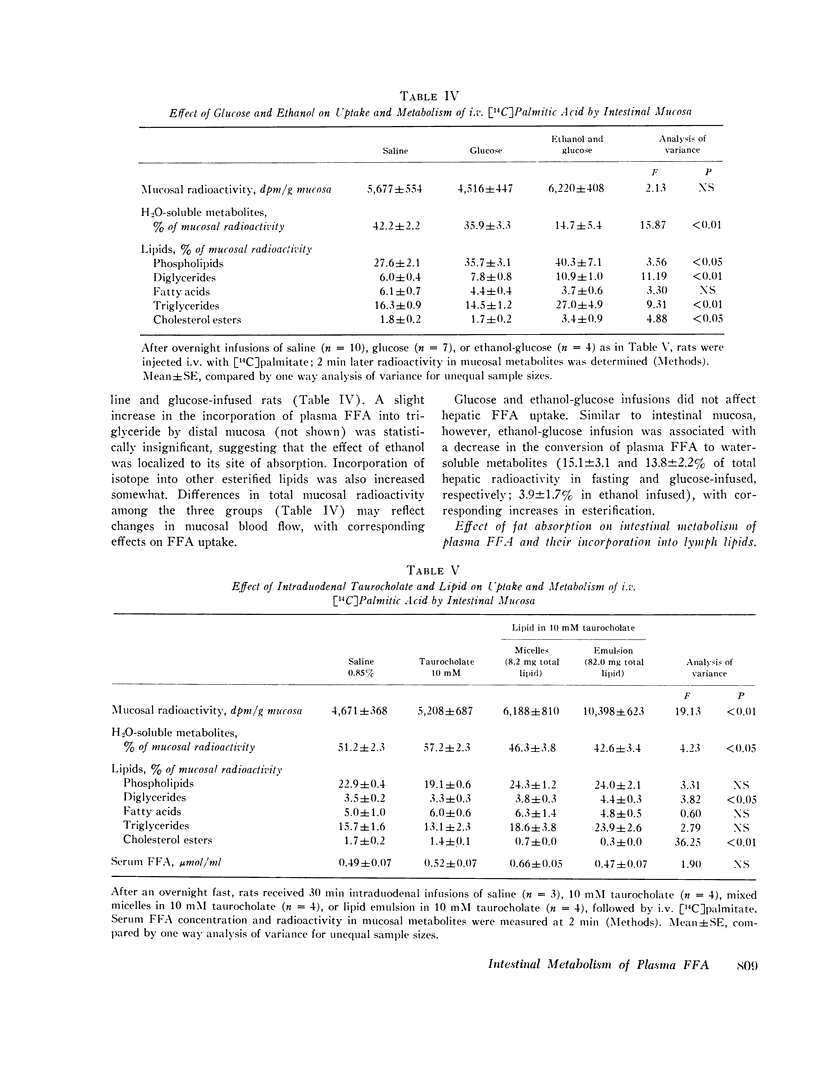
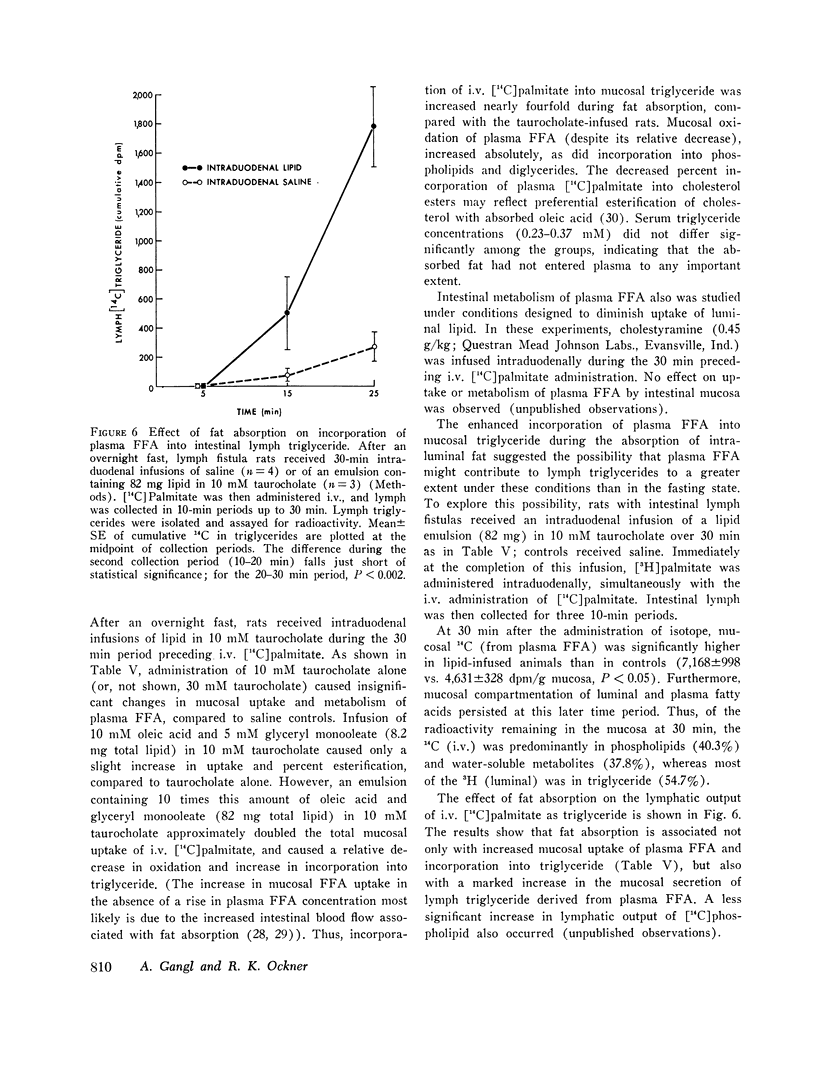
Abstract
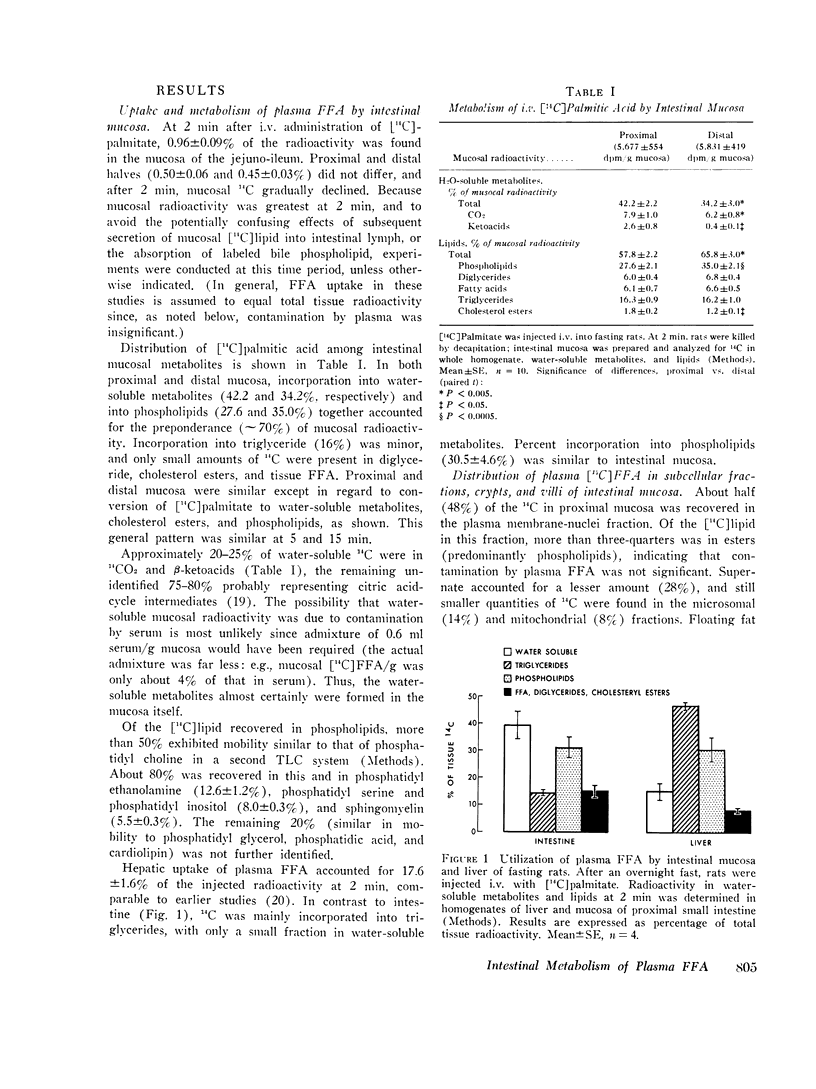
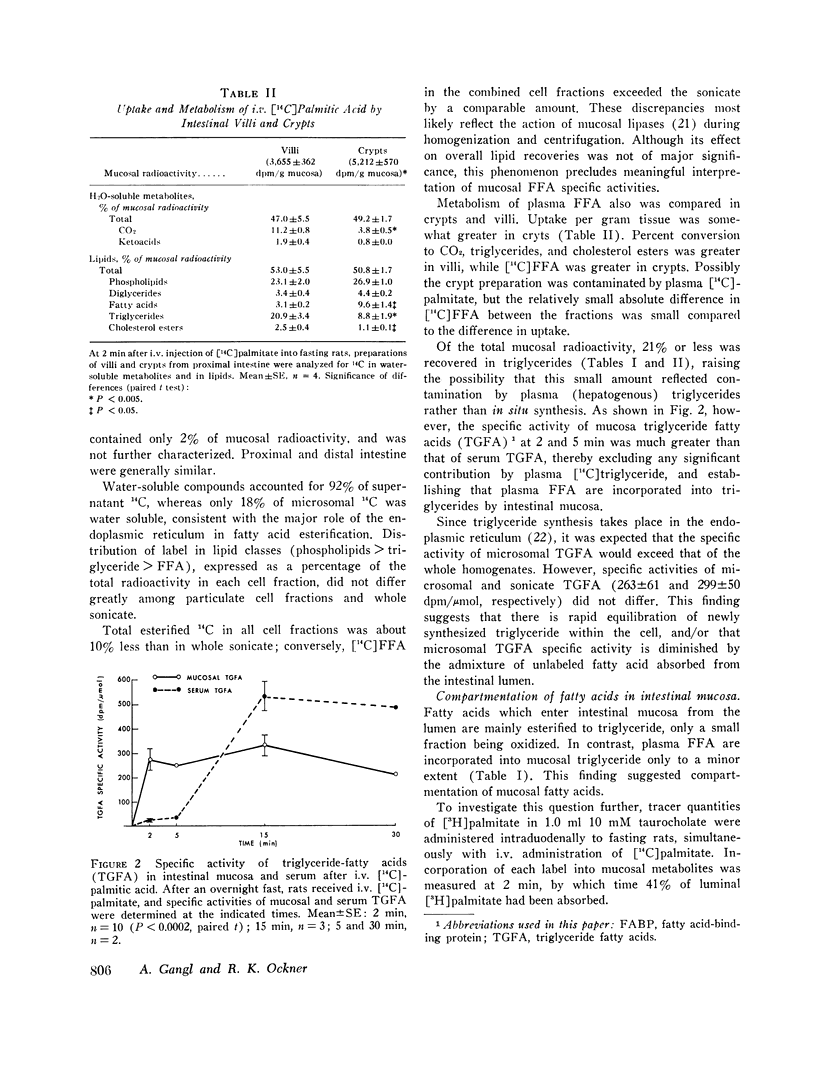
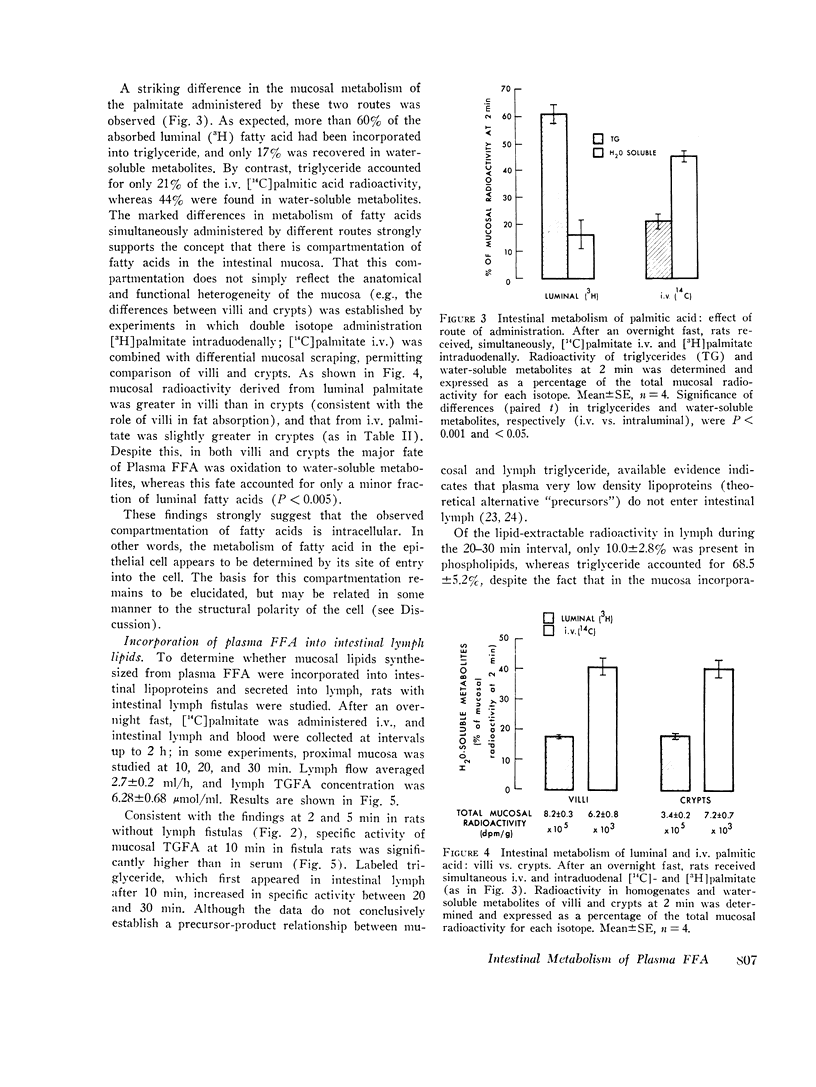
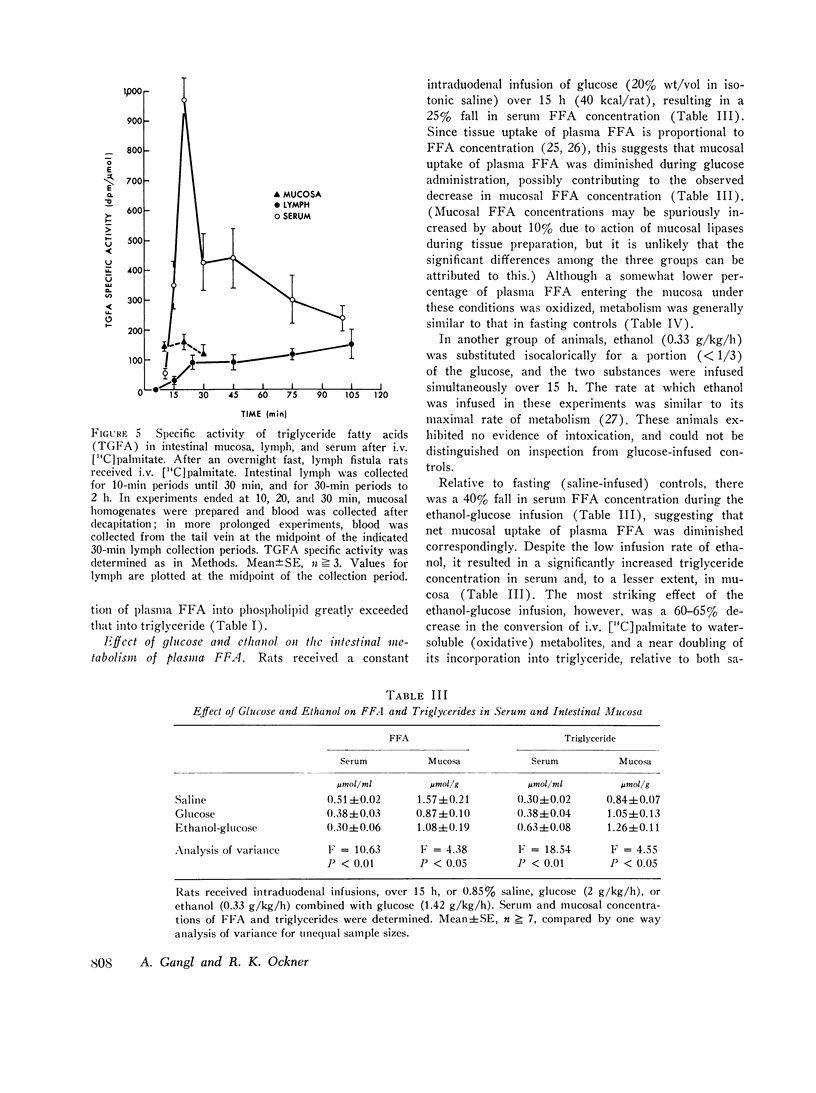
Fatty acid metabolism in intestinal mucosa has been examined primarily in regard to lipid absorption. Since earlier studies suggested intestinal utilization of plasma free fatty acids (FFA), we investigated mucosal metabolism of plasma FFA in rats. Mucosal radioactivity (1 per cent of administered) was maximal 2 min after i.v. [14C]palmitate. Of mucosal 14C, 42 percent was in water-soluble metabolites, including CO2 and ketoacids, 28 percent in phospholipids, and only 16 per cent in triglycerides. The specific activity of mucosal triglyceride fatty acids (TGFA) was 11 times that of serum TGFA, confirming in situ synthesis. Double isotope experiments showed marked differences in the metabolism of fatty acids entering mucosa simultaneously from lumen and plasma. Whereas luminal fatty acids were chiefly esterified to triglyceride, plasma FFA were preferentially oxidized and incorporated into phospholipids. Crypts did not differ from villi, indicating that intestinal metabolism of plasma FFA is related to their site of entry into epithelial cells. Mucosal metabolism of i.v. [14C]palmitate was minimally affected by glucose administration. However, intraduodenal isocaloric ethanol inhibited mucosal oxidation of FFA by 60 per cent, and increased incorporation into triglycerides nearly twofold. During lipid absorption, mucosal uptake of plasma FFA