the lower limit of quantitation of 1 ng/mL were included in the analysis with a likelihood-based approach using method M3 as previously described (30). Each strain of mice was analyzed separately, and the model parameters were used to develop a limited sampling strategy using the D-optimality algorithm in ADAPT 5 (31). The limited sampling strategy consisted of three time points at which plasma samples could be drawn in each microdialysis experiment in order to estimate the plasma exposure using the population priors.
In vitro probe recovery studies
To study erlotinib and OSI-420 dialyzability as well as strategies required to enhance their relative recovery through microdialysis probes, a stock solution containing 1 μg/mL erlotinib and 0.5 μg/mL OSI-420 in artificial CSF (aCSF, (32)) was prepared. A 1 mm microdialysis probe (MBR-1-5 brain probe, BASi, IN) was inserted into this solution and perfused with: (a) aCSF, (b) 10% HPBCD in aCSF, and (c) bovine serum albumin (BSA; 4% in aCSF) for 1 hour followed by 10% HPBCD in aCSF. To assess the effect of flow rate on the recovery of erlotinib and OSI-420 from the stock solution, perfusates were pumped through the probe at 0.3, 0.5, 1, and 2 μL/min and dialysates were collected. Dialysates and stock solution samples were analyzed using LC MS/MS. Relative recovery (%) was calculated as CDial/Cstock*100, where CDial is the erlotinib or OSI-420 concentration in the dialysates and Cstock is the erlotinib or OSI-420 concentration in the stocks. All in vitro recovery experiments were performed at room temperature under stirred conditions.
Erlotinib brain microdialysis studies
In vivo microdialysis experiments were conducted to sample erlotinib and OSI-420 in the ECF of the mouse brain after a single 50 mg/kg oral dose of erlotinib suspended in 0.2% carboxymethylcellulose and 0.05% Tween 20. First, a microdialysis guide cannula (MD-2255, Bioanalytical Systems- West Lafayette, IN) was inserted vertically into the striatum in the cerebral cortex (1.1 mm anterior to bregma suture, 1.1 mm lateral to sagittal suture, 2.0 mm ventral). The surgery was performed under anesthesia (100 mg/kg ketamine and 10 mg/kg xylazine) as previously reported (24, 33). Mice recovered for at least 3 days before the microdialysis experiment. The day of the experiment, a 1-mm-length microdialysis probe (MBR-1-5, BASi, IN) was primed and flushed with aCSF containing 10% HPBCD. The newly primed probe was then slowly inserted in the guide cannula and allowed to equilibrate for 1 hour at 0.5 μL/min. Under slight isoflurane anesthesia (2.5% in oxygen), the mouse received a 50 mg/kg dose of erlotinib, by oral gavage. Then, dialysates were collected for 24 hours, using a fraction collector CMA 142 (North Chelmsford, MA). We used the limited sampling strategy described above to collect plasma samples. At the end of the experiment, the animal was euthanized and the brain was fixed in 10% neutral buffered formalin for 72 hours and embedded in paraffin. H&E-stained sections (4 μm) were examined microscopically to examine the brain tissue surrounding the cannula and probe.
In vivo microdialysis probe recovery using zero flow rate (ZFR) method
After the first 5 hours of sample collection, dialysates were collected at different flow rates 0.2, 0.5, 1, and 4 μL/min. Dialysate concentrations were allowed to stabilize for 10-15 min between each change. The recovery experiment lasted 2.5 hours after which the flow rate was set back to 0.5 μL/min for the remainder of the experiment. Samples were analyzed using LC MS/MS and concentrations were plotted against flow rate. Extrapolation to zero flow rate was performed as previously described (34) using non-linear regression analysis in GraphPad Prism version 5.0b for Mac OS X (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA) to fit the data using the following formula:
where r (mass transport coefficient) and A (surface area of the dialysis membrane) are constants, estimated using non-linear regression, C0 represents erlotinib or OSI-420 concentrations in the dialysed tissue, CDial is erlotinib or OSI-420 concentration in dialysates, and X is the flow rate at which the dialysate was obtained at different flow rates. Since the microdialysis experiment was performed at 0.5 μL/min perfusion rate, in vivo recovery was calculated as: CDial at 0.5 μL/min / C0 (34, 35).
Pharmacokinetic analysis of microdialysis studies
A pharmacokinetic model was fit simultaneously to the plasma and brain ECF microdialysis data. In order to incorporate information from the previous plasma pharmacokinetic experiment, pharmacokinetic data from both experiments was pooled and analyzed together. Modeling was performed with NONMEM VII using the importance sampling EM algorithm. The model was based on the model described above for plasma data, with additional compartments for erlotinib and OSI-420 in brain ECF. In addition to the previous parameters, this model included first-order rate constants describing the transfer of erlotinib into and out of the brain ECF (k24 and k42), first-order rate constants describing the transfer of OSI-420 into and out of the brain ECF (k35 and k53), and a single volume of distribution parameter for erlotinib and OSI-420 in the brain ECF (Vbrain). IIV was included on D1, CLERL/F, VERL/F, CLOSI/FE, VOSI/FE, and inter-compartment rate parameters.
