Abstract
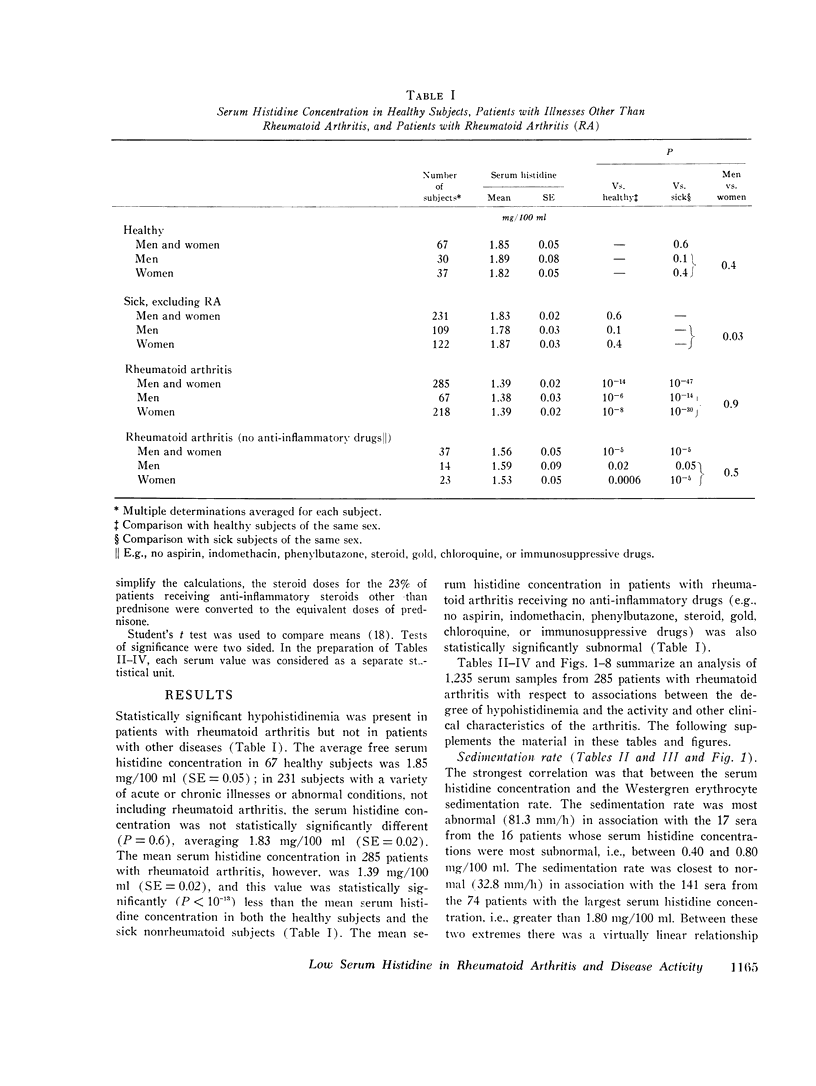
