Abstract
Hepatic stellate cells (HSC) are important mediators of liver fibrosis. Hormones linked to downstream intracellular Ca2+ signals upregulate HSC proliferation, but the mechanisms by which this occurs are unknown. Nuclear and cytosolic Ca2+ signals may have distinct effects on cell proliferation, so we expressed plasmid and adenoviral constructs containing the Ca2+ chelator parvalbumin (PV) linked to either a nuclear localization sequence (NLS) or a nuclear export sequence (NES) to block Ca2+ signals in distinct compartments within LX-2 immortalized human HSC and primary rat HSC. PV-NLS and PV-NES constructs each targeted to the appropriate intracellular compartment and blocked Ca2+ signals only within that compartment. PV-NLS and PV-NES constructs inhibited HSC growth. Furthermore, blockade of nuclear or cytosolic Ca2+ signals arrested growth at the G2/mitosis (G2/M) cell-cycle interface and prevented the onset of mitosis. Blockade of nuclear or cytosolic Ca2+ signals downregulated phosphorylation of the G2/M checkpoint phosphatase Cdc25C. Inhibition of calmodulin kinase II (CaMK II) had identical effects on LX-2 growth and Cdc25C phosphorylation. We propose that nuclear and cytosolic Ca2+ are critical signals that regulate HSC growth at the G2/M checkpoint via CaMK II-mediated regulation of Cdc25C phosphorylation. These data provide a new logical target for pharmacological therapy directed against progression of liver fibrosis.
Keywords: Cyclin, Cdc25C, Parvalbumin, Nuclear calcium, Cytosolic calcium, Liver fibrosis, Hepatic stellate cell
1. Introduction
Hepatic stellate cells (HSC) are important fibrogenic cells within the liver. Although HSC in the uninjured liver secrete little collagen and other scar matrix, compelling evidence demonstrates that HSC in the injured liver undergo structural and functional alterations promoting scar formation; such HSC are often referred to as “activated” HSC. Activated HSC undergo myofibroblastic differentiation, markedly increase secretion of collagen and other matrix proteins, migrate to regions of injury, interact with inflammatory cells, and rapidly increase proliferation [1]. Each of these responses has been identified as a potential target for anti-fibrotic therapy; hence, intense study has been dedicated to each.
Despite ongoing studies on each of these subjects, HSC growth is poorly understood. Known regulators of HSC proliferation are varied. Bile acids have been shown to upregulate HSC proliferation via the epidermal growth factor receptor [2]. The mechanisms involved included the extracellular signal-related kinase (ERK) and c-Jun nuclear kinase (JNK) pathways, suggesting that multiple second messenger systems may be linked to HSC proliferation [1,3]. In contrast, the cAMP pathway has been shown to inhibit HSC growth [4]. Finally, studies have suggested that Ca2+-agonist hormones can induce HSC proliferation [5], although the mechanisms are not well understood.
The potential role of intracellular Ca2+ (Cai2+) signaling in HSC growth is of great interest. HSC express a variety of plasma membrane receptors linked to Cai2+ signals, including those for endothelin [6], monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 [7], and vasopressin [8]. HSC also express P2Y receptors, which are G protein-coupled receptors linked to inositol trisphosphate-mediated increases in Cai2+ [9]. Inhibition of such P2Y receptors blocks carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-mediated cirrhosis in rats and decreases proliferation of HSC isolated from CCl4-treated animals [10]. Activated HSC express the inositol trisphosphate receptor (IP3R) Type I exclusively, and the Type I IP3R is found in a unique distribution in activated HSC [11]. Specifically, these cells express the Type I IP3R in distinct functional regions within the nucleus and in peripheral membranous cell extensions of the cytosol. In both regions, rich stores of Ca2+ are found in identical compartments, suggesting that these are distinct functional compartments regulating distinct physiological activities.
Recent studies have shown that mobilizable Ca2+ stores within the nucleus are found in regions rich in endoplasmic reticulum lipids [12]. This novel cell compartment has been designated the nucleoplasmic reticulum (NR). Expression of targeted forms of the endogenous intracellular Ca2+ chelator parvalbumin (PV) has been used to show that Ca2+ signals mediated via the NR are necessary for proliferation of hepatoma cells [13]. Thus, we used the same tools to test whether similar NR-mediated Ca2+ signals are important regulators of HSC proliferation. In contrast to the findings in hepatoma cells, HSC proliferation was regulated both by nuclear and extra-nuclear Ca2+ signals. Moreover, the mechanism for such change occurred at a distinct segment of the cell cycle, suggesting that HSC growth is mediated by Cai2+ signals in a novel fashion.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Chemicals and other materials
Fetal bovine serum (FBS) and penicillin-streptomycin were purchased from Invitrogen (San Diego, CA). FuGENE-6 was purchased from Roche Applied Sciences (Palo Alto, CA). Mouse monoclonal antibodies to phospho-Cdc25C, Cdc25C, phospho-Cdc2, Cdc2, and rabbit polyclonal antibodies to calmodulin kinase II (CaMK II) and phosphorylated CaMK II were purchased from Cell Signaling Technology (Danvers, MA). Vasopressin (VP) and 1,2-Bis (2-amino-5-fluorophenoxy) ethane-N,N,N2,N2-tetraacetic acid tetrakis (acetoxymethyl) ester (BAPTA/AM) were purchased from Sigma–Aldrich (St. Louis, MO). Mouse monoclonal antibodies to β-actin were purchased from Sigma–Aldrich (St. Louis, MO). Horseradish peroxidase (HRP) conjugated rabbit anti-mouse and anti-rabbit antibodies were purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Santa Cruz, CA). ECL Plus chemiluminescence reagents were purchased from GE Healthcare (Chalfont, St. Giles, UK). Fluorescent antibodies to phospho-histone 3 were purchased from Upstate Biotechnology, Chicago, IL. Fluorescent antibodies to γ-tubulin were purchased from Sigma–Aldrich. 4′,6′-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) was purchased from Invitrogen/Molecular Probes (Eugene, OR). The CaMK II inhibitor KN-93 and its inactive derivative KN-92 were purchased from EMD Biosciences (Gibbstown, NJ). All other chemicals and materials were of the highest quality available commercially.
2.2. Cell culture
All experiments were performed using either primary rat HSC (see following section) or LX-2 cells. LX-2 cells are spontaneously immortalized human HSC with key similarities to primary myofibroblastic (activated) HSC [14,15]. Cells were cultured in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM) with 10% FBS (except where specified) and 1% penicillin–streptomycin. For all experiments, media were replaced every 3 days.
2.3. Isolation and usage of primary rat HSC
Primary rat HSC were isolated from adult male Sprague–Dawley rats (Harlan Sprague–Dawley, Indianapolis, IN) using methods published previously [9,16]. Briefly, HSC were separated using in situ pronase–collagenase perfusion of the liver followed by density gradient centrifugation and plated in plastic dishes. Cells were cultured in DMEM with or without 10% FBS and with 1% penicillin–streptomycin. All experiments were performed at Day 7 following HSC isolation, at which time cells are known to be myofibroblastic [17].
2.4. Design and usage of PV constructs
Plasmid and adenovirus constructs for DsRed alone, PV ligated to a nuclear localization sequence (NLS) and DsRed (PV-NLS-DsRed), and PV ligated to a nuclear export sequence (NES) and DsRed (PV-NES-DsRed), as described previously [13], were used for all experiments. Expression of constructs in LX-2 cells was accomplished by plasmid transfection with FuGENE-6 according to manufacturer instructions. Expression of constructs in HSC was accomplished by adenoviral infection. Adenoviral constructs were amplified using HEK-293 cells then purified. HSC were plated in 96-well plates at Day 5 following isolation and infected with DsRed, PV-NLS-DsRed, or PV-NES-DsRed for 48 h so that analysis was performed at Day 7 following isolation.
2.5. Visualization of DsRed fluorescence
Targeting of PV constructs was accomplished by live cell confocal fluorescence microscopy. Transfected LX-2 and HSC were grown on glass coverslips, loaded with the nuclear fluorescent dye TOPRO-3 (Invitrogen Molecular Probes), perifused with HEPES buffer, and observed using a Zeiss LSM 510 confocal microscopy system equipped with Kr–Ar and He–Ne lasers. Cells were excited at 568 nm at observed at >585nm to detect DsRed.
