Abstract
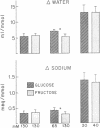
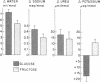
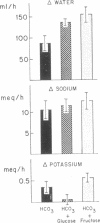
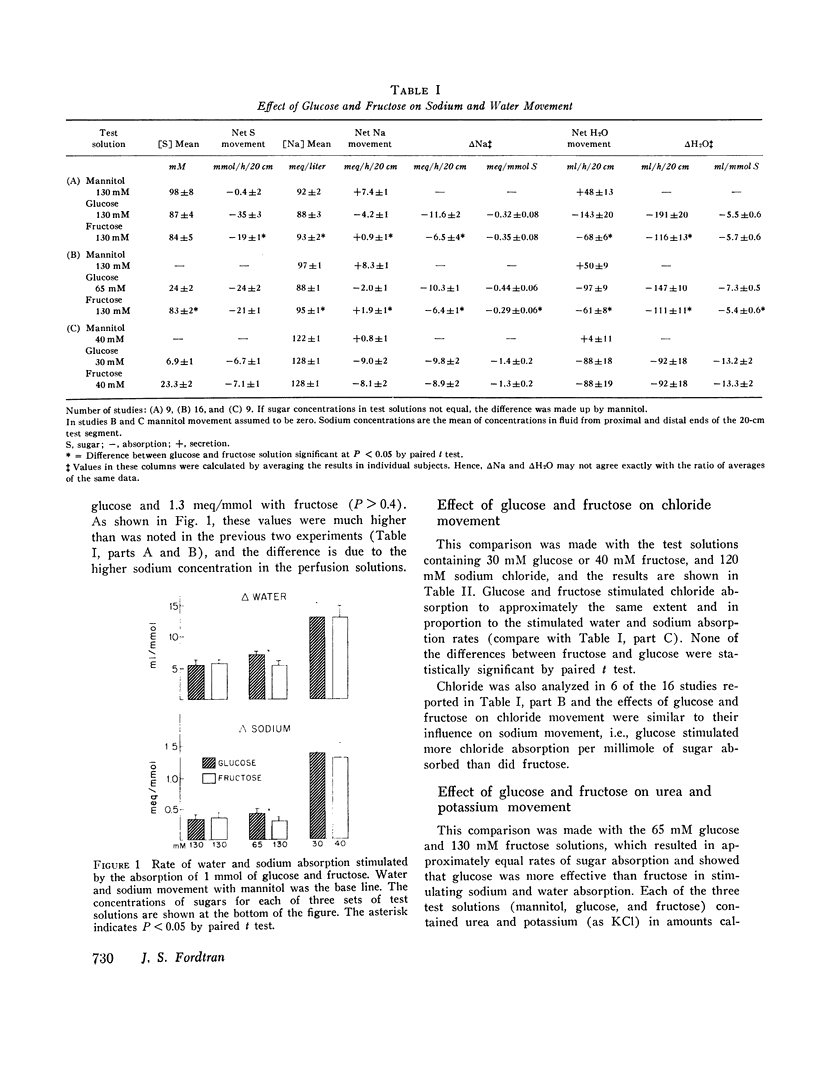
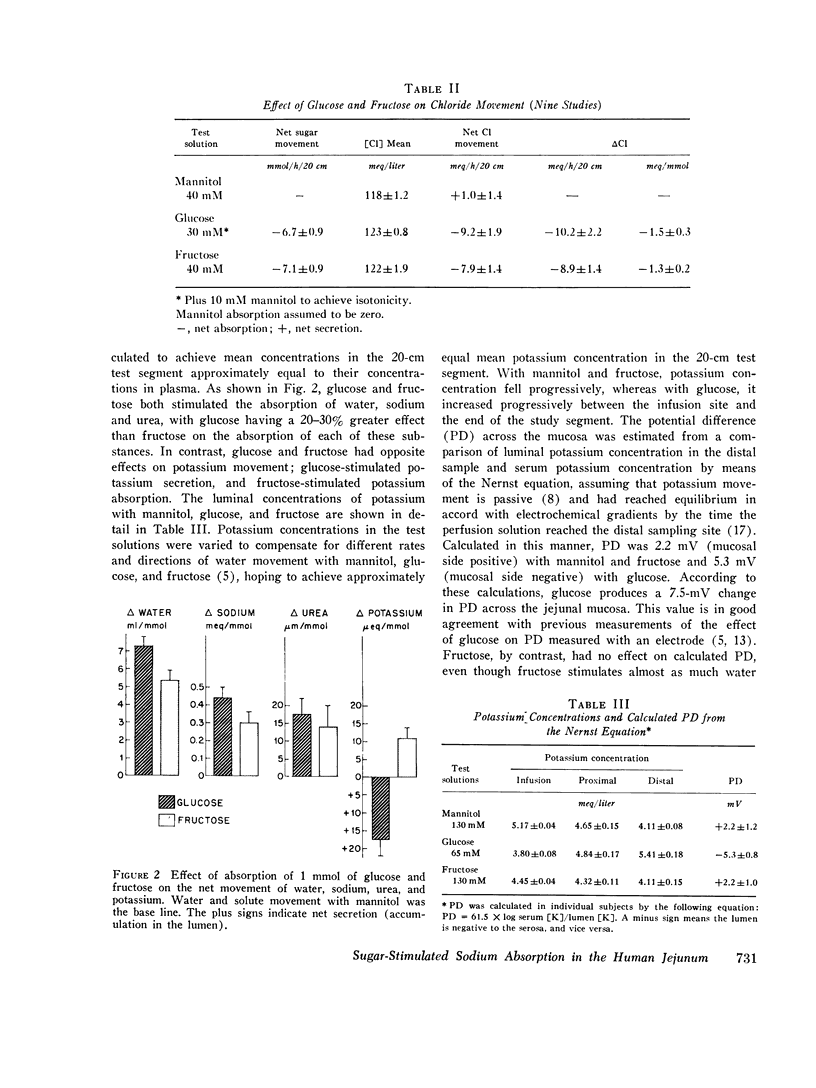
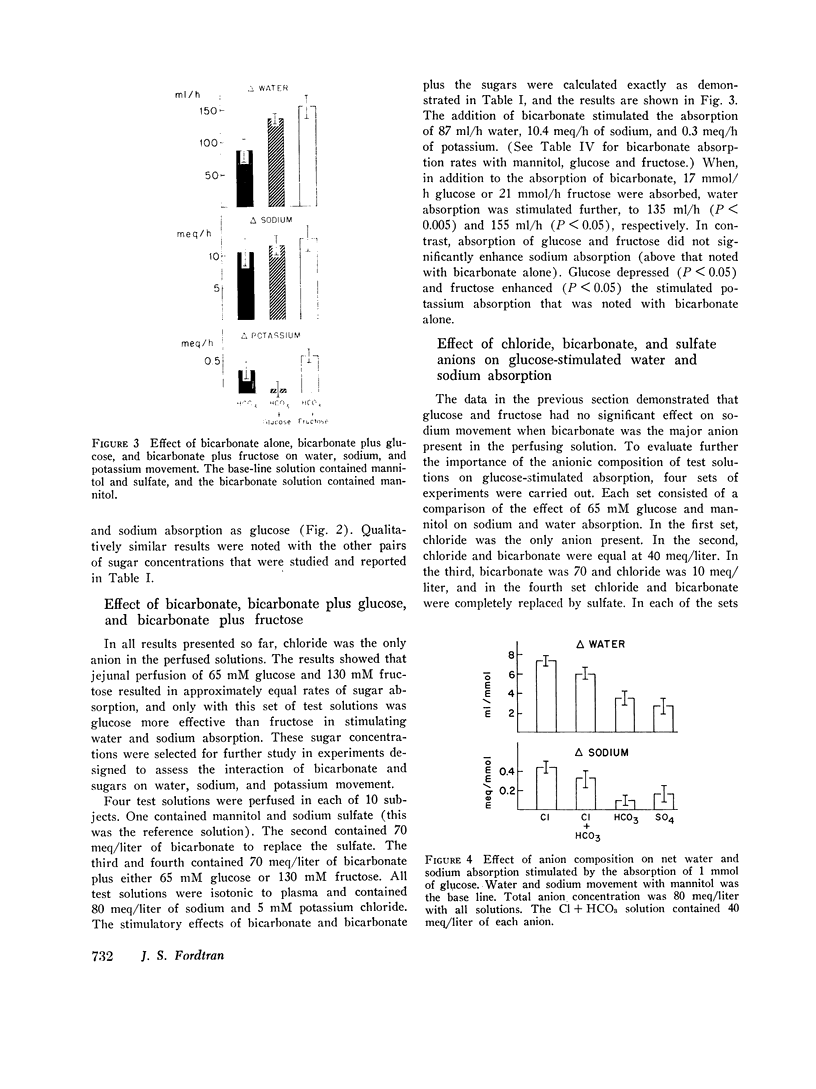
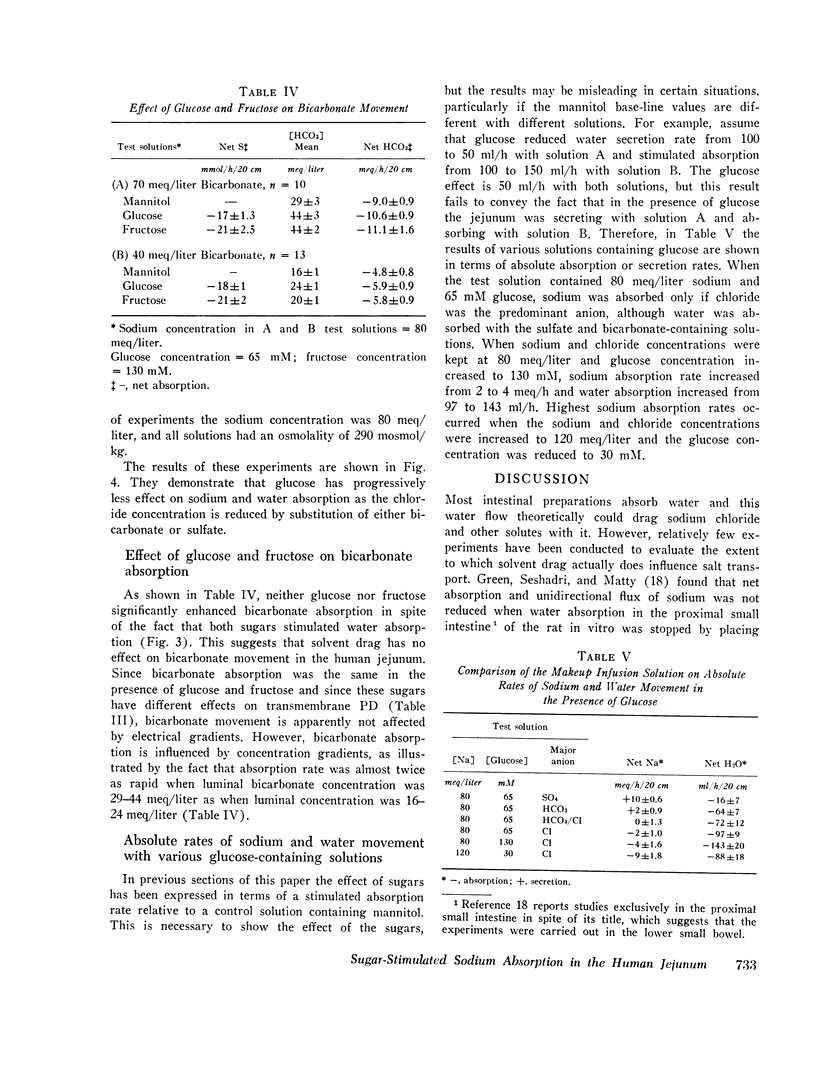
The effects of glucose and fructose on water and sodium absorption in the human jejunum were compared to assess the relative contribution of active and passive sugar stimulation of sodium transport. The effect of fructose is assumed to be entirely passive, and the difference between the effects of fructose and glucose is assumed to be a measure of sugar-stimulated, active sodium absorption. Water and sodium movement with mannitol was the base line. Three sets of test solutions with differing sugar concentrations were studied. Fructose stimulated 66-100 per cent as much net sodium and water absorption as glucose. Fructose stimulated potassium absorption, whereas glucose stimulated potassium secretion. Urea absorption was stimulated by both sugars. Glucose and fructose stimulated sodium absorption when chloride was the major anion, but they had relatively little effect on net sodium movement when chloride was replaced by bicarbonate or sulfate. It is concluded that glucose stimulates passive and active sodium transport in the human jejunum. Stimulated active sodium absorption generates an electrical potential across the mucosa that causes sodium (and potassium) secretion and partly or completely nullifies the effect of active sodium transport on net sodium movement. Net sodium absorption sitmulated by glucose is mainly (66-100 per cent) the passive consequence of solvent flow. The accompanying anion determines the degree to which sugars stimulate sodium absorption (C1 greater than SO-4 greater than HCO3). The effects of bicarbonate and sugars on jejunal sodium absorption are not additive.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bieberdorf F. A., Gorden P., Fordtran J. S. Pathogenesis of congenital alkalosis with diarrhea. Implications for the physiology of normal ileal electrolyte absorption and secretion. J Clin Invest. 