Abstract
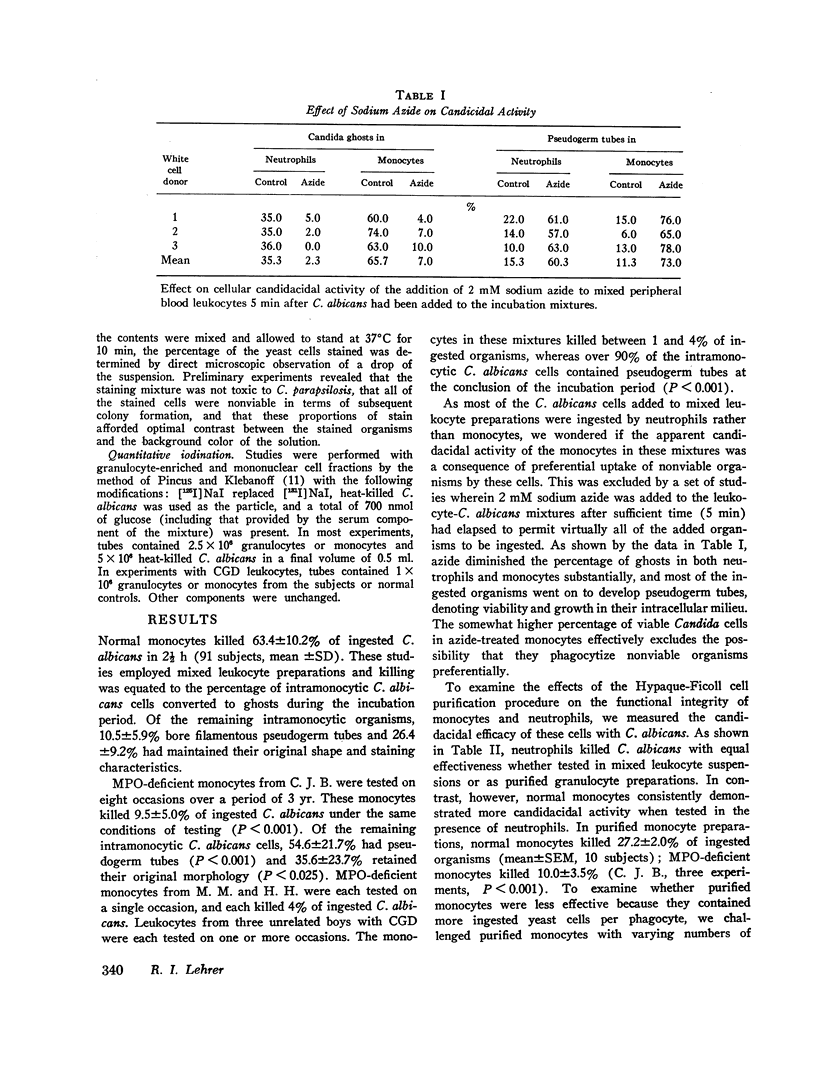
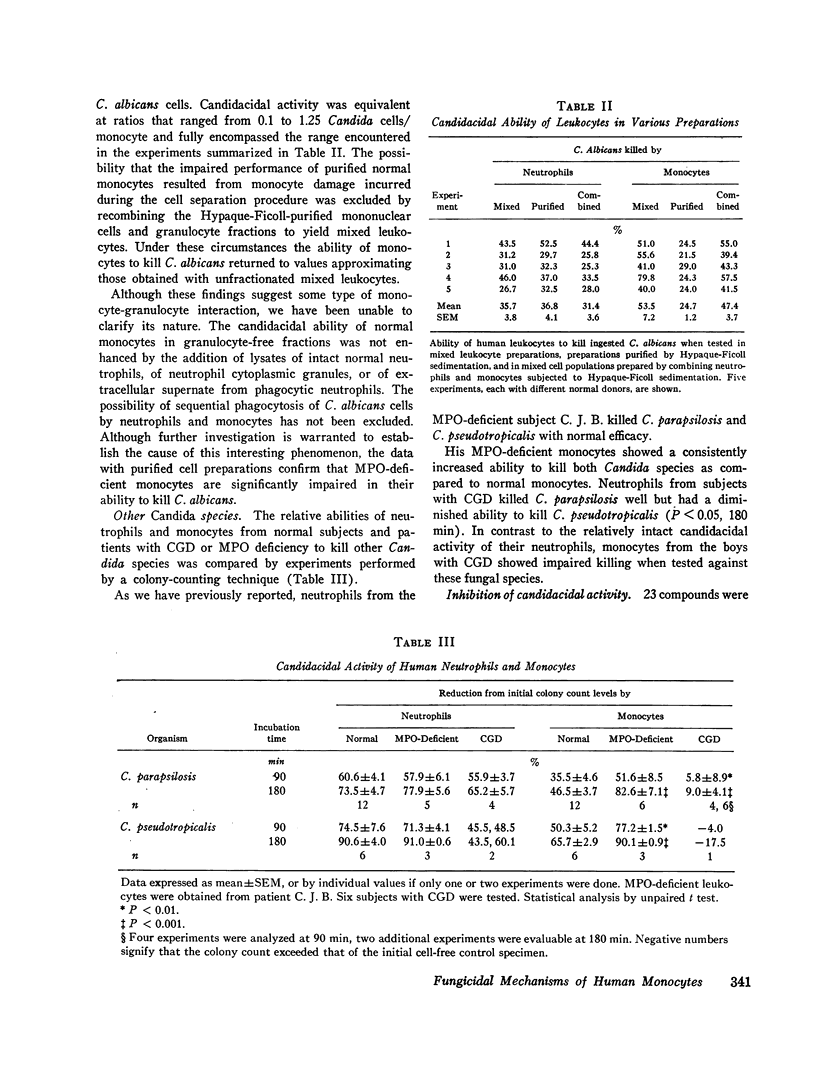
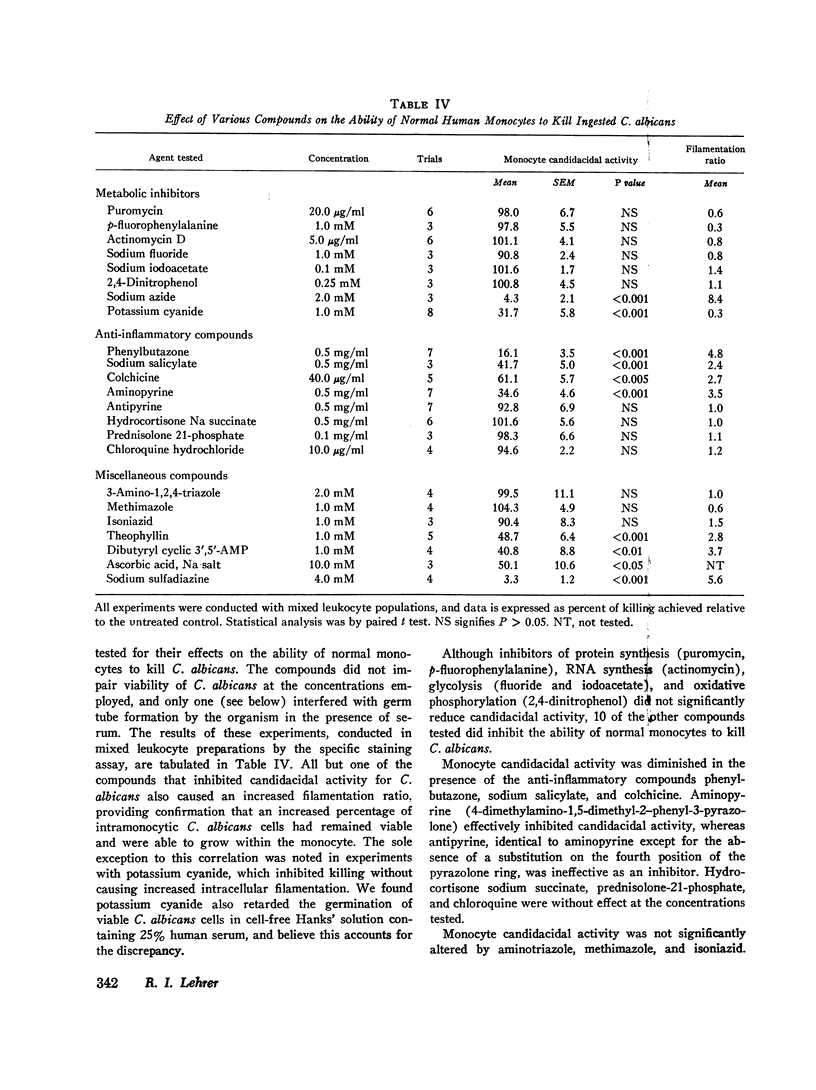
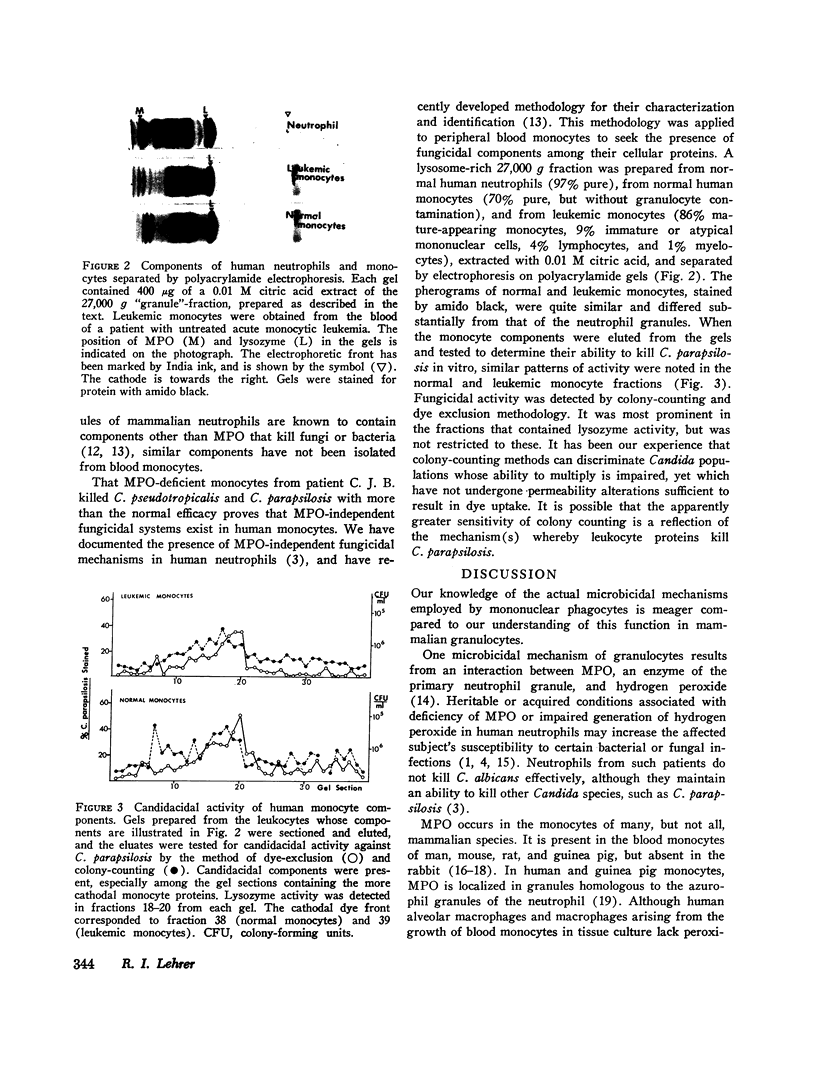
We tested the ability of human peripheral blood monocytes to kill Candida albicans and Candida parapsilosis. Evidence that multiple fungicidal mechanisms operate in normla monocytes was found. Normal monocytes ingested and killed viable C. albicans, and could iodinate heat-killed C. albicans. Both functions were defective in monocytes from subjects with myeloperoxidase deficiency or chronic granulomatous disease. Methimazole, isoniazid, and aminotriazole inhibited iodination by normal monocytes without impairing their ability to kill C. albicans, indicating that iodination was not essential to the myeloperoxidase-hydrogen peroxide-mediated fungicidal system of the monocyte. C. parapsilosis, an organism killed with supranormal efficacy by monocytes from a patient with hereditary myeloperoxidase deficiency, was selected to examine the myeloperoxidase-independent fungicidal mechanisms of monocytes. Monocytes were obtained from the blood of normal or leukemic subjects and homogenized in 0.34 M sucrose to yield fractions rich in cytoplasmic granules. These fractions were extracted with 0.01 M citric acid and the soluble components were separated by micropreparative polyacrylamide electrophoresis. Monocytes were found to contain cationic proteins, other than myeloperoxidase, that kill C. parapsilosis in vitro.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baehner R. L., Johnston R. B., Jr Monocyte function in children with neutropenia and chronic infections. Blood. 1972 Jul;40(1):31–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline M. J., Lehrer R. I. Phagocytosis by human monocytes. Blood. 