2.6. Measurement of intracellular Ca2+ signals
Changes in intracellular Ca2+ over time in LX-2 and HSC subcellular compartments were detected by confocal video microscopy as described previously [9,18]. Briefly, cells were plated on glass coverslips, loaded with the cell-permeant Ca2+-sensitive fluorophore fluo-4/AM (which has been used to detect Ca2+ signals in the nucleus and extra-nuclear cytoplasm [12]), and perifused first with HEPES buffer, then with HEPES buffer containing VP (2 µM). Changes in fluo-4 fluorescence were detected using a Zeiss LSM510 confocal imaging system equipped with a Kr–Ar laser. Serial images were collected at least once per second, and data were exported to a spreadsheet for quantitative description and analysis. In separate experiments, the effect of PV-NLS-DsRed or PV-NES-DsRed expression on stored Ca2+ in transfected LX-2 cells was determined. Cells were loaded with the low-affinity Ca2+ dye Mag-fluo-4/AM (previously shown to identify HSC Ca2+ stores [11]) as described above. Changes in Mag-fluo-4 fluorescence were determined as described previously, and transfected cells were identified by DsRed fluorescence.
2.7. Measurement of bromo-deoxyuridine (BrdU) incorporation
Changes in cell proliferation were determined by BrdU incorporation using a commercial ELISA kit (Roche Applied Sciences) according to manufacturer instructions. Experimental design was as follows: first cells were plated in 96-well plates and transfected or infected with DsRed alone (control), PV-NLS-DsRed, PV-NES-DsRed, or were left untransfected/uninfected in the presence or absence of FBS. Detection of BrdU uptake was determined 48 h after transfection. Cells were labeled with BrdU labeling solution for 2 h, and then the reaction was stopped by fixation. Detection of BrdU was accomplished by anti-BrdU antibody. Colorimetric substrate detection was accomplished using a multi-plate reader (Bio-Tek Instruments, Winooski, VT). In separate experiments, LX-2 cells were either untreated, or treated overnight with the CaMK II inhibitor KN-93 or its inactive form KN-92 (20 µM each), and BrdU incorporation was determined as described above. In separate experiments, LX-2 cells were cultured in serum-free conditions, 10% FBS, or serum-free +VP (2 µM) in the presence or absence of BAPTA/AM (50 µM) overnight. BrdU uptake was assessed as described above.
2.8. Cell cycle analysis
LX-2 cells were either untransfected, or transfected with DsRed, PV-NLS-DsRed, or PV-NES-DsRed, washed in PBS, and fixed overnight in 70% ethanol at 4 °C. After washing in PBS, DNase (100 µg/ml) was added for 5min at room temperature. Cells were then labeled with TOPRO-3 (1 µM), and cell cycle was determined by fluorescent activated cell sorting (FACS) using the FACSCalibur (BD Biosciences, Rockville, MD) sorter for sorting and Flowjo software Version 8.7 (TreeStar, Inc., Ashland, OR) for analysis.
2.9. Determination of mitotic index
LX-2 cells were transfected identically to those in the prior section, and mitotic indexes were determined by immunofluorescence as described previously [13]. Briefly, cells were labeled with antibodies to phospho-histone 3 and γ-tubulin, and nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. Fluorescence was visualized with a Nikon Eclipse E800 (Nikon Instruments, Inc., Melville, NY) fluorescence microscope. Mitotic cells were defined by the presence of DNA condensation and phospho-histone 3 positivity. Mitotic index was calculated at the percentage of mitotic cells as a function of total cell number. At least 10 fields representing a total of >100 cells were visualized for each condition.
2.10. Immunofluorescence
Distribution of CaMKII in LX-2 cells was detected by immunofluorescence as described above. Briefly, cells were cultured in either serum free or 10% FBS conditions and labeled with rabbit polyclonal antibodies to phospho-CaMK II, total CaMK II, or no primary antibody (negative control). Cells were then labeled with FITC-conjugated anti-rabbit antibody, and nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. Fluorescence was visualized with a Nikon Eclipse E800 fluorescence microscope.
2.11. Immunoblot
LX-2 cells were plated, and expression of targeted PV constructs was accomplished as described above. Cells were washed ×2 with PBS, then solubilized in trypsin lysis buffer at 4 °C. Cell lysates were denatured at 95 °C for 5 min, then subjected to SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis followed by Electrophoretic transfer to a PVDF membrane. Blotting was performed using mouse monoclonal primary antibodies to phospho-Cdc25C, Cdc25C, phospho-Cdc2, Cdc2 (diluted 1:1000 each) or β-actin (1:5000) in 5% non-fat milk in PBS with 1% Tween 20 overnight. Secondary labeling with horseradish-peroxidase-conjugated anti-mouse IgG (1:5000) was performed, and bands were detected using chemiluminescence. Images were scanned and quantified using a commercial densitometer (Fotodyne, Hartland, WI). In separate experiments, LX-2 cells were either untreated, or treated overnight with the CaMK II inhibitor KN-93 or its inactive form KN-92 (20 µM each), and immunoblot analysis was performed to detect phospho-Cdc25C or β-actin as described above.
2.12. Immunoblot of fractionated cells
LX-2 cells were transfected with DsRed, PV-NLS-DsRed, or PV-NES-DsRed as described above. Cells were washed twice with ice-cold phosphate-buffered saline, harvested by scraping, and lysed in lysis buffer containing 20 mM [4-(2-hydroethyl)-1-piperazine ethanesulfonic acid], 10mM KCl, 2mM MgCl2, and 0.5% Nonidet P-40 at pH 7.0. Cells were incubated on ice for 10 min then vortexed. The homogenate was centrifuged at 1500 × g for 5 min to sediment the nuclei. The supernatant was then centrifuged at a maximum speed of 16,100 × g for 20 min, and the resulting supernatant formed the non-nuclear fraction. The nuclear pellet was washed ×3 with lysis buffer to remove any contamination fromcytoplasmic membranes. Immunoblots of nuclear and cytosolic fractions were performed as described above using antibodies to DsRed (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA), γ-tubulin (Cell Signaling Technology), and lamin B1 (Abcam, Cambridge, MA).
2.13. Statistical analysis
All data are reported as mean±standard deviation. Data were analyzed by 2-tailed t-test using open-source software (http://www.quantitativeskills.com/sisa/statistics/t-test.htm).