Individual posthoc parameters were used to simulate the concentration-time curve from 0 to 24 h in plasma and brain ECF for erlotinib and OSI-420 for each mouse from which the area under the concentration-time curves for plasma and brain (AUC0-24,Plasma and AUC0-24,Brain) were calculated with the log-linear trapezoidal method. Unbound plasma AUC (AUC0-24,uPlasma) for erlotinib and OSI-420 were obtained by multiplying AUC0-24,Plasma by the appropriate unbound fraction (fu). The extent of brain penetration (PBrain) for erlotinib and OSI-420 was calculated as the brain ECF-to-unbound plasma AUC ratio:
Differences in PBrain between wild-type mice and other mouse strains were assessed using the Mann-Whitney test.
Intracellular drug accumulation studies
To study the role of several efflux and influx transporters in erlotinib intracellular accumulation, we used an array of cell lines expressing specific efflux or influx transporters and compared the accumulation of erlotinib or OSI-420 in the cell lines over-expressing each transporter to that transfected with an empty vector. Intracellular accumulation of erlotinib and OSI-420 were measured in Saos2 cells transfected with human BCRP or MRP4 and LLC-PK1 cells transfected with MDR1, in presence or absence of the P-gp/BCRP inhibitor, elacridar. Uptake experiments were done using HEK293 cells transfected with cDNAs coding for members of human OCT, OAT, and OCTN families. Briefly, 5 × 105 cells of each cell line were plated in 6-well plates in triplicates. Cells were allowed to attach overnight. For cells expressing the OAT1, 2, 3, and their vector control, sodium butyrate (5 μmol/L) was added to the medium for 24 h to induce expression of the respective transporter genes (26). At the day of experiment, medium was removed and cells were incubated with media containing 0.5 μg/mL of either erlotinib or OSI-420 at 37°C. At a predetermined time interval, the experiment was terminated by removing the incubation medium and adding ice-cold PBS. Cells were washed twice with ice-cold PBS, gently scraped, collected, and centrifuged for 4 minutes at 3000 rpm at 0°C. Subsequently, cells were resuspended in 100 μL of 5 mM ammonium formate for cell lysis. The BCA assay was used to determine protein concentrations. Erlotinib and OSI-420 concentrations in the lysis supernatants were determined using LC MS/MS (28).
Results
Erlotinib and OSI-420 protein binding in mouse plasma
Using equilibrium dialysis we assessed the extent of plasma protein binding for erlotinib and OSI-420. The range of concentrations used was similar to those expected after administering erlotinib orally to mice at 20 mg/kg. The time after which the dialysis reached equilibrium was 10 hours. Erlotinib, as well as its metabolite, was found to be highly protein bound in mouse plasma. Unbound fraction (fu) of erlotinib was 4.8% ± 0.7% and for OSI-420 was 6.6 % ± 0.7%. No significant differences were found in unbound fractions of erlotinib or OSI-420 between strains (Supplementary Table 2).
Limited sampling models for erlotinib and OSI-420
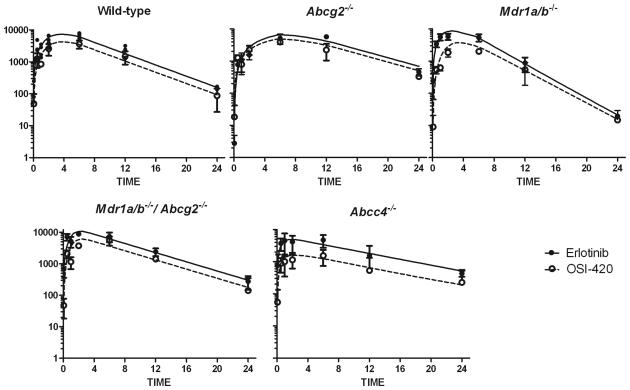
The erlotinib dosage used in preclinical studies has ranged from 5 to 150 mg/kg/day orally for up to 4 weeks (36, 37). In our studies, we sought to use an erlotinib dosage that achieves a systemic exposure similar to that observed in patients (4, 21). First, we conducted a plasma pharmacokinetic study of a single erlotinib dose administered orally at a dosage of 50 mg/kg in wild-type, Abcg2−/−, Mdr1a/b−/−, Mdr1a/b−/−Abcg2−/−, and Abcc4−/− mice. This single dose of erlotinib was tolerated well by all strains. Between the different absorption models, a sequential zero-order and first-order model described the data best based on goodness-of-fit plots and lowered the OFV between 6 and 35 units for different strains compared to first-order absorption alone and lowered the OFV between 9 and 33 units for different strains for zero-order absorption alone. The final model is shown in Fig. 1. Concentration-time plots for erlotinib and OSI-420 along with the model-predicted concentrations are shown in Fig. 2. and Supplementary Fig. 3. Pharmacokinetic parameters for all strains are listed in Supplementary Table 1. The AUC0-24,Plasma in each strain was compared to wild-type mice. Mean AUC0-24,Plasma for Abcg2−/−, Mdr1a/b−/−, Mdr1a/b−/−Abcg2−/−, and Abcc4−/− strains were 1.25, 0.9, 1.3, 0.9 fold compared to that of wild-type mice. Using the population parameters, we determined the optimal sampling time points to calculate the plasma AUC of erlotinib and OSI-420, constraining to three time points over 18 h. The optimal time points were similar in all strains: one early time point after the administration (5 min), one coinciding with the plateau (range from 7.8 to 9 hours), and one late time point (18 hours). For the ease of conducting the experiments, we chose to obtain plasma samples at 0.08, 8, and 18 hours from all strains.
