Abstract
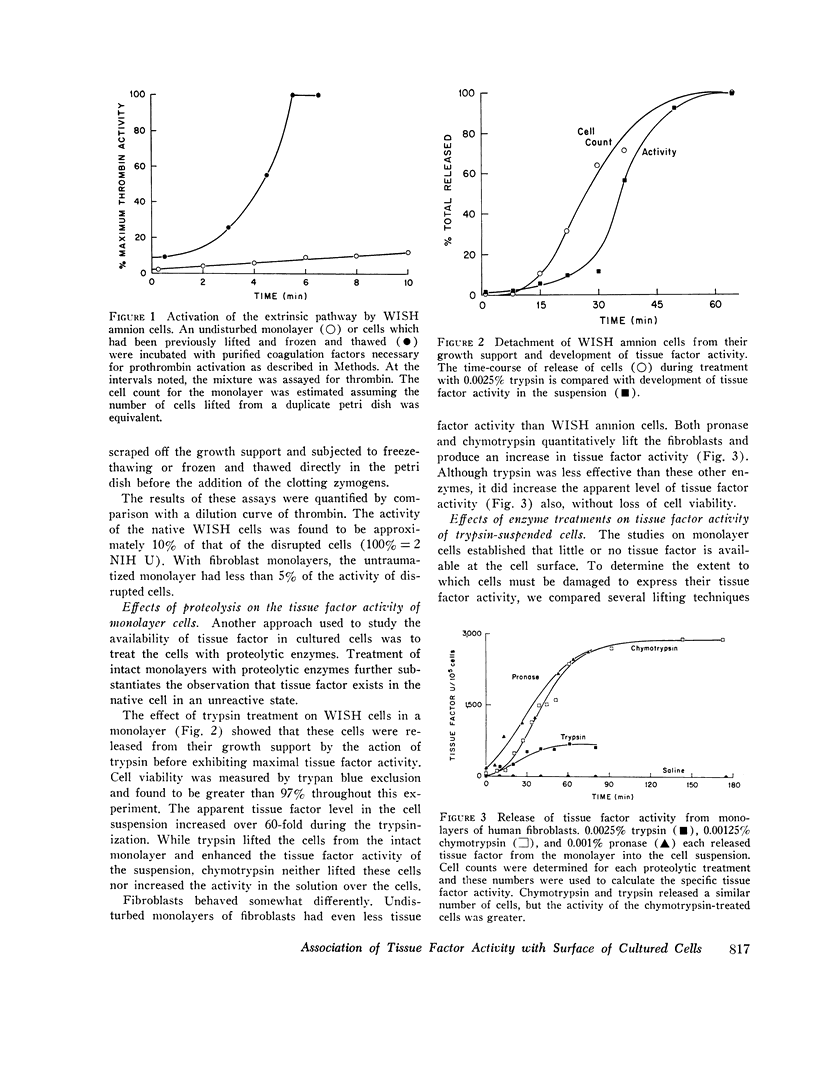
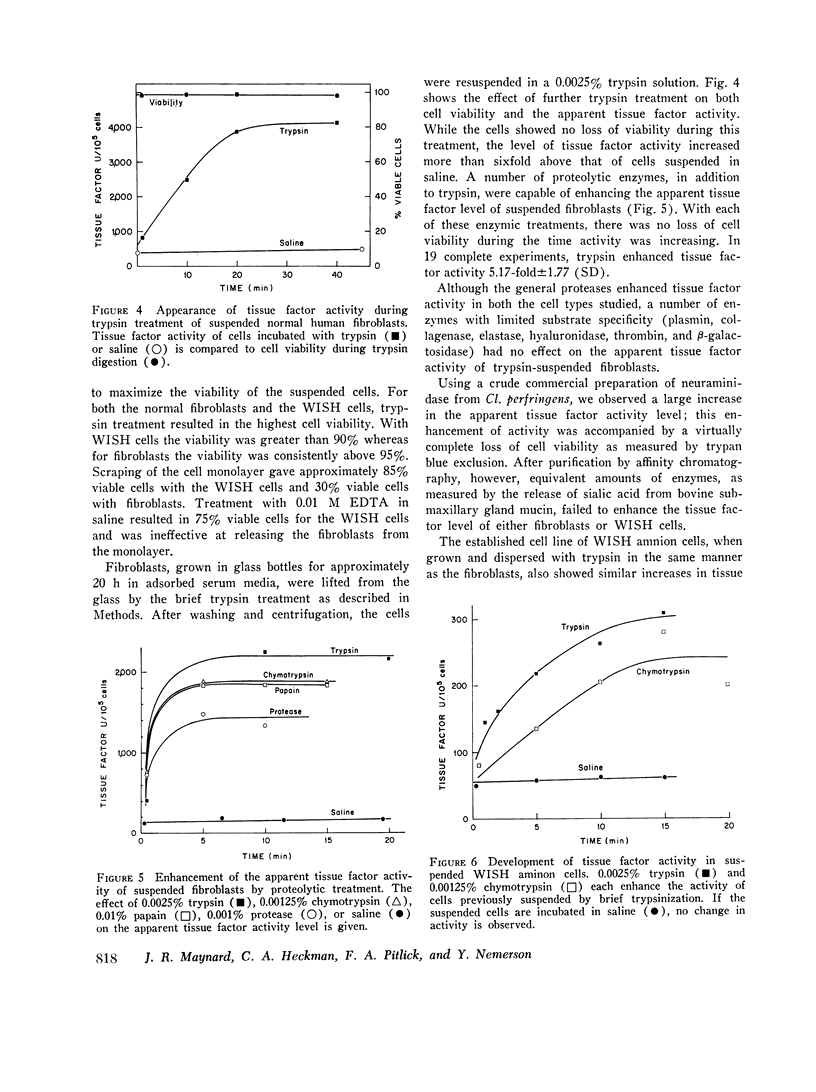
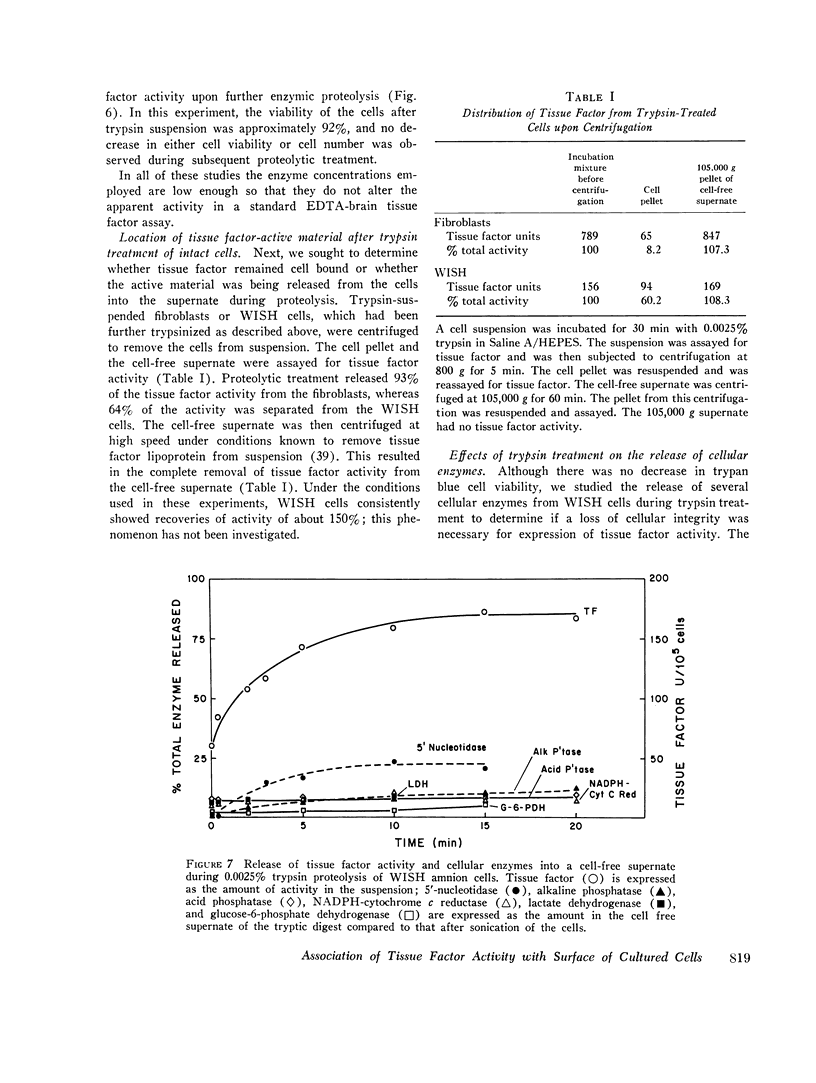
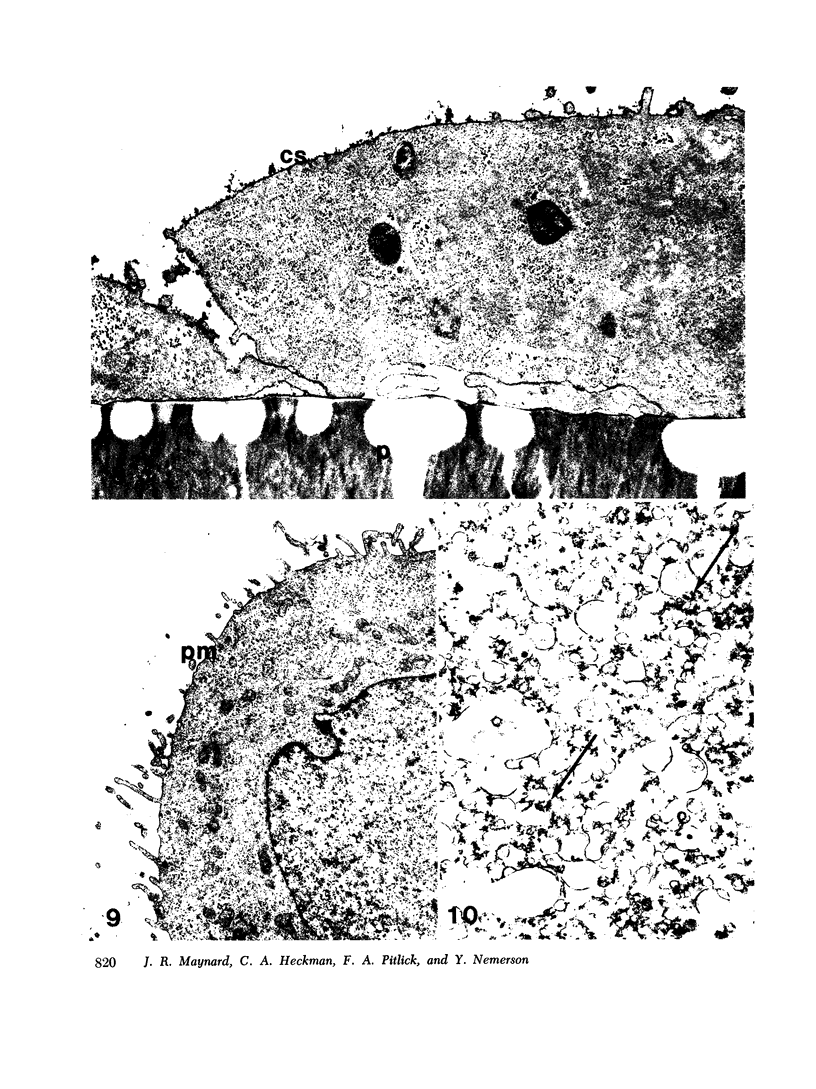
Tissue factor occurs in a dormant state on the surface of cultured normal human fibroblasts and WISH 1 amnion cells. The activity of undisturbed monolayers or cells lifted with brief trypsin treatment (0.125 per cent trypsin for 1 min) increases up to 60-fold upon prolonged digestion with dilute trypsin (0.0025 per cent trypsin for 30 min); activity appears subsequent to cell detachment. Up to 70 per cent of the total cellular tissue factor becomes active under these conditions and is released from the cells. The ruthenium red staining coat of the cells is lost during detachment, but cell viability (more than 90 per cent exclude trypan blue) and cell morphology do not change during the subsequent development of tissue factor activity. Furthermore, less than 10 percent of four intracellular enzymes and less than 20 per cent of two plasma membrane enzymes are released during this period of time. We therefore conclude that cells in culture do have tissue factor activity, that it exists in a latent form, and that total cell disruption is not necessary for this activity to initiate blood coagulation.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashford T. P., Freiman D. G. Platelet aggregation at sites of minimal endothelial injury. An electron microscopic study. Am J Pathol. 1968 Oct;53(4):599–607. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BELL W. N., ALTON H. G. A brain extract as a substitute for platelet suspensions in the thromboplastin generation test. Nature. 1954 Nov 6;174(4436):880–881. doi: 10.1038/174880a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Codington J. F., Sanford B. H., Jeanloz R. W. Glycoprotein coat of the TA3 cell. Isolation and partial characterization of a sialic acid containing glycoprotein fraction. Biochemistry. 1972 Jul 4;11(14):2559–2564. doi: 10.1021/bi00764a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulter H. D. Rapid and improved methods fr embedding biological tissues in Epon 812 and Araldite 502. J Ultrastruct Res. 1967 Oct 31;20(5):346–355. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(67)80104-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P., Illiano G. Purification of neuraminidases from Vibrio Cholerae, Clostridium Perfringens and influenza virus by affinity chromatography. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jul 2;44(1):178–184. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(71)80175-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePierre J. W., Karnovsky M. L. Ecto-enzyme of granulocytes: 5'-nucleotidase. Science. 1974 Mar 15;183(4129):1096–1098. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4129.1096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EMMELOT P., BOS C. J., BENEDETTI E. L., RUEMKE P. STUDIES ON PLASMA MEMBRANES. I. CHEMICAL COMPOSITION AND ENZYME CONTENT OF PLASMA MEMBRANES ISOLATED FROM RAT LIVER. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Jul 15;90:126–145. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90125-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esnouf M. P., Lloyd P. H., Jesty J. A method for the simultaneous isolation of factor X and prothrombin from bovine plasma. Biochem J. 1973 Apr;131(4):781–789. doi: 10.1042/bj1310781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green D., Ryan C., Malandruccolo N., Nadler H. L. Characterization of the coagulant activity of cultured human fibroblasts. Blood. 1971 Jan;37(1):47–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jesty J., Nemerson Y. Purification of Factor VII from bovine plasma. Reaction with tissue factor and activation of Factor X. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 25;249(2):509–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. D., Wakil S. J. A requirement for phospholipids by the microsomal reduced diphosphopyridine nucleotide-cytochrome c reductase. J Biol Chem. 1967 Nov 25;242(22):5267–5273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraemer P. M. Heparan sulfates of cultured cells. I. Membrane-associated and cell-sap species in Chinese hamster cells. Biochemistry. 1971 Apr 13;10(8):1437–1445. doi: 10.1021/bi00784a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraemer P. M. Regeneration of sialic acid on the surface of Chinese hamster cells in culture. II. Incorporation of radioactivity from glucosamine-1-14C. J Cell Physiol. 