3. Results
3.1. Ca2+ signals in LX-2 and HSC subcellular compartments are inhibited by targeted PV constructs
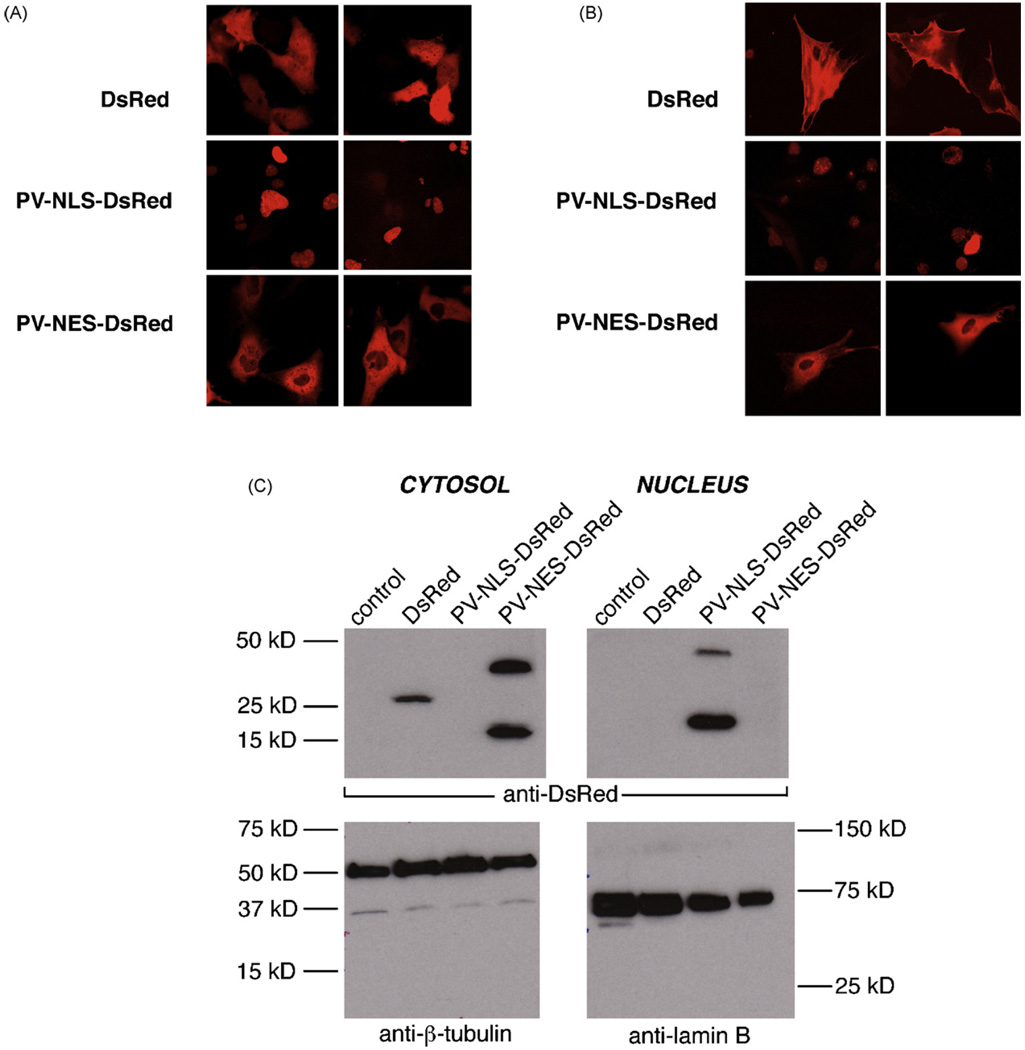
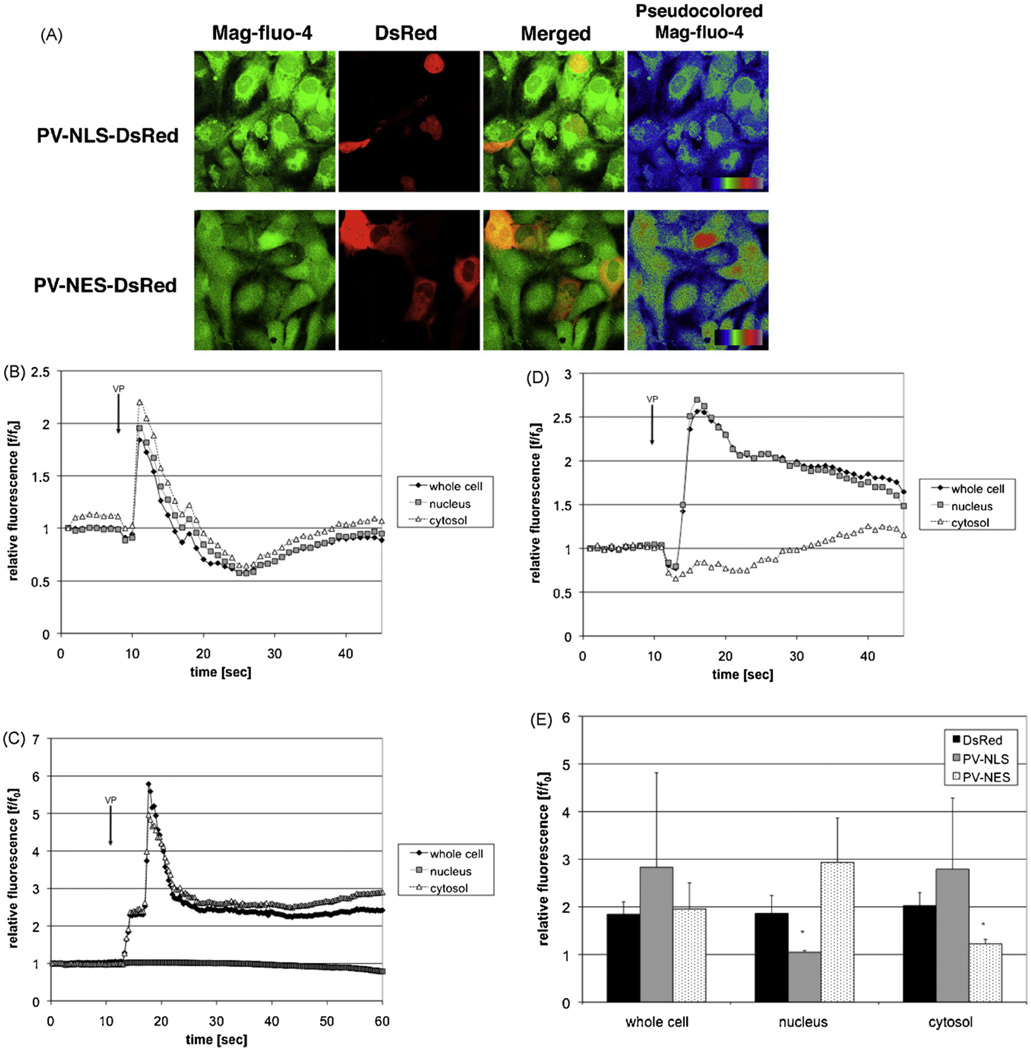
PV constructs including either a nuclear localization sequence (NLS) or nuclear export sequence (NES) for subcellular targeting and the fluorophore DsRed for detection of targeting were used for the studies described in this manuscript [13]. Controls included untransfected/uninfected cells or cells transfected with DsRed alone. The usefulness of this approach for studies in HSC was determined in two ways. First, appropriate targeting of constructs was verified by confocal microscopic examination of transfected LX-2 cells and primary rat HSC. As seen in Fig. 1, DsRed expression was seen throughout the nucleus and cytoplasm. In contrast, PV-NLS-DsRed expression was noted only in nuclei, and PV-NES-DsRed expression was noted only in the extra-nuclear cytoplasm of LX-2 cells (Fig. 1A) and HSC (Fig. 1B). Furthermore, confirmation of appropriate PV targeting was accomplished by immunoblot (Fig. 1C), showing that PV-NLS-DsRed was detected only in nuclear protein fractions and that PV-NES-DsRed was detected only in cytosolic protein fractions. Second, functional blockade of Ca2+ signaling was assessed by confocal video microscopy. No change in baseline Ca2+ stores was noted in LX-2 cells transfected with PV-NLS-DsRed or PV-NES-DsRed (Fig. 2A). However, as seen in Fig. 2B–E, transfection with DsRed had no effect on intracellular Ca2+ signals induced by perifusion with VP [8]. In contrast, transfection with PV-NLS-DsRed blocked nuclear but not cytosolic Ca2+ signals, and transfection with PV-NES-DsRed blocked cytosolic but not nuclear Ca2+ signals. Taken together, these findings indicate that targeted PV constructs are useful and appropriate for these studies, as they induce specific subcellular blockade of hormone-induced Ca2+ signals.
Fig. 1.
PV constructs can be targeted to subcellular regions within LX-2 cells and primary myofibroblastic HSC. (A) Expression in LX-2 cells. LX-2 cells were transfected with DsRed, PV-NLS-DsRed, or PV-NES-DsRed, and fluorescence distribution was determined by confocal microscopy. Two representative images are seen for each condition. As seen in the upper figure, DsRed fluorescence is seen throughout the cell. On the other hand, as seen in the middle figure, PV-NLS-DsRed fluorescence is limited to the nucleus, and PV-NES-DsRed fluorescence is limited to the extra-nuclear cytoplasm. (B) Expression in primary rat HSC. HSC were infected with DsRed, PV-NLS-DsRed, or PV-NES-DsRed, and fluorescence distribution was determined as described above. All cells are shown at 630× magnification. (C) Verification of PV construct targeting in transfected LX-2 cells. LX-2 cells were transfected as described above then saponified. Crude protein extracts were separated into nuclear and cytosolic fractions. Expression of DsRed (predicted MW 30 kD with non-specific band at 20 kD reported by manufacturer), β-tubulin (cytosolic marker, 55 kD), and lamin B (nuclear marker, 68 kD) were determined by immunoblot. DsRed and PV-NES-DsRed were detected only in cytosolic fractions, and PV-NLS-DsRed was detected only in nuclear fractions, demonstrating the specificity of targeting of these constructs. The predicted MW of PV-DsRed constructs is 42 kD, based on a MWof 12 kD for PV and 30 kD for DsRed.