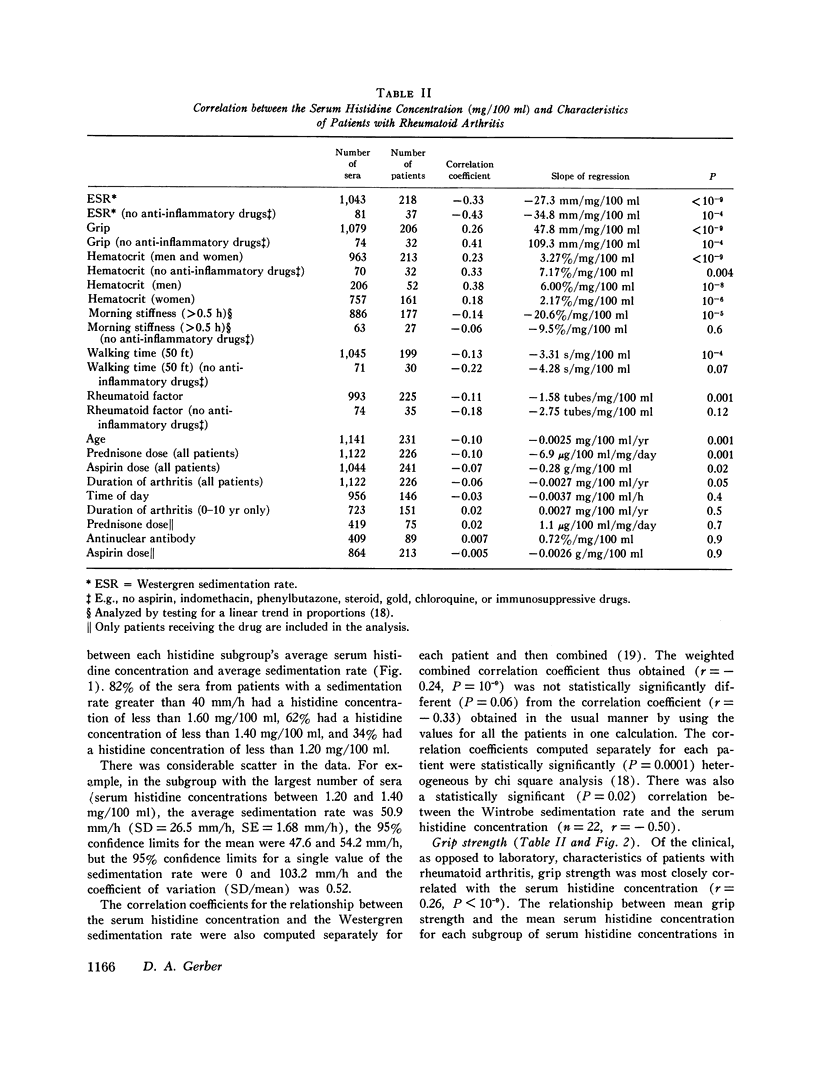
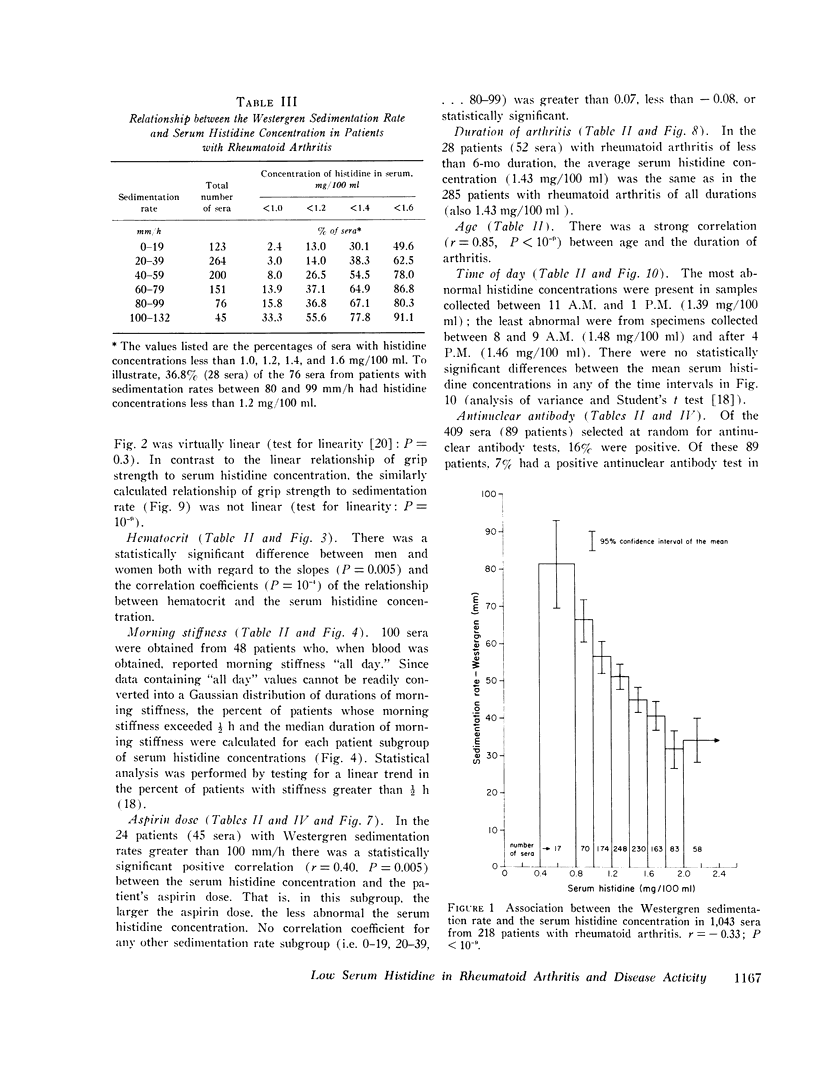
