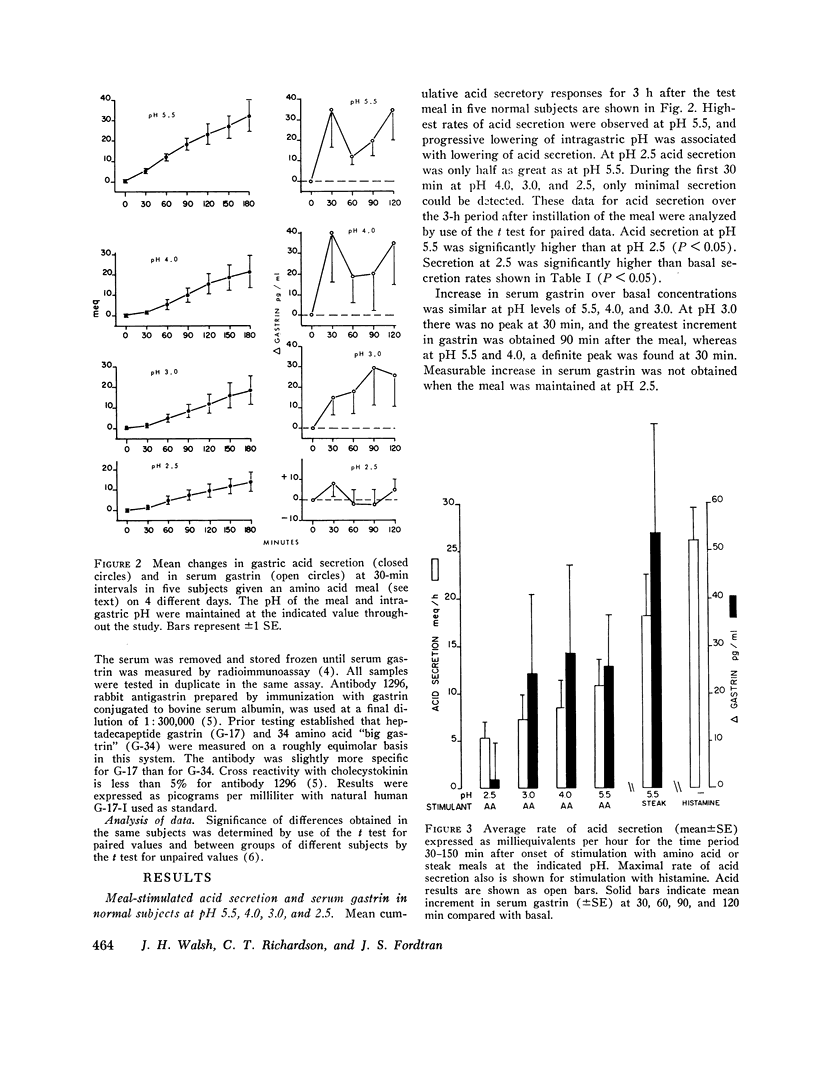
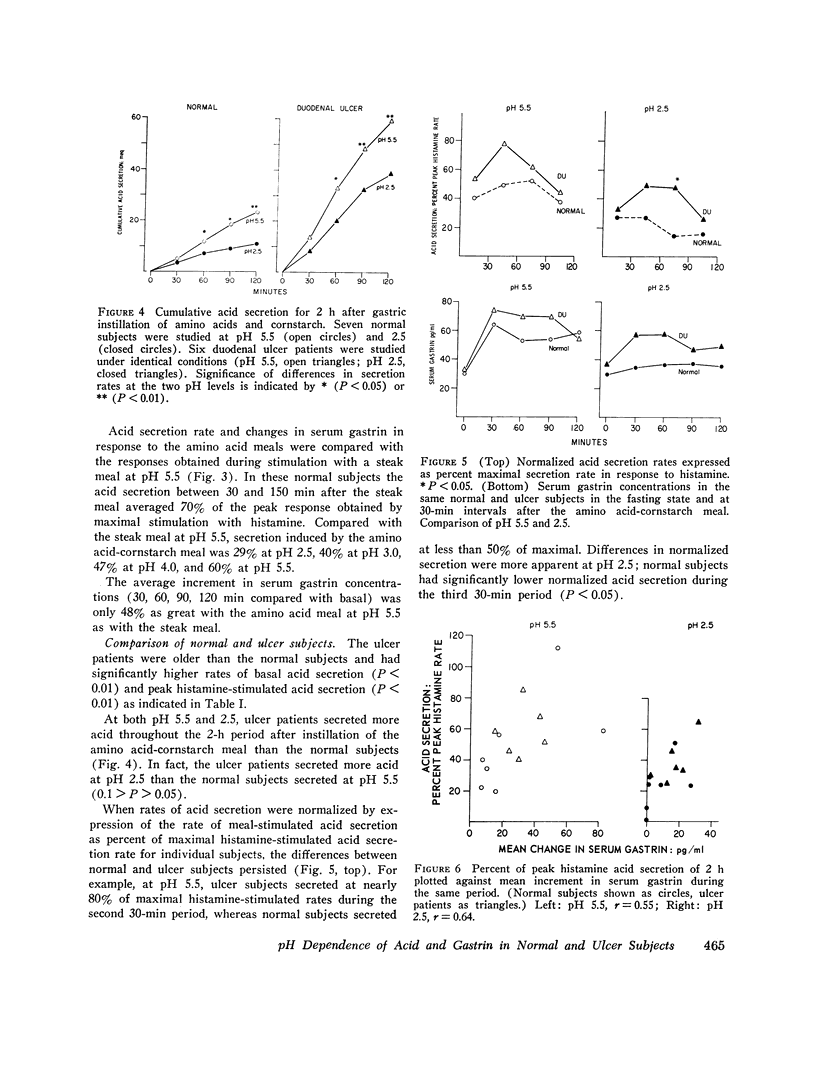
Abstract
By use of a recently described method, which estimates the rate of gastric acid secretion by measuring the rate of sodium bicarbonate infusion needed to keep intragastric pH constant, gastric acid secretion rates and changes in serum gastrin were measured in five normal subjects while gastric pH was kept at 5.5, 4.0, 3.0, or 2.5. Preliminary experiments revealed that the method did not accurately measure acid secretion at a pH lower than 2.5. Stimulation of acid secretion was produced by gastric instillation of a solution of amino acids and cornstarch. The secretion rate with the amino acid meal was highest at pH 5.5 and was 60% of that produced by a steak meal at the same pH. As the pH of the amino acid meal was decreased, there was a stepwise reduction in acid secretion so that at pH 2.5 the rate was only half as great as at pH 5.5. The amino acid meal produced increases in serum gastrin that were also less marked than those produced by a steak meal. With amino acid stimulation, serum gastrin responses were similar at pH 5.5, 4.0, and 3.0, but no increase in gastrin could be measured when the meal was maintained at pH 2.5. A group of six patients with duodenal ulcers was compared with seven normal subjects at pH 5.5 and 2.5. Ulcer patients released more gastrin and secreted more acid at each time period at both pH values. More important, the degree of inhibition at pH 2.5 was significantly less in ulcer patients. For example, during the 2nd h after stimulation acid secretion was inhibited by only 30% in ulcer patients compared with 70% in normal subjects. These findings suggest a defect in autoregulation of gastrin release and gastric acid secretion at low pH in ulcer patients which may play a role in pathogenesis of this disease.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berson S. A., Yalow R. S. Gastrin in duodenal ulcer. N Engl J Med. 1971 Feb 25;284(8):445–446. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197102252840812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debas H. T., Walsh J. H., Grossman M. I. Pure human minigastrin: secretory potency and disappearance rate. Gut. 1974 Sep;15(9):686–689. doi: 10.1136/gut.15.9.686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fordtran J. S., Walsh J. H. Gastric acid secretion rate and buffer content of the stomach after eating. Results in normal subjects and in patients with duodenal ulcer. J Clin Invest. 