Fig. 2.
Targeted PV constructs block Ca2+ signals within distinct subcellular regions within LX-2 cells. (A) PV constructs do not alter stored Ca2+. LX-2 cells were transfected with PV-NLS-DsRed or PV-NES-DsRed and loaded with the low-affinity Ca2+ fluorophoreMag-fluo-4, which is an indicator of stored Ca2+. As can be seen by the representative confocal images, no change in Mag-fluo-4 fluorescence can be seen in transfected cells. (B–D) Representative tracings of confocal video microscopy experiments. LX-2 cells were transfected with DsRed (B), PV-NLS-DsRed (C), or PV-NES-DsRed (D), and Ca2+ signals were assessed using confocal video microscopy. Representative tracings showing Ca2+ changes over time after perifusion with VP (2 µM) [8] are shown. Simultaneous Ca2+ increases of similar magnitude were observed in cells transfected with DsRed alone. However, in cells transfected with PV-NLS-DsRed, Ca2+ increases were limited to the extra-nuclear cytoplasm. In contrast, cells transfected with PV-NES-DsRed had Ca2+ increases limited to the nucleus. E. Composite of confocal video microscopy experiments. Peak fluorescence/baseline fluorescence ratios (f/f0) were determined for each condition. PV-NLS-DsRed-expressing cells exhibited no increase in Ca2+ within nuclei, and PV-NES-DsRed-expressing cells exhibited no increase in Ca2+ within the cytosol (n = 4 separate perifusions; *p < 0.05 vs. DsRed).
3.2. Nuclear and cytosolic Ca2+ signals each regulate LX-2 and HSC proliferation
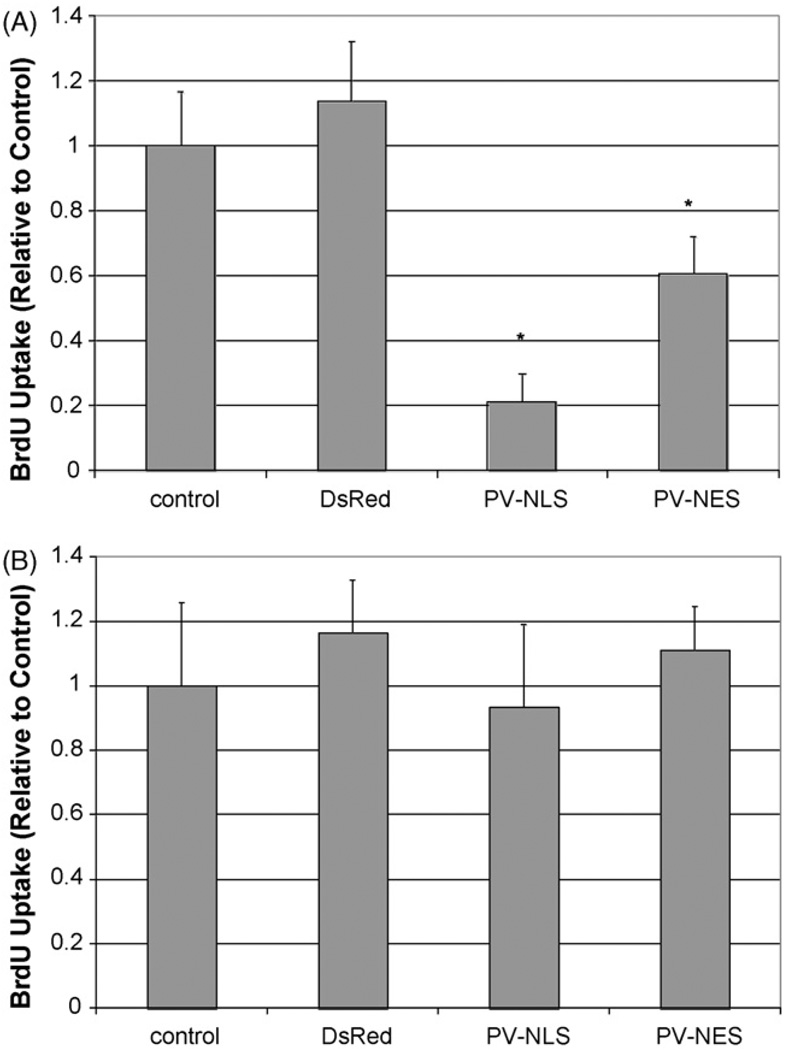
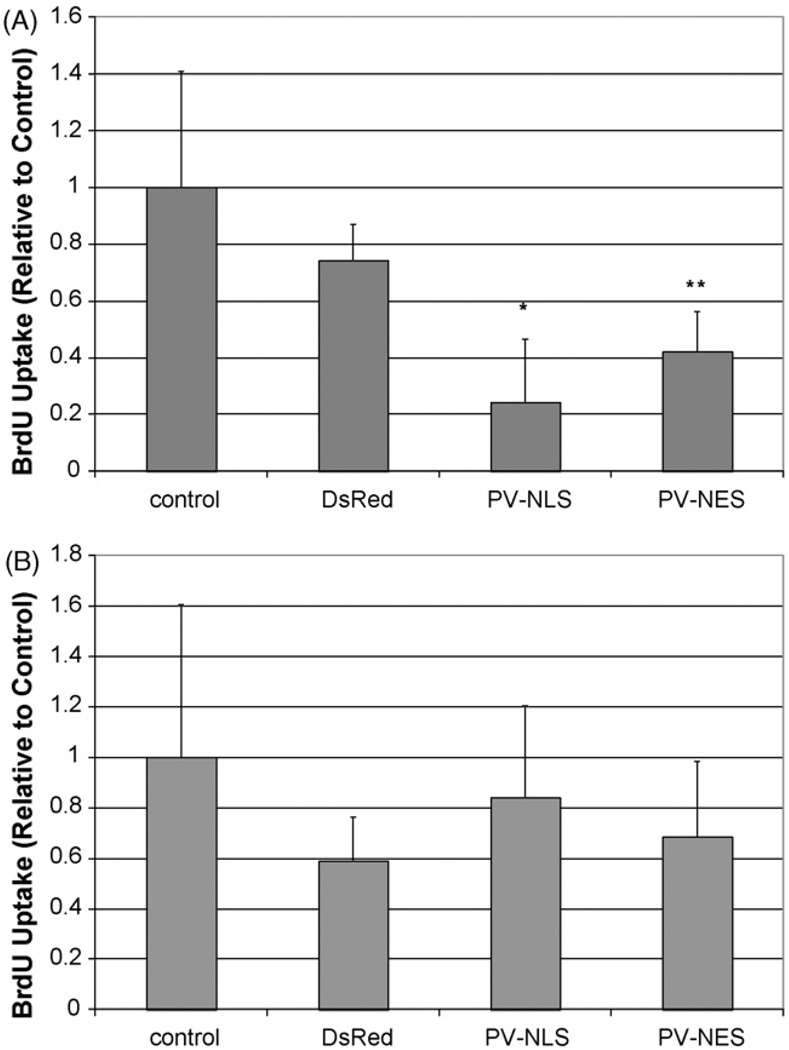
The proliferation of LX-2 cells and HSC after transfection or infection with targeted PV constructs is seen in Figs. 3 and 4, respectively. Transfection of LX-2 cells or HSC with either PV-NLS-DsRed or PV-NES-DsRed constructs blocked serum-sensitive proliferation of cells. For both groups, the effect of PV-NLS-DsRed appeared to be of greater magnitude than that of PV-NES-DsRed; however, a significant difference was seen only in LX-2 cells (p < 10−5 for PV-NLS-DsRed vs. PV-NES-DsRed). These studies demonstrate that growth of LX-2 cells and HSC are regulated by both nuclear and cytosolic Ca2+ signals. Finally, the effect of blockade of Ca2+ signals throughout the cell on LX-2 growth was determined by treating the cells with the cell-permeant Ca2+ chelator BAPTA/AM. Interestingly, BAPTA/AM blocked growth of HSC in serum-free, 10% FBS, and VP-treated conditions (Fig. 5). Furthermore, VP did not increase LX-2 proliferation, unlike in the previous report of Bataller et al. [8], perhaps due to differences between primary HSC and LX-2 cells or methodological differences in assessment of cell proliferation.
