Abstract
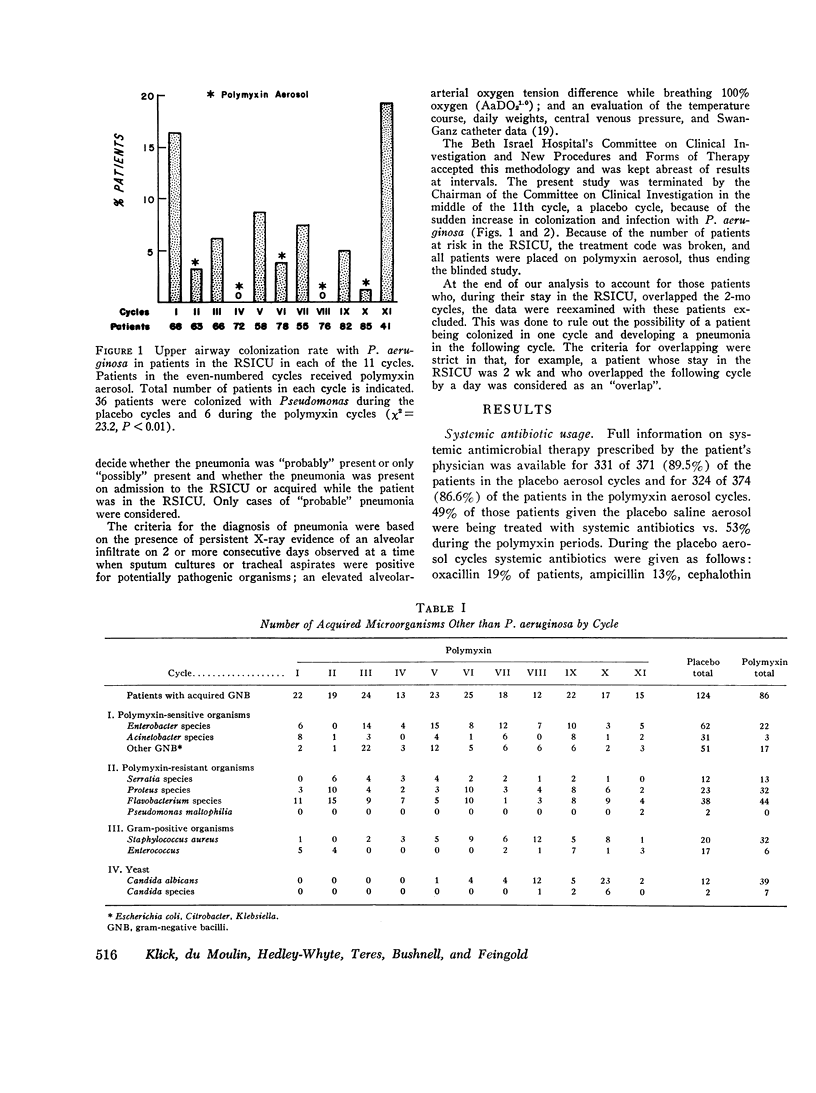
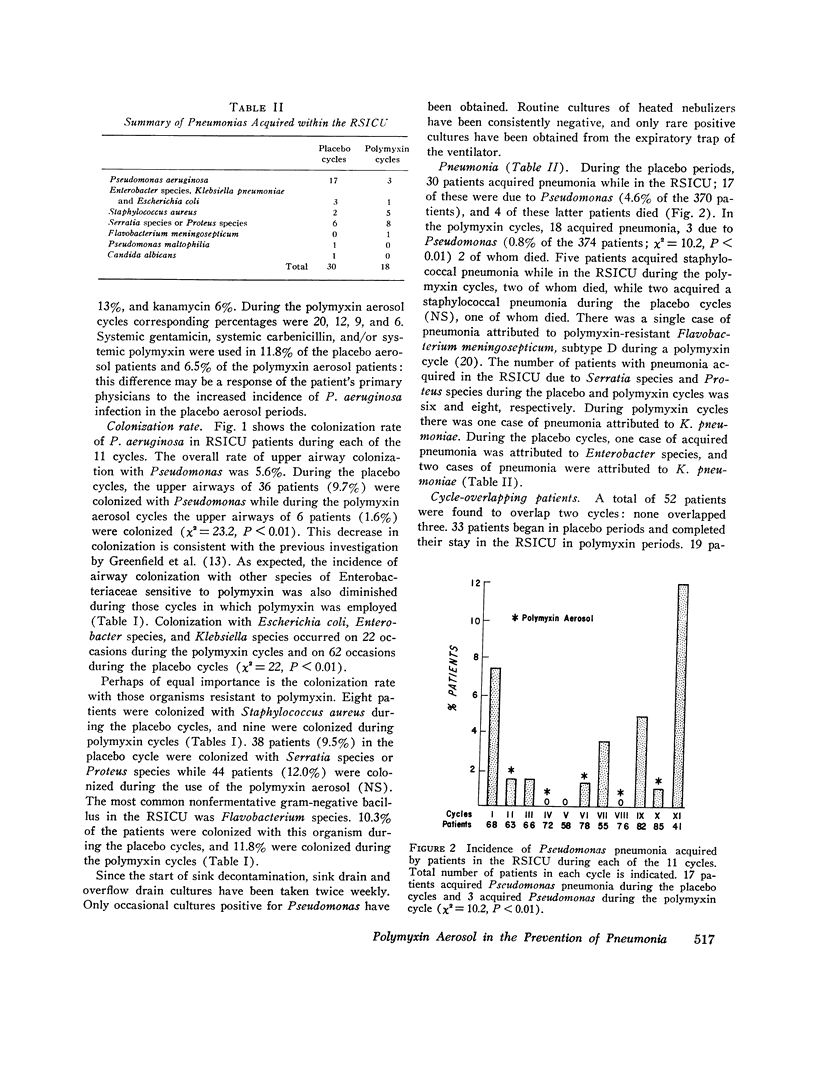
All 744 patients admitted to a Respiratory-Surgical Intensive Care Unit (RSICU) were included in a prospective study of the effects of a polymyxin (2.5 mg/kg body wt/day in six divided doses) or a placebo aerosol sprayed into the posterior pharynx and tracheal tube (if present), during 11 alternating 2-mo treatment cycles. The incidence of upper airway colonization in the RSICU with Pseudomonas aeruginosa was 1.6% during the polymyxin treatment cycles (total 374 patients) and 9.7% during the placebo cycles (370 patients) (X2 equals 23.2, P less than 0.01). 3 patients in the RSICU acquired Pseudomonas pneumonia, as defined by independent "blinded" assessors, during the polymyxin cycles while 17 acquired a Pseudomonas pneumonia during the placebo cycles (X2 equals 10.2, P less than 0.01). The overall mortality was similar in both placebo and polymyxin-treated groups (12.2 vs. 12.0%). Systemic antibiotic usage was similar in the different cycles; 49% of patients in the placebo and 53% in the polymyxin-treated groups received systemic antibiotics while in the RSICU.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Babington P. C., Baker A. B., Johnston H. H. Retrograde spread of organisms from ventilator to patient via the expiratory limb. Lancet. 1971 Jan 9;1(7689):61–62. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90781-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer A. W., Kirby W. M., Sherris J. C., Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Apr;45(4):493–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuPont H. L., Spink W. W. Infections due to gram-negative organisms: an analysis of 860 patients with bacteremia at the University of Minnesota Medical Center, 1958-1966. Medicine (Baltimore) 1969 Jul;48(4):307–332. doi: 10.1097/00005792-196907000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies R. R., Govan J. R. Typing of Pseudomonas pyocyanea by pyocine production. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1966 Apr;91(2):339–345. doi: 10.1002/path.1700910207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenfield S., Teres D., Bushnell L. S., Hedley-Whyte J., Feingold D. S. Prevention of gram-negative bacillary pneumonia using aerosol polymyxin as prophylaxis. I. Effect on the colonization pattern of the upper respiratory tract of seriously ill patients. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2935–2940. doi: 10.1172/JCI107490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedley-Whyte J., Pontoppidan H., Morris M. J. The response of patients with respiratory failure and cardiopulmonary disease to different levels of constant volume ventilation. J Clin Invest. 1966 Oct;45(10):1543–1554. doi: 10.1172/JCI105461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johanson W. G., Jr, Pierce A. K., Sanford J. P., Thomas G. D. Nosocomial respiratory infections with gram-negative bacilli. The significance of colonization of the respiratory tract. Ann Intern Med. 1972 Nov;77(5):701–706. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-77-5-701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johanson W. G., Pierce A. K., Sanford J. P. Changing pharyngeal bacterial flora of hospitalized patients. Emergence of gram-negative bacilli. N Engl J Med. 1969 Nov 20;281(21):1137–1140. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196911202812101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klastersky J., Huysmans E., Weerts D., Hensgens C., Daneau D. Endotracheally administered gentamicin for the prevention of infections of the respiratory tract in patients with tracheostomy: a double-blind study. Chest. 1974 Jun;65(6):650–654. doi: 10.1378/chest.65.6.650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner A. M., Federman M. J. Gram-negative bacillary pneumonia. J Infect Dis. 1971 Oct;124(4):425–427. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.4.425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowbury E. J., Thom B. T., Lilly H. A., Babb J. R., Whittall K. Sources of infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa in patients with tracheostomy. J Med Microbiol. 1970 Feb;3(1):39–56. doi: 10.1099/00222615-3-1-39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody M. R., Young V. M., Kenton D. M., Vermeulen G. D. Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a center for cancer research. I. Distribution of intraspecies types from human and environmental sources. J Infect Dis. 1972 Feb;125(2):95–101. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.2.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mushin R., Ziv G. Epidemiological aspects of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in man, animals and the environment. Application of pyocin typing. Isr J Med Sci. 1973 Feb;9(2):155–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprunt K., Redman W. Evidence suggesting importance of role of interbacterial inhibition in maintaining balance of normal flora. Ann Intern Med. 1968 Mar;68(3):579–590. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-68-3-579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens R. M., Teres D., Skillman J. J., Feingold D. S. Pneumonia in an intensive care unit. A 30-month experience. Arch Intern Med. 1974 Jul;134(1):106–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teres D., Schweers P., Bushnell L. S., Hedley-Whyte J., Feingold D. S. Sources of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in a respiratory-surgical intensive-therapy unit. Lancet. 1973 Feb 24;1(7800):415–417. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)90266-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M. E., Piper E., Maurer I. M. Contamination of an operating theatre by gram-negative bacteria. Examination of water supplies, cleaning methods and wound infections. J Hyg (Lond) 1972 Mar;70(1):63–73. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400022105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tillotson J. R., Finland M. Bacterial colonization and clinical superinfection of the respiratory tract complicating antibiotic treatment of pneumonia. J Infect Dis. 1969 Jun;119(6):597–624. doi: 10.1093/infdis/119.6.597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



