Abstract
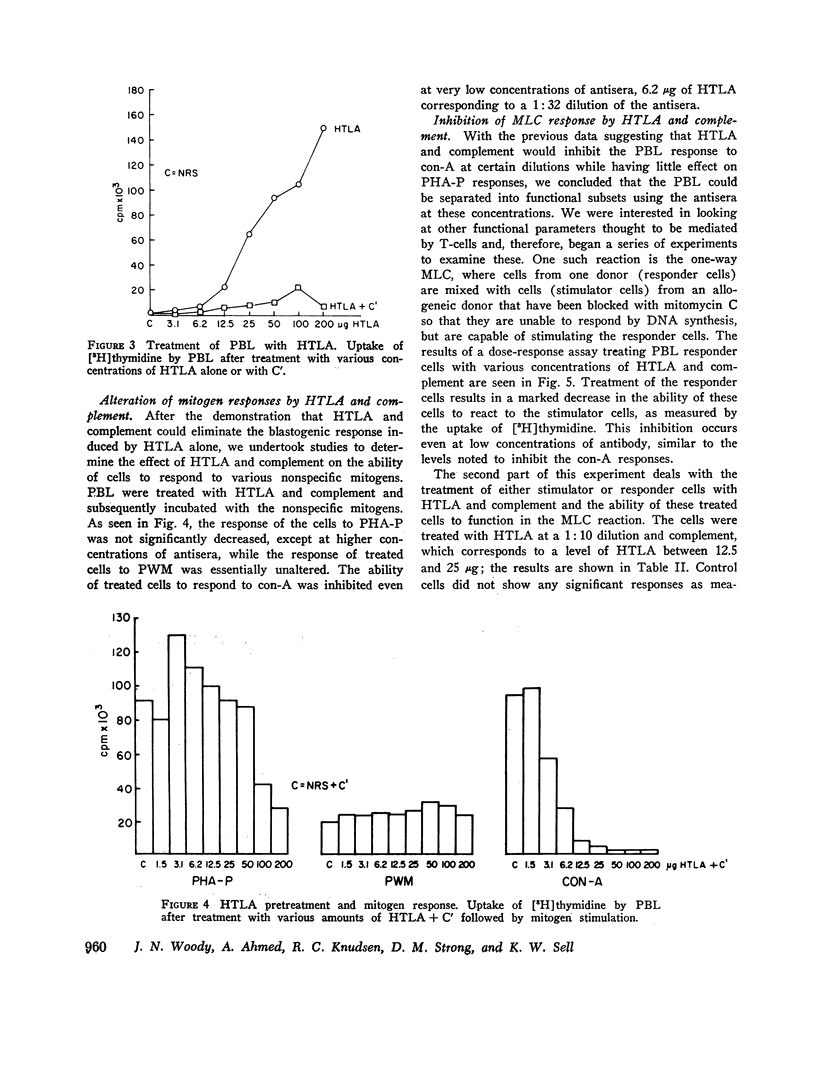
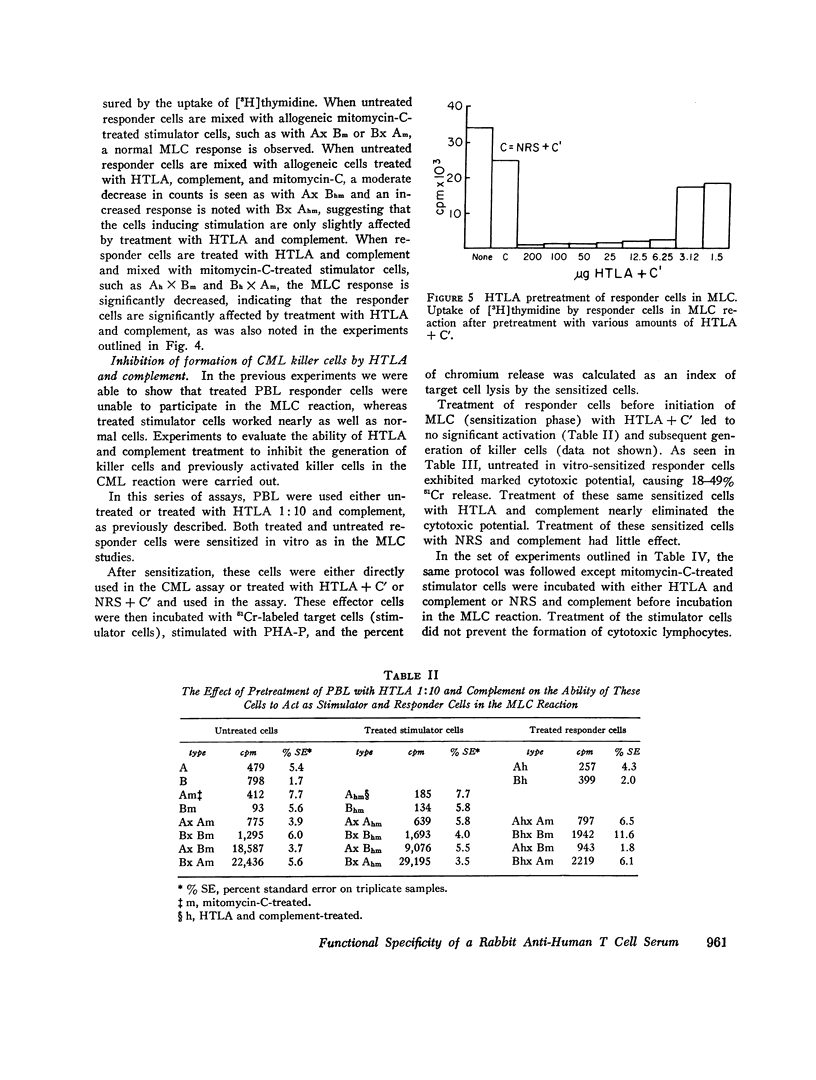
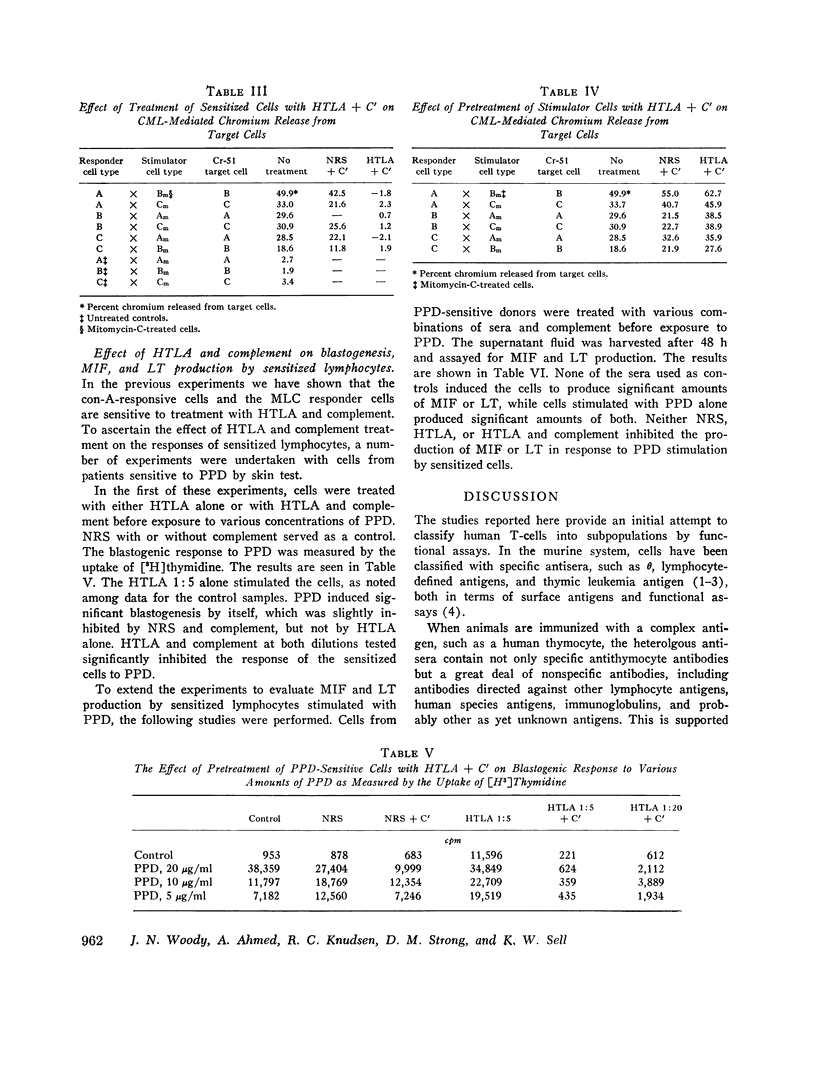
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBL) were evaluated by their responses to phytohemmagglutinin (PHA-P), concanavallin A (con-A), and pokeweed mitogen (PWM), both before and after treatment with an antiserum against human thymic lymphocyte antigens (HTLA) that had been made T-cell-specific by multiple absorptions with immunoglobulin EAC-positive lymphoblast cell lines (B cells). Cells treated with HTLA were examined for their ability to react in a mixed lymphocyte culture (MLC) and to form killer cells in a cell-mediated lymphocytotoxicity (CML) system. Sensitized cells were also examined for their ability to respond to purified protein derivative (PPD) by blastogenesis, migration inhibitory factor release (MIP), and lymphotoxin (LT) production, both before and after treatment with HTLA and complement. The HTLA was in itself highly stimulatory to PBL. However, with the addition of complement and subsequent cell destruction, a marked decrease in its stimulatory response was noted. PBL treated with HTLA and complement exhibited marked inhibition of responsiveness to con-A with little decrease in PHA-P -OR PWM stimulation except at very high concentration of HTLA. MLC reaction was inhibited only when responder cells were treated with HTLA + C'. Treatment of stimulator cells with HTLA + C' did not significantly alter the MLC response. The HTLA + C'-treated cells failed to form killer cells in the CML reaction and inhibited PPD-induced blasto-genesis from PPD-sensitized individuals; however, treatment of sensitized cells with HTLA + C' had little effects on the release of MIF and LT. It is suggested that subpopulations of T-cells carry surface antigens that bind with this specific antisera, and that the con-A-responsive cells, the responder cells in the MLC, and killer T-cells comprise a separate subset from cells responding to PHA-P or PWM, OR THE MIF-and LT-producing cells.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed A., Strong D. M., Sell K. W., Thurman G. B., Knudsen R. C., Wistar R., Jr, Grace W. R. Demonstration of a blocking factor in the plasma and spinal fluid of patients with subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. I. Partial characterization. J Exp Med. 1974 Apr 1;139(4):902–924. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.4.902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aiuti F., Wigzell H. Function and distribution pattern of human T lymphocytes. I. Production of anti-T lymphocyte specific sera as estimated by cytotoxicity and elimination of function of lymphocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Feb;13(2):171–181. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aiuti F., Wigzell H. Function and distribution pattern of human T lymphocytes. II. Presence of T lymphocytes in normal humans and in humans with various immunodeficiency disorders. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Feb;13(2):183–189. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach F. H., Segall M., Zier K. S., Sondel P. M., Alter B. J., Bach M. L. Cell mediated immunity: separation of cells involved in recognitive and destructive phases. Science. 1973 Apr 27;180(4084):403–406. doi: 10.1126/science.180.4084.403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach F. H., Segall M., Zier K. S., Sondel P. M., Alter B. J., Bach M. L. Cell mediated immunity: separation of cells involved in recognitive and destructive phases. Science. 1973 Apr 27;180(4084):403–406. doi: 10.1126/science.180.4084.403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthold D. R., Kysela S., Steinberg A. D. Decline in suppressor T cell function with age in female NZB mice. J Immunol. 1974 Jan;112(1):9–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bobrove A. M., Strober S., Herzenberg L. A., DePamphilis J. D. Identification and quantitation of thymus-derived lymphocytes in human peripheral blood. J Immunol. 1974 Feb;112(2):520–527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyse E. A., Miyazawa M., Aoki T., Old L. J. Ly-A and Ly-B: two systems of lymphocyte isoantigens in the mouse. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1968 Jun 11;170(1019):175–193. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1968.0032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger D. R., Wilson B. J., Malley A., Vetto R. M. The effect of antilymphocyte antibody on lymphocyte transformation. Selective suppression of mitogen, mixed lymphocyte culture, and antigen stimulation of human lymphocytes. Transplantation. 1974 Jun;17(6):541–550. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197406000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger G. A., Kolb W. P. Lymphocyte in vitro cytotoxicity: mechanisms of immune and non-immune small lymphocyte mediated target L cell destruction. J Immunol. 1968 Jul;101(1):111–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger G. A., Moore G. E., White J. G., Matzinger P., Sundsmo J. S., Shupe S., Kolb W. P., Kramer J., Glade P. R. Production of lymphotoxin and migration inhibitory factor by established human lymphocytic cell lines. J Immunol. 