Fig. 1.
Compartmental pharmacokinetic model for erlotinib and OSI-420. D1, duration of zero-order absorption; ka, first-order absorption rate constant; VERL/F, apparent volume of distribution of erlotinib; CLERL/F, apparent clearance of erlotinib; VOSI/FE, apparent volume of distribution of OSI-420; CLOSI/FE, apparent clearance of OSI-420; k24/k42, first-order rate constants of erlotinib in the brain extracellular fluid; k35/k53, first-order rate constants of OSI-420 in the brain extracellular fluid; VBrain, apparent volume of distribution of the brain extracellular fluid.
Fig.2.
Plasma concentration-time plots of erlotinib (■) and OSI-420 (○) after oral administration of a single dose of 20 mg/kg erlotinib. Model-fitted curves are represented for erlotinib (solid line) and OSI-420 (dashed line)
In vitro microdialysis studies
Because reproducible dialysis of lipophilic drugs can be difficult using conventional microdialysis methods (38, 39), we anticipated that the microdialysis of erlotinib would require the inclusion of an affinity-based trapping agent, such as HPBCD, in the perfusate. Such modifications in the perfusate have been used before to increase the recovery of poorly dialyzable drugs (40). Results of our preliminary in vitro microdialysis experiments supported that erlotinib and OSI-420 had relatively low relative recovery (1 and 2%, respectively) using aCSF as a perfusate. The addition of 10% HPBCD in aCSF improved the recovery of erlotinib and OSI-420 by ~ 8-fold (Supplementary Figure 1A). Second, we tested the effect of different flow rates (0.3, 0.5, 1, and 2 μL/min) on relative recovery. Increasing the flow rate yielded lower relative recovery. Lastly, we evaluated the effect of perfusing the microdialysis tubes with 4% BSA in order to prevent the binding of the drug to the tubes and thus improve the recovery. This strategy did not improve the relative recovery and added complexity due to tube blockage and flow resistance (data not shown). Thus, we decided to use 10% HPBCD in aCSF at 0.5 μL/min at room temperature for the in vivo microdialysis experiments to obtain sufficient recovery with adequate sample volume (30 μL/h). The in vitro recovery at that flow rate was 18% ± 2.5% and 20% ± 1.3% for erlotinib and OSI-420, respectively.
Zero Flow Rate (ZFR) for estimation of in vivo recovery
To calculate erlotinib and OSI-420 concentrations in brain ECF, microdialysate concentrations were corrected for probe recovery in each mouse using the ZFR method. This method is based on the fact that at slow perfusion rates and steady-state tissue concentrations of the analyte, extrapolation to a hypothetical flow rate value of zero will provide the absolute value of analyte in the dialysed tissue (CECF) (35). Probe recovery can then be calculated by dividing the concentration obtained at the flow rate at which the experiment is conducted (i.e., CDial at 0.5 μL/min) by CECF. First, we validated in vitro the use of the ZFR recovery method for recovery estimation. Dialysates were collected from a stock containing 1 μg/mL of each erlotinib and 0.5 μg/mL OSI-420 at different flow rates and the concentrations were plotted against flow rate. The estimated value of CECF in vitro obtained from extrapolation to zero flow rate using non-linear regression was 96%±15% and 93%±12% for erlotinib and OSI-420, respectively (results from 6 in vitro experiments; Supplementary Figure 1B). The ZFR requires that the concentration remain relatively constant while collecting the dialysates at different flow rates. Initial microdialysis experiments (n=4) conducted under stable flow rate of 0.5 μL/min showed that brain ECF concentrations dropped by only 10-15% over the 5 to 8 hr period. Assuming relatively stable target tissue concentrations, we decided to perform the recovery experiment after 5 hours from drug administration. After the recovery experiment, the flow rate was switched back to 0.5 μL/min and dialysates were collected up to 24 hours. The in vivo recovery for erlotinib was 39%±13% and for OSI-420 was 24%±13%.
Increased ECF penetration of erlotinib and OSI-420 in Abcg2−/− and Mdr1a/b−/−Abcg2−/− mice
Using microdialysis, we sampled brain ECF from wild-type, Abcg2−/−, Mdr1a/b−/−, Mdr1a/b−/−Abcg2−/−, and Abcc4−/− mouse strains after a single oral dose of erlotinib. Brain penetration ratios are shown in Fig. 3A. In wild-type mice, PBrain (mean ± SD) for erlotinib and OSI-420 was 0.27 ± 0.11 and 0.07 ± 0.02, respectively. Abcg2−/− mice showed 5-fold higher erlotinib penetration (1.4 ± 0.9, p < 0.05, n=5) and 7-fold higher OSI-420 penetration (0.51 ± 0.04, p < 0.05) than wild-type mice. However, neither erlotinib penetration (0.49 ± 0.3) nor OSI-420 penetration (0.04 ± 0.02) was enhanced in Mdr1a/b−/− mice (n=4, p > 0.05 for both). In the Mdr1a/b−/−Abcg2−/− mice, erlotinib brain penetration was 0.7 ± 0.26, ~3-fold higher than in wild-type mice (p < 0.01, n=5), and OSI-420 brain penetration (0.34 ± 0.21) was 4-fold higher (p < 0.01). Brain penetration of Abcc4−/− mice was similar to wild-type mice for both erlotinib (0.32 ± 0.24, p > 0.05, n=4) and OSI-420 (0.08 ± 0.06, p > 0.05). Histological examination verified the localization of the probe track in the brain ECF and indicated no bleeding due to probe insertion (Supplementary Figure 2).
