Abstract
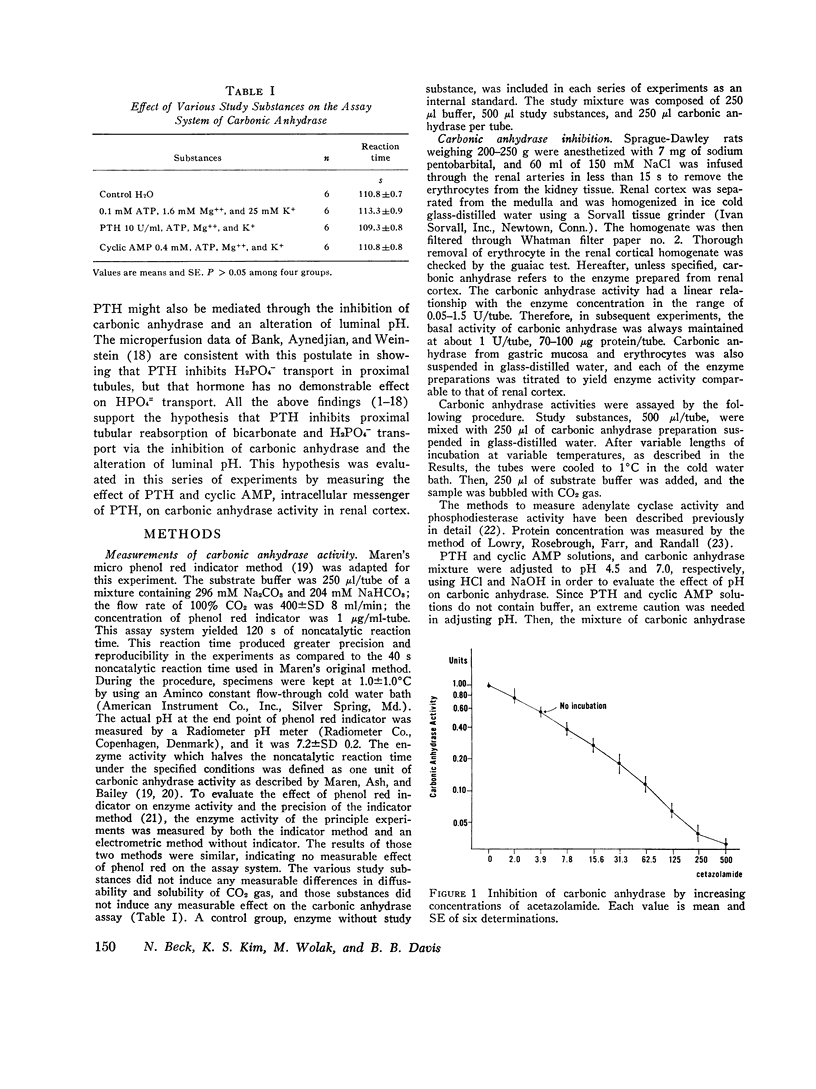
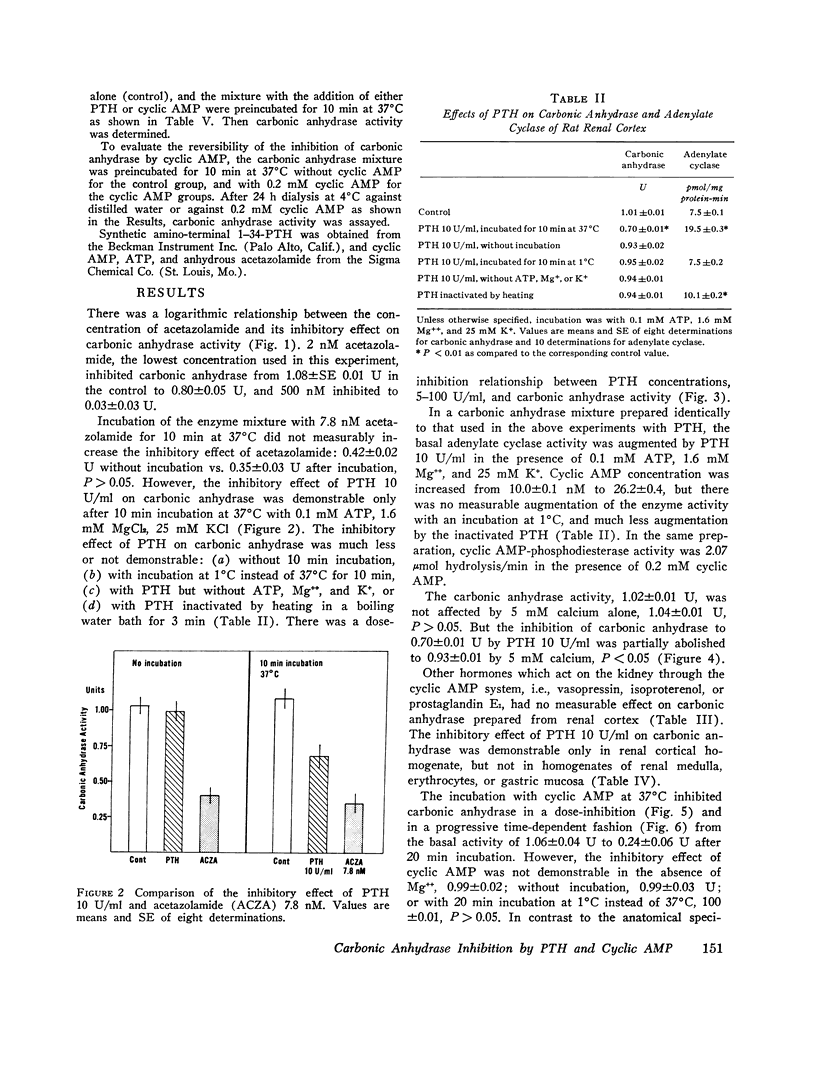
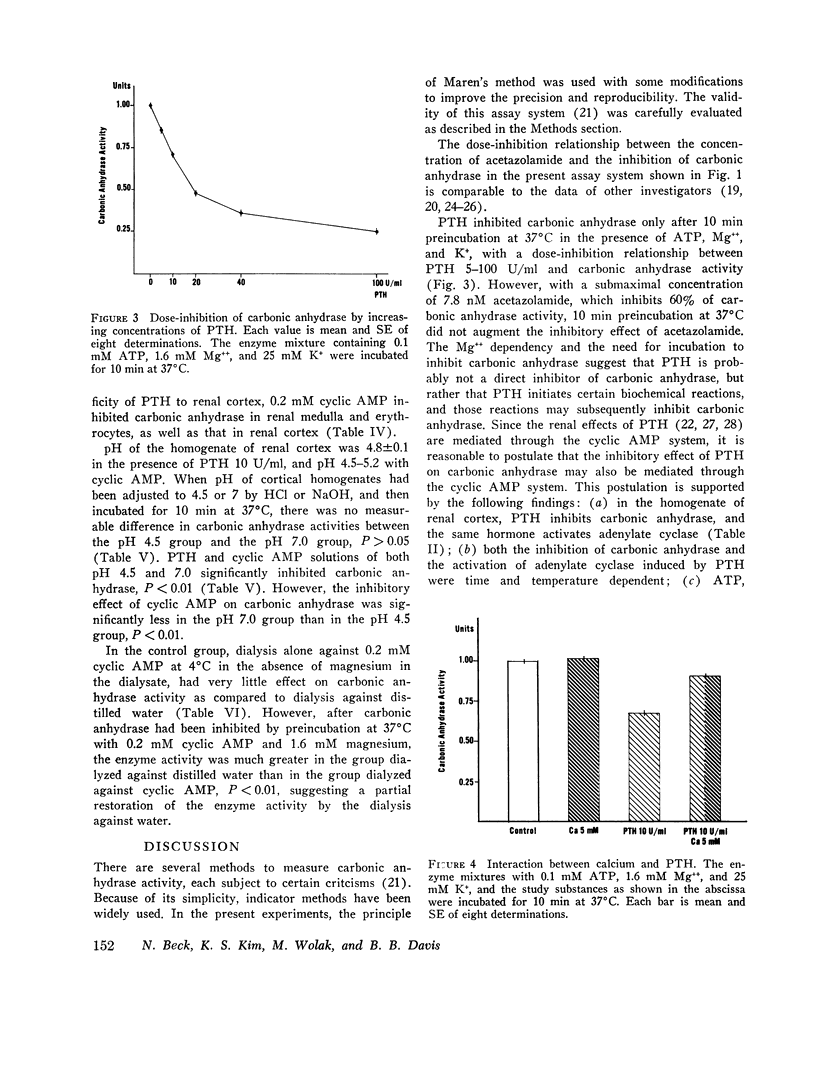
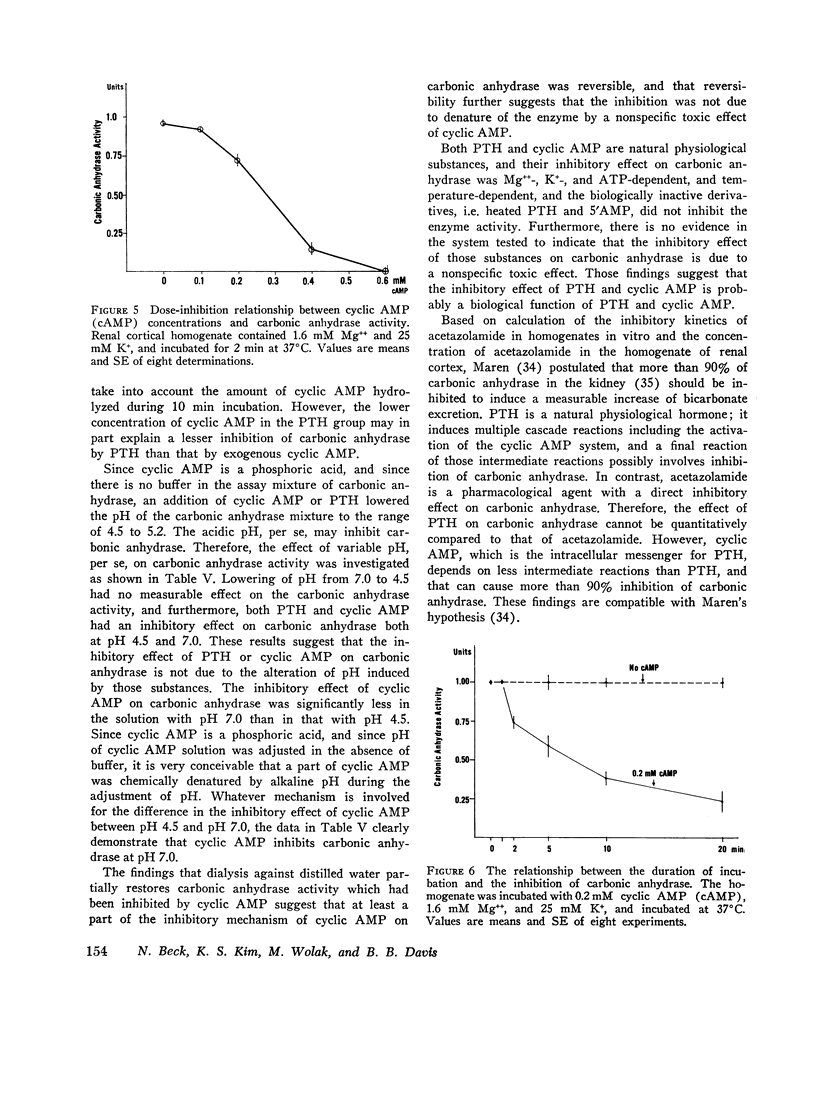
It has been demonstrated that parathyroid hormone (PTH) inhibits the proximal tubular reabsorption of bicarbonate, and increases the urinary excretion of that ion. There is also a qualitative similarity between the alterations of the proximal tubular reabsorption of phosphate, sodium, and water after PTH administration and after acetazolamide administration. These findings suggest that the renal effect of PTH is possibly mediated through the inhibition of carbonic anhydrase in proximal tubules. Therefore, a possible inhibitory effect of PTH on carbonic anhydrase was evaluated in the homogenate of rat renal cortex by an indicator titration method. Incubation of cortical homogenates with PTH for 10 min at 37degreesC inhibited carbonic anhydrase activity. The inhibitory effect of PTH was ATP-, Mg++-, and K+-dependent and temperature-dependent; inactivation of PTH by heating at 100degreesC abolished the effect of PTH both to activate adenylate cyclase and to inhibit carbonic anhydrase. Calcium 5 mM also partially abolished effects of PTH to activate adenylate cyclase and to inhibit carbonic anhydrase. The inhibitory effect of PTH on carbonic anhydrase was specific to renal cortex. Cyclic AMP, the intracellular messenger substance for PTH, also inhibited carbonic anhydrase in renal cortex. The cyclic AMP-induced inhibition was also Mg++ dependent and temperature dependent, and required preincubation at 37degreesC. But 5'-AMP, a metabolic derivative of cyclic AMP without its biological effect, had no inhibitory effect on carbonic anhydrase. All the above results are consistent with the hypothesis that PTH inhibits proximal tubular reabsorption of bicarbonate and phosphate through the inhibition of carbonic anhydrase, and that inhibitory effect is mediated through the cyclic AMP system.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agus Z. S., Gardner L. B., Beck L. H., Goldberg M. Effects of parathyroid hormone on renal tubular reabsorption of calcium, sodium, and phosphate. Am J Physiol. 