1973 Mar;52(3):645–657. doi: 10.1172/JCI107226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg J. I., Grossman M. I., Maxwell V., Walsh J. H. Increased sensitivity to stimulation of acid secretion by pentagastrin in duodenal ulcer. J Clin Invest. 1975 Feb;55(2):330–337. doi: 10.1172/JCI107936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. R., Grossman M. I. Intestinal hormones as inhibitors of gastric secretion. Gastroenterology. 1971 Jan;60(1):120–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuigan J. E., Trudeau W. L. Differences in rates of gastrin release in normal persons and patients with duodenal-ulcer disease. N Engl J Med. 1973 Jan 11;288(2):64–66. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197301112880202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeder D. D., Jackson B. M., Ban J. L., Davidson W. D., Thompson J. C. Effect of food on serum gastrin concentrations in duodenal ulcer and control patients. Surg Forum. 1970;21:290–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehefeld J. F. Three components of gastrin in human serum. Gel filtration studies on the molecular size of immunoreactive serum gastrin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Dec 28;285(2):364–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrumpf E., Stadaas J. Effect of gastric distention on motility and plasma gastrin concentration before and after secretin administration. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1974;9(2):119–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. H., Walsh J. H. Gastrin release in postoperative ulcer patients: evidence for release of duodenal gastrin. Gastroenterology. 1973 Mar;64(3):363–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh J. H., Debas H. T., Grossman M. I. Pure human big gastrin. Immunochemical properties, disappearance half time, and acid-stimulating action in dogs. J Clin Invest. 1974 Aug;54(2):477–485. doi: 10.1172/JCI107783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wormsley K. G., Grossman M. I. Maximal histalog test in control subjects and patients with peptic ulcer. Gut. 1965 Oct;6(5):427–435. doi: 10.1136/gut.6.5.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yalow R. S., Berson S. A. Further studies on the nature of immunoreactive gastrin in human plasma. Gastroenterology. 1971 Feb;60(2):203–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yalow R. S., Wu N. Additional studies on the nature of big big gastrin. Gastroenterology. 1973 Jul;65(1):19–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