Fig. 3.
Brain penetration of erlotinib and OSI-420 after a single oral dose of erlotinib. A, penetration of unbound erlotinib and OSI-420 to brain ECF expressed as PBrain (mean ± SD from 4 to 7 mice). * P < 0.05 and ** P < 0.01, Mann Whitney test of each knockout model compared with wild-type mice. B, representative unbound erlotinib concentration-time plots in brain ECF (○) and plasma (?) in wild-type, Abcg2−/−, Mdr1a/b−/−, Mdr1a/b−/−Abcg2−/− and Abcc4−/− mice. Model curves from individual predicted parameters are represented for plasma (dashed line) and brain ECF (solid line).
Intracellular accumulation experiments
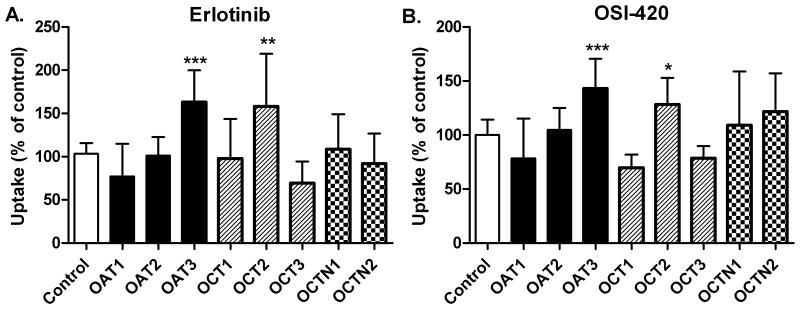
Intracellular accumulation of erlotinib and OSI-420 was significantly reduced in Saos2-BCRP cells as compared to Saos2-pcDNA3.1, indicating the significant role of BCRP in erlotinib transport. Accumulation of OSI-420, but not erlotinib, in LLCPK1-MDR1 cells was significantly reduced as compared to controls (LLCPK1 cells). Saos2-MRP4 cells did not show a significant difference in either erlotinib or OSI-420 accumulation (Fig. 4A). Pre-incubation for 30 minutes with the specific P-gp and BCRP inhibitor, elacridar significantly increased erlotinib and OSI-420 accumulation in Saos2-BCRP cells (p <0.01), and OSI-420 accumulation in LLCPK1-MDR1 cells (p <0.001) (Fig. 4B). Furthermore, we sought to determine whether erlotinib is a substrate for influx transporters using HEK-293 cells transfected with specific uptake transporters. Uptake of erlotinib and OSI-420 was significantly higher in presence of organic anion transporter-3 (OAT3) (p <0.001) as compared to the HEK-293 cells transfected with empty vector. Additionally, expression of the organic cation transporter-2 (OCT2) significantly increased erlotinib and OSI-420 uptake (p <0.01) (Fig. 5).
Fig. 4.
Erlotinib and OSI-420 intracellular accumulation in vitro in cell lines expressing efflux transporters. Values are the percentage of the maximum accumulation (mean ± SD; n=4-6) in control cells (Saos2-pcDNA for BCRP and MRP4 or LLC-PK1 for P-gp). A, time-course of drug accumulation in cell lines. Control, cells lines transfected with an empty vector control; Transfected, cell lines transfected with a vector expressing the indicated transporter; Transfected + Elacridar, transporter-transfected cells treated with 4 μM of the P-gp/BCRP inhibitor elacridar. B, intracellular accumulation data from 15 min and 30 min time-points combined. *P < 0.001 as compared to accumulation in control cells (ANOVA with posthoc Dunnet's test).
Fig. 5.
Transport of erlotinib, A and OSI-420, B by human organic ion transporters. Results are shown for drug accumulation in HEK293 cells after 5 minutes incubation in each cell line. Columns represent (mean ± SD) 8 to 18 observations per expressed transporter, and are expressed as percentage of their respective control (white bar). Only one control bar is shown for clarity purposes. The contribution of each transporter towards erlotinib or OSI-420 uptake was established by comparing data obtained in HEK293 cells overexpressing the transporter and HEK293 cells transfected with an empty vector.* P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001 versus control, one-way ANOVA was performed followed by a post Dunnett test.
Discussion
Using microdialysis sampling, transporter deficient mice, pharmacokinetic modeling, and cell lines transfected with efflux and uptake transporters, we elucidated the roles of transport mechanisms involved in erlotinib disposition in brain parenchyma. Our in vitro and in vivo data show that Bcrp1 is the primary efflux mechanism for erlotinib and OSI-420 at the murine BBB, whereas P-gp and Mrp4 have little or no effect on erlotinib CNS penetration. In vitro, intracellular accumulation of erlotinib and OSI-420 showed that only OSI-420, not erlotinib, accumulation was reduced in cells overexpressing MDR1. The present study also showed that erlotinib and OSI-420 are substrates for the human organic uptake transporter OAT3 and, to a lesser extent, OCT2.
