Abstract
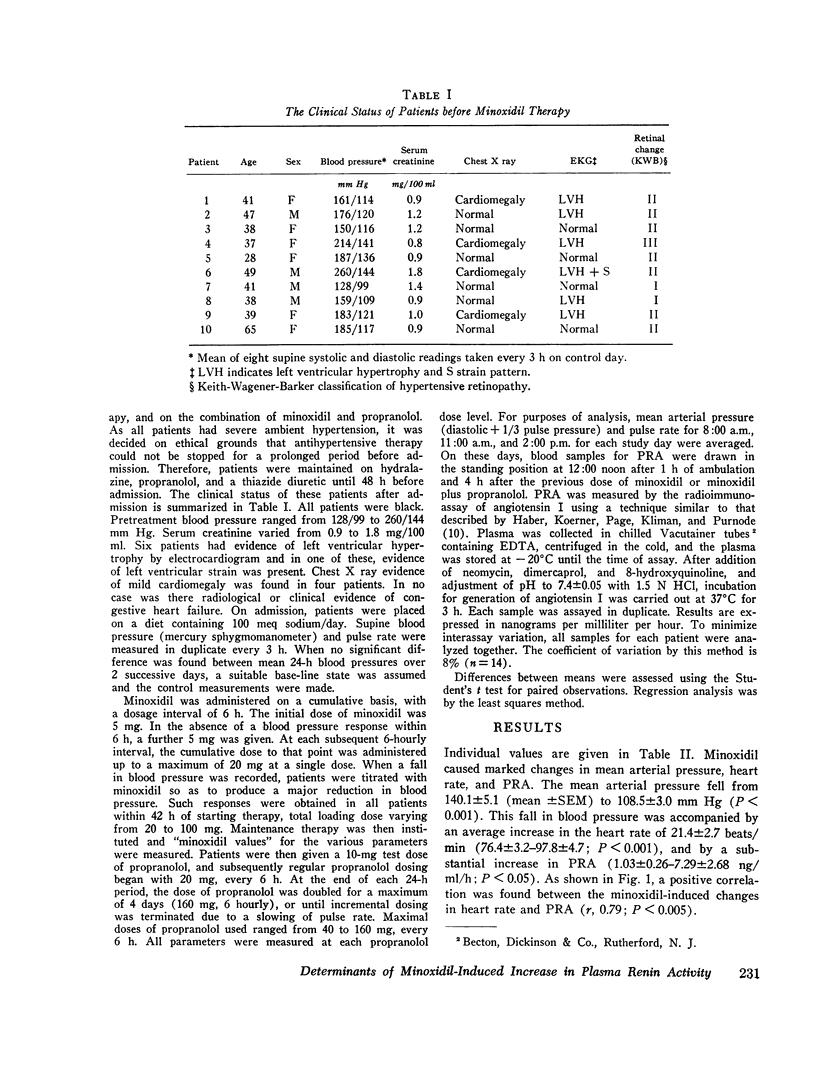
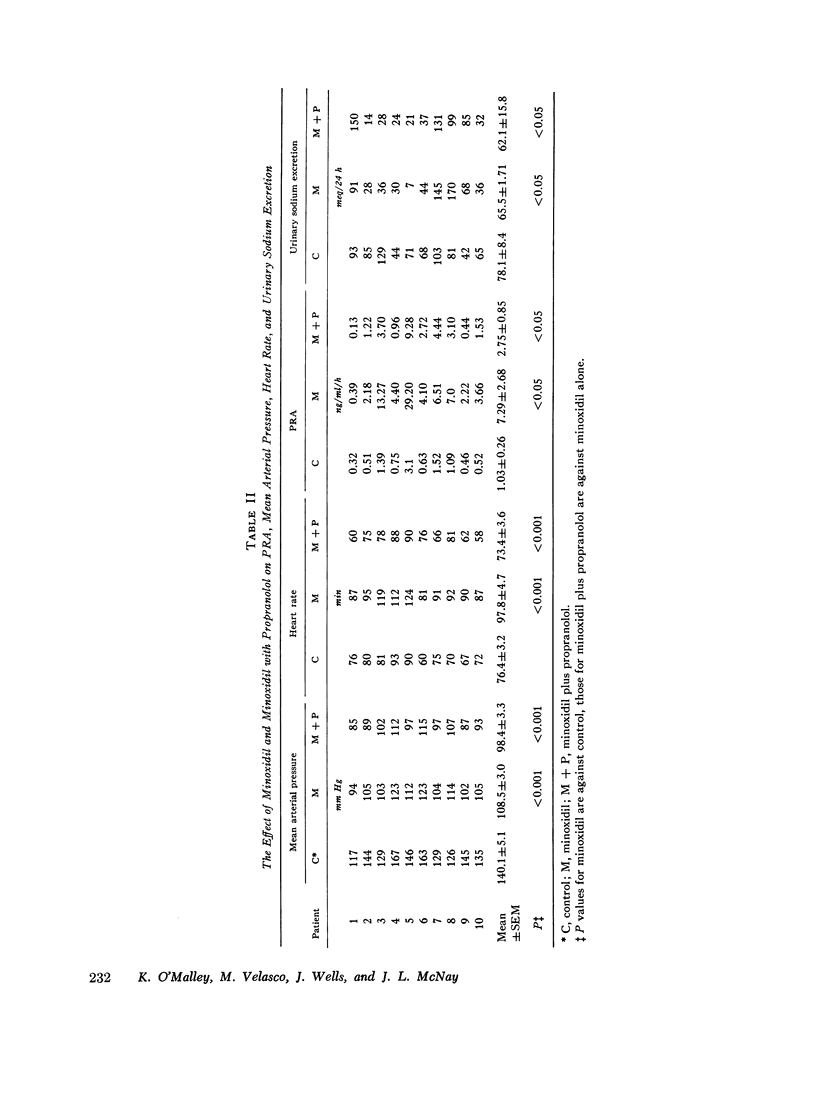
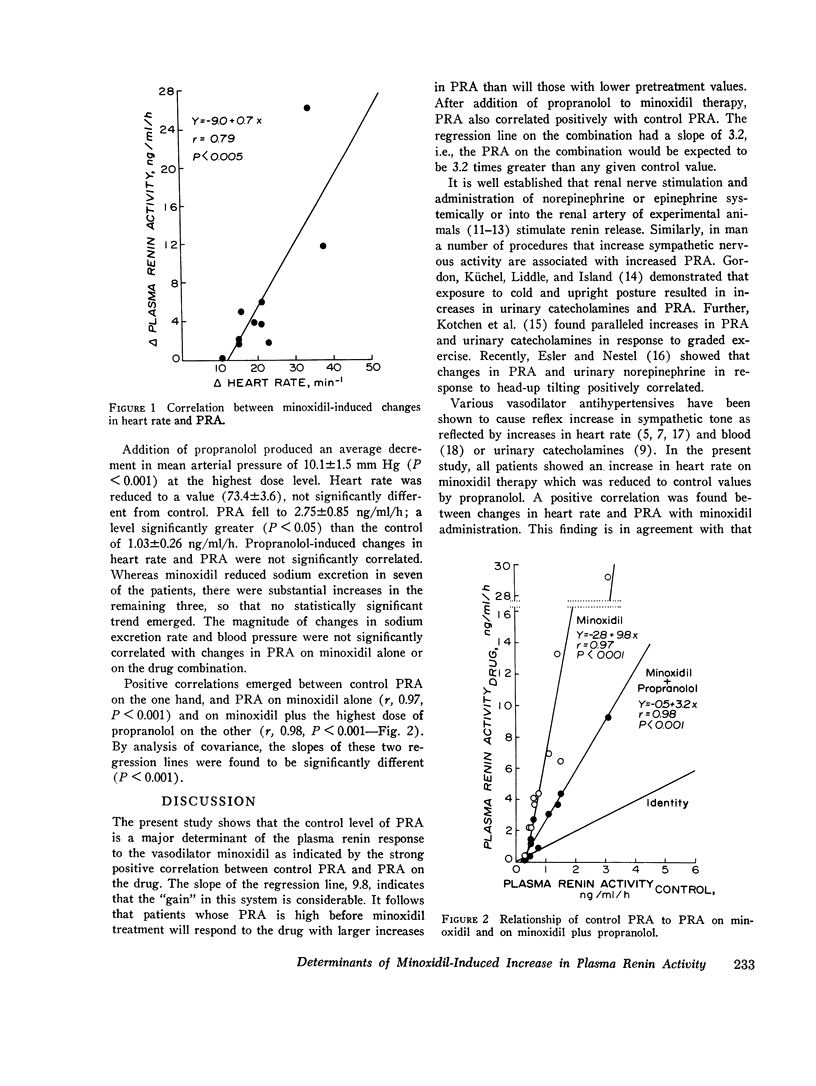
A study was made of the possible mechanism(s) underlying minoxidil-induced increase in plasma renin activity (PRA). 10 patients with essential hypertension were treated with minoxidil and subsequently with a combination of minoxidil plus propranolol. Minoxidil lowered mean arterial pressure 31.6 plus or minus 3.3 mm Hg, mean plus or minus SEM. There was an associated increase in both PRA, 6.26 plus or minus 2.43 NG/ML/H, and heart rate, 21.4 plus or minus 2.7 beats/min. The changes in PRA and heart rate were positively correlated, r, 0.79. Addition of propranolol reduced mean arterial pressure by a further 10.1 plus or minus 1.5 mm Hg and returned heart rate to control levels. Propranolol reduced PRA significantly but not to control levels. Control PRA positively correlated with PRA on minoxidil, r, 0.97, and with PRA on minoxidil plus propranolol, r, 0.98. We conclude that control PRA is a major determinant of change in PRA with minoxidil. Minoxidil increased PRA by at least two mechanisms: (a) an adrenergic mechanism closely related to change in heart rate and blocked by propranolol, and (b) a mechanism(s) not sensitive to propranolol and possibly related to decrease in renal perfusion pressure.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABLAD B. A study of the mechanism of the hemodynamic effects of hydralazine in man. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1963;20(Suppl 1):1–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bühler F. R., Laragh J. H., Baer L., Vaughan E. D., Jr, Brunner H. R. Propranolol inhibition of renin secretion. A specific approach to diagnosis and treatment of renin-dependent hypertensive diseases. N Engl J Med. 1972 Dec 14;287(24):1209–1214. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197212142872401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esler M. D., Nestel P. J. Renin and sympathetic nervous system responsiveness to adrenergic stimuli in essential hypertension. Am J Cardiol. 1973 Oct;32(5):643–649. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(73)80057-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore E., Weil J., Chidsey C. Treatment of essential hypertension with a new vasodilator in combination with beta-adrenergic blockade. N Engl J Med. 1970 Mar 5;282(10):521–527. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197003052821001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon R. D., Küchel O., Liddle G. W., Island D. P. Role of the sympathetic nervous system in regulating renin and aldosterone production in man. J Clin Invest. 1967 Apr;46(4):599–605. doi: 10.1172/JCI105561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb T. B., Katz F. H., Chidsey C. A., 3rd Combined therapy with vasodilator drugs and beta-adrenergic blockade in hypertension. A comparative study of minoxidil and hydralazine. Circulation. 1972 Mar;45(3):571–582. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.45.3.571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haber E., Koerner T., Page L. B., Kliman B., Purnode A. Application of a radioimmunoassay for angiotensin I to the physiologic measurements of plasma renin activity in normal human subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1969 Oct;29(10):1349–1355. doi: 10.1210/jcem-29-10-1349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. A., Davis J. O., Witty R. T. Effects of catecholamines and renal nerve stimulation on renin release in the nonfiltering kidney. Circ Res. 1971 Dec;29(6):646–653. doi: 10.1161/01.res.29.6.646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko Y., Ikeda T., Takeda T., Inoue G., Tagawa H., Ueda H. Renin release in patients with benign essential hypertension. Circulation. 1968 Aug;38(2):353–362. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.38.2.353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotchen T. A., Hartley L. H., Rice T. W., Mougey E. H., Jones L. G., Mason J. W. Renin, norepinephrine, and epinephrine responses to graded exercise. J Appl Physiol. 1971 Aug;31(2):178–184. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1971.31.2.178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Küchel O., Fishman L. M., Liddle G. W., Michelakis A. Effect of diazoxide on plasma renin activity in hypertensive patients. Ann Intern Med. 1967 Oct;67(4):791–799. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-67-4-791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laragh J. H., Baer L., Brunner H. R., Buhler F. R., Sealey J. E., Vaughan E. D., Jr Renin, angiotensin and aldosterone system in pathogenesis and management of hypertensive vascular disease. Am J Med. 1972 May;52(5):633–652. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(72)90054-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed S., Fasola A. F., Privitera P. J., Lipicky R. J., Martz B. L., Gaffney T. E. Effect of methyldopa on plasma renin activity in man. Circ Res. 1969 Nov;25(5):543–548. doi: 10.1161/01.res.25.5.543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettinger W. A., Mitchell H. C. Minoxidil--an alternative to nephrectomy for refractory hypertension. N Engl J Med. 1973 Jul 26;289(4):167–171. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197307262890401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda H., Kaneko Y., Takeda T., Ikeda T., Yagi S. Observation on the mechanism of renin release by hydralazine in hypertensive patients. Circ Res. 1970 Oct;27(Suppl):201–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vander A. J. Effect of catecholamines and the renal nerves on renin secretion in anesthetized dogs. Am J Physiol. 1965 Sep;209(3):659–662. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.209.3.659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wathen R. L., Kingsbury W. S., Stouder D. A., Schneider E. G., Rostorfer H. H. Effects of infusion of catecholamines and angiotensin II on renin release in anesthetized dogs. Am J Physiol. 1965 Nov;209(5):1012–1024. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.209.5.1012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winer N., Chokshi D. S., Yoon M. S., Freedman A. D. Adrenergic receptor mediation of renin secretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1969 Sep;29(9):1168–1175. doi: 10.1210/jcem-29-9-1168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarday Z., Viktora J., Wolff F. The effect of diazoxide on catecholamines. Metabolism. 1966 Mar;15(3):257–261. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(66)90023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