Fig. 3.
Ca2+ chelation within nuclei or extra-nuclear cytoplasm inhibits LX-2 cell proliferation. (A) Proliferation in the presence of serum. LX-2 cells were either untransfected or transfected with DsRed, PV-NLS-DsRed, or PV-NES DsRed, and proliferation was determined by BrdU uptake. Relative to control, proliferation of cells transfected with either PV-NLS-DsRed or PV-NES-DsRed was diminished (*p < 10−5; n = 10 for each condition). (B) Proliferation in the absence of serum. LX-2 cells were transfected identically to those in (A); however, cells were grown in serum-free media. As seen, no change in proliferation was noted.
Fig. 4.
Ca2+ chelation within nuclei or extra-nuclear cytoplasm inhibits proliferation of activated primary rat HSC. (A) Proliferation in the presence of serum. Primary rat HSC were either uninfected or infected with adenoviral vectors containing DsRed, PV-NLS-DsRed, or PV-NES DsRed, and proliferation was determined by BrdU uptake. Relative to control, proliferation of cells transfected with either PV-NLS-DsRed or PV-NES-DsRed was diminished (*p < 0.01; **p < 0.05; n = 5 for each condition). (B) Proliferation in the absence of serum. Primary rat HSC were infected identically to those in (A); however, cells were grown in serum-free media. As seen, no change in proliferation was noted.
Fig. 5.
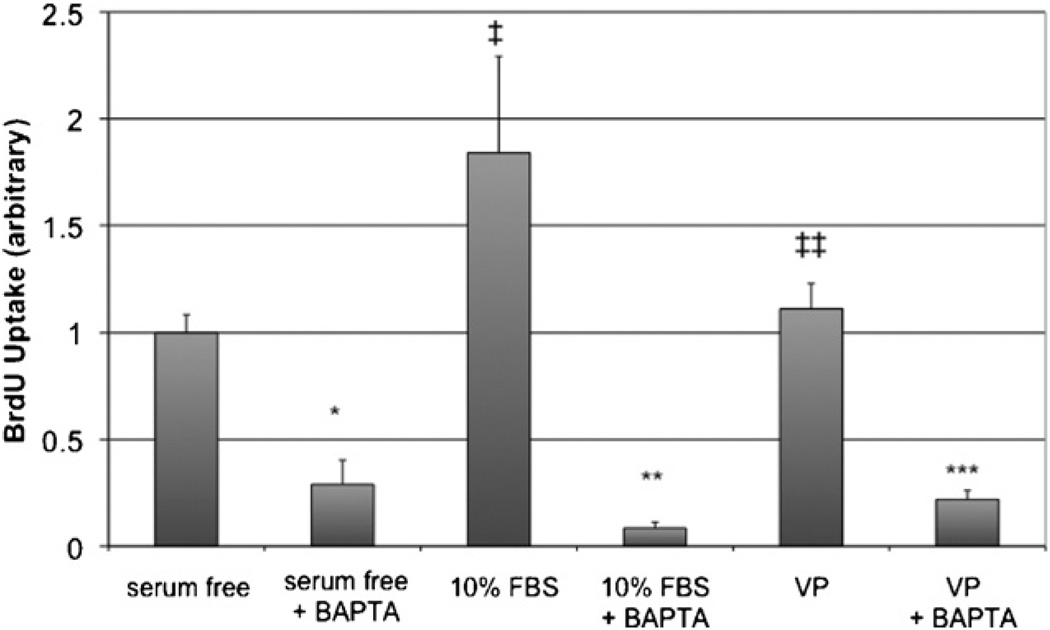
The Ca2+ chelator BAPTA/AM inhibits LX-2 proliferation. The effect of the cell-permeant Ca2+ chelator BAPTA/AM on cell proliferation was determined in cells under serum-free, serum-treated, and VP-treated conditions. Serum significantly increased LX-2 growth (‡p < 0.02 vs. control), whereas, VP had no effect (‡‡ p = NS). BAPTA/AM significantly blocked LX-2 growth in all conditions (*p < 10−5 vs. serum-free; **p = 0.001 vs. 10% FBS; ***p < 10−5 vs. VP; n = 5 for all conditions).
3.3. Blockade of nuclear or cytosolic Ca2+ signals arrests LX-2 cells in G2 phase and prevents entry of LX-2 cells into mitosis
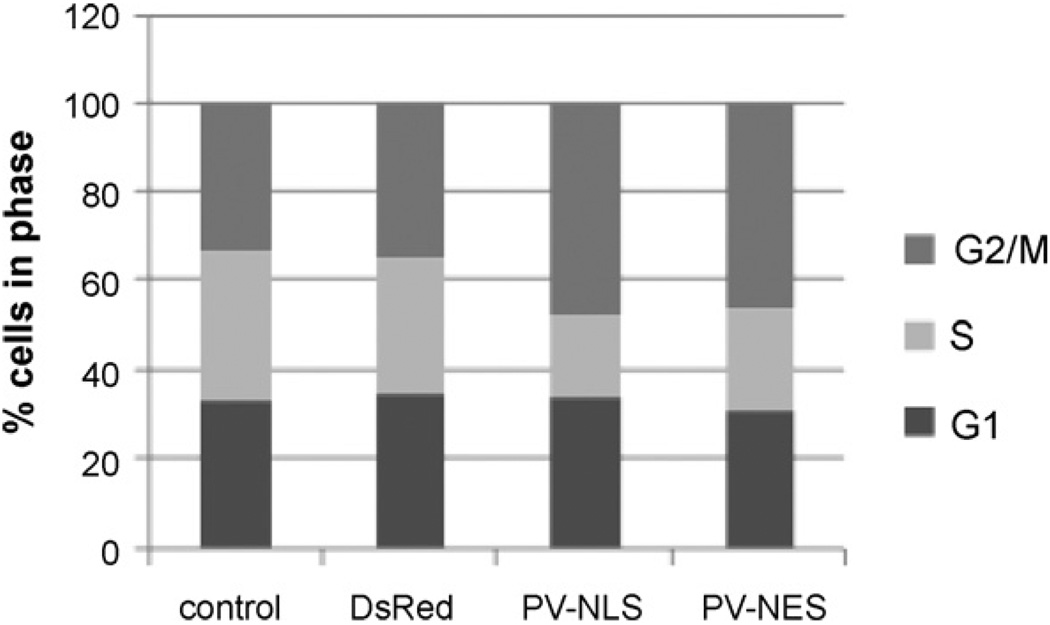
The effect of transfection of LX-2 cells with PV-NLS-DsRed or PVNES-DsRed constructs on cell cycle phase was determined using flow cytometry. As shown in Fig. 6, the percentage of cells in G2/M phases detected by flow cytometry increased from 33–35% to 46–47% after transfection with either PV-NLS-DsRed or PV-NES-DsRed. The percentages of control cells in G2/M phases are similar to results published previously [19]. To clarify the functional effects of Ca2+ blockade on cell cycle activity the mitotic index for each group was determined. To our knowledge, the mitotic index of HSC or LX-2 cells has not been reported previously. The number of untransfected cells undergoing mitosis was 13%, and the number of Ds-Red transfected cells undergoing mitosis was 10%. In contrast, cells transfected with PV-NLS-DsRed or PV-NES-DsRed exhibited no mitotic figures. These data show that blockade of nuclear or cytosolic Ca2+ signals prevents progression of LX-2 cells from G2 phase to mitosis.
Fig. 6.
