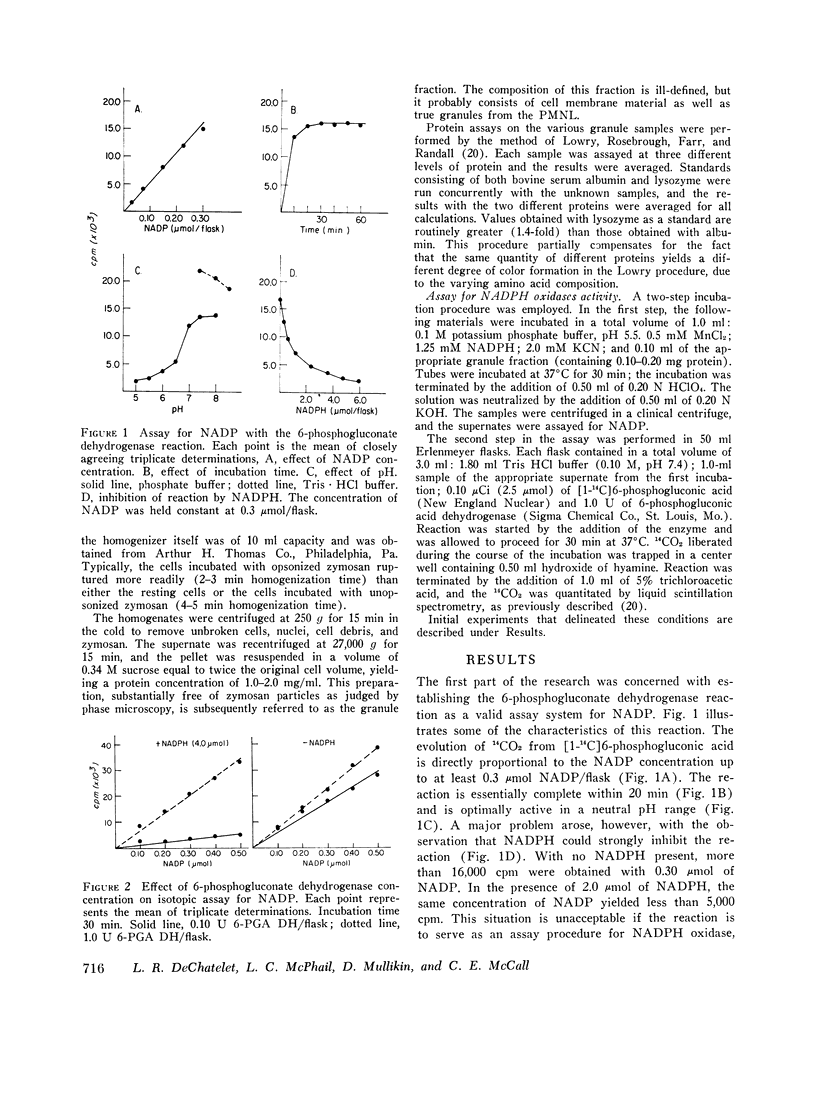
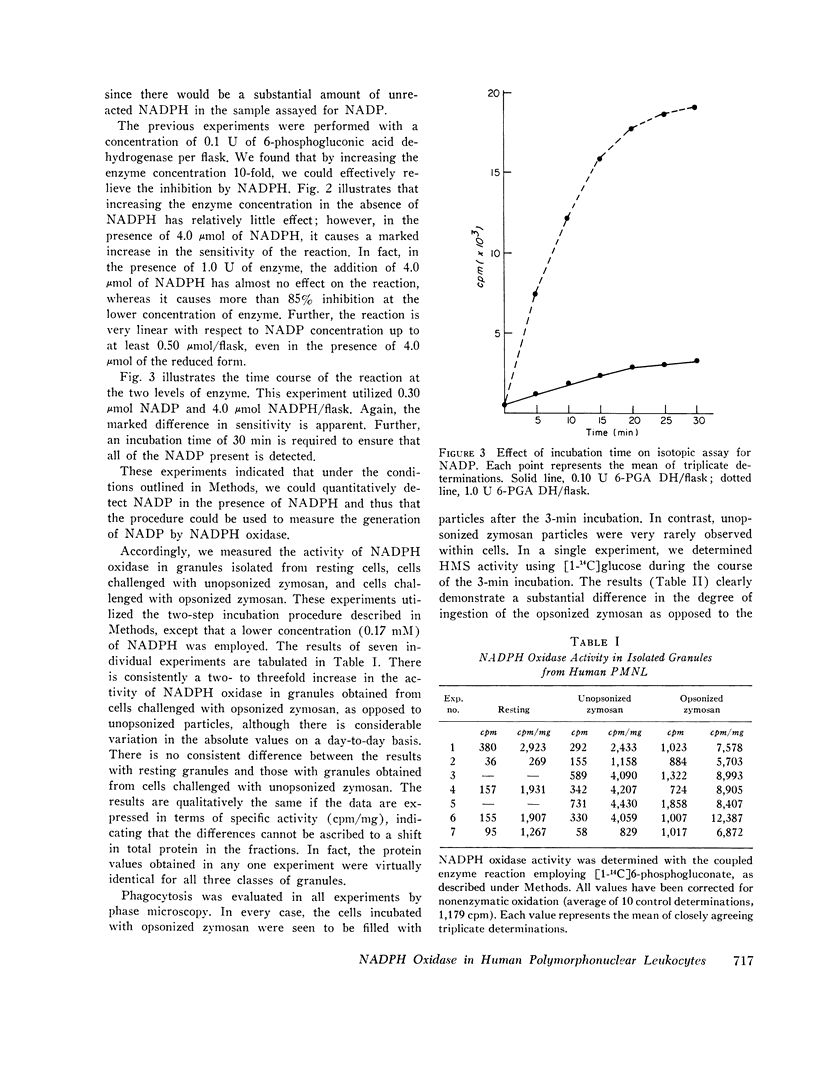
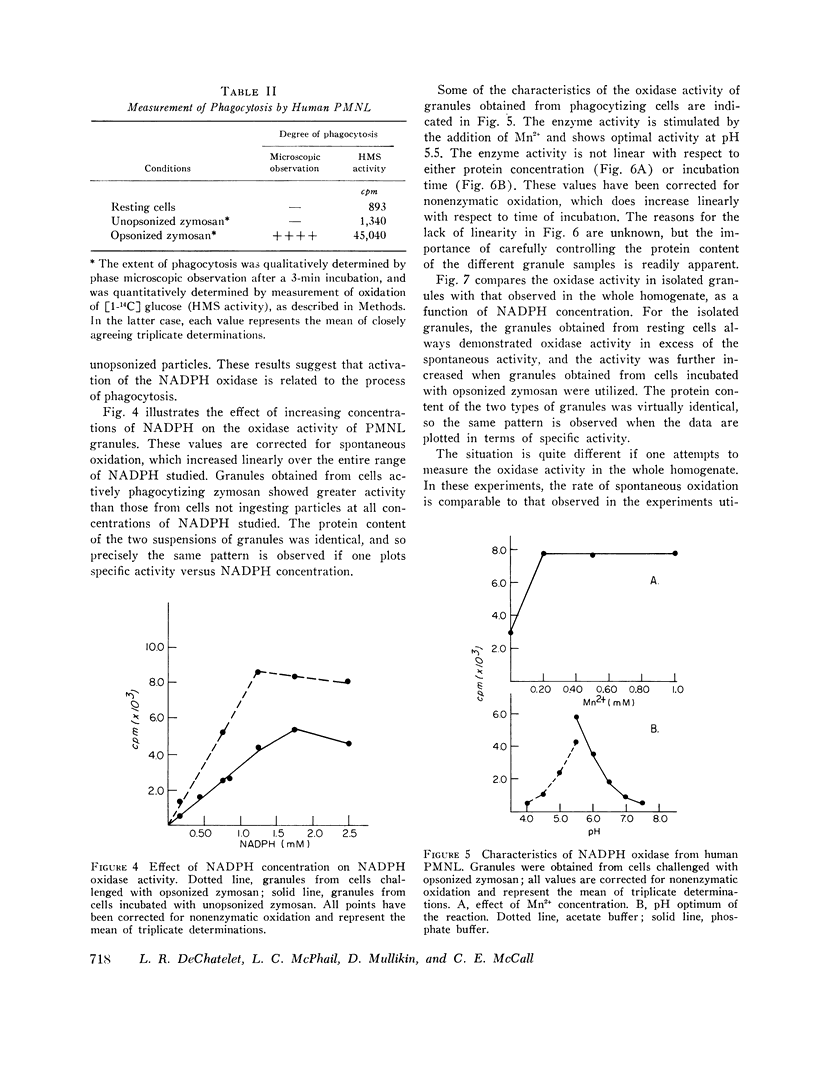
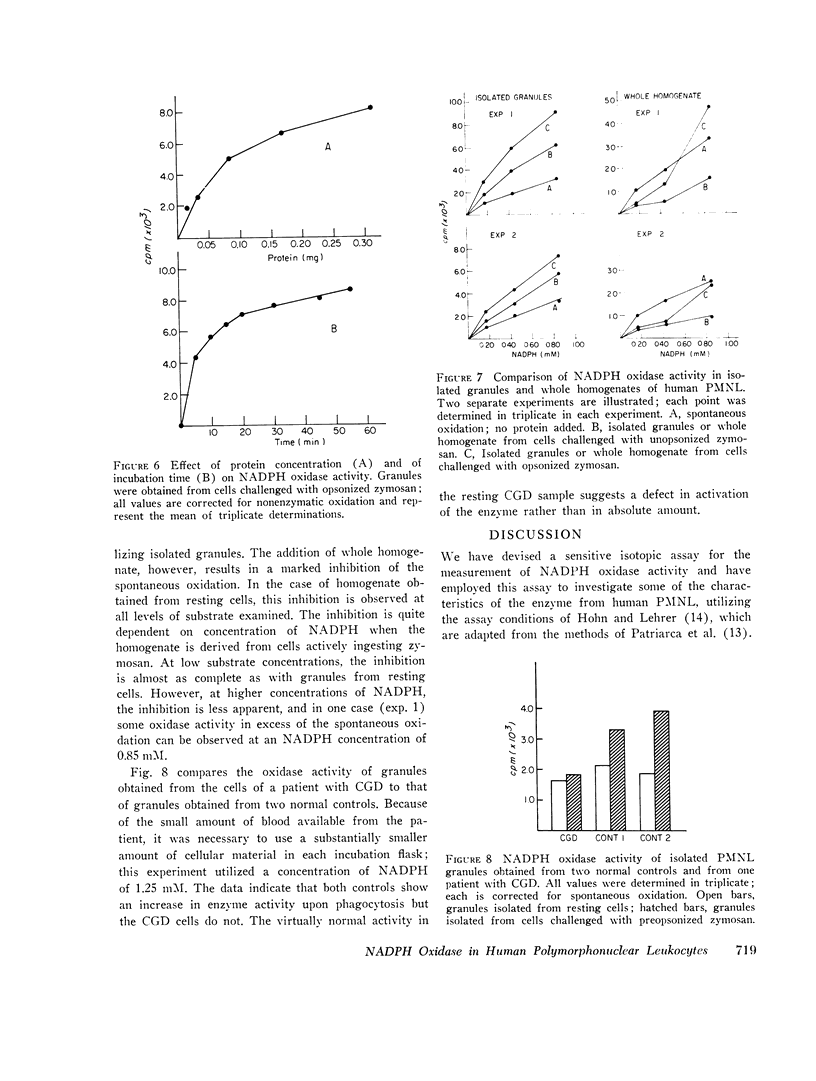
Abstract
An isotopic assay for NADPH ixodase that measures the amount of NADP formed by the 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase reaction has been developed. Under appropriate conditions, the amount of NADP present is directly proportional to the amount of 14CO2 released from [1-14C]6-phosphogluconic acid. Because this assay employs radioisotopes, it is far more sensitive than conventional assays for the enzyme. The human granule NADPH oxidase, as measured by this assay, is active in the presence of CN minus, is stimulated by Mn-2+, and has a pth optimum of 5.5. Granules isolated from cells that have been allowed to ingest zymosan consistently exhibited more enzyme activity than did granules isolated from either resting cells or cells challenged with zymosan that was not preopsonized. This effect was observed over a wide range of substrate concentrations and could not be explained by differences in protein concentrations between the various samples. If whole homogenates are used in place of isolated granules, the enzyme activity can be observed only with a homogenate of phagocytizing cells and even then only at a high concentration of NADPH. This suggests that an inhibitor of the enzyme might be present within the cell. One patient with chronic granulomatous disease was studied. There was no difference in tnadph oxidase activity of