Our technical approach of using microdialysis allowed the characterization of unbound (active) erlotinib concentrations in brain ECF. Our technique overcomes the limitations of (a) the CSF aspiration technique, which characterizes drug exposure in a very specialized CNS compartment (24), and (b) the whole brain homogenization technique, which does not discern between free and bound drug entities or between different CNS compartments (brain parenchyma, CSF, and brain vessels). Our study shows that the inclusion of HPBCD in the perfusate increases the recovery of erlotinib, probably by including the drug into the core of the HPBCD molecule (41).
Although HPBCD proved indispensible for the detection of erlotinib and OSI-420 in the dialysate, its presence provided a challenge as we performed the recovery experiments. Because HPBCD forms inclusion complexes with erlotinib in the perfusate limiting drug movement to brain ECF, we could not use retrodialysis or no-net-flux to estimate in vivo recovery values. Instead we chose to use the zero flow rate method to estimate recovery, realizing that as with all methods to calculate recovery, this approach has limitations. For example, the ZFR method should be applied when the target tissue (e.g., brain ECF) is at a steady-state. Our initial microdialysis experiments (n=4) conducted under constant flow rate of 0.5 μL/min showed that brain ECF concentrations dropped by only ~12% over the 5 to 8 hr period. Thus, we assessed recovery during a period 5 to 8 hours after the erlotinib dose was administered. Because we calculated the recovery during this time interval (i.e., 5 to 8 hours), we were only able to collect a single sample per flow rate. Although this short time frame may not have allowed adequate time to achieve stable recoveries at each flow rate, comparing in vitro recovery values obtained with either changing the flow rate or under constant (i.e., stable) flow rate yielded similar recovery values suggesting that stable recoveries can be achieved with our experimental approach (Supplementary Table 3).
Our study has established that penetration of unbound erlotinib from plasma across the BBB of wild type mice is limited (27%) and even lower for OSI-420 (7%). Thus, even though OSI-420 exhibits anti-tumor activity (3, 42), its low CNS penetration and systemic exposure (~10-20% that of erlotinib in humans (2, 21)) suggest a minor role for OSI-420 in erlotinib clinical activity in brain tumors.
Our data show that Bcrp1 is the major efflux transporter limiting penetration of erlotinib and OSI-420 into murine brain ECF. In vitro studies showed reduced erlotinib and OSI-420 accumulation in Saos2-BCRP cells. Interestingly, a single nucleotide polymorphism in the ABCG2 promoter that correlates with lower BCRP expression was associated with higher erlotinib plasma exposure, indicating the important role of BCRP in erlotinib disposition (43). Our results contrast with the conclusions by Kodaira et al stating that P-gp is the major efflux transporter for erlotinib at the murine BBB (44). This discrepancy can be explained by the different experimental designs used in each study. In the latter study, the authors administered erlotinib via the jugular vein for 2 hours and then analyzed erlotinib concentration in brain homogenates. They compared the erlotinib concentration in brain homogenates to that in plasma only at one time point (i.e., 2 hrs), and did not account for erlotinib plasma protein binding. This study design has several limitations. First, the homogenate technique could provide different results as it describes drug accumulation in the whole brain rather than in specific compartments, and second, relying on only one time point to determine the penetration ratio can mask the whole exposure profile for erlotinib in plasma as it provides only a “snap shot” of the penetration profile. In our study, we used the oral route for administering erlotinib to mimic the clinical situation. Our studies also took into consideration the plasma protein binding of both erlotinib and OSI-420.
While intracellular accumulation experiments showed that OSI-420 is a P-gp substrate, OSI-420 brain penetration was not increased in Mdr1a/b−/− mice. This can be due to the compensatory upregulation of Bcrp1 in Mdr1a/b−/− mice resulting in increased overall drug efflux from the brain. Our group previously used semi-quantitative immunohistochemical analysis to show that Bcrp1 is expressed at a higher level in the brain of Mdr1a/b−/− mice than that in wild-type mice (24).
In vitro screening of uptake transporters using HEK-293 transfected cells identified erlotinib and OSI-420 as substrates for OAT3 and OCT2. The affinity of these transporters for both anionic and cationic molecules has been previously reported (45, 46). While HEK-293/OCT2 cells showed significantly higher erlotinib uptake, OCT2 contribution towards erlotinib uptake should be cautiously interpreted given the ~40 fold higher expression of SLC22A2 gene, encoding OCT2, in these cells (47). Studying erlotinib disposition in OCT2-deficient mice will clarify the affinity of OCT2 towards erlotinib.