Ca2+ chelation within nuclei or extra-nuclear cytoplasm arrests HSC at the G2 phase of the cell cycle. LX-2 cells were either untransfected or transfected with DsRed, PV-NLS-DsRed, or PV-NES-DsRed, and cell cycle was determined by FACS analysis. Relative to control or DsRed-transfected cells, the fraction of cells in G2/M phase was increased from 33–35% to 46–48%, with a consequent decrease in cell fraction in S phase from 30–33% to 18–23%. No change in fraction of cells in G1 phase was noted, as the fraction in all cells was 31–35%.
3.4. Blockade of nuclear or cytosolic Ca2+ signals inhibits phosphorylation of Cdc25C cyclin phosphatase
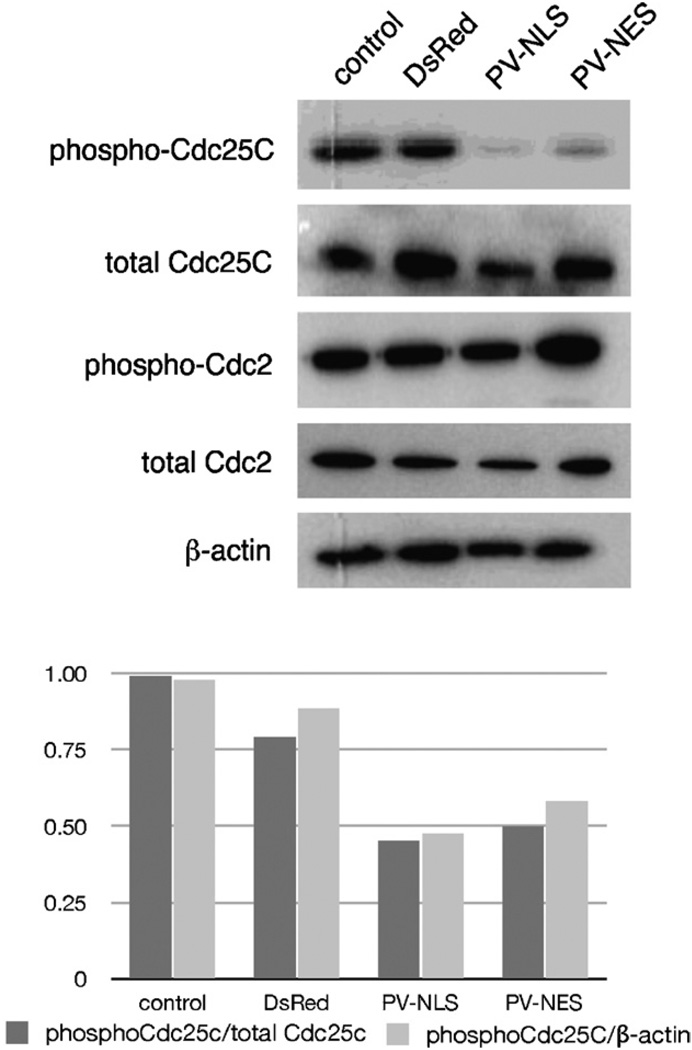
Cdc25C is a phosphatase that regulates progression from G2 into mitosis via removal of inhibitory phosphate groups from Cdc2/CDK1 [20]. Hence, we investigated changes in phosphorylation of Cdc25C after transfection with PV-NLS-DsRed and PV-NES-DsRed by immunoblot. Transfection with either PV-NLS-DsRed or PV-NES-DsRed downregulated relative expression of Cdc25C (Fig. 7). Note that no changes in Cdc2 phosphorylation are noted, since both active and inactive forms of this protein are phosphorylated. These data show that blockade of Ca2+ signals within either the nucleus or cytosol downregulates phosphorylation of the cell cycle checkpoint phosphatase Cdc25C.
Fig. 7.
Ca2+ chelation within nuclei or extra-nuclear cytoplasm inhibits phosphorylation of the cyclin phosphatase Cdc25C. (A) Immunoblot. LX-2 cells were transfected identically to those in Fig. 5, and expression of phosphorylated and total cyclins was determined by immunoblot. A marked downregulation of phospho-Cdc25C is noted in cells transfected with PV-NLS-DsRed or PV-NES-DsRed. (B) Densitometry. The downregulation of phospho-Cdc25C seen in Fig. 6A was quantitated by densitometry analysis. Downregulation of phospho-Cdc25C was approximately 50% as compared to either total Cdc25C or β-actin.
3.5. Blockade of CaMK II inhibits LX-2 proliferation and phosphorylation of Cdc25C in a manner identical to that seen after blockade of nuclear or cytosolic Ca2+ signals
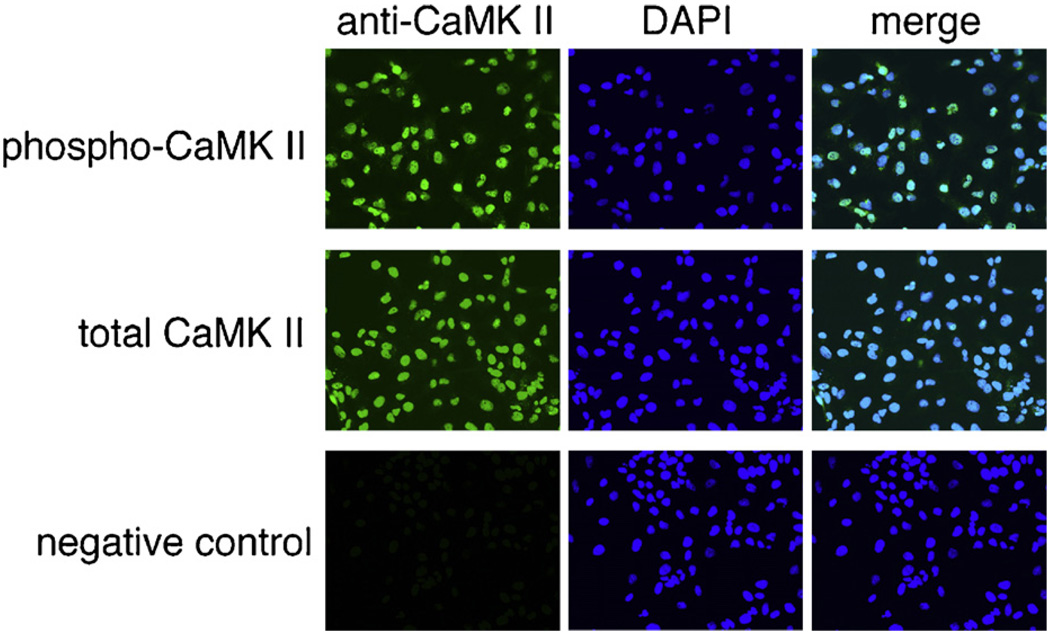
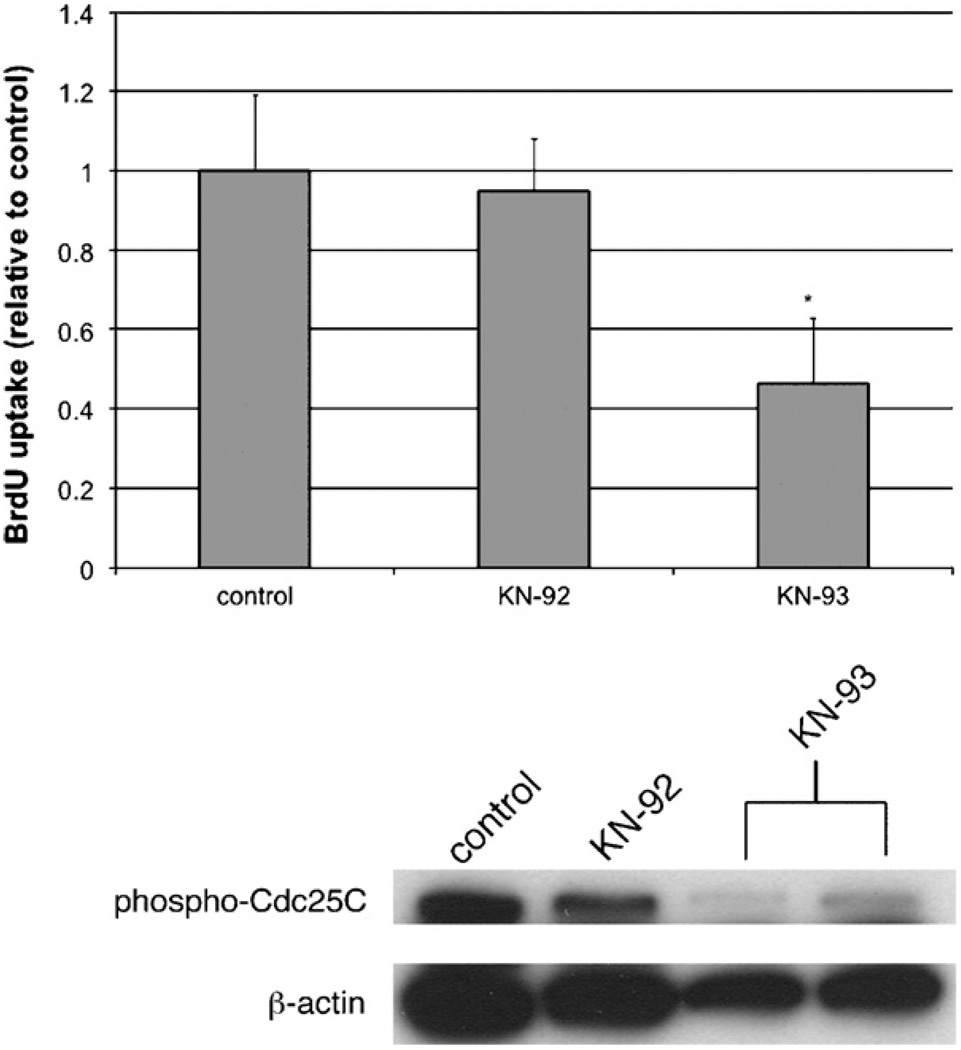
To determine the mechanism by which both nuclear and cytosolic Ca2+ signals may regulate proliferation of LX-2 cells, we investigated the potential role of the downstream Ca2+ effector molecular CaMK II. Since the end result of nuclear or cytosolic Ca2+ blockade was transduced in the nucleus, we first investigated the distribution of CaMK II in LX-2 cells. Fig. 8 demonstrates that phosphorylated and total CaMK II co-localize strongly with nuclear staining of LX-2 cells, providing evidence that they are nuclear proteins. No difference was noted in cells cultured in serum-free conditions (not shown) or 10% FBS. The effects of the CaMK II inhibitor KN-93 on LX-2 proliferation and Cdc25C phosphorylation are shown in Fig. 8. KN-93, but not its inactive form KN-92, inhibited proliferation of LX-2 cells to a similar degree as seen after blockade of Cai2+ signals (Fig. 9A). These data are also in agreement with previously published data [21]. In addition, KN-93 upregulated the number of cells in G2/M phase from 25.5% (control) or 25.6% (KN-92) to 34.0% (KN-93), analogous to the findings noted in Fig. 6. Finally, KN-93, but not KN-92, downregulated expression of phospho-Cdc25C (Fig. 9B), demonstrating that this is a common pathway inducing downregulation of LX-2 proliferation.
Fig. 8.
CaMK II is localized in nuclei of LX-2 cells. The expression of phosphorylated and total CaMK II in LX-2 cells was determined by immunofluorescence. Both phospho-CaMK II and total CaMK II were found in the same region as nuclei as evidenced by almost complete co-localization. No fluorescence was noted in control cells not treated with primary antibody, providing evidence of antibody specificity. Images seen are at 400× magnification.
Fig. 9.
The CaMK II inhibitor KN-93 inhibits LX-2 growth and expression of phospho-Cdc25C. (A) BrdU uptake. The effects of KN-93 on LX-2 growth were determined after treatment with KN-93 or its inactive metabolite KN-92. KN-93, but not KN-92, downregulated proliferation of LX-2 cells (*p < 10−5; n = 8 wells per condition). (B) Immunoblot. The effects of KN-93 and KN-92 on expression of phosphorylated Cdc25C were determined by immunoblot. KN-93, but not KN-92 decreased expression of phospho-Cdc25C.
4. Discussion
