Abstract
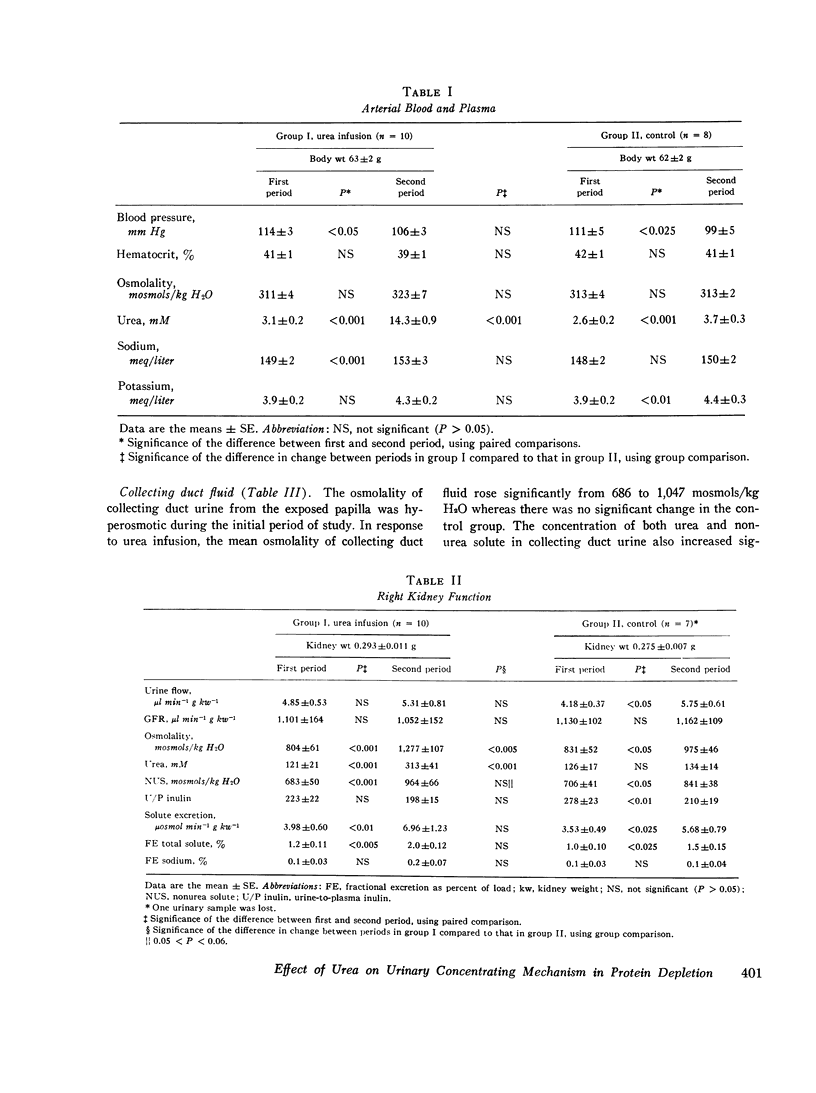
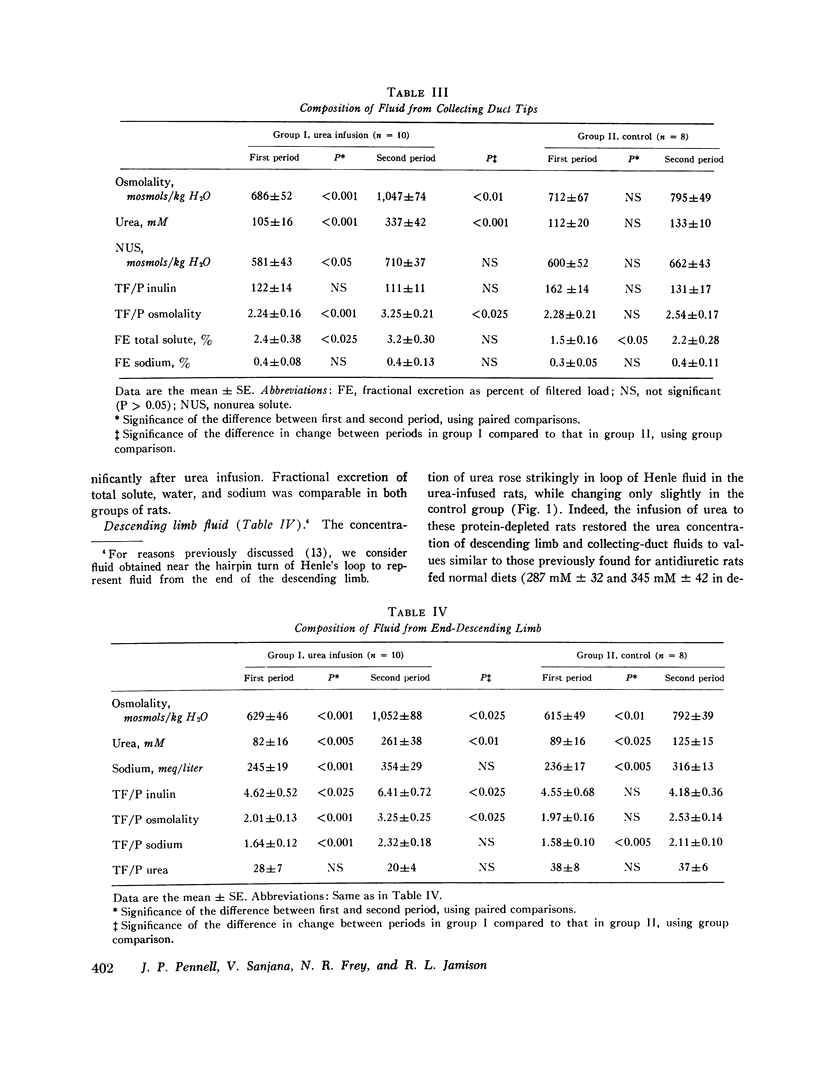
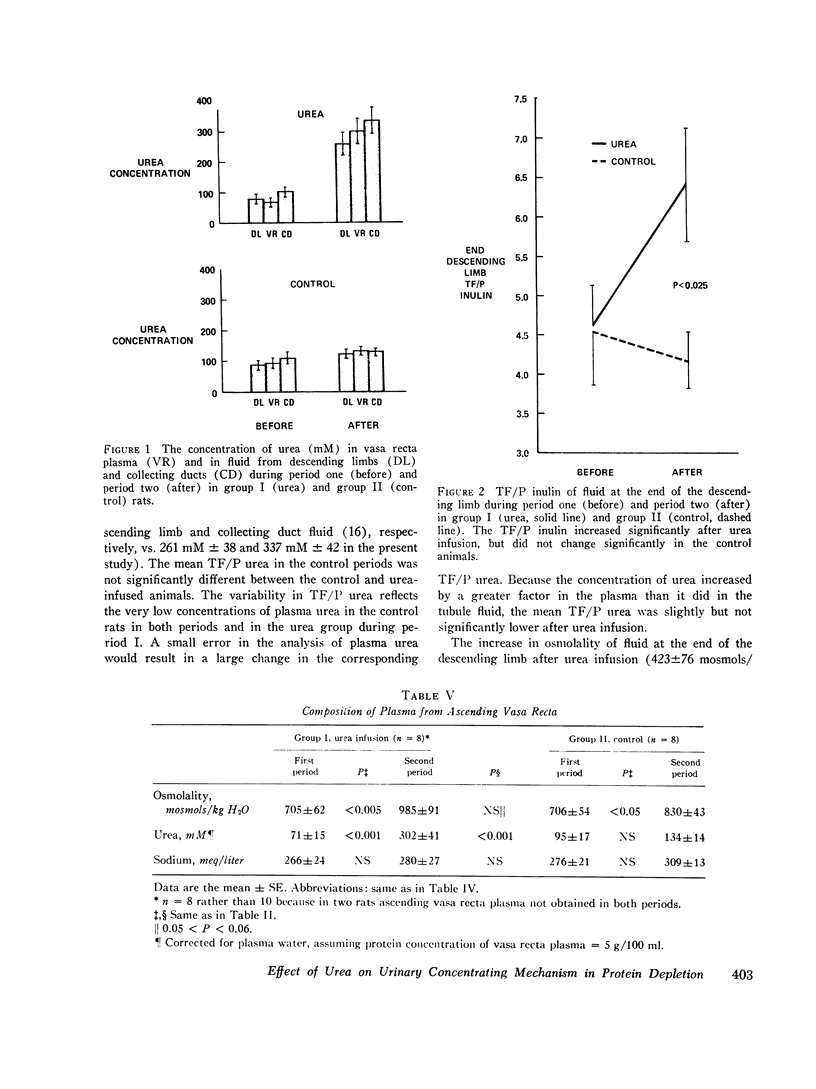
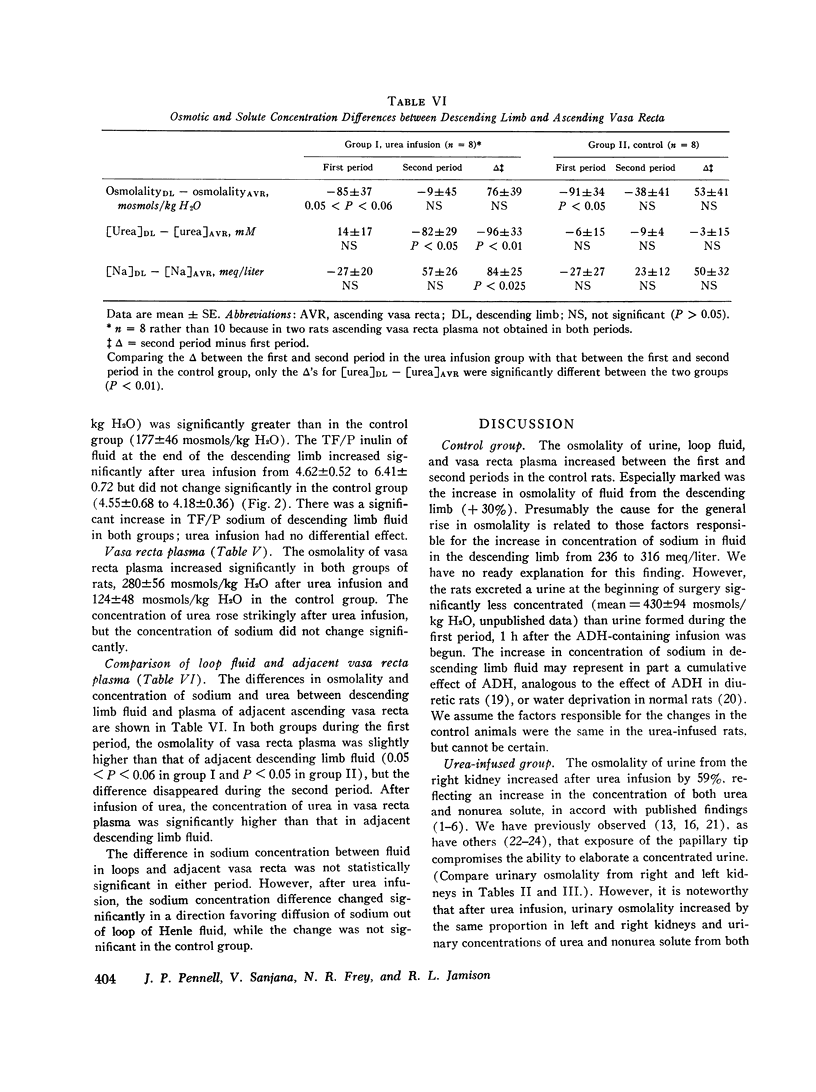
To explore the role of urea in the urinary concentrating mechanism, the contents of vasa recta, Henle's descending limbs and collecting ducts were sampled by micropuncture of the renal papilla before and after infusion of urea in 10 protein-depleted rats. Eight protein-depleted rats not given urea were similarly studied as a control group. After urea administration, osmolality and the concentrations of urea and nonurea solute of urine from both exposed and contralateral kideny increased significantly. The osmolality and urea concentration of fluid from the end of Henle's descending limb and vasa recta plasma and the tubule fluid-to-plasma inulin ratio in the end-descending limb all increased significantly after urea infusion. We interpret these observations to indicate that urea enhances urinary concentration by increasing the abstraction of water from the juxtamedullary nephron (presumably the descending limb), in agreement with the prediction of recent passive models of the urinary concentrating mechanism. However, the concentration of urea in fluid from the descending limb after urea infusion was high (261 plus or minus 31 mM) and the difference in solium concentration between descending limb fluid and vasa recta was small and statistically insignificant.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRAY G. A., PRESTON A. S. Effect of urea on urine concentration in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1961 Nov;40:1952–1960. doi: 10.1172/JCI104420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baines A. D., de Rouffignac C. Functional heterogeneity of nephrons. II. Filtration rates, intraluminal flow velocities and fractional water reabsorption. Pflugers Arch. 1969;308(3):260–276. doi: 10.1007/BF00586558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burg M. B., Green N. Function of the thick ascending limb of Henle's loop. Am J Physiol. 1973 Mar;224(3):659–668. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.224.3.659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRAWFORD J. D., DOYLE A. P., PROBST J. H. Service of urea in renal water conservation. Am J Physiol. 