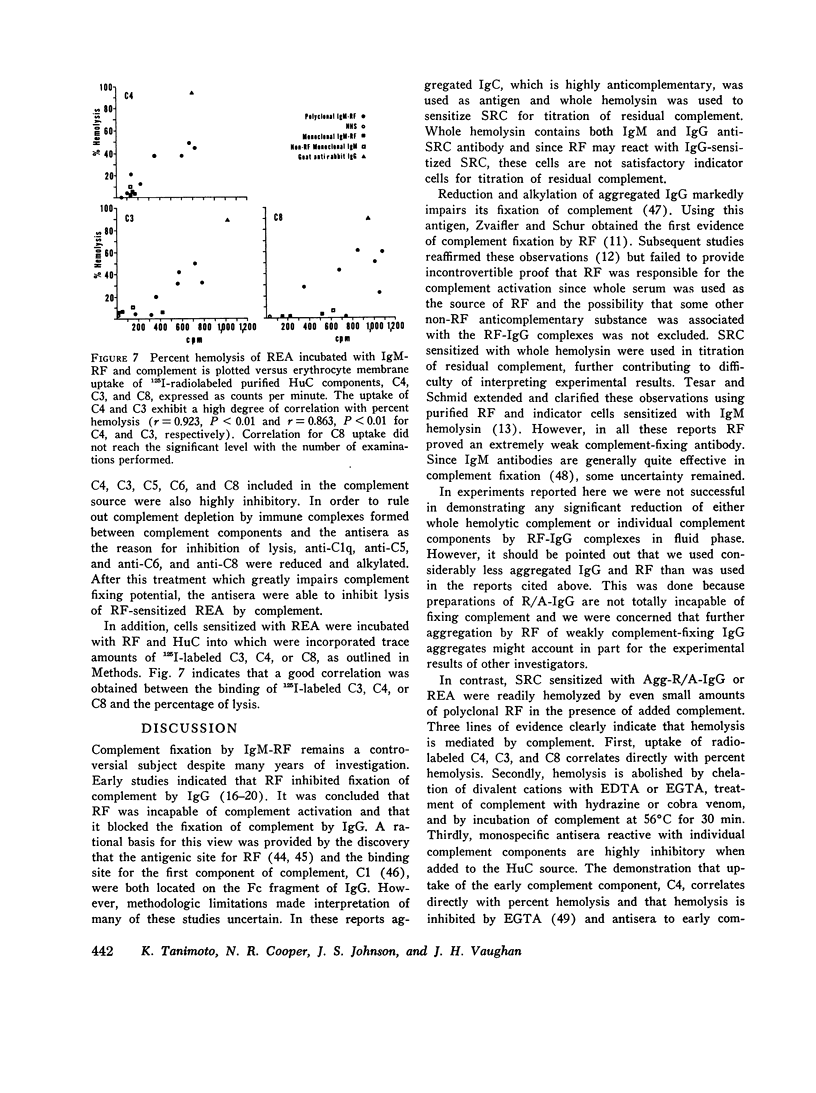
Abstract
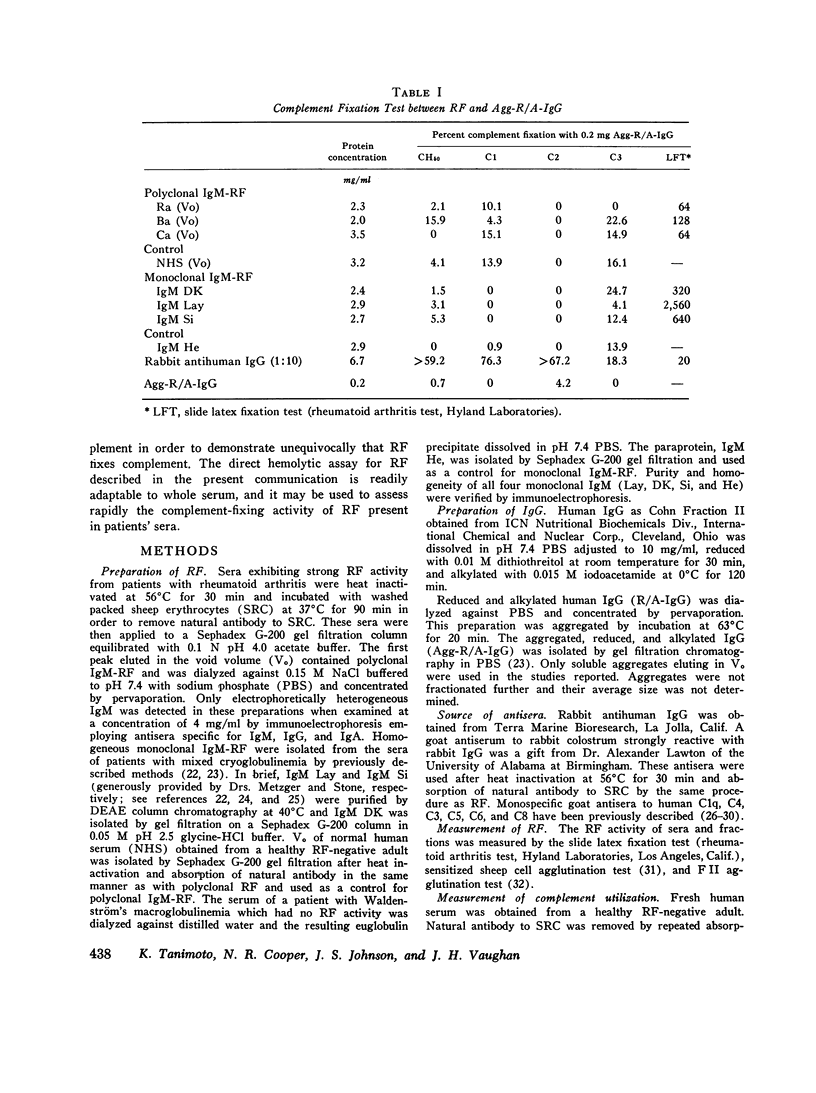
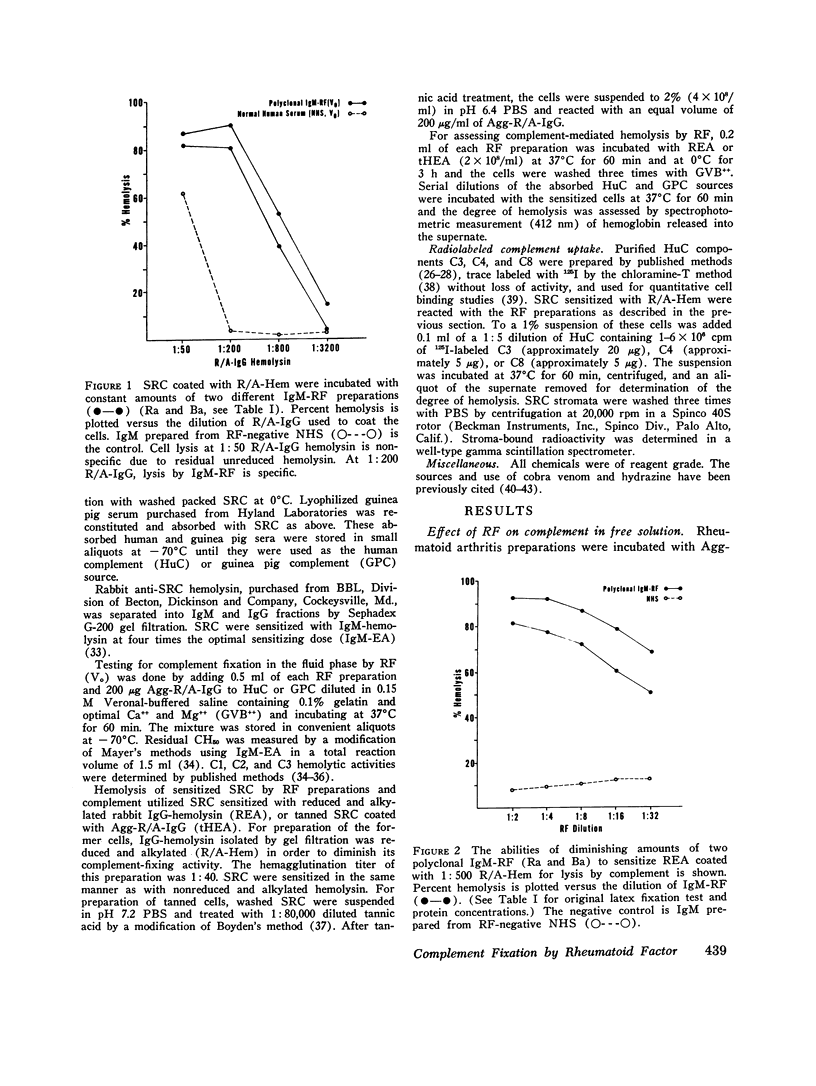
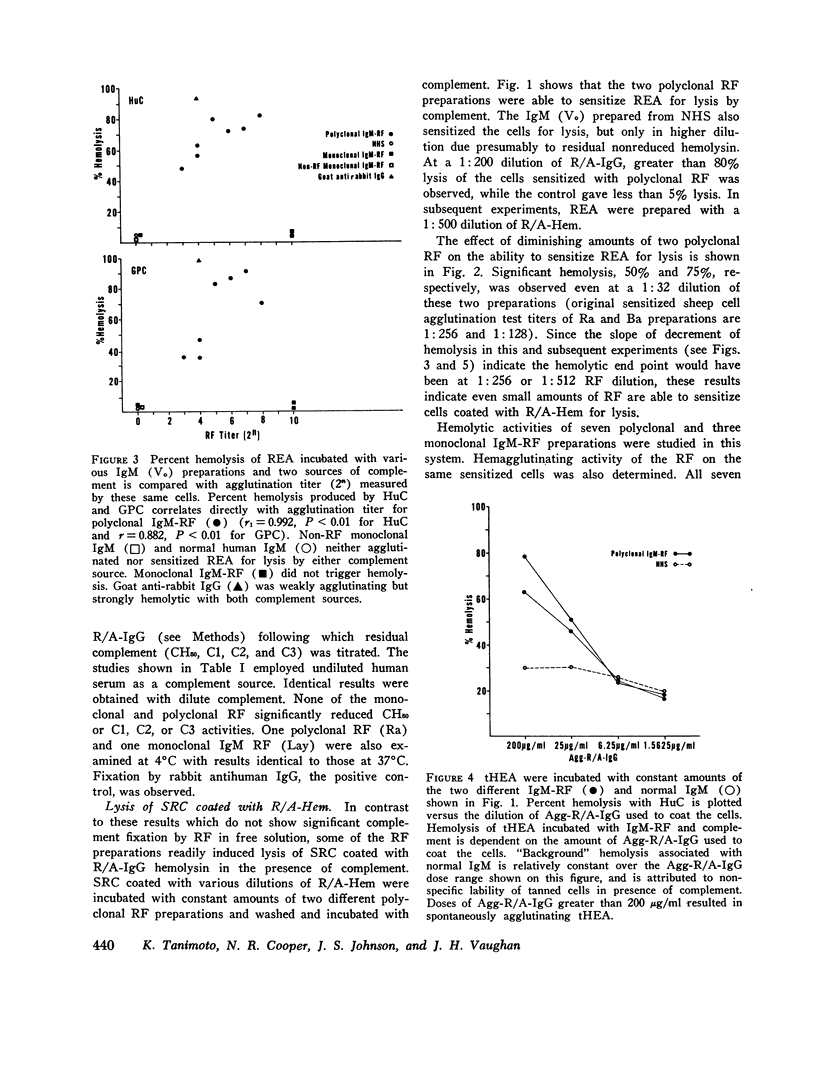
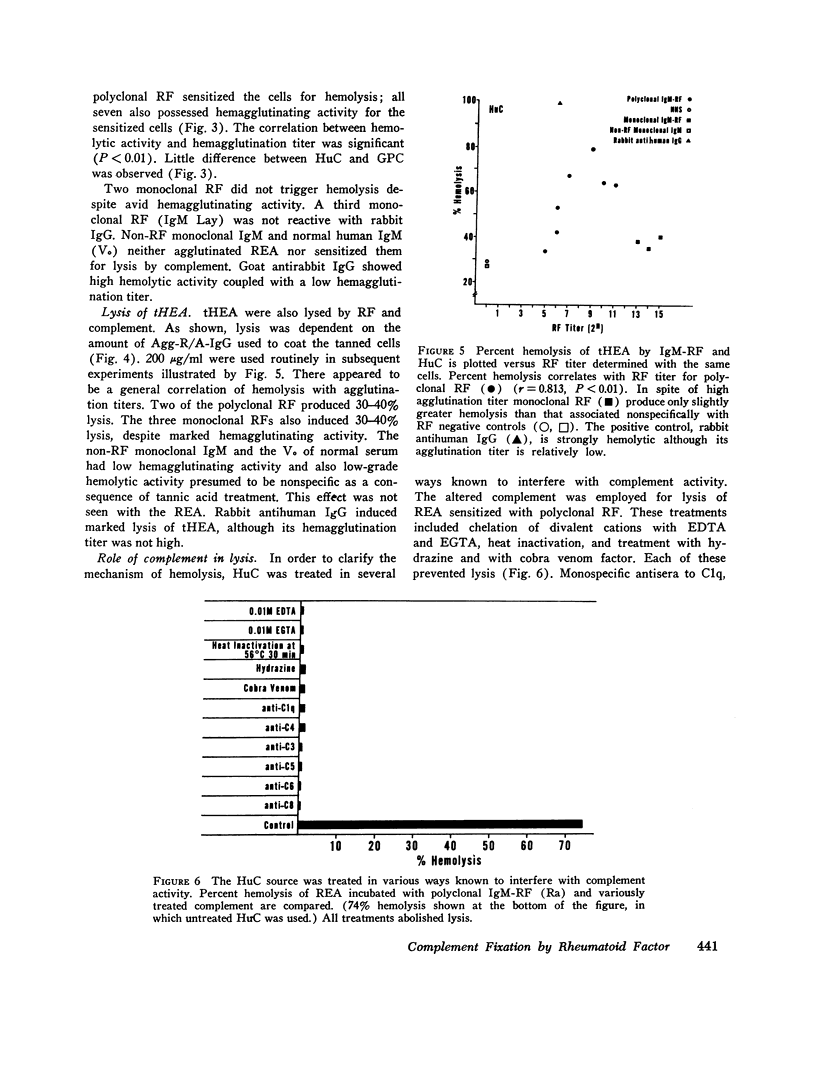
The capacity for fixation and activation of hemolytic complement by polyclonal IgM rheumatoid factors (RF) isolated from sera of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and monoclonal IgM-RF isolated from the cryoprecipitates of patients with IgM-IgG mixed cryoglobulinemia was examined. RF mixed with aggregated, reduced, and alkylated human IgG (Agg-R/A-IgG) in the fluid phase failed to significantly reduce the level of total hemolytic complement, CH50, or of individual complement components, C1, C2, C3, and C5. However, sheep erythrocytes (SRC) coated with Agg-R/A-IgG or with reduced and alkylated rabbit IgG anti-SRC antibody were hemolyzed by complement in the presence of polyclonal IgM-RF. Human and guinea pig complement worked equally well. The degree of hemolysis was in direct proportion to the hemagglutination titer of the RF against the same coated cells. Monoclonal IgM-RF, normal human IgM, and purified Waldenström macroglobulins without antiglobulin activity were all inert. Hemolysis of coated SRC by RF and complement was inhibited by prior treatment of the complement source with chelating agents, hydrazine, cobra venom factor, specific antisera to C1q, CR, C5, C6, or C8, or by heating at 56 degrees C for 30 min. Purified radiolabeled C4, C3, and C8 included in the complement source were bound to hemolysed SRC in direct proportion to the degree of hemolysis. These data indicate that polyclonal IgM-RF fix and activate complement via the classic pathway. The system described for assessing complement fixation by isolated RF is readily adaptable to use with whole human serum.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arroyave C. M., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Isolation of the sixth component of complement from human serum. Immunochemistry. 1971 Nov;8(11):995–1006. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90487-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENACERRAF B., OVARY Z., BLOCH K. J., FRANKLIN E. C. Properties of guinea pig 7S antibodies. I. Electrophoretic separation of two types of guinea pig 7S antibodies. J Exp Med. 1963 Jun 1;117:937–949. doi: 10.1084/jem.117.6.937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BORSOS T., RAPP H. J. CHROMATOGRAPHIC SEPARATION OF THE FIRST COMPONENT OF COMPLEMENT AND ITS ASSAY ON A MOLECULAR BASIS. J Immunol. 1963 Dec;91:851–858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOYDEN S. V. The adsorption of proteins on erythrocytes treated with tannic acid and subsequent hemagglutination by antiprotein sera. J Exp Med. 1951 Feb;93(2):107–120. doi: 10.1084/jem.93.2.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borsos T., Rapp H. J. Complement fixation on cell surfaces by 19S and 7S antibodies. Science. 1965 Oct 22;150(3695):505–506. doi: 10.1126/science.150.3695.505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane C. G., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The derivation of two distinct anaphylatoxin activities from the third and fifth components of human complement. J Exp Med. 1968 Feb 1;127(2):371–386. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.2.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conn D. L., McDuffie F. C., Dyck P. J. Immunopathologic study of sural nerves in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1972 Mar-Apr;15(2):135–143. doi: 10.1002/art.1780150202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper N. R., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The reaction mechanism of human C5 in immune hemolysis. J Exp Med. 1970 Oct 1;132(4):775–793. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.4.775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper N. R., Polley M. J., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The second component of human complement (C2): quantitative molecular analysis of its reactions in immune hemolysis. Immunochemistry. 1970 Apr;7(4):341–356. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(70)90237-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS J. S., 4th, BOLLET A. J. PROTECTION OF A COMPLEMENT-SENSITIVE ENZYME SYSTEM BY RHEUMATOID FACTOR. J Immunol. 