1970 Jun;104(6):1476–1485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knudsen R. C., Ahmed A. A., Sell K. W. An in vitro microassay for lymphotoxin using microculture plates and the multiple automated sample harvester. J Immunol Methods. 1974 May;5(1):55–63. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(74)90045-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leckband E., Boyse E. A. Immunocompetent cells among mouse thymocytes: a minor population. Science. 1971 Jun 18;172(3989):1258–1260. doi: 10.1126/science.172.3989.1258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minowada J., Onuma T., Moore G. E. Rosette-forming human lymphoid cell lines. I. Establishment and evidence for origin of thymus-derived lymphocytes. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1972 Sep;49(3):891–895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosier D. E., Pierce C. W. Functional maturation of thymic lymphocyte populations in vitro. J Exp Med. 1972 Dec 1;136(6):1484–1500. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.6.1484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen F. L., Fanger M. W. Studies on the human T-lymphocyte population. I. The development and characterization of a specific anti-human T-cell antibody. J Immunol. 1974 Oct;113(4):1128–1137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REIF A. E., ALLEN J. M. THE AKR THYMIC ANTIGEN AND ITS DISTRIBUTION IN LEUKEMIAS AND NERVOUS TISSUES. J Exp Med. 1964 Sep 1;120:413–433. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.3.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scher I., Strong D. M., Ahmed A., Knudsen R. C., Sell K. W. Specific murine B-cell activation by synthetic single-and double-stranded polynucleotides. J Exp Med. 1973 Dec 1;138(6):1545–1563. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.6.1545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sell K., Woody J., Smith J., Darrow C., Kayhoe D. Evaluation of human cultured lymphoblasts as a source of antigen for production of immunosuppressive antilymphocyte serum. Transplant Proc. 1973 Mar;5(1):541–547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shacks S. J., Chiller J., Granger G. A. Studies on in vitro models of cellular immunity: the role of T and B cells in the secretion of lymphotoxin. Cell Immunol. 1973 May;7(2):313–321. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(73)90253-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirai T., Mellors R. C. Natural thymocytotoxic autoantibody and reactive antigen in New Zealand black and other mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jul;68(7):1412–1415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.7.1412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stobo J. D., Paul W. E. Functional heterogeneity of murine lymphoid cells. II. Acquisition of mitogen responsiveness and of theta antigen during the ontogeny of thymocytes and "T" lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1972 Aug;4(4):367–380. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(72)90039-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strong D. M., Ahmed A. A., Thurman G. B., Sell K. W. In vitro stimulation of murine spleen cells using a microculture system and a multiple automated sample harvester. J Immunol Methods. 1973 Apr;2(3):279–291. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(73)90054-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strong D. M., Ahmed A. A., Thurman G. B., Sell K. W. In vitro stimulation of murine spleen cells using a microculture system and a multiple automated sample harvester. J Immunol Methods. 1973 Apr;2(3):279–291. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(73)90054-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERASAKI P. I., MCCLELLAND J. D. MICRODROPLET ASSAY OF HUMAN SERUM CYTOTOXINS. Nature. 1964 Dec 5;204:998–1000. doi: 10.1038/204998b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERASAKI P. I., MCCLELLAND J. D. MICRODROPLET ASSAY OF HUMAN SERUM CYTOTOXINS. Nature. 1964 Dec 5;204:998–1000. doi: 10.1038/204998b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talal N., Steinberg A. D. The pathogenesis of autoimmunity in New Zealand black mice. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1974;64(0):79–103. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-65848-8_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thurman G. B., Strong D. M., Ahmed A., Green S. S., Sell K. W., Hartzman R. J., Bach F. H. Human mixed lymphocyte cultures. Evaluation of a microculture technique utilizing the Multiple Automated Sample Harvester (MASH). Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Oct;15(2):289–302. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. C., Jr, DeBoard J. R., Mellbye O. J., Messner R. P., Lindström F. D. Studies of T- and B-lymphocytes in patients with connective tissue diseases. J Clin Invest. 1973 Feb;52(2):283–295. doi: 10.1172/JCI107184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worth H. H., Cooper A. G., Brown M. C. Inhibition of human lymphocyte rosetting by anti-T sera. Nat New Biol. 1973 May 23;243(125):109–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yata J., Klein G., Kobayashi N., Furukawa T., Yanagisawa M. Human thymus-lymphoid tissue antigen and its presence in leukaemia and lymphoma. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Dec;7(6):781–792. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