1968 Sep;32(3):423–435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotran R. S., Litt M. Ultrastructural localization of horseradish peroxidase and endogenous peroxidase activity in guinea pig peritoneal macrophages. J Immunol. 1970 Dec;105(6):1536–1546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daems W. T., Poelman R. E., Brederoo P., van Lohuzen E. J. Peroxidatic activity in resident peritoneal macrophages and exudate monocytes of the guinea pig after ingestion of latex particles. J Histochem Cytochem. 1973 Jan;21(1):93–95. doi: 10.1177/21.1.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis W. C., Huber H., Douglas S. D., Fudenberg H. H. A defect in circulating mononuclear phagocytes in chronicgranulomatous disease of childhood. J Immunol. 1968 Nov;101(5):1093–1095. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond R. D., Root R. K., Bennett J. E. Factors influencing killing of Cryptococcus neoformans by human leukocytes in vitro. J Infect Dis. 1972 Apr;125(4):367–376. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.4.367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J. Iodination of bacteria: a bactericidal mechanism. J Exp Med. 1967 Dec 1;126(6):1063–1078. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.6.1063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J. Myeloperoxidase-halide-hydrogen peroxide antibacterial system. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2131–2138. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2131-2138.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I., Cline M. J. Interaction of Candida albicans with human leukocytes and serum. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jun;98(3):996–1004. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.3.996-1004.