Abstract
Analyses of the control of glucose metabolism by insulin have been hampered by changes in bloog glucose concentration induced by insulin administration with resultant activation of hypoglycemic counterregulatory mechanisms. To eliminate such mechanisms, we have employed the glucose clamp technique which allows maintenance of fasting blood glucose concentration during and after the administration of insulin. Analyses of six studies performed in young healthy men in the postabsorptive state utilizing the concurrent administration of [14C]glucose and 1 mU/kg per min (40 mU/m2 per min) porcine insulin led to the development of kinetic models for insulin and for glucose. These models account quantitatively for the control of insulin on glucose utilization and on endogenous glucose production during nonsteady states.
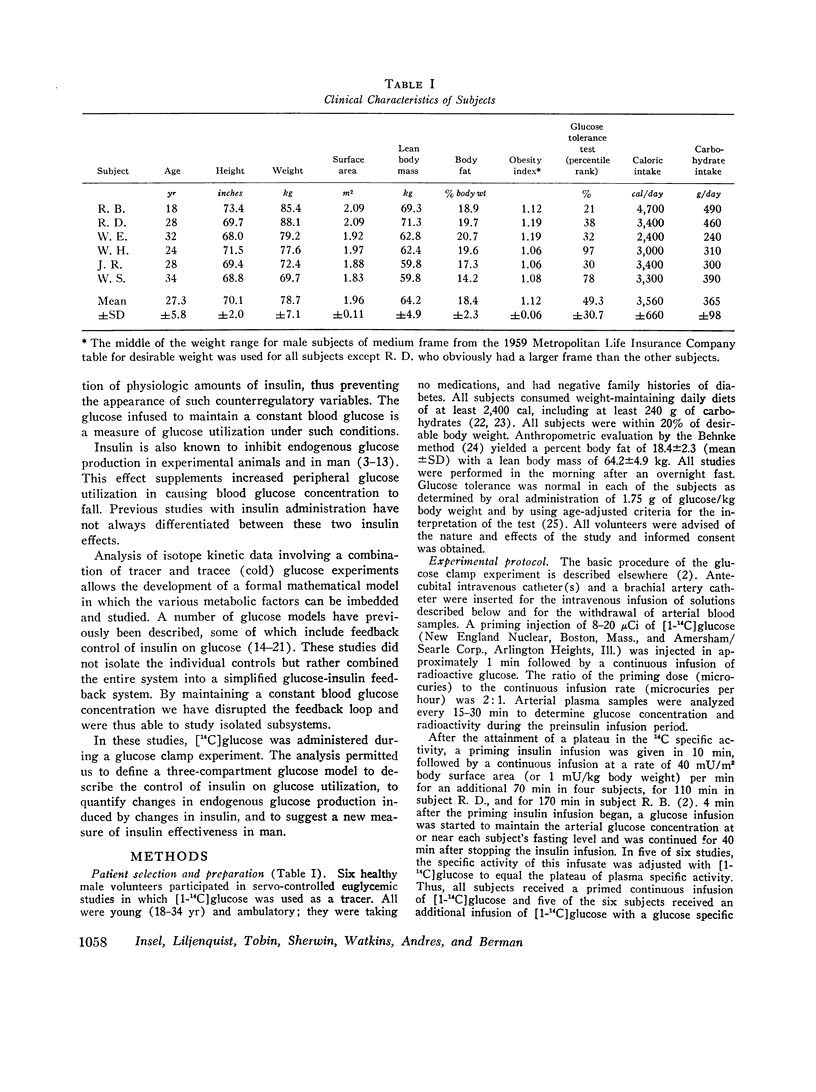
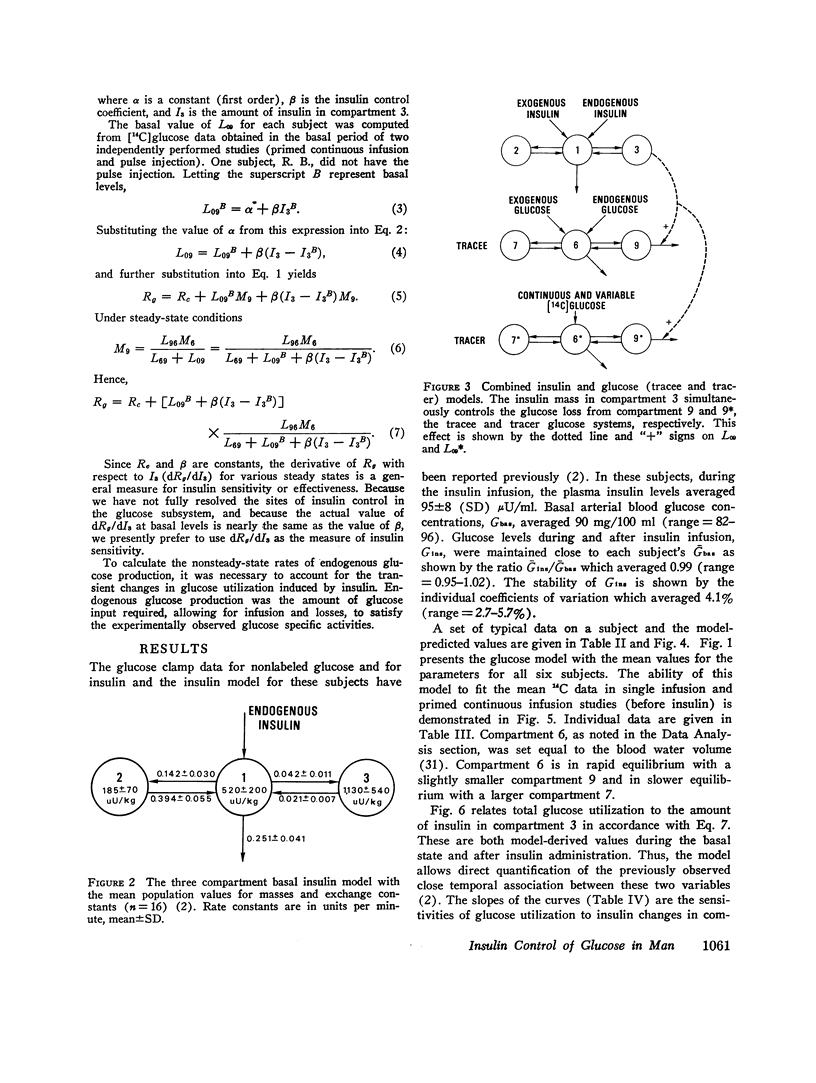
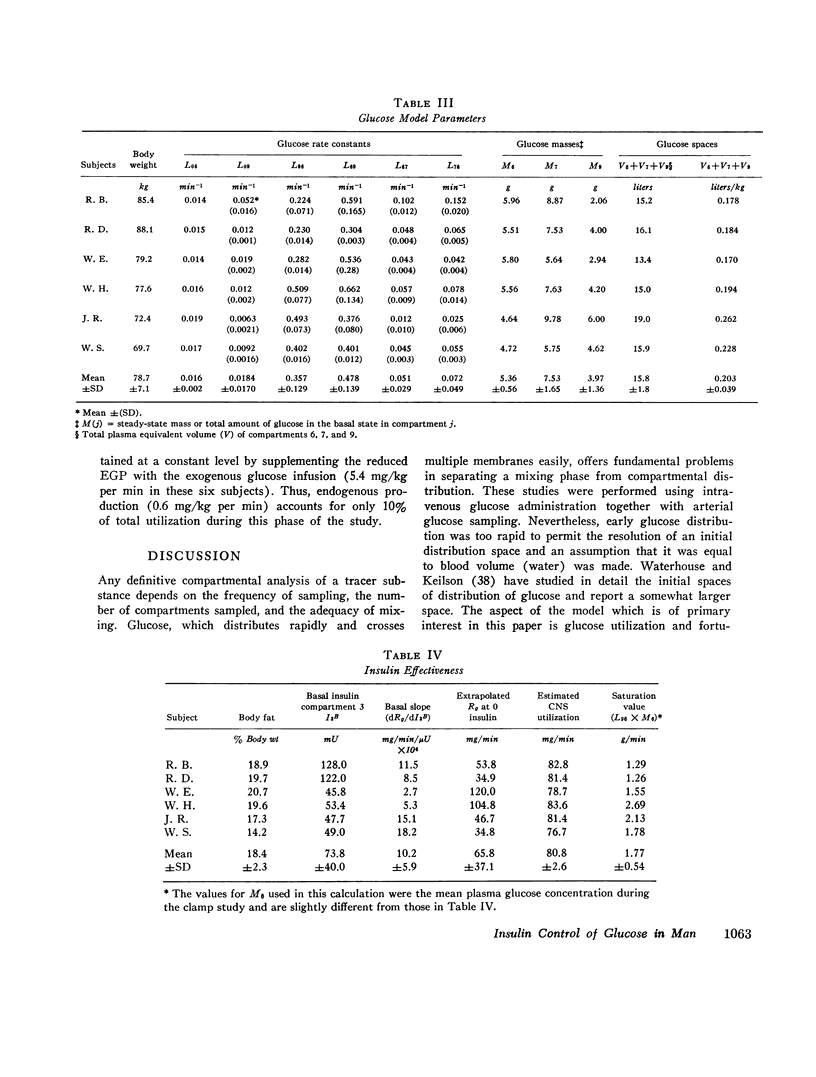
The glucose model, a parallel three-compartment model, has a central compartment (mass = 68±7 mg/kg; space of distribution = blood water volume) in rapid equilibrium with a smaller compartment (50±17 mg/kg) and in slow equilibrium with a larger compartment (96±21 mg/kg). The total plasma equivalent space for the glucose system averaged 