Abstract
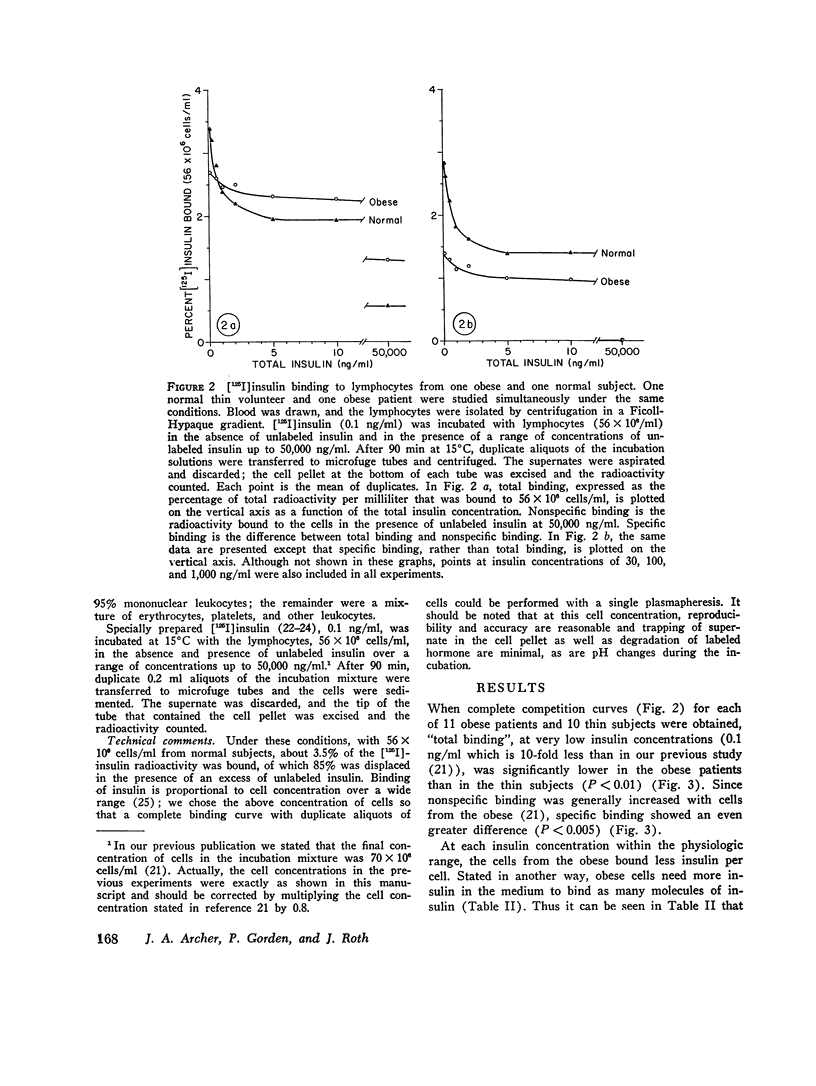
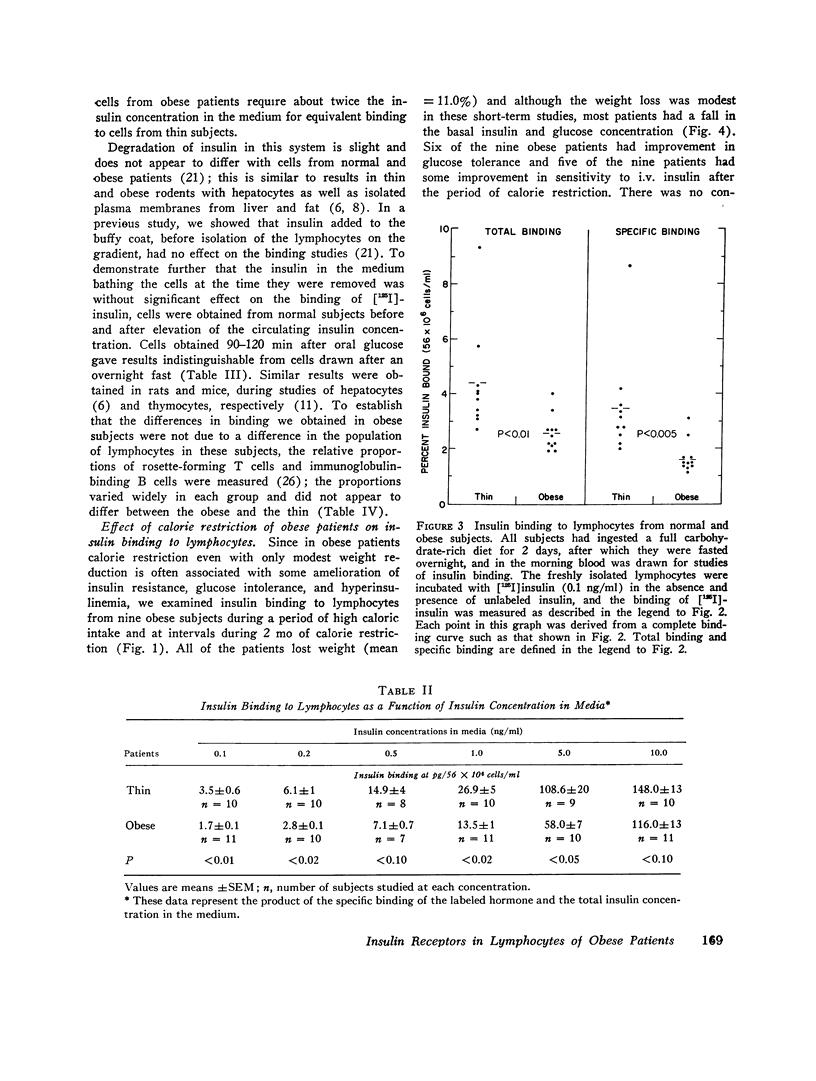
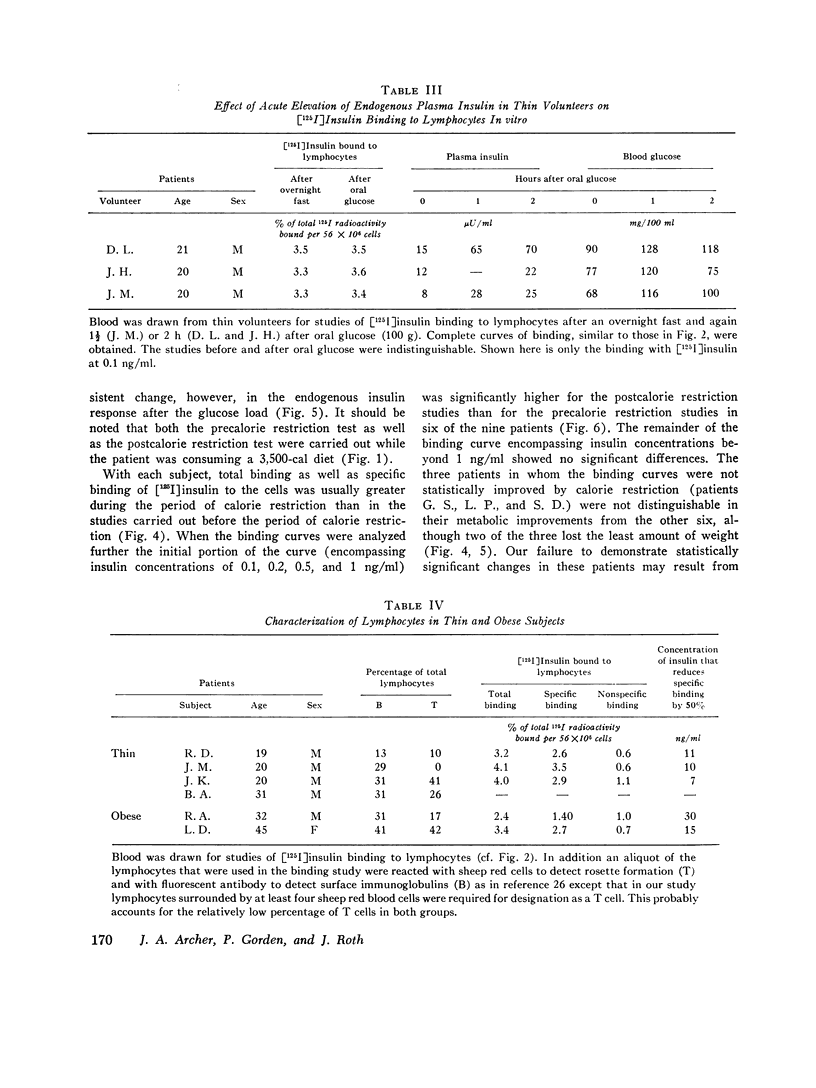
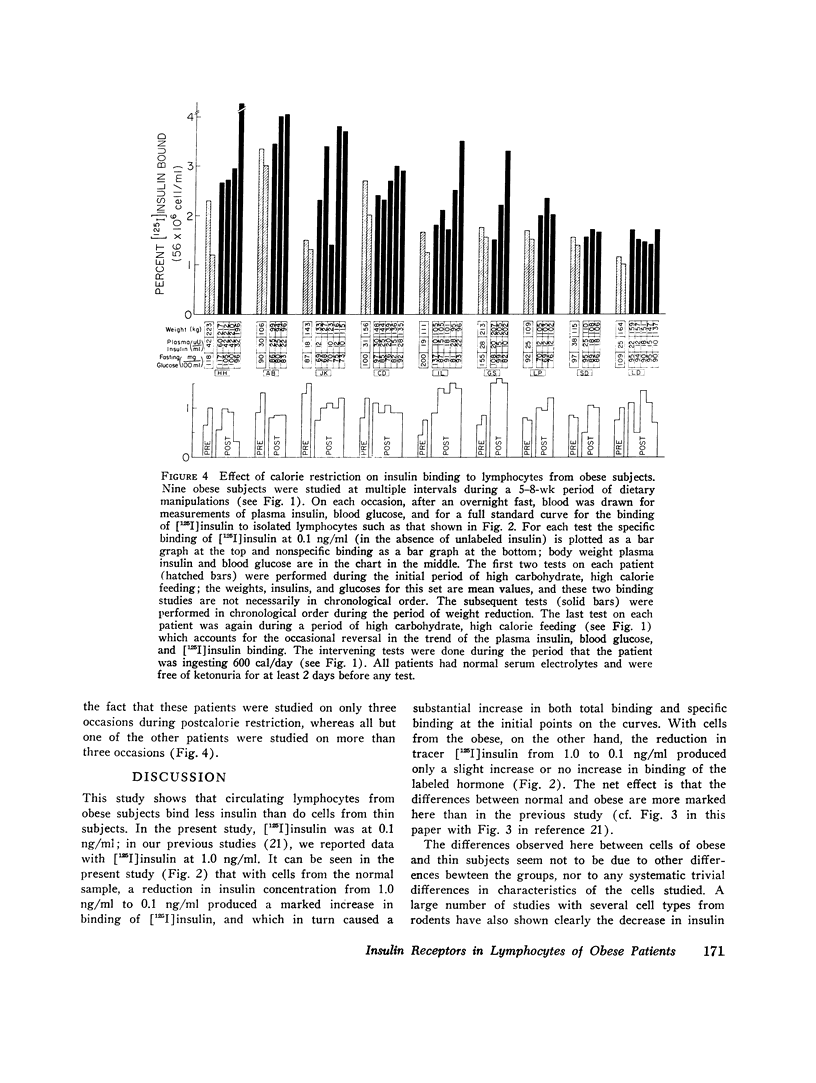
With insulin at 0.1 ng/ml, the binding of (125I)insulin in vitro to circulating lymphocytes from 11 obese patients was less than that observed with cells from 10 thin volunteers. Furthermore, with obese cells, unlabeled insulin was less effective in competing with labeled hormone for binding, both at low and high concentrations of unlabeled insulin. These differences were not accounted for by the high concentrations of insulin in the circulation of the obese patients at the time fthe blood was drawn, or by differences in degradation of hormone, or in the characteristics of the cell population. The decrease in binding appears to be due to a lowering of the receptor concentration, but some loss of affinity has not been excluded. Institution of a calorie restricted diet (nine patients) which ameliorated the hyperinsulinemia, produced an improvement in hormone binding. Since the insulin receptors of lymphocytes in metabolic disorders seem to reflect the state of insulin receptors or target cells such as liver and fat, the lymphocytes or other leukocytes appear to be ideal for studies of impaired cell responsiveness to hormones in man.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archer J. A., Gorden P., Gavin J. R., 3rd, Lesniak M. A., Roth J. Insulin receptors in human circulating lymphocytes: application to the study of insulin resistance in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1973 Apr;36(4):627–633. doi: 10.1210/jcem-36-4-627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Separation of leukocytes from blood and bone marrow. Introduction. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:7–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Insulin receptors in the liver: specific binding of ( 125 I)insulin to the plasma membrane and its relation to insulin bioactivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Aug;68(8):1833–1837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.8.1833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Monoiodoinsulin: demonstration of its biological activity and binding to fat cells and liver membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Apr 16;43(2):400–408. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90767-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavin J. R., 3rd, Gorden P., Roth J., Archer J. A., Buell D. N. Characteristics of the human lymphocyte insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1973 Mar 25;248(6):2202–2207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavin J. R., 3rd, Roth J., Jen P., Freychet P. Insulin receptors in human circulating cells and fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):747–751. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavin J. R., 3rd, Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr, de Meyts P., Buell D. N. Insulin-dependent regulation of insulin receptor concentrations: a direct demonstration in cell culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):84–88. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfine I. D., Gardner J. D., Neville D. M., Jr Insulin action in isolated rat thymocytes. I. Binding of 125 I-insulin and stimulation of -aminoisobutyric acid transport. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):6919–6926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorden P., Gavin J. R., 3rd, Kahn C. R., Archer J. A., Lesniak M., Hendricks C., Neville D. M., Jr, Roth J. Application of radioreceptor assay to circulating insulin, growth hormone, and to their tissue receptors in animals and man. Pharmacol Rev. 1973 Jun;25(2):179–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorden P. Glucose intolerance with hypokalemia. Failure of short-term potassium depletion in normal subjects to reproduce the glucose and insulin abnormalities of clinical hypokalemia. Diabetes. 1973 Jul;22(7):544–551. doi: 10.2337/diab.22.7.544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Freychet P., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Quantitative aspects of the insulin-receptor interaction in liver plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 10;249(7):2249–2257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Neville D. M., Jr, Gorden P., Freychet P., Roth J. Insulin receptor defect in insulin resistance: studies in the obese-hyperglycimic mouse. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jul 11;48(1):135–142. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90354-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Neville D. M., Jr, Roth J. Insulin-receptor interaction in the obese-hyperglycemic mouse. A model of insulin resistance. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 10;248(1):244–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porte D., Jr, Bagdade J. D. Human insulin secretion: as integrated approach. Annu Rev Med. 1970;21:219–240. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.21.020170.001251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinowitz D. Some endocrine and metabolic aspects of obesity. Annu Rev Med. 1970;21:241–258. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.21.020170.001325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J. Peptide hormone binding to receptors: a review of direct studies in vitro. Metabolism. 1973 Aug;22(8):1059–1073. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(73)90225-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soll A. H., Goldfine I. D., Roth J., Kahn C. R. Thymic lymphocytes in obese (ob-ob) mice. A mirror of the insulin receptor defect in liver and fat. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4127–4131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wybran J., Chantler S., Fudenberg H. H. Isolation of normal T cells in chronic lymphatic leukaemia. Lancet. 1973 Jan 20;1(7795):126–129. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)90196-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Meyts P., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr, Gavin J. R., 3rd, Lesniak M. A. Insulin interactions with its receptors: experimental evidence for negative cooperativity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Nov 1;55(1):154–161. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(73)80072-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