Our results could be clinically significant as Oat3 localized at the apical border of the choroid plexus can restrict the penetration of its substrates in the CSF (16). Our group previously demonstrated that Bcrp1 and P-gp, localized apically at the choroid plexus, pump their substrate, topotecan, in the CSF (24, 33). Thus, Oat3 can oppose the transport direction of P-gp and Bcrp1 at the choroid plexus decreasing CSF drug accumulation. In rodents, Oat3 is predominantly expressed at the basolateral border of brain endothelial cells where it has been implicated in the brain to blood transport of its substrates (17, 48). Further, OCT2 is expressed at the apical border of the endothelial cells and was shown to increase the brain accumulation of their substrates (15). Thus, in absence of Bcrp1 (i.e., Abcg2−/− and Mdr1a/b−/−Abcg2−/− mice), the net erlotinib ECF accumulation would be determined by factors that favor brain ECF penetration (e.g., lack of Bcrp1, Oat3 at the choroid plexus, and OCT2 at the BBB) and those moving the drug from the brain to the blood or the CSF (e.g., Oat3 at the BBB, and P-gp at the choroid plexus) as schematized in Fig. 6. This may explain the more than unity ECF accumulation for ABC transporters substrates in Abcg2−/− and Mdr1a/b−/−Abcg2−/− mice observed in our study and others (9, 18, 44). Another transporter of potential interest is the organic anion transporting polypeptide (OATP2). OATP2 is expressed on both the apical and basolateral membranes of brain endothelial cells and probably mediates the accumulation of its substrates across the intact BBB vessels (18, 19, 49). Further studies are warranted to identify the role of uptake transporters in erlotinib CNS penetration.
Fig. 6.
Proposed model for the role of efflux and uptake transporters in erlotinib CNS penetration. A, schematic diagram for endothelial cells with transporters localized on either apical border (facing blood) or basolateral border (facing brain ECF). B, schematic diagram of the choroid plexus forming the BCSFB. Transporters are localized on either the apical border (facing CSF) or basolateral border (facing blood). The arrows represent the direction of drug transport.
Regarding the implications of our results on erlotinib elimination, OCT2 and OAT3 transporters are abundantly expressed in the kidney (50). These transporters may explain the renal clearance component of erlotinib elimination, which accounts for ~10% of the overall elimination (2). However, transporters expressed in the liver such as OAT2 and OCT1 were not found to transport erlotinib indicating the involvement of other transport mechanisms such as OATP1B1 and OAT1B3.
In conclusion, erlotinib is a Bcrp1 substrate whereas its metabolite is a substrate for both P-gp and Bcrp1. Erlotinib brain ECF accumulation was restricted mainly by Bcrp1. Intracellular accumulation studies confirmed the role of BCRP in erlotinib efflux and the dual P-gp/BCRP inhibitor, elacridar, increased erlotinib accumulation in cells in vitro. This study also indicates that erlotinib and OSI-420 are substrates for the uptake transporters OAT3 and OCT2. Further study is warranted to assess the role of these transporters in erlotinib brain accumulation. Our future experiments will focus on studying the effect of ABC transporter inhibitors on erlotinib penetration in high-grade glioma using genetically engineered animal models that recapitulate the genetics, the biology, and the histology of human tumors.
Statement of Translational Relevance.
Drug transporters expressed at the blood-brain barrier or on tumor cell membranes may limit the accumulation of effective concentrations of erlotinib and its active metabolite OSI-420 within brain tumors. In this study, we identify specific efflux (BCRP) and uptake transporters (OCT2, OAT3) which affect accumulation of erlotinib and OSI-420, either within the brain extracellular fluid or within cells. This information contributes to our understanding of the factors that limit penetration of erlotinib into the brain and into tumor cells, and thus may limit its effectiveness. In the future, BCRP inhibitors may be useful for increasing brain concentrations of erlotinib.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank Drs. Alex Sparreboom, Heinz Bonisch, Yuichi Sugiyama, and Akira Tsuji for providing us with HEK293 cells transfected with organic ion transporters. We thank Dr. John Scheutz for providing the Saos2-BCRP cells. We also thank Dr. Carl Panetta for helpful discussions regarding the pharmacokinetic modeling.
This work was supported in part by grants CA23099 and CA21765 from the U.S. Public Health Service and by the American Lebanese Syrian Associated Charities (ALSAC).