1973 May;224(5):1143–1148. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.224.5.1143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agus Z. S., Puschett J. B., Senesky D., Goldberg M. Mode of action of parathyroid hormone and cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate on renal tubular phosphate reabsorption in the dog. J Clin Invest. 1971 Mar;50(3):617–626. doi: 10.1172/JCI106532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnaud C. D., Tsao H. S., Littledike T. Radioimmunoassay of human parathyroid hormone in serum. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jan;50(1):21–34. doi: 10.1172/JCI106476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bank N., Aynedjian H. S., Weinstein S. W. A microperfusion study of phosphate reabsorption by the rat proximal renal tubule. Effect of parathyroid hormone. J Clin Invest. 1974 Nov;54(5):1040–1048. doi: 10.1172/JCI107847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck L. H., Goldberg M. Effects of acetazolamide and parathyroidectomy on renal transport of sodium, calcium, and phosphate. Am J Physiol. 1973 May;224(5):1136–1142. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.224.5.1136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck N. P., Kaneko T., Zor U., Field J. B., Davis B. B. Effects of vasopressin and prostaglandin E 1 on the adenyl cyclase-cyclic 3',5'-adenosine monophosphate system of the renal medulla of the rat. J Clin Invest. 1971 Dec;50(12):2461–2465. doi: 10.1172/JCI106746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck N. P., Reed S. W., Murdaugh H. V., Davis B. B. Effects of catecholamines and their interaction with other hormones on cyclic 3',5'-adenosine monophosphate of the kidney. J Clin Invest. 1972 Apr;51(4):939–944. doi: 10.1172/JCI106888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck N., Singh H., Reed S. W., Davis B. B. Direct inhibitory effect of hypercalcemia on renal actions of parathyroid hormone. J Clin Invest. 