Abstract
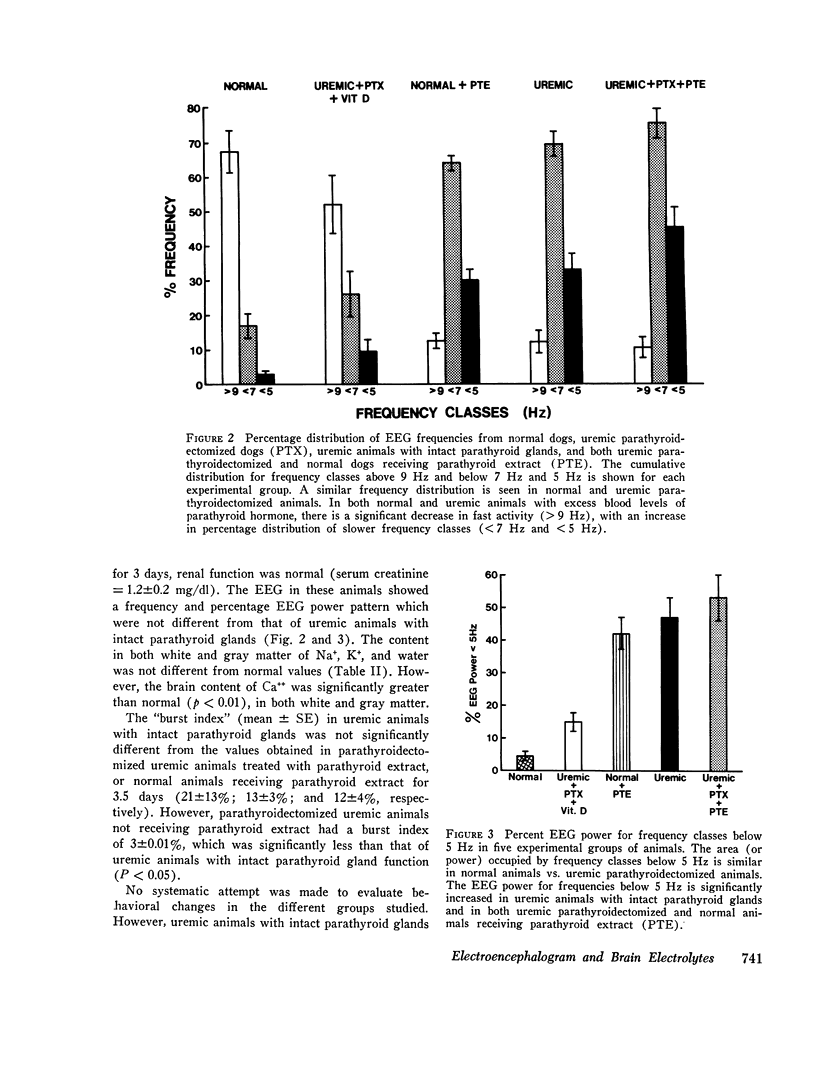
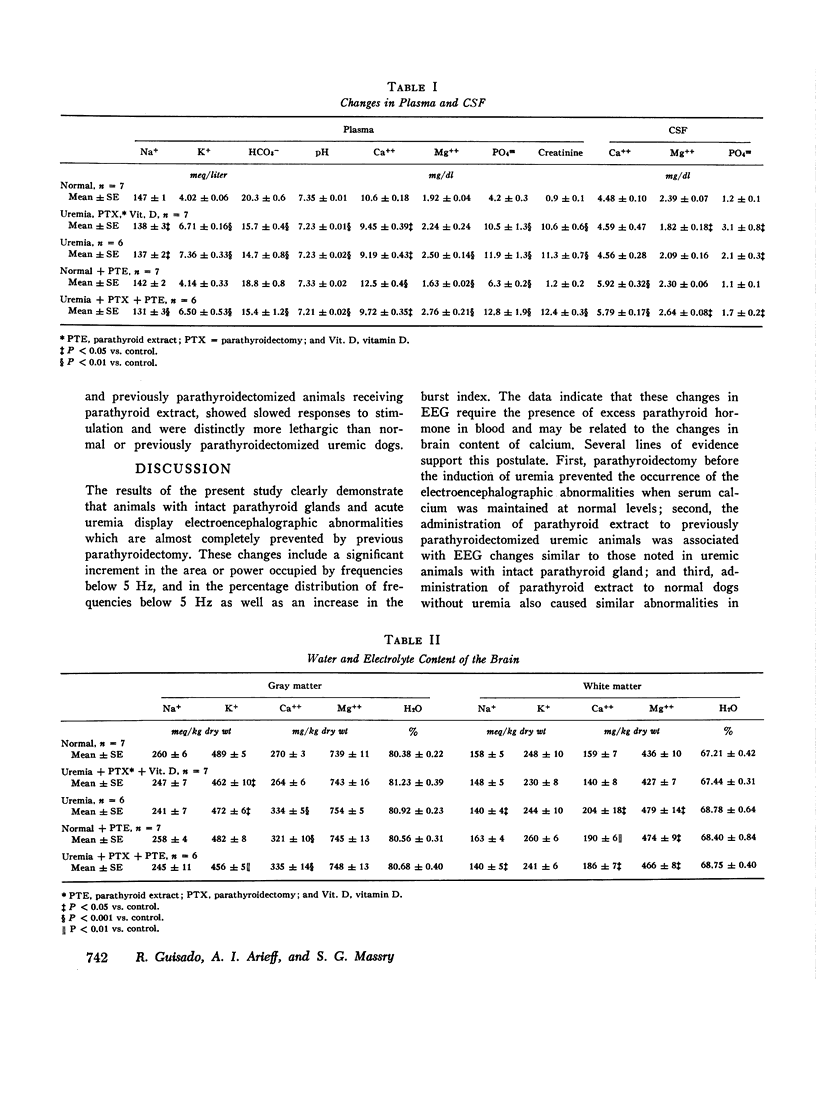
Studies were carried out in order to evaluate the effects of changes in brain calcium and the influence of parathyroidectomy and administration of parathyroid extract on the electroencephalogram (EEG) of normal and uremic dogs. Manual analysis of frequency and power distribution of the EEG in uremic dogs revealed a significant increase in both the percentage distribution and the area or power occupied by frequencies below 5 Hz. In addition, high amplitude bursts of delta activity were apparent in the uremic dog. These changes were largely prevented by parathyroidectomy before the induction of uremia, but the administration of parathyroid extract to either normal dogs, or to previously parathyroidectomized uremic dogs, induced EEG changes similar to those noted in uremic animals with intact parathyroid glands. In all groups of animals which showed EEG changes, brain content of calcium was significantly higher than in either normal dogs or previously parathyroidectomized uremic dogs. Changes in arterial pH and bicarbonate, or in the concentrations of Na+, K+, urea, or creatinine in plasma or cerebrospinal fluid were similar in uremic animals with intact parthyroid glands and in previously parathyroidectomized uremia dogs. The results indicate that the EEG changes found in dogs with acute renal failure require the presence of excess parathyroid hormone in blood, and they may be related to the observed changes in brain content of calcium.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen E. M., Singer F. R., Melamed D. Electroencephalographic abnormalities in hypercalcemia. Neurology. 1970 Jan;20(1):15–22. doi: 10.1212/wnl.20.1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arieff A. I., Massry S. G., Barrientos A., Kleeman C. R. Brain water and electrolyte metabolism in uremia: effects of slow and rapid hemodialysis. Kidney Int. 1973 Sep;4(3):177–187. doi: 10.1038/ki.1973.100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arieff A. I., Massry S. G. Calcium metabolism of brain in acute renal failure. Effects of uremia, hemodialysis, and parathyroid hormone. J Clin Invest. 1974 Feb;53(2):387–392. doi: 10.1172/JCI107571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkow J. W., Fine B. S., Zimmerman L. E. Unusual ocular calcification in hyperparathyroidism. Am J Ophthalmol. 1968 Nov;66(5):812–824. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(68)92795-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein D. S., Pletka P., Hattner R. S., Hampers C. L., Merrill J. P. Effect of total parathyroidectomy and uremia on the chemical composition of bone, skin and aorta in the rat. Isr J Med Sci. 1971 Mar;7(3):513–514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blioch Z. L., Glagoleva I. M., Liberman E. A., Nenashev V. A. A study of the mechanism of quantal transmitter release at a chemical synapse. J Physiol. 1968 Nov;199(1):11–35. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borle A. B. Kinetic analyses of calcium movements in cell cultures. IV. Effects of phosphate and parathyroid hormone in kidney cells. Endocrinology. 