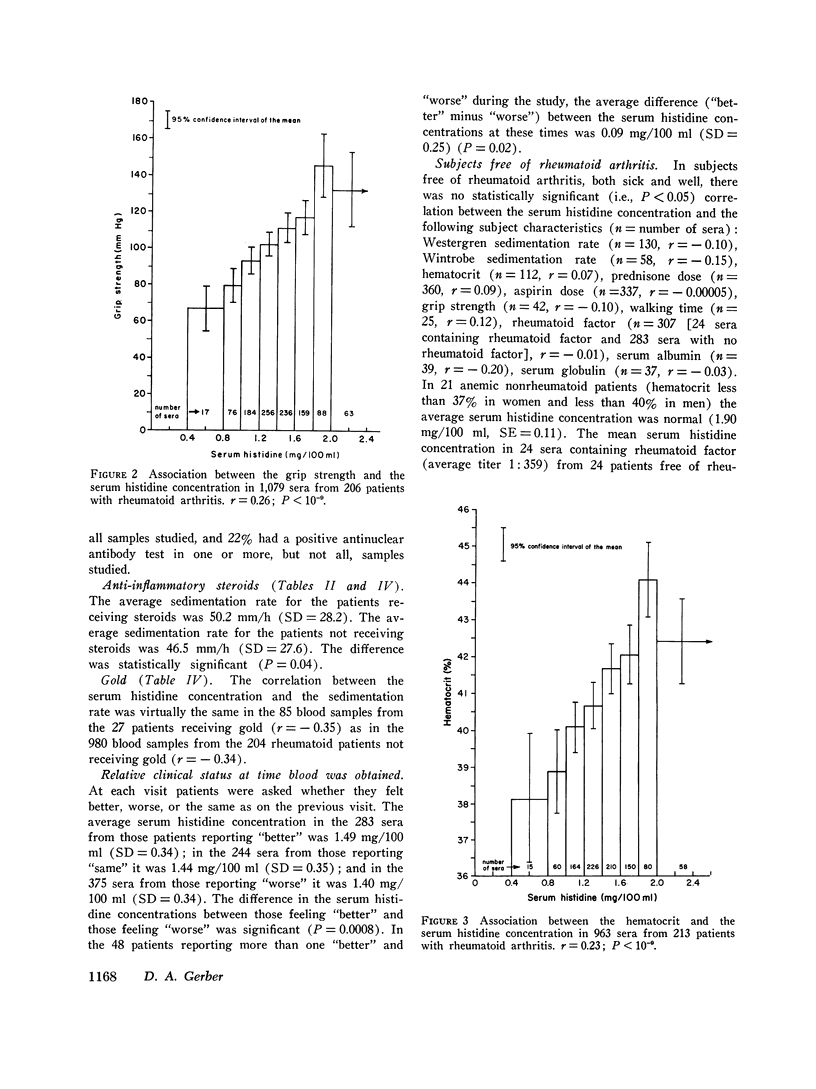