1974 Mar;53(3):717–725. doi: 10.1172/JCI107610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein B. A., Clapp J. R. Micropuncture study of bicarbonate reabsorption by the dog nephron. Am J Physiol. 1968 Feb;214(2):251–257. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.214.2.251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLAPP J. R., WATSON J. F., BERLINER R. W. EFFECT OF CARBONIC ANHYDRASE INHIBITION ON PROXIMAL TUBULAR BICARBONATE REABSORPTION. Am J Physiol. 1963 Oct;205:693–696. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1963.205.4.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COUNIHAN T. B., EVANS B. M., MILNE M. D. Observations on the pharmacology of the carbonic anhydrase inhibitor diamox. Clin Sci. 1954 Nov;13(4):583–598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase L. R., Aurbach G. D. Parathyroid function and the renal excretion of 3'5'-adenylic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Aug;58(2):518–525. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.2.518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DATTA P. K., SHEPARD T. H., 2nd Intracellular localization of carbonic anhydrase in rat liver and kidney tissues. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 Mar;81(1):124–129. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90182-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS R. P. THE MEASUREMENT OF CARBONIC ANHYDRASE ACTIVITY. Methods Biochem Anal. 1963;11:307–327. doi: 10.1002/9780470110294.ch7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellsworth R., Nicholson W. M. FURTHER OBSERVATIONS UPON THE CHANGES IN THE ELECTROLYTES OF THE URINE FOLLOWING THE INJECTION OF PARATHYROID EXTRACT. J Clin Invest. 1935 Nov;14(6):823–827. doi: 10.1172/JCI100730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOURMAN P., McCONKEY B., SMITH J. W. Defects of water reabsorption and of hydrogen-ion excretion by the renal tubules in hyperparathyroidism. Lancet. 1960 Mar 19;1(7125):619–623. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(60)90503-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulop M., Brazeau P. The phosphaturic effect of sodium bicarbonate and acetazolamide in dogs. J Clin Invest. 1968 May;47(5):983–991. doi: 10.1172/JCI105813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellman D. E., Au W. Y., Bartter F. C. Evidence for a direct effect of parathyroid hormone on urinary acidification. Am J Physiol. 1965 Sep;209(3):643–650. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.209.3.643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEEMAN C. R., COOKE R. E. The acute effects of parathyroid hormone on the metabolism of endogenous phosphate. J Lab Clin Med. 1951 Jul;38(1):112–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kernohan J. C. A method for studying the kinetics of the inhibition of carbonic anhydrase by sulphonamides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 May 5;118(2):405–412. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6593(66)80049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunau R. T., Jr The influence of the carbonic anhydrase inhibitor, benzolamide (CL-11,366), on the reabsorption of chloride, sodium, and bicarbonate in the proximal tubule of the rat. J Clin Invest. 1972 Feb;51(2):294–306. doi: 10.1172/JCI106814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOTSPEICH W. D., MALVIN R. L. Relation between tubular transport of inorganic phosphate and bicarbonate in the dog. Am J Physiol. 1956 Sep;187(1):51–56. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1956.187.1.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAREN T. H. A simplified micromethod for the determination of carbonic anhydrase and its inhibitors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1960 Sep;130:26–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAREN T. H., ASH V. I., BAILEY E. M., Jr Carbonic anhydrase inhibition. II. A method for determination of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, particularly of diamox. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1954 Nov;95(5):244–255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAREN T. H., PARCELL A. L., MALIK M. N. A kinetic analysis of carbonic anhydrase inhibition. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1960 Dec;130:389–400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAREN T. H. The relation between enzyme inhibition and physiological response in the carbonic anhydrase system. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1963 Feb;139:140–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus R., Aurbach G. D. Bioassay of parathyroid hormone in vitro with a stable preparation of adenyl cyclase from rat kidney. Endocrinology. 1969 Nov;85(5):801–810. doi: 10.1210/endo-85-5-801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maren T. H. Carbonic anhydrase: chemistry, physiology, and inhibition. Physiol Rev. 1967 Oct;47(4):595–781. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1967.47.4.595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelakis A. M. Hormonal effects on cyclic AMP in a renal-cell suspension system. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Oct;135(1):13–16. doi: 10.3181/00379727-135-34977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORDIN B. E. The effect of intravenous parathyroid extract on urinary pH, bicarbonate and electrolyte excretion. Clin Sci. 1960 May;19:311–319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puschett J. B., Goldberg M. The relationship between the renal handling of phosphate and bicarbonate in man. J Lab Clin Med. 1969 Jun;73(6):956–969. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RECTOR F. C., Jr, CARTER N. W., SELDIN D. W. THE MECHANISM OF BICARBONATE REABSORPTION IN THE PROXIMAL AND DISTAL TUBULES OF THE KIDNEY. J Clin Invest. 1965 Feb;44:278–290. doi: 10.1172/JCI105142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RECTOR F. C., Jr, SELDIN D. W., ROBERTS A. D., Jr, SMITH J. S. The role of plasma CO2 tension and carbonic anhydrase activity in the renal reabsorption of bicarbonate. J Clin Invest. 1960 Nov;39:1706–1721. doi: 10.1172/JCI104193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



