Abstract
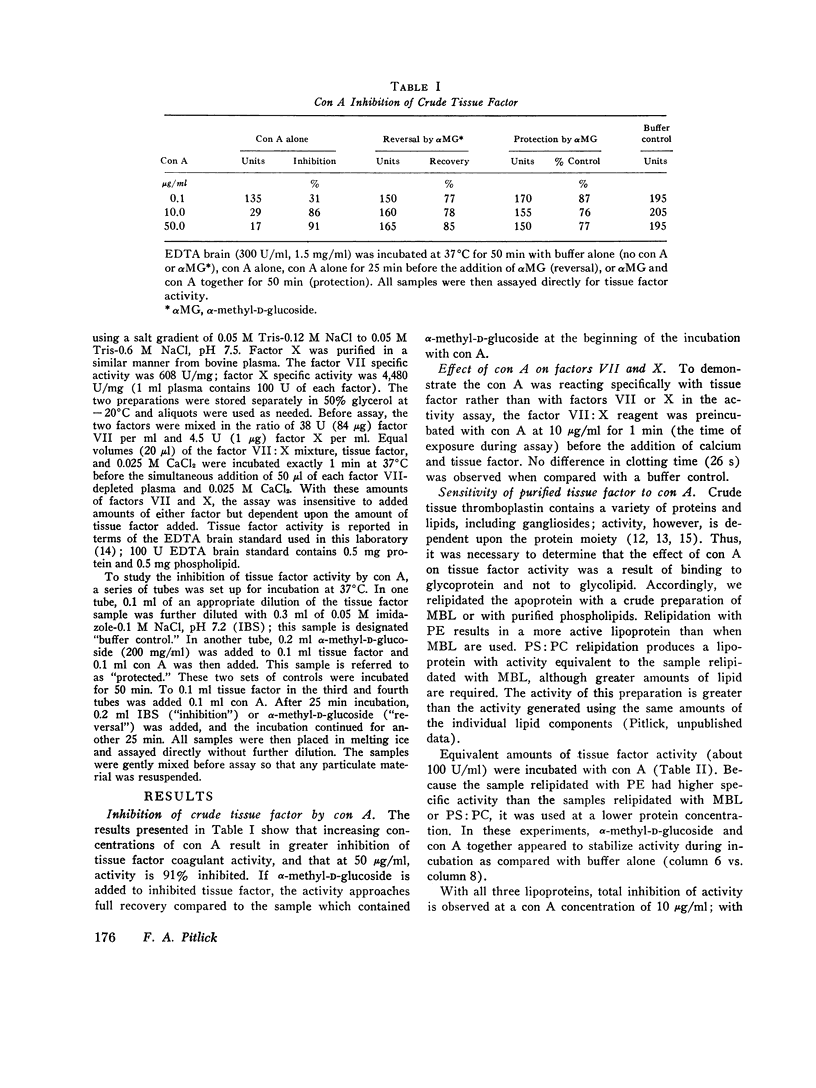
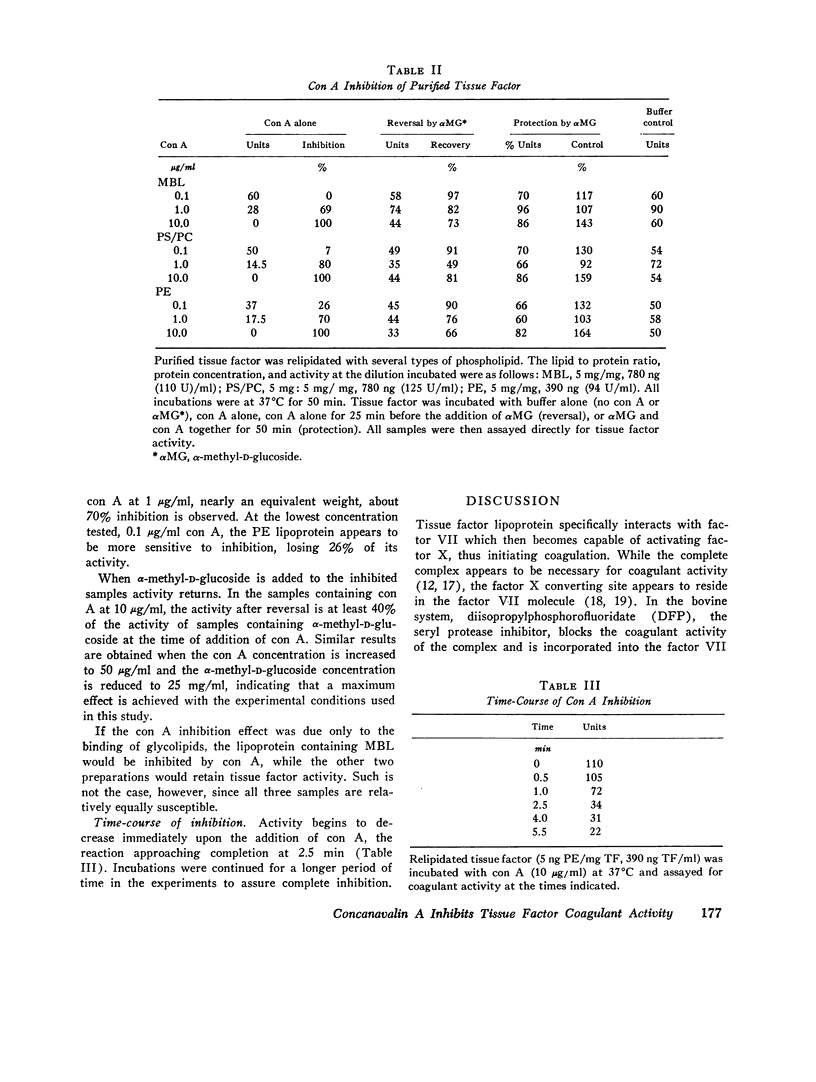
Concanavalin A (con A) is a potent inhibitor of coagulant activity of native tissue factor. Coagulant activity is recovered by addition of alpha-methyl-D-glucoside to inhibited tissue factor. Inclusion of alpha-methyl-D-glucose during incubation of con A with tissue factor preserves coagulant activity. These data suggest that con A interacts reversibly with a carbohydrate residue in such a way as to inhibit coagulant activity of the molecule. Purified tissue factor apoprotein has been recombined with mixed brain phospholipids or purified phospholipids (phosphatidyl ethanolamine or a mixture of phosphatidyl choline with phosphatidyl serine). These preparations were also completely but reversibly inhibited by con A. Thus, purified tissue factor apoprotein appears to donate the affected carbohydrate residue.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agrawal B. B., Goldstein I. J. Protein-carbohydrate interaction. VI. Isolation of concanavalin A by specific adsorption on cross-linked dextran gels. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Oct 23;147(2):262–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger M. M. A difference in the architecture of the surface membrane of normal and virally transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Mar;62(3):994–1001. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.3.994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDSTEIN I. J., HOLLERMAN C. E., MERRICK J. M. PROTEIN-CARBOHYDRATE INTERACTION. I. THE INTERACTION OF POLYSACCHARIDES WITH CONCANAVALIN A. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jan 4;97:68–76. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(65)90270-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDSTEIN I. J., HOLLERMAN C. E., SMITH E. E. PROTEIN-CARBOHYDRATE INTERACTION. II. INHIBITION STUDIES ON THE INTERACTION OF CONCANAVALIN A WITH POLYSACCHARIDES. Biochemistry. 1965 May;4:876–883. doi: 10.1021/bi00881a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inbar M., Sachs L. Interaction of the carbohydrate-binding protein concanavalin A with normal and transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Aug;63(4):1418–1425. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.4.1418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jesty J., Nemerson Y. Purification of Factor VII from bovine plasma. Reaction with tissue factor and activation of Factor X. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 25;249(2):509–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalb A. J., Lustig A. The molecular weight of concanavalin A. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Oct 21;168(2):366–367. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(68)90161-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S. C., Li Y. T. Studies on the glycosidases of jack bean meal. 3. Crystallization and properties of beta-N-acetylhexosaminidase. J Biol Chem. 1970 Oct 10;245(19):5153–5160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y. T. Studies on the glycosidases in jack bean meal. I. Isolation and properties of alpha-mannosidase. J Biol Chem. 1967 Dec 10;242(23):5474–5480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemerson Y. Characteristics and lipid requirements of coagulant proteins extracted from lung and brain: the specifity of protein component of tissue factor. J Clin Invest. 