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I., Cline M. J. Leukocyte myeloperoxidase deficiency and disseminated candidiasis: the role of myeloperoxidase in resistance to Candida infection. J Clin Invest. 1969 Aug;48(8):1478–1488. doi: 10.1172/JCI106114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I. Functional aspects of a second mechanism of candidacidal activity by human neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1972 Oct;51(10):2566–2572. doi: 10.1172/JCI107073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I., Goldberg L. S., Apple M. A., Rosenthal N. P. Refractory megaloblastic anemia with myeloperoxidase-deficient neutrophils. Ann Intern Med. 1972 Mar;76(3):447–453. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-76-3-447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols B. A., Bainton D. F., Farquhar M. G. Differentiation of monocytes. Origin, nature, and fate of their azurophil granules. J Cell Biol. 1971 Aug;50(2):498–515. doi: 10.1083/jcb.50.2.498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus S. H., Klebanoff S. J. Quantitative leukocyte iodination. N Engl J Med. 1971 Apr 8;284(14):744–750. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197104082841402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quie P. G., White J. G., Holmes B., Good R. A. In vitro bactericidal capacity of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes: diminished activity in chronic granulomatous disease of childhood. J Clin Invest. 1967 Apr;46(4):668–679. doi: 10.1172/JCI105568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REISFELD R. A., LEWIS U. J., WILLIAMS D. E. Disk electrophoresis of basic proteins and peptides on polyacrylamide gels. Nature. 