1959 Mar;196(3):545–548. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1959.196.3.545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EPSTEIN F. H., KLEEMAN C. R., PURSEL S., HENDRIKX A. The effect of feeding protein and urea on the renal concentrating process. J Clin Invest. 1957 May;36(5):635–641. doi: 10.1172/JCI103463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOTTSCHALK C. W., MYLLE M. Micropuncture study of the mammalian urinary concentrating mechanism: evidence for the countercurrent hypothesis. Am J Physiol. 1959 Apr;196(4):927–936. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1959.196.4.927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENDRIKX A., EPSTEIN F. H. Effect of feeding protein and urea on renal concentrating ability in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1958 Dec;195(3):539–542. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1958.195.3.539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai M., Kokko J. P. Sodium chloride, urea, and water transport in the thin ascending limb of Henle. Generation of osmotic gradients by passive diffusion of solutes. J Clin Invest. 1974 Feb;53(2):393–402. doi: 10.1172/JCI107572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamison R. L., Bennett C. M., Berliner R. W. Countercurrent multiplication by the thin loops of Henle. Am J Physiol. 1967 Feb;212(2):357–366. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.212.2.357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamison R. L., Buerkert J., Lacy F. A micropuncture study of Henle's thin loop in Brattleboro rats. Am J Physiol. 1973 Jan;224(1):180–185. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.224.1.180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamison R. L., Buerkert J., Lacy F. A micropuncture study of collecting tubule function in rats with hereditary diabetes insipidus. J Clin Invest. 1971 Nov;50(11):2444–2452. doi: 10.1172/JCI106743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamison R. L., Lacy F. B. Effect of saline infusion on superficial and juxtamedullary nephrons in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1971 Sep;221(3):690–697. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.3.690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamison R. L. Micropuncture study of segments of thin loop of Henle in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1968 Jul;215(1):236–242. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.215.1.236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamison R. L. Micropuncture study of superficial and juxtamedullary nephrons in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1970 Jan;218(1):46–55. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.218.1.46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klahr S., Alleyne G. A. Effects of chronic protein-calorie malnutrition on the kidney. Kidney Int. 1973 Mar;3(3):129–141. doi: 10.1038/ki.1973.21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokko J. P. Membrane characteristics governing salt and water transport in the loop of Henle. Fed Proc. 1974 Jan;33(1):25–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokko J. P., Rector F. C., Jr Countercurrent multiplication system without active transport in inner medulla. Kidney Int. 1972 Oct;2(4):214–223. doi: 10.1038/ki.1972.97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokko J. P. Urea transport in proximal tubule and the descending limb of Henle. J Clin Invest. 1972 Aug;51(8):1999–2008. doi: 10.1172/JCI107006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINSKY N. G., BERLINER R. W. The role of urea in the urine concentrating mechanism. J Clin Invest. 1959 May;38(5):741–748. doi: 10.1172/JCI103854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARSH D. J., SOLOMON S. ANALYSIS OF ELECTROLYTE MOVEMENT IN THIN HENLE'S LOOPS OF HAMSTER PAPILLA. Am J Physiol. 1965 Jun;208:1119–1128. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.208.6.1119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malnic G., Klose R. M., Giebisch G. Micropuncture study of distal tubular potassium and sodium transport in rat nephron. Am J Physiol. 1966 Sep;211(3):529–547. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.3.