1964 Jan;92:139–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeHoratius R. J., Williams R. C., Jr Rheumatoid factor accentuation of pulmonary lesions associated with experimental diffuse proliferative lung disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1972 May-Jun;15(3):293–301. doi: 10.1002/art.1780150311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S., Frank M. M., Johnson J. S. The relationship between antibody affinity and the efficiency of complement fixation. J Immunol. 1970 Jul;105(1):215–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrone S., Cooper N. R., Pellegrino M. A., Reisfeld R. A. Interaction of histocompatibility (HL-A) antibodies and complement with synchronized human lymphoid cells in continuous culture. J Exp Med. 1973 Jan 1;137(1):55–68. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.1.55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine D. P., Marney S. R., Jr, Colley D. G., Sergent J. S., Des Prez R. M. C3 shunt activation in human serum chelated with EGTA. J Immunol. 1972 Oct;109(4):807–809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franco A. E., Schur P. H. Hypocomplementemia in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1971 Mar-Apr;14(2):231–238. doi: 10.1002/art.1780140206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODMAN J. W. Reaction of rheumatoid sera with fragments of papain-digested rabbit gamma globulin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1961 Apr;106:822–825. doi: 10.3181/00379727-106-26488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough W. W., Davis J. S., 4th Effects of rheumatoid factor on complement levels in vivo. Arthritis Rheum. 1966 Aug;9(4):555–565. doi: 10.1002/art.1780090402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Götze O., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The C3-activator system: an alternate pathway of complement activation. J Exp Med. 1971 Sep 1;134(3 Pt 2):90s–108s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEIMER R., LEVIN F. M., KAHN M. F. INHIBITION OF COMPLEMENT FIXATION BY HUMAN SERUM. II. THE ACTIVITY OF A GAMMA-LM GLOBULIN AND RHEUMATOID FACTOR IN COMPLEMENT FIXATION REACTIONS. J Immunol. 1963 Dec;91:866–872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEIMER R., LEVIN F. M., PRIMACK A., CORCOS J. M., NOSENZO C. Inhibition of complement fixation by human serum. J Immunol. 