Abstract
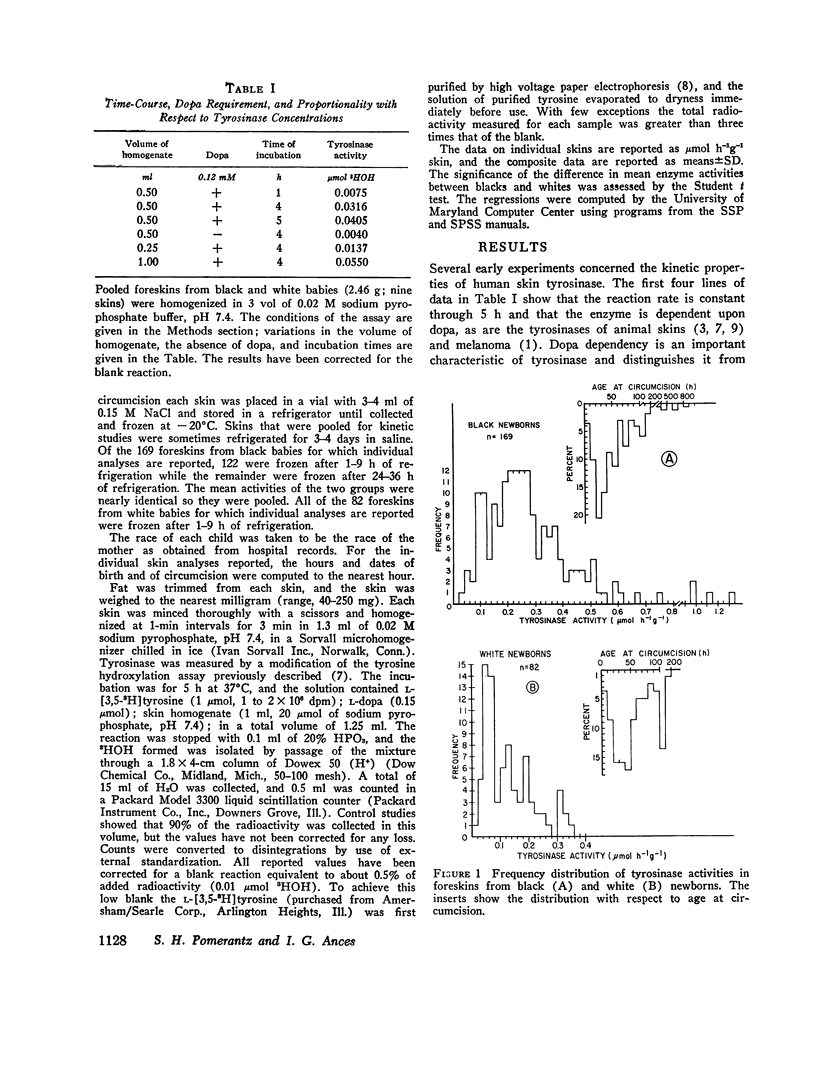
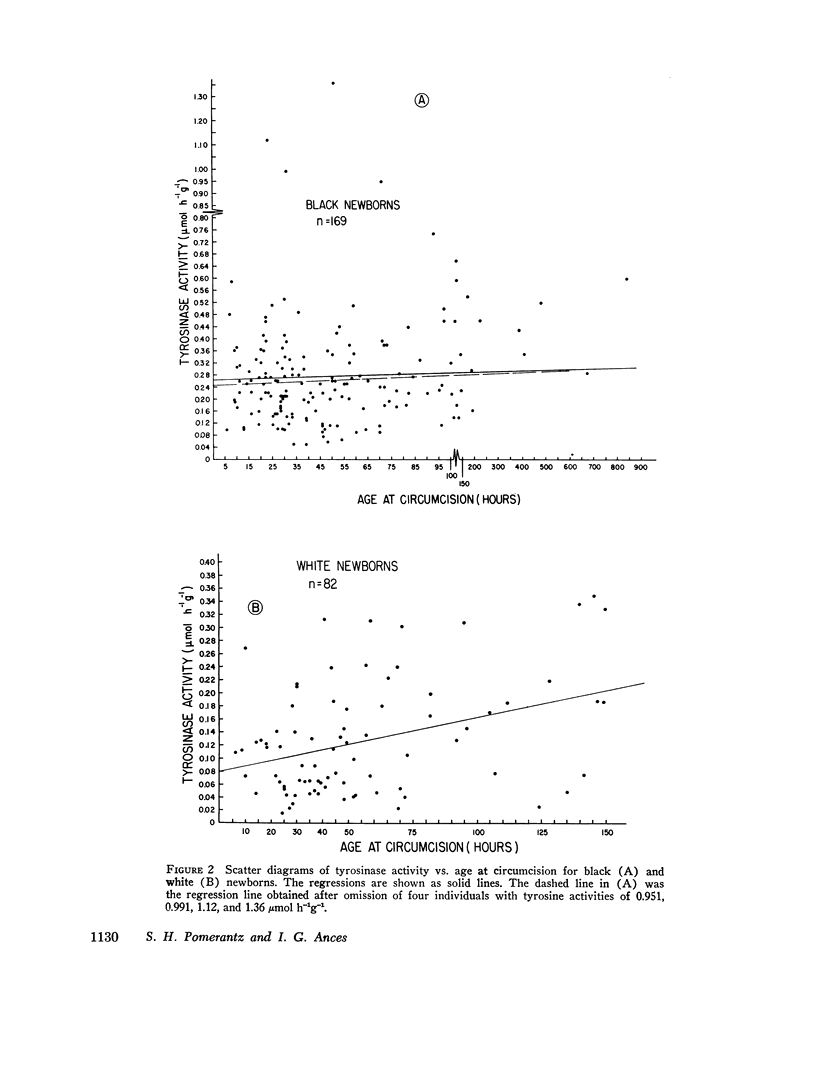
Tyrosinase has been measured in homogenates of foreskins from newborn babies. The tyrosine hydroxylation reaction is dependent upon 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine as a cosubstrate, and the Km for tyrosine is 0.15 mM, similar to the value observed for other mammalian tyrosinases. The mean enzyme activity for black babies (n = 169) is about two and one-fourth times that for white babies (n = 82). For white babies there is a significant correlation between age at circumcision and tyrosinase activity. For black babies this correlation becomes significant when four individuals with extremely high tyrosinase activities are omitted from the series.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ATFIELD G. N., MORRIS C. J. Analytical separations by highvoltage paper electrophoresis. Amino acids in protein hydrolysates. Biochem J. 1961 Dec;81:606–614. doi: 10.1042/bj0810606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ances I. G., Pomerantz S. H. Serum concentrations of beta-melanocyte-stimulating hormone in human pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1974 Aug 15;119(8):1062–1068. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(74)90259-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barisas B. G., McGuire J. S. A proteolytically activated tyrosinase from frog epidermis. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 25;249(10):3151–3156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnett J. B., Seiler H. Multiple forms of tyrosinase from human melanoma. J Invest Dermatol. 1969 Feb;52(2):199–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnett J. B. The tyrosinases of mouse melanoma. Isolation and molecular properties. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 25;246(10):3079–3091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. M., Chavin W. Tyrosinase activity in a highly pigmented human melanoma and in negro skin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1974 Feb;145(2):695–698. doi: 10.3181/00379727-145-37877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearing V. J. Mammalian melanogenesis: tyrosinase versus peroxidase involvement, and activation mechanisms. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Oct;158(2):720–725. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90566-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holstein T. J., Quevedo W. C., Jr, Burnett J. B. Multiple forms of tyrosinase in rodents and lagomorphs with special reference to their genetic control in mice. J Exp Zool. 1971 Jun;177(2):173–183. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401770205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holstein T. J., Stowell C. P., Quevedo W. C., Jr, Zarcaro R. M., Bienieki T. C. Peroxidase, "protyrosinase," and the multiple forms of tyrosinase in mice. Yale J Biol Med. 1973 Dec;46(5):560–571. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAGATSU T., LEVITT M., UDENFRIEND S. TYROSINE HYDROXYLASE. THE INITIAL STEP IN NOREPINEPHRINE BIOSYNTHESIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Sep;239:2910–2917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson R. L., Gaylor J., Everett M. A. Skin color, melanin, and erythema. Arch Dermatol. 1973 Oct;108(4):541–544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel R. P., Okun M. R., Edelstein L. M., Cariglia N. Peroxidatic oxidation of tyrosine to melanin in supernatant of crude mouse melanoma homogenates. Biochem J. 1974 Aug;142(2):441–443. doi: 10.1042/bj1420441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomerantz S. H., Chuang L. Effects of beta-MSH, cortisol and ACTH on tyrosinase in the skin of newborn hamsters and mice. Endocrinology. 1970 Aug;87(2):302–310. doi: 10.1210/endo-87-2-302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomerantz S. H. L-tyrosine-3,5-3H assay for tyrosinase development in skin of newborn hamsters. Science. 1969 May 16;164(3881):838–839. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3881.838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomerantz S. H., Li J. P. Purification and properties of tyrosinase isoenzymes from hamster melanoma. Yale J Biol Med. 1973 Dec;46(5):541–552. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomerantz S. H. The tyrosine hydroxylase activity of mammalian tyrosinase. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jan 10;241(1):161–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenhouse E. Genetic effect on fine structure and development of pigment granules in mouse hair bulb melanocytes. I. The b and d loci. Dev Biol. 1968 Apr;17(4):351–365. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(68)90069-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenhouse E. Genetic effects on fine structure and development of pigment granules in mouse hair bulb melanocytes. II. The c and p loci, and ddpp interaction. Dev Biol. 1968 Apr;17(4):366–381. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(68)90070-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