1972 Aug;51(8):1958–1968. doi: 10.1172/JCI107002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binder H. J. Sodium transport across isolated human jejunum. Gastroenterology. 1974 Aug;67(2):231–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook G. C. Absorption products of D(-) fructose in man. Clin Sci. 1969 Dec;37(3):675–687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran P. F. Ion transport in intestine and its coupling to other transport processes. Fed Proc. 1965 Sep-Oct;24(5):993–999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fordtran J. S., Locklear T. W. Ionic constituents and osmolality of gastric and small-intestinal fluids after eating. Am J Dig Dis. 1966 Jul;11(7):503–521. doi: 10.1007/BF02233563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fordtran J. S., Rector F. C., Jr, Carter N. W. The mechanisms of sodium absorption in the human small intestine. J Clin Invest. 1968 Apr;47(4):884–900. doi: 10.1172/JCI105781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fordtran J. S., Rector F. C., Jr, Ewton M. F., Soter N., Kinney J. Permeability characteristics of the human small intestine. J Clin Invest. 1965 Dec;44(12):1935–1944. doi: 10.1172/JCI105299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fordtran J. S., Rector F. C., Jr Stimulation of intestinal sodium absorption by sugars. Am J Clin Nutr. 1971 May;24(5):503–504. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/24.5.503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fordtran J. S., Rector F. C., Locklear T. W., Ewton M. F. Water and solute movement in the small intestine of patients with sprue. J Clin Invest. 1967 Mar;46(3):287–298. doi: 10.1172/JCI105531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fordtran J. S. Segmental perfusion techniques. Gastroenterology. 1969 May;56(5):987–989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN K., SESHADRI B., MATTY A. J. Independence of transfer of solute and solvent across the rat ileum. Nature. 