1962 Sep;89:382–390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HELLER G., JACOBSON A. S., KOLODNY M. H. A modification of the hemagglutination test for rheumatoid arthritis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1949 Nov;72(2):316–323. doi: 10.3181/00379727-72-17420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HELLER G., JACOBSON A. S., KOLODNY M. H., KAMMERER W. H. The hemagglutination test for rheumatoid arthritis. II. The influence of human plasma fraction II (gamma globulin) on the reaction. J Immunol. 1954 Jan;72(1):66–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirose S. I., Osler A. G. Interaction of rheumatoid factors with urea-denatured human gamma-globulin and its subunits. J Immunol. 1967 Mar;98(3):628–637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer L. W., Borsos T., Rapp H. J., Vannier W. E. Heterogeneity of rabbit IgM antibody as detected by C'1a fixation. J Exp Med. 1968 Mar 1;127(3):589–603. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.3.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka T., Ishizaka K., Salmon S., Fudenberg H. Biologic activities of aggregated gamma-globulin. 8. Aggregated immunoglobulins of different classes. J Immunol. 1967 Jul;99(1):82–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka T., Tada T., Ishizaka K. Fixation of C' and C'la by rabbit gamma-G- and gamma-M-antibodies with particulate and soluble antigens. J Immunol. 1968 Jun;100(6):1145–1153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KNIKER W. T., COCHRANE C. G. PATHOGENIC FACTORS IN VASULAR LESIONS OF EXPERIMENTAL SERUM SICKNESS. J Exp Med. 1965 Jul 1;122:83–98. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler P. F., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Complement-immunoglobulin relation: deficiency of C'1q associated with impaired immunoglobulin G synthesis. Science. 1969 Jan 31;163(3866):474–475. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3866.474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUELLER-EBERHARD H. J., BIRO C. E. ISOLATION AND DESCRIPTION OF THE FOURTH COMPONENT OF HUMAN COMPLEMENT. J Exp Med. 1963 Sep 1;118:447–466. doi: 10.1084/jem.118.3.447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manni J. A., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The eighth component of human complement (C8): isolation, characterization, and hemolytic efficiency. J Exp Med. 1969 Nov 1;130(5):1145–1160. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.5.1145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick J. N., Day J., Morris C. J., Hill A. G. The potentiating effect of rheumatoid arthritis serum in the immediate phase of nephrotoxic nephritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1969 Jan;4(1):17–28. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDuffie F. C., Brumfield H. W. Effect of rheumatoid factor on complement-mediated phagocytosis. J Clin Invest. 1972 Dec;51(12):3007–3014. doi: 10.1172/JCI107128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger H. Characterization of a human macroglobulin. V. A Waldenström macroglobulin with antibody activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 May;57(5):1490–1497. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.5.1490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mongan E. S., Cass R. M., Jacox R. F., Vaughen J. H. A study of the relation of seronegative and seropositive rheumatoid arthritis to each other and to necrotizing vasculitis. Am J Med. 1969 Jul;47(1):23–35. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(69)90238-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Eberhard H. J. Chemistry and reaction mechanisms of complement. Adv Immunol. 1968;8:1–80. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60464-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Eberhard H. J., Fjellström K. E. Isolation of the anticomplementary protein from cobra venom and its mode of action on C3. J Immunol. 1971 Dec;107(6):1666–1672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NILSSON U. R., MUELLER-EBERHARD H. J. ISOLATION OF BETA IF-GLOBULIN FROM HUMAN SERUM AND ITS CHARACTERIZATION AS THE FIFTH COMPONENT OF COMPLEMENT. J Exp Med. 1965 Aug 1;122:277–298. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.2.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normansell D. E. Anti- -globulins in rheumatoid arthritis sera. 3. The reactivity of anti- -globulin rheumatoid factors with heterologous G-globulin. Immunochemistry. 1972 Jul;9(7):725–736. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(72)90016-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normansell D. E. Anti- -globulins in rheumatoid arthritis sera. II. The reactivity of anti- -globulin rheumatoid factors with altered G-globulin. Immunochemistry. 1971 Jul;8(7):593–602. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90200-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normansell D. E. Anti-gamma-globulins in rheumatoid arthritis sera. I. Studies on the 22S complex. Immunochemistry. 1970 Sep;7(9):787–797. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(70)90220-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussenzweig V., Benacerraf B. Antihapten antibody specificity and L chain type. J Exp Med. 1967 Oct 1;126(4):727–743. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.4.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERNIS B., BALLABIO C. B., CHIAPPINO G. PRESENZA DEL FATTORE REUMATOIDE NELLE LESIONI VASCOLARI IN CASI DI ARTRITE REUMATOIDE AGGRAVATA (MALIGNA). STUDIO CON ANTICORPI FLUORESCENTI. Reumatismo. 1963 May-Jun;15:187–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickering R. J., Wolfson M. R., Good R. A., Gewurz H. Passive hemolysis by serum and cobra venom factor: a new mechanism inducing membrane damage by complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Feb;62(2):521–527. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.2.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaut A. G., Cohen S., Tomasi T. B., Jr Immunoglobulin M: fixation of human complement by the Fc fragment. Science. 1972 Apr 7;176(4030):55–56. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4030.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddy S., Gigli I., Austen K. F. The complement system of man (second of four parts). N Engl J Med. 1972 Sep 14;287(11):545–549. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197209142871106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMID F. R., COOPER N. S., ZIFF M., McEWEN C. Arteritis in rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Med. 1961 Jan;30:56–83. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(61)90064-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid F. R., Roitt I. M., Rocha M. J. Complement fixation by a two-component antibody system: immunoglobulin G and immunoglobulin M anti-globulin (rheumatoid factor). Parodoxical effect related to immunoglobulin G concentration. J Exp Med. 1970 Oct 1;132(4):673–693. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.4.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone M. J., Metzger H. Binding properties of a Waldenström macroglobulin antibody. J Biol Chem. 1968 Nov 25;243(22):5977–5984. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone M. J. Studies on monoclonal antibodies. I. The specificity and binding properties of a Waldenström macroglobulin with anti- G activity. J Lab Clin Med. 1973 Mar;81(3):393–409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tesar J. T., Schmid F. R. Conversion of soluble immune complexes into complement-fixing aggregates by IgM-rheumatoid factor. J Immunol. 1970 Nov;105(5):1206–1214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIEDERMANN G., OVARY Z., MIESCHER P. A. INFLUENCE OF MERCAPTOETHANOL TREATMENT ON SKIN SENSITIZING AND COMPLEMENT BINDING ABILITY OF 7 S ANTI-DINITROPHENOL-BOVINE GAMMA GLOBULIN ANTIBODY. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Jun;116:448–452. doi: 10.3181/00379727-116-29275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein A., Peters K., Brown D., Bluestone R. Metabolism of the third component of complement (C3) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1972 Jan-Feb;15(1):49–56. doi: 10.1002/art.1780150108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yount W. J., Dorner M. M., Kunkel H. G., Kabat E. A. Studies on human antibodies. VI. Selective variations in subgroup composition and genetic markers. J Exp Med. 1968 Mar 1;127(3):633–646. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.3.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zvaifler N. J. Rheumatoid factor and the fixation of complement. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1969 Dec 10;168(1):146–160. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1969.tb43104.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zvaifler N. J., Schur P. Reactions of aggregated mercaptoethanol treated gamma globulin with rheumatoid factor--precipitin and complement fixation studies. Arthritis Rheum. 1968 Aug;11(4):523–536. doi: 10.1002/art.1780110402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