1962 Jul 21;195:281–283. doi: 10.1038/195281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodey G. E., Park B. H., Ford D. K., Gray B. H., Good R. A. Defective bactericidal activity of peripheral blood leukocytes in lipochrome histiocytosis. Am J Med. 1970 Sep;49(3):322–327. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(70)80023-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodey G. E., Park B. H., Windhorst D. B., Good R. A. Defective bactericidal activity of monocytes in fatal granulomatous disease. Blood. 1969 Jun;33(6):813–820. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steigbigel R. T., Lambert L. H., Jr, Remington J. S. Phagocytic and bacterial properties of normal human monocytes. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jan;53(1):131–142. doi: 10.1172/JCI107531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitelaw D. M. The intravascular lifespan of monocytes. Blood. 1966 Sep;28(3):455–464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widmann J. J., Cotran R. S., Fahimi H. D. Mononuclear phagocytes (Kupffer cells) and endothelial cells. Identification of two functional cell types in rat liver sinusoids by endogenous peroxidase activity. J Cell Biol. 1972 Jan;52(1):159–170. doi: 10.1083/jcb.52.1.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeya H. I., Spitznagel J. K. Cationic proteins of polymorphonuclear leukocyte lysosomes. I. Resolution of antibacterial and enzymatic activities. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):750–754. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.750-754.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Furth R., Hirsch J. G., Fedorko M. E. Morphology and peroxidase cytochemistry of mouse promonocytes, monocytes, and macrophages. J Exp Med. 1970 Oct 1;132(4):794–812. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.4.794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