doubled and incorporation into intestinal lymph triglycerides was increased sixfold. These studies demonstrate an intracellular compartmentation of fatty acids in the intestinal epithelium. In contrast to absorbed luminal fatty acids, plasma FFA in the fasting state are both an energy source and a substrate for the synthesis of tissue phospholipid. The fasting contribution of plasma FFA to mucosal and lymph triglyceride is minimal, but it increases during ethanol administration and fat absorption.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARMSTRONG D. T., STEELE R., ALTSZULER N., DUNN A., BISHOP J. S., DE BODO R. C. Regulation of plasma free fatty acid turnover. Am J Physiol. 1961 Jul;201:9–15. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1961.201.1.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRAGDON J. H., GORDON R. S., Jr Tissue distribution of C14 after the intravenous injection of labeled chylomicrons and unesterified fatty acids in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1958 Apr;37(4):574–578. doi: 10.1172/JCI103640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker N., Schotz M. C. Quantitative aspects of free fatty acid metabolism in the fasted rat. J Lipid Res. 1967 Nov;8(6):646–660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barona E., Pirola R. C., Leiber C. S. Small intestinal damage and changes in cell population produced by ethanol ingestion in the rat. Gastroenterology. 1974 Feb;66(2):226–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter J. Origin and characteristics of endogenous lipid in thoracic duct lymph in rat. J Lipid Res. 1966 Jan;7(1):158–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böttger I., Dobbs R., Faloona G. R., Unger R. H. The effects of triglyceride absorption upon glucagon, insulin, and gut glucagon-like immunoreactivity. J Clin Invest. 1973 Oct;52(10):2532–2541. doi: 10.1172/JCI107444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARK B., HUBSCHER G. Biosynthesis of glycerides in subcellular fractions of intestinal mucosa. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Jan 29;46:479–494. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90579-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DINELLA R. R., MENG H. C., PARK C. R. Properties of intestinal lipase. J Biol Chem. 1960 Nov;235:3076–3081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietschy J. M., Siperstein M. D. Cholesterol synthesis by the gastrointestinal tract: localization and mechanisms of control. J Clin Invest. 1965 Aug;44(8):1311–1327. doi: 10.1172/JCI105237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edson N. L. Ketogenesis-antiketogenesis: The influence of ammonium chloride on ketone-body formation in liver. Biochem J. 1935 Sep;29(9):2082–2094. doi: 10.1042/bj0292082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggstein M., Kreutz F. H. Eine neue Bestimmung der Neutralfette im Blutserum und Gewebe. I. Prinzip, Durchführung und Besprechung der Methode. Klin Wochenschr. 1966 Mar 1;44(5):262–267. doi: 10.1007/BF01747716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREDRICKSON D. S., GORDON R. S., Jr Transport of fatty acids. Physiol Rev. 1958 Oct;38(4):585–630. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1958.38.4.585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fara J. W., Rubinstein E. H., Sonnenschein R. R. Intestinal hormones in mesenteric vasodilation after intraduodenal agents. Am J Physiol. 1972 Nov;223(5):1058–1067. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.223.5.1058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenfeldt L., Wahren J. Human forearm muscle metabolism during exercise. 3. Uptake, release and oxidation of beta-hydroxybutyrate and observations on the beta-hydroxybutyrate/acetoacetate ratio. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1968;21(4):314–320. doi: 10.3109/00365516809076999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSTON J. M. The absorption of fatty acids by the isolated intestine. J Biol Chem. 1959 May;234(5):1065–1067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson E. D. The circulation of the gastrointestinal tract. Gastroenterology. 1967 Jan;52(1):98–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston J. M., Paultauf F., Schiller C. M., Schultz L. D. The utilization of the alpha-glycerophosphate and monoglyceride pathways for phosphatidyl choline biosynthesis in the intestine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Oct 6;218(1):124–133. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(70)90099-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones A. L., Ockner R. K. An electron microscopic study of endogenous very low density lipoprotein production in the intestine of rat and man. J Lipid Res. 1971 Sep;12(5):580–589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARMEN A., WHYTE M., GOODMAN D. S. FATTY ACID ESTERIFICATION AND CHYLOMICRON FORMATION DURING FAT ABSORPTION. 