1969 Feb;48(2):322–331. doi: 10.1172/JCI105988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemerson Y., Clyne L. P. An assay for coagulation factor VII using factor VII-depleted bovine plasma. J Lab Clin Med. 1974 Feb;83(2):301–303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemerson Y., Esnouf M. P. Activation of a proteolytic system by a membrane lipoprotein: mechanism of action of tissue factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):310–314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemerson Y., Pitlick F. A. Purification and characterization of the protein component of tissue factor. Biochemistry. 1970 Dec 22;9(26):5100–5105. doi: 10.1021/bi00828a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemerson Y. The phospholipid requirement of tissue factor in blood coagulation. J Clin Invest. 1968 Jan;47(1):72–80. doi: 10.1172/JCI105716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemerson Y. The reaction between bovine brain tissue factor and factors VII and X. Biochemistry. 1966 Feb;5(2):601–608. doi: 10.1021/bi00866a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson M. O., Liener I. E. The association and dissociation of concanavalin A, the phytohemagglutinin of the jack bean. Biochemistry. 1967 Dec;6(12):3801–3808. doi: 10.1021/bi00864a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterud B., Berre A., Otnaess A. B., Bjorklid E., Prydz H. Activation of the coagulation factor VII by tissue thromboplastin and calcium. Biochemistry. 1972 Jul 18;11(15):2853–2857. doi: 10.1021/bi00765a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickles F. R., Hardin J. A., Pitlick F. A., Hoyer L. W., Conrad M. E. Tissue factor activity in lymphocyte cultures from normal individuals and patients with hemophilia A. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jun;52(6):1427–1434. doi: 10.1172/JCI107316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinemann A., Stryer L. Accessibility of the carbohydrate moiety of rhodopsin. Biochemistry. 1973 Apr 10;12(8):1499–1502. doi: 10.1021/bi00732a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumner J. B., Howell S. F. Identification of Hemagglutinin of Jack Bean with Concanavalin A. J Bacteriol. 1936 Aug;32(2):227–237. doi: 10.1128/jb.32.2.227-237.1936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumner J. B., Howell S. F., Zeissig A. CONCANAVALIN A AND HEMAGGLUTINATION. Science. 1935 Jul 19;82(2116):65–66. doi: 10.1126/science.82.2116.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. L., Cunningham B. A., Edelman G. M. Unusual fragments in the subunit structure of concanavalin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1130–1134. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeldis S. M., Nemerson Y., Pitlick F. A., Lentz T. L. Tissue factor (thromboplastin): localization to plasma membranes by peroxidase-conjugated antibodies. Science. 1972 Feb 18;175(4023):766–768. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4023.766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