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh D. J. Solute and water flows in thin limbs of Henle's loop in the hamster kidney. Am J Physiol. 1970 Mar;218(3):824–831. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.218.3.824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan T., Berliner R. W. Permeability of the loop of Henle, vasa recta, and collecting duct to water, urea, and sodium. Am J Physiol. 1968 Jul;215(1):108–115. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.215.1.108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennell J. P., Lacy F. B., Jamison R. L. An in vivo study of the concentrating process in the descending limb of Henle's loop. Kidney Int. 1974 May;5(5):337–347. doi: 10.1038/ki.1974.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocha A. S., Kokko J. P. Sodium chloride and water transport in the medullary thick ascending limb of Henle. Evidence for active chloride transport. J Clin Invest. 1973 Mar;52(3):612–623. doi: 10.1172/JCI107223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt-Nielsen B., Robinson R. R. Contribution of urea to urinary concentrating ability in the dog. Am J Physiol. 1970 May;218(5):1363–1369. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.218.5.1363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schütz W., Schnermann J. Pelvic urine composition as a determinant of inner medullary solute concentration and urine osmolarity. Pflugers Arch. 1972;334(2):154–166. doi: 10.1007/BF00586788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson J. L. Concentration of urine in a central core model of the renal counterflow system. Kidney Int. 1972 Aug;2(2):85–94. doi: 10.1038/ki.1972.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valtin H. Sequestration of urea and nonurea solutes in renal tissues of rats with hereditary hypothalamic diabetes insipidus: effect of vasopressin and dehydration on the countercurrent mechanism. J Clin Invest. 1966 Mar;45(3):337–345. doi: 10.1172/JCI105348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINDHAGER E. E. ELECTROPHYSIOLOGICAL STUDY OF RENAL PAPILLA OF GOLDEN HAMSTERS. Am J Physiol. 1964 Apr;206:694–700. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.206.4.694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