What is known about factors driving HSC proliferation is limited, but growing. Prior studies have identified potentially important HSC mitogens. These are varied and include such diverse molecules as platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), vascular endothelial cell growth factor (VEGF), thrombin, and bile acids [2,22–24]. Multiple downstream signaling pathways have been identified that regulate HSC growth; these include the ERK pathway [25], JNK pathway [26], and phosphoinositide 3-kinase [27] pathways (although others have been implicated as well; for details, please see review by Gabele et al. [3]). Although HSC express a variety of receptors for Ca2+-agonist hormones [1], only angiotensin II and VP have been shown to regulate HSC proliferation directly [5,8]. Activation of P2Y receptors for extracellular nucleotides induces a number of downstream signals in HSC, including collagen biosynthesis and cell retraction [9,11]. P2Y receptors also couple to HSC proliferation, although the mechanism was previously unknown [10]. We now provide evidence that Ca2+ signals regulate HSC growth via specific cell cycle effects, likely via the checkpoint cyclin Cdc25C.
The concept that Ca2+ signals regulate HSC proliferation at the level of the G2 to mitosis checkpoint is interesting and novel. First, this concept demonstrates that Ca2+ regulates HSC growth in a way that may be distinct from the way Ca2+ regulates hepatocyte growth. Nuclear, but not cytosolic, Ca2+ regulates growth of SKHep1 and HepG2 hepatoma cells [13], whereas both nuclear and cytosolic Ca2+ regulate growth of HSC and LX-2 cells. However, since these studies were not performed in primary hepatocytes, this proposition will need to be verified. Furthermore, the effect of nuclear Ca2+ chelation on blockade of hepatoma cell growth appears to occur at the level of progression through early prophase [13]; in contrast, nuclear or cytosolic Ca2+ chelation prevents progression of LX-2 cells from G2 phase into mitosis. An alternative explanation may be that these hepatoma cells are cancer cells, and may thus have a distinct alteration in growth regulation. A second potentially important point to glean from these studies is the critical connection of Ca2+ signals and Cdc25C. Patel and colleagues demonstrated that Ca2+ and calmodulin (CaM) regulate phosphorylation of Cdc25C in HeLa cells; the mechanism depended on CaM kinase II [28]. Here we confirm that the CaMK II inhibitor KN-93 blocked LX-2 proliferation, as noted in a recent study [21], and we now provide evidence that this compound also blocks G2/M progression and Cdc25C phosphorylation. Finally, growth arrest of HSC at the G2/mitosis interface has been demonstrated previously [29], suggesting that this may be a critical checkpoint in the HSC cell cycle and thus a valid potential target for anti-fibrotic drug therapy.
Thus, a reasonable interpretation of our findings in the context of published findings is as follows. Binding of a ligand, such as angiotensin II, to its receptor, induces phospholipase C- and inositol trisphosphate-mediated generation of Ca2+ within the cytosol and in nuclei. Ca2+ generated in each region induces conformational activation of calmodulin. Calmodulin activated in the cytosol migrates to the nucleus, and calmodulin activated in the nucleus remains in that location. Activated calmodulin induces phosphorylation and maximal activation of CaMK II, which is localized to the nucleus. CaMK II then either directly or indirectly phosphorylates Cdc25C, leading to progression through the G2/M interface.
In summary, we propose that we have discovered a novel mechanism in which Ca2+ signals activate nuclear CaMK II to regulate HSC proliferation. Because HSC proliferation appears pivotal to the progression of liver fibrosis, this may be an important target for novel anti-fibrotic pharmacologic approaches.
Acknowledgements
The authors would sincerely like to thank Dr. Scott Friedman (Mt. Sinai School of Medicine, New York) for kindly providing LX-2 cells for these studies.
Financial support: this work was supported by a Grant-in-Aid from the American Heart Association and NIH R01 DK076735 (both to J.A.D.) and a Student Research grant from the Egyptian Government Ministry of Higher Education (to E.M.S.).
Abbreviations
- HSC
hepatic stellate cell
- PV
parvalbumin
- NLS
nuclear localization sequence
- NES
nuclear export sequence
- G2/M
G2/mitosis
- Cai2+
intracellular Ca2+
- NR
nucleoplasmic reticulum
- FBS
fetal bovine serum
- HRP
horseradish peroxidase
- DAPI
4′,6′-diamidino-2-phenylindole
- DMEM
Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium
- ATP
adenosine triphosphate
- JNK
c-jun nuclear kinase
- ERK
extracellular-related kinase
- CaM
calmodulin
- CaMK II
calmodulin kinase II
Footnotes
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest that could inappropriately influence the work.