1970 Jun;86(6):1389–1393. doi: 10.1210/endo-86-6-1389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury M. W., Kleeman C. R. Stability of the potassium content of cerebrospinal fluid and brain. Am J Physiol. 1967 Aug;213(2):519–528. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.213.2.519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury M. W., Leeman C. R., Bagdoyanh, Berberian A. The calcium and magnesium content of skeletal muscle, brain, and cerebrospinal fluid as determined by atomic bsorption flame photometry. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 May;71(5):884–892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Care A. D., Sherwood L. M., Potts J. T., Jr, Aurbach G. D. Perfusion of the isolated parathyroid gland of the goat and sheep. Nature. 1966 Jan 1;209(5018):55–57. doi: 10.1038/209055a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase L. R., Aurbach G. D. The effect of parathyroid hormone on the concentration of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate in skeletal tissue in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1970 Apr 10;245(7):1520–1526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond I., Goldberg A. L. Uptake and release of 45Ca by brain microsomes, synaptosomes and synaptic vesicles. J Neurochem. 1971 Aug;18(8):1419–1431. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1971.tb00005.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas W. W. Stimulus-secretion coupling: the concept and clues from chromaffin and other cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1968 Nov;34(3):451–474. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1968.tb08474.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsberry D. D. Computer processing of electroencephalographic data. Am J Vet Res. 1972 Jan;33(1):235–241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman R. A. Permeability changes in experimental uremic encephalopathy. Arch Intern Med. 1970 Nov;126(5):835–837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedmann N., Rasmussen H. Calcium, manganese and hepatic gluconeogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Oct 27;222(1):41–52. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(70)90349-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEYMAN A., PATTERSON J. L., Jr, JONES R. W., Jr Cerebral circulation and metabolism in uremia. Circulation. 1951 Apr;3(4):558–563. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.3.4.558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KEYNES R. D. Movements of labelled calcium in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1957 Sep 30;138(2):253–281. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagstam K. E. EEG frequency content related to chemical blood parameters in chronic uraemia. Scand J Urol Nephrol. 1971;7:1–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JARNEFELT J. Properties and possible mechanism of the Na ion and K ion stimulated microsomal adenosinetriphosphatase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Jun 4;59:643–654. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90644-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KILEY J., HINES O. ELECTROENCEPHALOGRAPHIC EVALUATION OF UREMIA. WAVE FREQUENCY EVALUATIONS ON 40 UREMIC PATIENTS. Arch Intern Med. 1965 Jul;116:67–73. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1965.03870010069009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAIDLAW J. The application in general medical conditions of a visual method of assessing and representing generalized electroencephalographic abnormalities. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1959 Feb;22(1):69–76. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.22.1.69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lust W. D., Robinson J. D. Calcium accumulation by isolated nerve ending particles from brain. II. Factors influencing calcium movements. J Neurobiol. 1969;1(3):317–328. doi: 10.1002/neu.480010307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massry S. G., Arieff A. I., Coburn J. W., Palmieri G., Kleeman C. R. Divalent ion metabolism in patients with acute renal failure: studies on the mechanism of hypocalcemia. Kidney Int. 1974 Jun;5(6):437–445. doi: 10.1038/ki.1974.62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massry S. G., Coburn J. W., Lee D. B., Jowsey J., Kleeman C. R. Skeletal resistance to parathyroid hormone in renal failure. Studies in 105 human subjects. Ann Intern Med. 1973 Mar;78(3):357–364. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-78-3-357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn P. J., Dawson R. M. The pH dependence of calcium adsorption onto anionic phospholipid monolayers. Chem Phys Lipids. 1972 Jan;8(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(72)90038-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss E., Canterbury J. M., Bercovitz M. A., Kaplan E. L. The role of phosphate in the secretion of parathyroid hormone in man. J Clin Invest. 1970 Nov;49(11):2146–2149. doi: 10.1172/JCI106432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHEINBERG P. Effects of uremia on cerebral blood flow and metabolism. Neurology. 1954 Feb;4(2):101–105. doi: 10.1212/wnl.4.2.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swash M., Rowan A. J. Electroencephalographic criteria of hypocalcemia and hypercalcemia. Arch Neurol. 1972 Mar;26(3):218–228. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1972.00490090044003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teschan P. E., Carter C. B., Taub E. Experimental studies of toxic factors in uremic encephalopathy. Arch Intern Med. 1970 Nov;126(5):838–840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler H. R. Neurologic disorders in renal failure. Am J Med. 1968 May;44(5):734–748. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(68)90255-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Den Noort S., Eckel R. E., Brine K., Hrdlicka J. T. Brain metabolism in uremic and adenosine-infused rats. J Clin Invest. 1968 Sep;47(9):2133–2142. doi: 10.1172/JCI105899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