the patients' cells when granules from resting and phagocytizing cells were compared. In contrast, the enzyme activity in granules from two control patients doubled upon phagocytosis. These results are consistent with a role for NADPH oxidase in the initiation of the respiratory burst accompanying phagocytosis by human neutrophils.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen R. C., Stjernholm R. L., Steele R. H. Evidence for the generation of an electronic excitation state(s) in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes and its participation in bactericidal activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 May 26;47(4):679–684. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90545-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babior B. M., Kipnes R. S., Curnutte J. T. Biological defense mechanisms. The production by leukocytes of superoxide, a potential bactericidal agent. J Clin Invest. 1973 Mar;52(3):741–744. doi: 10.1172/JCI107236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baehner R. L., Gilman N., Karnovsky M. L. Respiration and glucose oxidation in human and guinea pig leukocytes: comparative studies. J Clin Invest. 1970 Apr;49(4):692–700. doi: 10.1172/JCI106281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baehner R. L., Karnovsky M. L. Deficiency of reduced nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide oxidase in chronic granulomatous disease. Science. 1968 Dec 13;162(3859):1277–1279. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3859.1277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baehner R. L., Nathan D. G. Quantitative nitroblue tetrazolium test in chronic granulomatous disease. N Engl J Med. 1968 May 2;278(18):971–976. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196805022781801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper M. R., DeChatelet L. R., McCall C. E., LaVia M. F., Spurr C. L., Baehner R. L. Complete deficiency of leukocyte glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase with defective bactericidal activity. J Clin Invest. 1972 Apr;51(4):769–778. doi: 10.1172/JCI106871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeChatelet L. R., Cooper M. R. A modified procedure for the determination of leukocyte alkaline phosphatase. Biochem Med. 1970 Aug;4(1):61–68. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(70)90103-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dechatelet L. R., Cooper M. R., McCall C. E. Dissociation by colchicine of the hexose monophosphate shunt activation from the bactericidal activity of the leukocyte. Infect Immun. 1971 Jan;3(1):66–72. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.1.66-72.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes B., Page A. R., Good R. A. Studies of the metabolic activity of leukocytes from patients with a genetic abnormality of phagocytic function. J Clin Invest. 