Footnotes
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
References
- 1.Shepherd FA, Rodrigues Pereira J, Ciuleanu T, et al. Erlotinib in previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:123–32. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa050753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ling J, Johnson KA, Miao Z, et al. Metabolism and excretion of erlotinib, a small molecule inhibitor of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase, in healthy male volunteers. Drug Metab Dispos. 2006;34:420–6. doi: 10.1124/dmd.105.007765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Moyer JD, Barbacci EG, Iwata KK, et al. Induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest by CP-358,774, an inhibitor of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase. Cancer Res. 1997;57:4838–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Broniscer A, Baker SJ, Stewart CF, et al. Phase I and pharmacokinetic studies of erlotinib administered concurrently with radiotherapy for children, adolescents, and young adults with high-grade glioma. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15:701–7. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-1923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Sun M, Behrens C, Feng L, et al. HER family receptor abnormalities in lung cancer brain metastases and corresponding primary tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15:4829–37. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-2921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.van den Bent MJ, Brandes AA, Rampling R, et al. Randomized phase II trial of erlotinib versus temozolomide or carmustine in recurrent glioblastoma: EORTC brain tumor group study 26034. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:1268–74. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.17.5984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Loscher W, Potschka H. Drug resistance in brain diseases and the role of drug efflux transporters. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2005;6:591–602. doi: 10.1038/nrn1728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Shen DD, Artru AA, Adkison KK. Principles and applicability of CSF sampling for the assessment of CNS drug delivery and pharmacodynamics. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2004;56:1825–57. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2004.07.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Lassman AB, Rossi MR, Raizer JJ, et al. Molecular study of malignant gliomas treated with epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors: tissue analysis from North American Brain Tumor Consortium Trials 01-03 and 00-01. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:7841–50. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-0421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Giacomini KM, Huang SM, Tweedie DJ, et al. Membrane transporters in drug development. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2010;9:215–36. doi: 10.1038/nrd3028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kodaira H, Kusuhara H, Ushiki J, Fuse E, Sugiyama Y. Kinetic analysis of the cooperation of P-glycoprotein (P-gp/Abcb1) and breast cancer resistance protein (Bcrp/Abcg2) in limiting the brain and testis penetration of erlotinib, flavopiridol, and mitoxantrone. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010;333:788–96. doi: 10.1124/jpet.109.162321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Leggas M, Adachi M, Scheffer GL, et al. Mrp4 confers resistance to topotecan and protects the brain from chemotherapy. Mol Cell Biol. 2004;24:7612–21. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.17.7612-7621.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Carcaboso AM, Elmeliegy MA, Shen J, et al. Tyrosine kinase inhibitor gefitinib enhances topotecan penetration of gliomas. Cancer Res. 70:4499–508. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-4264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ose A, Kusuhara H, Endo C, et al. Functional characterization of mouse organic anion transporting peptide 1a4 in the uptake and efflux of drugs across the blood-brain barrier. Drug Metab Dispos. 2010;38:168–76. doi: 10.1124/dmd.109.029454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Lin CJ, Tai Y, Huang MT, et al. Cellular localization of the organic cation transporters, OCT1 and OCT2, in brain microvessel endothelial cells and its implication for MPTP transport across the blood-brain barrier and MPTP-induced dopaminergic toxicity in rodents. J Neurochem. 114:717–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.06801.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Nagata Y, Kusuhara H, Endou H, Sugiyama Y. Expression and functional characterization of rat organic anion transporter 3 (rOat3) in the choroid plexus. Mol Pharmacol. 2002;61:982–8. doi: 10.1124/mol.61.5.982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kikuchi R, Kusuhara H, Sugiyama D, Sugiyama Y. Contribution of organic anion transporter 3 (Slc22a8) to the elimination of p-aminohippuric acid and benzylpenicillin across the blood-brain barrier. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2003;306:51–8. doi: 10.1124/jpet.103.049197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kusuhara H, Sugiyama Y. Active efflux across the blood-brain barrier: role of the solute carrier family. NeuroRx. 2005;2:73–85. doi: 10.1602/neurorx.2.1.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Bronger H, Konig J, Kopplow K, et al. ABCC drug efflux pumps and organic anion uptake transporters in human gliomas and the blood-tumor barrier. Cancer Res. 2005;65:11419–28. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-1271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Togashi Y, Masago K, Fukudo M, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid concentration of erlotinib and its active metabolite OSI-420 in patients with central nervous system metastases of non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 5:950–5. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e3181e2138b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Broniscer A, Panetta JC, O'Shaughnessy M, et al. Plasma and cerebrospinal fluid pharmacokinetics of erlotinib and its active metabolite OSI-420. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:1511–5. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-2372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Stain-Texier F, Boschi G, Sandouk P, Scherrmann JM. Elevated concentrations of morphine 6-beta-D-glucuronide in brain extracellular fluid despite low blood-brain barrier permeability. Br J Pharmacol. 1999;128:917–24. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kaddoumi A, Choi SU, Kinman L, et al. Inhibition of P-glycoprotein activity at the primate blood-brain barrier increases the distribution of nelfinavir into the brain but not into the cerebrospinal fluid. Drug Metab Dispos. 2007;35:1459–62. doi: 10.1124/dmd.107.016220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Shen J, Carcaboso AM, Hubbard KE, et al. Compartment-specific roles of ATP-binding cassette transporters define differential topotecan distribution in brain parenchyma and cerebrospinal fluid. Cancer Res. 2009;69:5885–92. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-0700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Hayer-Zillgen M, Bruss M, Bonisch H. Expression and pharmacological profile of the human organic cation transporters hOCT1, hOCT2 and hOCT3. Br J Pharmacol. 2002;136:829–36. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Tahara H, Kusuhara H, Maeda K, Koepsell H, Fuse E, Sugiyama Y. Inhibition of oat3-mediated renal uptake as a mechanism for drug-drug interaction between fexofenadine and probenecid. Drug Metab Dispos. 2006;34:743–7. doi: 10.1124/dmd.105.008375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Nezu J, Tamai I, Oku A, et al. Primary systemic carnitine deficiency is caused by mutations in a gene encoding sodium ion-dependent carnitine transporter. Nat Genet. 1999;21:91–4. doi: 10.1038/5030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Zhao M, He P, Rudek MA, Hidalgo M, Baker SD. Specific method for determination of OSI-774 and its metabolite OSI-420 in human plasma by using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2003;793:413–20. doi: 10.1016/s1570-0232(03)00356-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Beal SL. NONMEM Users' Guide. Introduction to version IV. Ellicott City, MD: ICON Development Solutions: 2006. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Ahn JE, Karlsson MO, Dunne A, Ludden TM. Likelihood based approaches to handling data below the quantification limit using NONMEM VI. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn. 2008;35:401–21. doi: 10.1007/s10928-008-9094-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.D'argenio DZ, Schumitzky A. ADAPT 5 User's Guide: Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Systems Analysis Software. Biomedical Simulations Resource; Los Angeles: 2009. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Leggas M, Zhuang Y, Welden J, Self Z, Waters CM, Stewart CF. Microbore HPLC method with online microdialysis for measurement of topotecan lactone and carboxylate in murine CSF. J Pharm Sci. 2004;93:2284–95. doi: 10.1002/jps.20134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Zhuang Y, Fraga CH, Hubbard KE, et al. Topotecan central nervous system penetration is altered by a tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Cancer Res. 2006;66:11305–13. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-0929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Menacherry S, Hubert W, Justice JB., Jr In vivo calibration of microdialysis probes for exogenous compounds. Anal Chem. 1992;64:577–83. doi: 10.1021/ac00030a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Jacobson I, Sandberg M, Hamberger A. Mass transfer in brain dialysis devices--a new method for the estimation of extracellular amino acids concentration. J Neurosci Methods. 1985;15:263–8. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(85)90107-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Sarkaria JN, Yang L, Grogan PT, et al. Identification of molecular characteristics correlated with glioblastoma sensitivity to EGFR kinase inhibition through use of an intracranial xenograft test panel. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007;6:1167–74. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-06-0691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Marchetti S, de Vries NA, Buckle T, et al. Effect of the ATP-binding cassette drug transporters ABCB1, ABCG2, and ABCC2 on erlotinib hydrochloride (Tarceva) disposition in in vitro and in vivo pharmacokinetic studies employing Bcrp1−/−/Mdr1a/1b−/− (triple-knockout) and wild-type mice. Mol Cancer Ther. 2008;7:2280–7. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-07-2250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Wang S, Guo P, Wang X, Zhou Q, Gallo JM. Preclinical pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic models of gefitinib and the design of equivalent dosing regimens in EGFR wild-type and mutant tumor models. Mol Cancer Ther. 2008;7:407–17. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-07-2070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Loos WJ, Zamboni WC, Engels FK, et al. Pitfalls of the application of microdialysis in clinical oncology: controversial findings with docetaxel. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2007;45:288–94. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2007.07.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Duo J, Fletcher H, Stenken JA. Natural and synthetic affinity agents as microdialysis sampling mass transport enhancers: current progress and future perspectives. Biosens Bioelectron. 2006;22:449–57. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2006.05.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Khramov AN, Stenken JA. Enhanced microdialysis recovery of some tricyclic antidepressants and structurally related drugs by cyclodextrin-mediated transport. Analyst. 1999;124:1027–33. doi: 10.1039/a901236b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Meany HJ, Fox E, McCully C, Tucker C, Balis FM. The plasma and cerebrospinal fluid pharmacokinetics of erlotinib and its active metabolite (OSI-420) after intravenous administration of erlotinib in non-human primates. Cancer chemotherapy and pharmacology. 2008;62:387–92. doi: 10.1007/s00280-007-0616-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Rudin CM, Liu W, Desai A, et al. Pharmacogenomic and pharmacokinetic determinants of erlotinib toxicity. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:1119–27. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.13.1128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Kodaira H, Kusuhara H, Ushiki J, Fuse E, Sugiyama Y. Kinetic analysis of the cooperation of P-glycoprotein (P-gp/Abcb1) and breast cancer resistance protein (Bcrp/Abcg2) in limiting the brain and testis penetration of erlotinib, flavopiridol, and mitoxantrone. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 333:788–96. doi: 10.1124/jpet.109.162321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Arndt P, Volk C, Gorboulev V, et al. Interaction of cations, anions, and weak base quinine with rat renal cation transporter rOCT2 compared with rOCT1. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2001;281:F454–68. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.2001.281.3.F454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Ahn SY, Eraly SA, Tsigelny I, Nigam SK. Interaction of organic cations with organic anion transporters. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:31422–30. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.024489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Filipski KK, Loos WJ, Verweij J, Sparreboom A. Interaction of Cisplatin with the human organic cation transporter 2. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:3875–80. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-4793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Mori S, Takanaga H, Ohtsuki S, et al. Rat organic anion transporter 3 (rOAT3) is responsible for brain-to-blood efflux of homovanillic acid at the abluminal membrane of brain capillary endothelial cells. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2003;23:432–40. doi: 10.1097/01.WCB.0000050062.57184.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Gao B, Stieger B, Noe B, Fritschy JM, Meier PJ. Localization of the organic anion transporting polypeptide 2 (Oatp2) in capillary endothelium and choroid plexus epithelium of rat brain. J Histochem Cytochem. 1999;47:1255–64. doi: 10.1177/002215549904701005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Bleasby K, Castle JC, Roberts CJ, et al. Expression profiles of 50 xenobiotic transporter genes in humans and pre-clinical species: a resource for investigations into drug disposition. Xenobiotica. 2006;36:963–88. doi: 10.1080/00498250600861751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.