1962 Dec 29;196:1322–1323. doi: 10.1038/1961322a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy M. J., Deren J. J. Selective permeability of the small intestine for fructose. Am J Physiol. 1971 Oct;221(4):1051–1056. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.4.1051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLDSWORTH C. D., DAWSON A. M. ABSORPTION OF FRUCTOSE IN MAN. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Jan;118:142–145. doi: 10.3181/00379727-118-29780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLDSWORTH C. D., DAWSON A. M. THE ABSORPTION OF MONOSACCHARIDES IN MAN. Clin Sci. 1964 Dec;27:371–379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modigliani R., Bernier J. J. Absorption of glucose, sodium, and water by the human jejunum studied by intestinal perfusion with a proximal occluding balloon and at variable flow rates. Gut. 1971 Mar;12(3):184–193. doi: 10.1136/gut.12.3.184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Banwell J. G., Rupak D. M., Mitra R. C., Caranasos G. J., Keimowitz R. I., Mondal A., Manji P. M. Effect of intragastric glucose-electrolyte infusion upon water and electrolyte balance in Asiatic cholera. Gastroenterology. 1968 Sep;55(3):333–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHULTZ S. G., ZALUSKY R., GASS A. E., Jr ION TRANSPORT IN ISOLATED RABBIT ILEUM. 3. CHLORIDE FLUXES. J Gen Physiol. 1964 Nov;48:375–378. doi: 10.1085/jgp.48.2.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHULTZ S. G., ZALUSKY R. ION TRANSPORT IN ISOLATED RABBIT ILEUM. I. SHORT-CIRCUIT CURRENT AND NA FLUXES. J Gen Physiol. 1964 Jan;47:567–584. doi: 10.1085/jgp.47.3.567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltzman D. A., Rector F. C., Jr, Fordtran J. S. The role of intraluminal sodium in glucose absorption in vivo. J Clin Invest. 1972 Apr;51(4):876–885. doi: 10.1172/JCI106882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz S. G., Curran P. F. Coupled transport of sodium and organic solutes. Physiol Rev. 1970 Oct;50(4):637–718. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1970.50.4.637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz S. G., Curran P. F. Stimulation of intestinal sodium absorption by sugars. Am J Clin Nutr. 1970 Apr;23(4):437–440. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/23.4.437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz S. G., Curran P. F. Stimulation of intestinal sodium absorption by sugars: reply to Dr. Fordtran. Am J Clin Nutr. 1971 May;24(5):504–505. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/24.5.504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz S. G., Frizzell R. A. An overview of intestinal absorptive and secretory processes. Gastroenterology. 1972 Jul;63(1):161–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz S. G., Strecker C. K. Fructose influx across the brush border of rabbit ileum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Sep 15;211(3):586–588. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(70)90266-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sladen G. E., Dawson A. M. Interrelationships between the absorptions of glucose, sodium and water by the normal human jejunum. Clin Sci. 1969 Feb;36(1):119–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soergel K. H. An evaluation of perfusion techniques in the study of water and electrolyte absorption in man: the problem of endogenous secretions. Gut. 1969 Jul;10(7):601–601. doi: 10.1136/gut.10.7.601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnberg L. A., Bieberdorf F. A., Morawski S. G., Fordtran J. S. Interrelationships of chloride, bicarbonate, sodium, and hydrogen transport in the human ileum. J Clin Invest. 1970 Mar;49(3):557–567. doi: 10.1172/JCI106266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnberg L. A., Fordtran J. S., Carter N. W., Rector F. C., Jr Mechanism of bicarbonate absorption and its relationship to sodium transport in the human jejunum. J Clin Invest. 1970 Mar;49(3):548–556. doi: 10.1172/JCI106265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnberg L. A. Potassium transport in the human small bowel. Gut. 1971 Oct;12(10):811–818. doi: 10.1136/gut.12.10.811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]