1. TRIGLYCERIDES AND CHOLESTEROL ESTERS. J Lipid Res. 1963 Jul;4:312–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mistilis S. P., Birchall A. Induction of alcohol dehydrogenase in the rat. Nature. 1969 Jul 12;223(5202):199–200. doi: 10.1038/223199a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mistilis S. P., Ockner R. K. Effects of ethanol on endogenous lipid and lipoprotein metabolism in small intestine. J Lab Clin Med. 1972 Jul;80(1):34–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ONTKO J. A., JACKSON D. FACTORS AFFECTING THE RATE OF OXIDATION OF FATTY ACIDS IN ANIMAL TISSUES. EFFECT OF SUBSTRATE CONCENTRATION, PH, AND COENZYME A IN RAT LIVER PREPARATIONS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Nov;239:3674–3682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ockner R. K., Hughes F. B., Isselbacher K. J. Very low density lipoproteins in intestinal lymph: origin, composition, and role in lipid transport in the fasting state. J Clin Invest. 1969 Nov;48(11):2079–2088. doi: 10.1172/JCI106174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ockner R. K., Jones A. L. An electron microscopic and functional study of very low density lipoproteins in intestinal lymph. J Lipid Res. 1970 Jul;11(4):284–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ockner R. K., Manning J. A. Fatty acid-binding protein in small intestine. Identification, isolation, and evidence for its role in cellular fatty acid transport. J Clin Invest. 