15.8 liters or 20.3% body weight. Two modes of glucose loss are introduced in the model. One is a zero-order loss (insulin and glucose independent) from blood to the central nervous system; its magnitude was estimated from published data. The other is an insulin-dependent loss, occurring from the rapidly equilibrating compartment and, in the basal period, is smaller than the insulin-independent loss. Endogenous glucose production averaged 1.74 mg/kg per min in the basal state and enters the central compartment directly.
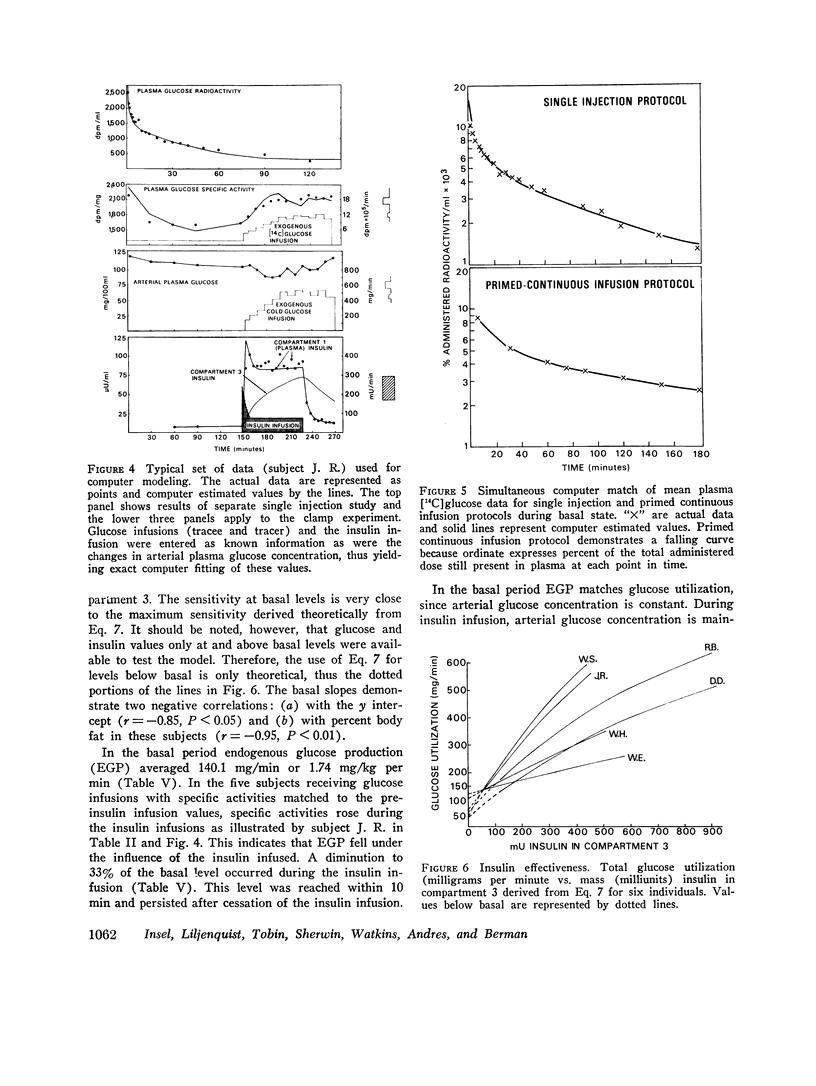
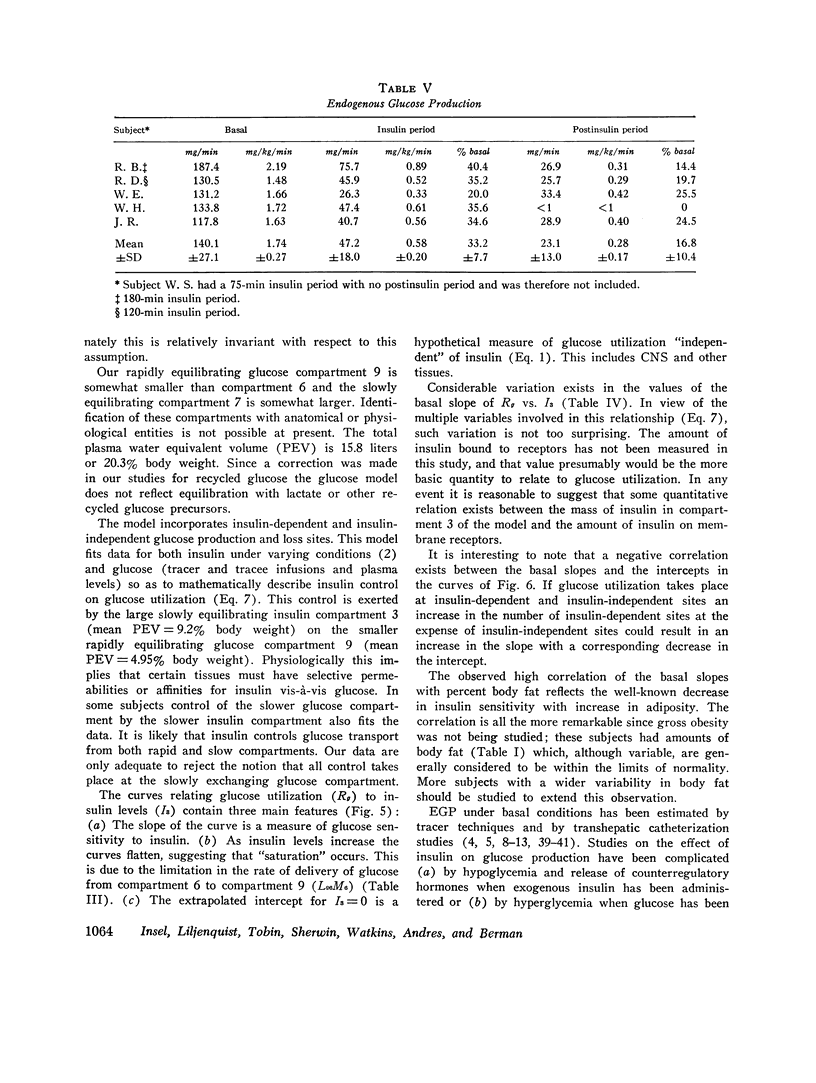
During the glucose clamp experiments plasma insulin levels reached a plateau of 95±8 μU/ml. Over the entire range of insulin levels studied, glucose losses were best correlated with levels of insulin in a slowly equilibrating insulin compartment of a three-compartment insulin model. A proportional control by this compartment on glucose utilization was adequate to satisfy the observed data. Insulin also rapidly decreased the endogenous glucose production to 33% of its basal level (0.58 mg/kg per min), this suppression being maintained for at least 40 min after exogenous insulin infusion was terminated and after plasma insulin concentrations had returned to basal levels.