1967 Apr;69(2):199–207. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040690210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langley O. K., Ambrose E. J. The linkage of sialic acid in the Ehrlich ascites-carcinoma cell surface membrane. Biochem J. 1967 Jan;102(1):367–372. doi: 10.1042/bj1020367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft J. H. Ruthenium red and violet. I. Chemistry, purification, methods of use for electron microscopy and mechanism of action. Anat Rec. 1971 Nov;171(3):347–368. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091710302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft J. H. Ruthenium red and violet. I. Chemistry, purification, methods of use for electron microscopy and mechanism of action. Anat Rec. 1971 Nov;171(3):347–368. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091710302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILSTONE J. H. THROMBOKINASE AS PRIME ACTIVATOR OF PROTHROMBIN: HISTORICAL PERSPECTIVES AND PRESENT STATUS. Fed Proc. 1964 Jul-Aug;23:742–748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemerson Y., Clyne L. P. An assay for coagulation factor VII using factor VII-depleted bovine plasma. J Lab Clin Med. 1974 Feb;83(2):301–303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemerson Y., Esnouf M. P. Activation of a proteolytic system by a membrane lipoprotein: mechanism of action of tissue factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):310–314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemerson Y. The phospholipid requirement of tissue factor in blood coagulation. J Clin Invest. 1968 Jan;47(1):72–80. doi: 10.1172/JCI105716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemerson Y. The reaction between bovine brain tissue factor and factors VII and X. Biochemistry. 1966 Feb;5(2):601–608. doi: 10.1021/bi00866a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niewiarowski S., Bańkowski E., Rogowicka I. Studies on the adsorption and activation of the Hageman factor (factor XII) by collagen and elastin. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1965 Nov 15;14(3-4):387–400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickles F. R., Hardin J. A., Pitlick F. A., Hoyer L. W., Conrad M. E. Tissue factor activity in lymphocyte cultures from normal individuals and patients with hemophilia A. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jun;52(6):1427–1434. doi: 10.1172/JCI107316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silbert J. E., Kleinman H. K., Silbert C. K. Heparin and heparin-like substances of cells. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1975;52:51–60. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-0946-8_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snow C., Allen A. The release of radioactive nucleic acids and mucoproteins by trypsin and ethylenediaminetetra-acetate treatment of baby-hamster cells in tissue culture. Biochem J. 1970 Oct;119(4):707–714. doi: 10.1042/bj1190707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spurr A. R. A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 Jan;26(1):31–43. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(69)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stemerman M. B., Baumgartner H. R., Spaet T. H. The subendothelial microfibril and platelet adhesion. Lab Invest. 1971 Mar;24(3):179–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS C. H., Jr, KAMIN H. Microsomal triphosphopyridine nucleotide-cytochrome c reductase of liver. J Biol Chem. 1962 Feb;237:587–595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams W. J., Norris D. G. Purification of a bovine plasma protein (factor VII) which is required for the activity of lung microsomes in blood coagulation. J Biol Chem. 1966 Apr 25;241(8):1847–1856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilner G. D., Nossel H. L., LeRoy E. C. Activation of Hageman factor by collagen. J Clin Invest. 1968 Dec;47(12):2608–2615. doi: 10.1172/JCI105943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOUNG I. I. Serum 5-nucleotidase; characterization and evaluation in disease states. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1958 Oct 13;75(1):357–362. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1958.tb36883.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zacharski L. R., Bowie E. J., Titus J. L., Owen C. A., Jr Cell-culture synthesis of a factor VIII-like activity. Mayo Clin Proc. 1969 Nov;44(11):784–792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