References
- 1.Friedman SL. Hepatic stellate cells: protean, multifunctional, and enigmatic cells of the liver. Physiol. Rev. 2008;88:125–172. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00013.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Svegliati-Baroni G, Ridolfi F, Hannivoort R, Saccomanno S, Homan M, De Minicis S, Jansen PL, Candelaresi C, Benedetti A, Moshage H. Bile acids induce hepatic stellate cell proliferation via activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Gastroenterology. 2005;128:1042–1055. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2005.01.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Gabele E, Brenner DA, Rippe RA. Liver fibrosis: signals leading to the amplification of the fibrogenic hepatic stellate cell. Front Biosci. 2003;8:d69–d77. doi: 10.2741/887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Houglum K, Lee KS, Chojkier M. Proliferation of hepatic stellate cells is inhibited by phosphorylation of CREB on serine 133. J. Clin. Invest. 1997;99:1322–1328. doi: 10.1172/JCI119291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bataller R, Gines P, Nicolas JM, Gorbig MN, Garcia-Ramallo E, Gasull X, Bosch J, Arroyo V, Rodes J. Angiotensin II induces contraction and proliferation of human hepatic stellate cells. Gastroenterology. 2000;118:1149–1156. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(00)70368-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Rockey DC. Characterization of endothelin receptors mediating rat hepatic stellate cell contraction. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1995;207:725–731. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1995.1247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Marra F, Romanelli RG, Giannini C, Failli P, Pastacaldi S, Arrighi MC, Pinzani M, Laffi G, Montalto P, Gentilini P. Monocyte chemotactic protein-1 as a chemoattractant for human hepatic stellate cells. Hepatology. 1999;29:140–148. doi: 10.1002/hep.510290107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Bataller R, Nicolas JM, Gines P, Esteve A, Gorbig M. Nieves, Garcia-Ramallo E, Pinzani M, Ros J, Jimenez W, Thomas AP, Arroyo V, Rodes J. Arginine vasopressin induces contraction and stimulates growth of cultured human hepatic stellate cells. Gastroenterology. 1997;113:615–624. doi: 10.1053/gast.1997.v113.pm9247484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Dranoff JA, Ogawa M, Kruglov EA, Gaca MD, Sevigny J, Robson SC, Wells RG. Expression of P2Y nucleotide receptors and ectonucleotidases in quiescent and activated rat hepatic stellate cells. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2004;287:G417–G424. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00294.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Dranoff JA, Kruglov EA, Abreu-Lanfranco O, Nguyen T, Aurora G, Jain D. Prevention of liver fibrosis by the purinoceptor antagonist pyridoxalphosphate-6-azophenyl-2′,4′-disulfonate (PPADS) In Vivo. 2007;21:957–965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kruglov EA, Correa PR, Arora G, Yu J, Nathanson MH, Dranoff JA. Molecular basis for calcium signaling in hepatic stellate cells. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2007;292:G975–G982. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00401.2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Echevarria W, Leite MF, Guerra MT, Zipfel WR, Nathanson MH. Regulation of calcium signals in the nucleus by a nucleoplasmic reticulum. Nat. Cell Biol. 2003;5:440–446. doi: 10.1038/ncb980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Rodrigues MA, Gomes DA, Leite MF, Grant W, Zhang L, Lam W, Cheng YC, Bennett AM, Nathanson MH. Nucleoplasmic calcium is required for cell proliferation. J. Biol. Chem. 2007;282:17061–17068. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M700490200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Tugues S, Fernandez-Varo G, Munoz-Luque J, Ros J, Arroyo V, Rodes J, Friedman SL, Carmeliet P, Jimenez W, Morales-Ruiz M. Antiangiogenic treatment with sunitinib ameliorates inflammatory infiltrate, fibrosis, and portal pressure in cirrhotic rats. Hepatology. 2007;46:1919–1926. doi: 10.1002/hep.21921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Xu L, Hui AY, Albanis E, Arthur MJ, O’Byrne SM, Blaner WS, Mukherjee P, Friedman SL, Eng FJ. Human hepatic stellate cell lines, LX-1 and LX-2: new tools for analysis of hepatic fibrosis. Gut. 2005;54:142–151. doi: 10.1136/gut.2004.042127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Friedman SL, Roll FJ. Isolation and culture of hepatic lipocytes, Kupffer cells, and sinusoidal endothelial cells by density gradient centrifugation with Stractan. Anal. Biochem. 1987;161:207–218. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90673-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Liu C, Gaca MD, Swenson ES, Vellucci VF, Reiss M, Wells RG. Smads 2 and 3 are differentially activated by transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) in quiescent and activated hepatic stellate cells. Constitutive nuclear localization of Smads in activated cells is TGF-beta-independent. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:11721–11728. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M207728200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Nathanson MH, Burgstahler AD. Subcellular distribution of cytosolic Ca2+ in isolated rat hepatocyte couplets: evaluation using confocal microscopy. Cell Calcium. 1992;13:89–98. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(92)90002-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Aoyagi M, Sakaida I, Suzuki C, Segawa M, Fukumoto Y, Okita K. Prolyl 4-hydroxylase inhibitor is more effective for the inhibition of proliferation than for inhibition of collagen synthesis of rat hepatic stellate cells. Hepatol. Res. 2002;23:1–6. doi: 10.1016/s1386-6346(01)00162-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Alberts B. Molecular Biology of the Cell. New York: Garland Science; 2008. [Google Scholar]
- 21.An P, Zhu JY, Yang Y, Lv P, Tian YH, Chen MK, Luo HS. KN-93, a specific inhibitor of CaMKII inhibits human hepatic stellate cell proliferation in vitro. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007;13:1445–1448. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i9.1445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Marra F, Grandaliano G, Valente AJ, Abboud HE. Thrombin stimulates proliferation of liver fat-storing cells and expression of monocyte chemotactic protein-1: potential role in liver injury. Hepatology. 1995;22:780–787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Pinzani M. PDGF and signal transduction in hepatic stellate cells. Front Biosci. 2002;7:d1720–d1726. doi: 10.2741/A875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Yoshiji H, Kuriyama S, Yoshii J, Ikenaka Y, Noguchi R, Hicklin DJ, Wu Y, Yanase K, Namisaki T, Yamazaki M, Tsujinoue H, Imazu H, Masaki T, Fukui H. Vascular endothelial growth factor and receptor interaction is a prerequisite for murine hepatic fibrogenesis. Gut. 2003;52:1347–1354. doi: 10.1136/gut.52.9.1347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Marra F, Arrighi MC, Fazi M, Caligiuri A, Pinzani M, Romanelli RG, Efsen E, Laffi G, Gentilini P. Extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation differentially regulates platelet-derived growth factor’s actions in hepatic stellate cells, and is induced by in vivo liver injury in the rat. Hepatology. 1999;30:951–958. doi: 10.1002/hep.510300406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Schnabl B, Bradham CA, Bennett BL, Manning AM, Stefanovic B, Brenner DA. TAK1/JNK and p38 have opposite effects on rat hepatic stellate cells. Hepatology. 2001;34:953–963. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2001.28790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Marra F, Pinzani M, DeFranco R, Laffi G, Gentilini P. Involvement of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in the activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase by PDGF in hepatic stellate cells. FEBS Lett. 1995;376:141–145. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)01261-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Patel R, Holt M, Philipova R, Moss S, Schulman H, Hidaka H, Whitaker M. Calcium/calmodulin-dependent phosphorylation and activation of human Cdc25-C at the G2/M phase transition in HeLa cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:7958–7968. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.12.7958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Da Silva FM, Guimaraes EL, Grivicich I, Trindade VM, Guaragna RM, Borojevic R, Guma FC. Hepatic stellate cell activation in vitro: cell cycle arrest at G2/M and modification of cell motility. J. Cell Biochem. 2003;90:387–396. doi: 10.1002/jcb.10642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]