The change in glucose utilization per unit change in insulin in the slowly equilibrating insulin compartment is proposed as a new measure for insulin sensitivity. This defines insulin effects more precisely than previously used measures, such as plasma glucose/plasma insulin concentration ratios.
Glucose clamp studies and the modeling of the coupled kinetics of glucose and insulin offers a new and potentially valuable tool to the study of altered states of carbohydrate metabolism.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andres R. Aging and diabetes. Med Clin North Am. 1971 Jul;55(4):835–846. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)32479-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkins G. L. Investigation of some theoretical models relating the concentrations of glucose and insulin in plasma. J Theor Biol. 1971 Sep;32(3):471–494. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(71)90152-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAKER N., SHIPLEY R. A., CLARK R. E., INCEFY G. E. C14 studies in carbohydrate metabolism: glucose pool size and rate of turnover in the normal rat. Am J Physiol. 1959 Feb;196(2):245–252. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1959.196.2.245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEHNKE A. R. Anthropometric fractionation of body weight. J Appl Physiol. 1961 Nov;16:949–954. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1961.16.6.949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRITTON H. G. PERMEABILITY OF THE HUMAN RED CELL TO LABELLED GLUCOSE. J Physiol. 1964 Jan;170:1–20. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betz A. L., Gilboe D. D., Yudilevich D. L., Drewes L. R. Kinetics of unidirectional glucose transport into the isolated dog brain. Am J Physiol. 1973 Sep;225(3):586–592. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.225.3.586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. S., Larner J. Rapid activation-inactivation of liver uridine diphosphate glucose-glycogen transferase and phosphorylase by insulin and glucagon in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1967 Mar 25;242(6):1354–1356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buschiazzo P. M., Terrell E. B., Regen D. M. Sugar transport across the blood-brain barrier. Am J Physiol. 1970 Nov;219(5):1505–1513. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.219.5.1505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P., Desbuquois B., Krug F. Insulin-receptor interactions in liver cell membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jul 16;44(2):333–339. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90604-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEBODO R. C., STEELE R., ALTSZULER N., DUNN A., BISHOP J. S. ON THE HORMONAL REGULATION OF CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM; STUDIES WITH C14 GLUCOSE. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1963;19:445–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUNN D. F., FRIEDMANN B., MAASS A. R., REICHARD G. A., WEINHOUSE S. Effects of insulin on blood glucose entry and removal rates in normal dogs. J Biol Chem. 1957 Mar;225(1):225–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felig P., Wahren J. Influence of endogenous insulin secretion on splanchnic glucose and amino acid metabolism in man. J Clin Invest. 1971 Aug;50(8):1702–1711. doi: 10.1172/JCI106659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Insulin receptors in the liver: specific binding of ( 125 I)insulin to the plasma membrane and its relation to insulin bioactivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Aug;68(8):1833–1837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.8.1833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatewood L. C., Ackerman E., Rosevear J. W., Molnar G. D. Modeling blood glucose dynamics. Behav Sci. 1970 Jan;15(1):72–87. doi: 10.1002/bs.3830150108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HETENYI G., Jr, WRENSHALL G. A., BEST C. H. Rates of production, utilization, accumulation and apparent distribution space of glucose. Effects of insulin in dogs using a validated tracer method. Diabetes. 1961 Jul-Aug;10:304–311. doi: 10.2337/diab.10.4.304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas M. L., Shenkman L., Weissman P., Andres R. A semiautomated technic for radioimmunoassay. Double antibody assay of insulin. Diabetes. 1970 Feb;19(2):127–131. doi: 10.2337/diab.19.2.127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hetenyi G., Jr [The regulation of glucose production and utilization in the intact animal]. Acta Diabetol Lat. 1971 Mar-Apr;8(2):213–227. doi: 10.1007/BF01550867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronfeld D. S., Ramberg C. F., Jr, Shames D. M. Multicompartmental analysis of glucose kinetics in normal and hypoglycemic cows. Am J Physiol. 