1967 Sep;46(9):1422–1432. doi: 10.1172/JCI105634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnovsky M. L. Chronic granulomatous disease--pieces of a cellular and molecular puzzle. Fed Proc. 1973 Apr;32(4):1527–1533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J. Iodination of bacteria: a bactericidal mechanism. J Exp Med. 1967 Dec 1;126(6):1063–1078. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.6.1063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patriarca P., Cramer R., Moncalvo S., Rossi F., Romeo D. Enzymatic basis of metabolic stimulation in leucocytes during phagocytosis: the role of activated NADPH oxidase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Jul;145(1):255–262. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90034-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SBARRA A. J., KARNOVSKY M. L. The biochemical basis of phagocytosis. I. Metabolic changes during the ingestion of particles by polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 1959 Jun;234(6):1355–1362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraj R. J., Paul B. B., Strauss R. R., Jacobs A. A., Sbarra A. J. Oxidative peptide cleavage and decarboxylation by the MPO-H2O2-Cl- antimicrobial system. Infect Immun. 1974 Feb;9(2):255–260. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.2.255-260.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb L. S., Keele B. B., Jr, Johnston R. B., Jr Inhibition of phagocytosis-associated chemiluminescence by superoxide dismutase. Infect Immun. 1974 Jun;9(6):1051–1056. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.6.1051-1056.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