1974 Aug;54(2):326–338. doi: 10.1172/JCI107768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ockner R. K., Manning J. A., Poppenhausen R. B., Ho W. K. A binding protein for fatty acids in cytosol of intestinal mucosa, liver, myocardium, and other tissues. Science. 1972 Jul 7;177(4043):56–58. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4043.56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen O. E., Felig P., Morgan A. P., Wahren J., Cahill G. F., Jr Liver and kidney metabolism during prolonged starvation. J Clin Invest. 1969 Mar;48(3):574–583. doi: 10.1172/JCI106016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regouw B. J., Cornelissen P. J., Helder R. A., Spijkers J. B., Weeber Y. M. Specific determination of free fatty acid in plasma. Clin Chim Acta. 1971 Jan;31(1):187–195. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(71)90377-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers J. B., Riley E. M., Drummey G. D., Isselbacher K. J. Lipid absorption in adrenalectomized rats: the role of altered enzyme activity in the intestinal mucosa. Gastroenterology. 1967 Oct;53(4):547–556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SENIOR J. R., ISSELBACHER K. J. Activation of long-chain fatty acids by rat-gut mucosa. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Nov 4;44:399–400. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91594-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPECTOR A. A., STEINBERG D., TANAKA A. UPTAKE OF FREE FATTY ACIDS BY EHRLICH ASCITES TUMOR CELLS. J Biol Chem. 1965 Mar;240:1032–1041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPENCER R. P., BRODY K. R., LUTTERS B. M. SOME EFFECTS OF ETHANOL ON THE GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT. Am J Dig Dis. 1964 Sep;9:599–604. doi: 10.1007/BF02232118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauer F., Mahadevan S., Erfle J. D. The accumulation of citrate cycle intermediates in rat liver cells oxidizing palmitate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jun 8;239(1):26–32. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(71)90188-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shrivastava B. K., Redgrave T. G., Simmonds W. J. The source of endogenous lipid in the thoracic duct lymph of fasting rats. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1967 Jul;52(3):305–312. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1967.sp001916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skipski V. P., Peterson R. F., Barclay M. Quantitative analysis of phospholipids by thin-layer chromatography. Biochem J. 1964 Feb;90(2):374–378. doi: 10.1042/bj0900374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAUGHAN M., STEINBERG D., PITTMAN R. ON THE INTERPRETATION OF STUDIES MEASURING UPTAKE AND ESTERIFICATION OF (1-14-C)PALMITIC ACID BY RAT ADIPOSE TISSUE IN VITRO. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Apr 20;84:154–166. doi: 10.1016/0926-6542(64)90072-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidemann M. J., Krebs H. A. The fuel of respiration of rat kidney cortex. Biochem J. 1969 Apr;112(2):149–166. doi: 10.1042/bj1120149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