1971 Apr;220(4):886–893. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.4.886. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEONARDS J. R., LANDAU B. R., CRAIG J. W., MARTIN F. I., MILLER M., BARRY F. M. Regulation of blood glucose concentration: hepatic action of insulin. Am J Physiol. 1961 Jul;201:47–54. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1961.201.1.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long C. L., Spencer J. L., Kinney J. M., Geiger J. W. Carbohydrate metabolism in normal man and effect of glucose infusion. J Appl Physiol. 1971 Jul;31(1):102–109. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1971.31.1.102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MADISON L. L., COMBES B., ADAMS R., STRICKLAND W. The physiological significance of the secretion of endogenous insulin into the portal circulation. III. Evidence for a direct immediate effect of insulin on the balance of glucose across the liver. J Clin Invest. 1960 Mar;39:507–522. doi: 10.1172/JCI104065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MYERS J. D. Net splanchnic glucose production in normal man and in various disease states. J Clin Invest. 1950 Nov;29(11):1421–1429. doi: 10.1172/JCI102380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortimore G. E., King E., Jr, Mondon C. E., Glinsmann W. H. Effects of insulin on net carbohydrate alterations in perfused rat liver. Am J Physiol. 1967 Jan;212(1):179–183. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.212.1.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norwich K. H. Mathematical models of the kinetics of glucose and insulin in plasma. Bull Math Biophys. 1969 Mar;31(1):105–121. doi: 10.1007/BF02478212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARK C. R., JOHNSON L. H., WRIGHT J. H., Jr, BATSEL H. Effect of insulin on transport of several hexoses and pentoses into cells of muscle and brain. Am J Physiol. 1957 Oct;191(1):13–18. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1957.191.1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REICHARD G. A., JACOBS A. G., KIMBEL P., HOCHELLA N. J., WEINHOUSE S. Effects of insulin on blood glucose entry and removal rates in man. Diabetes. 1960 Nov-Dec;9:447–453. doi: 10.2337/diab.9.6.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEARLE G. L., MORTIMORE G. E., BUCKLEY R. E., REILLY W. A. Plasma glucose turnover in humans as studied with C14 glucose: influence of insulin and tolbutamide. Diabetes. 1959 May-Jun;8(3):167–173. doi: 10.2337/diab.8.3.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEGAL S., BERMAN M., BLAIR A. The metabolism of variously C14-labeled glucose in man and an estimation of the extent of glucose metabolism by the hexose monophosphate pathway. J Clin Invest. 1961 Jul;40:1263–1279. doi: 10.1172/JCI104356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEELE R., BISHOP J. S., DUNN A., ALTSZULER N., RATHBEB I., DEBODO R. C. INHIBITION BY INSULIN OF HEPATIC GLUCOSE PRODUCTION IN THE NORMAL DOG. Am J Physiol. 1965 Feb;208:301–306. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.208.2.301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheinberg P., Stead E. A. THE CEREBRAL BLOOD FLOW IN MALE SUBJECTS AS MEASURED BY THE NITROUS OXIDE TECHNIQUE. NORMAL VALUES FOR BLOOD FLOW, OXYGEN UTILIZATION, GLUCOSE UTILIZATION, AND PERIPHERAL RESISTANCE, WITH OBSERVATIONS ON THE EFFECT OF TILTING AND ANXIETY. J Clin Invest. 1949 Sep;28(5 Pt 2):1163–1171. doi: 10.1172/JCI102150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal H. L. Enzymatic interconversion of active and inactive forms of enzymes. Science. 1973 Apr 6;180(4081):25–32. doi: 10.1126/science.180.4081.25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segre G., Turco G. L., Vercellone G. Modeling blood glucose and insulin kinetics in normal, diabetic and obese subjects. Diabetes. 1973 Feb;22(2):94–103. doi: 10.2337/diab.22.2.94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen S. W., Reaven G. M., Farquhar J. W. Comparison of impedance to insulin-mediated glucose uptake in normal subjects and in subjects with latent diabetes. J Clin Invest. 1970 Dec;49(12):2151–2160. doi: 10.1172/JCI106433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwin R. S., Kramer K. J., Tobin J. D., Insel P. A., Liljenquist J. E., Berman M., Andres R. A model of the kinetics of insulin in man. J Clin Invest. 1974 May;53(5):1481–1492. doi: 10.1172/JCI107697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Meyts P., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr, Gavin J. R., 3rd, Lesniak M. A. Insulin interactions with its receptors: experimental evidence for negative cooperativity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Nov 1;55(1):154–161. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(73)80072-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