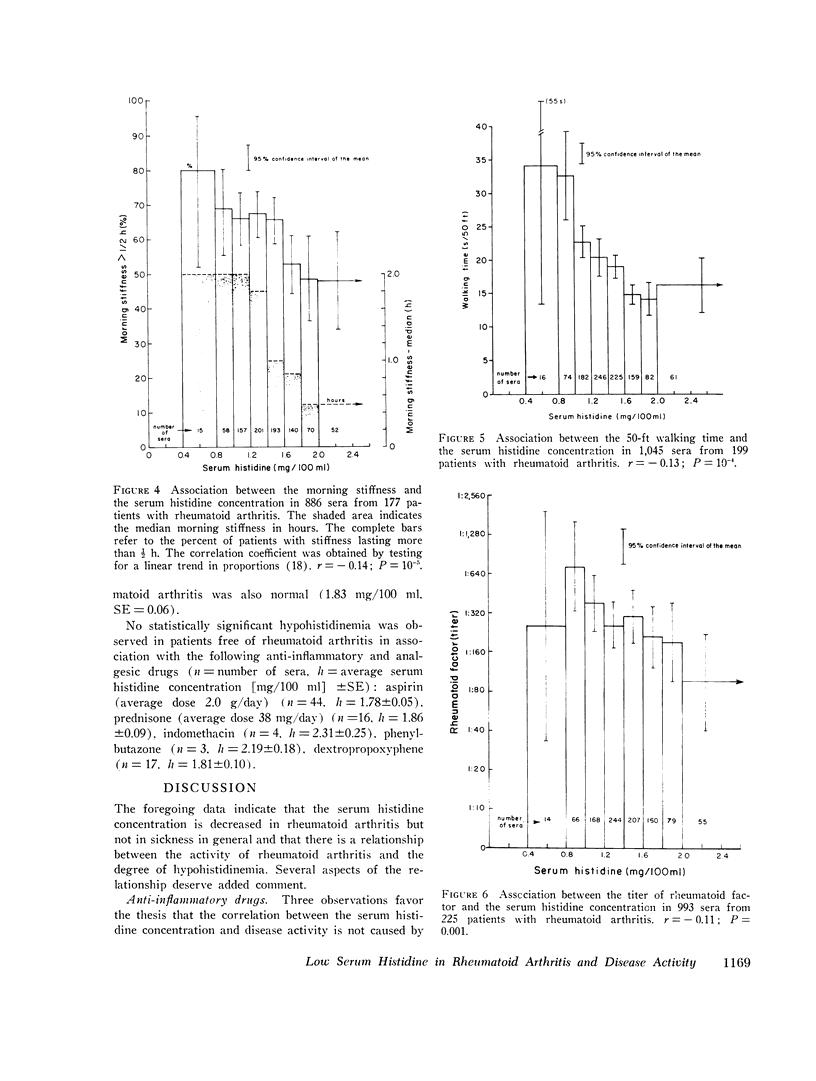
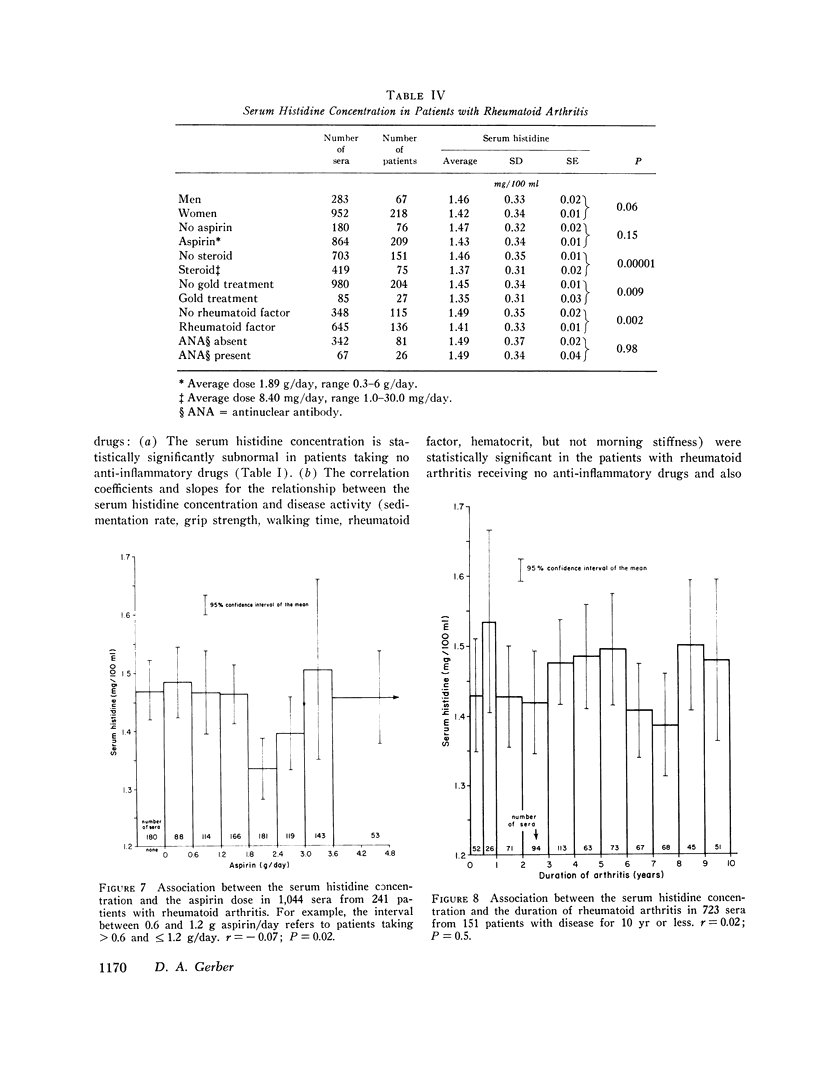
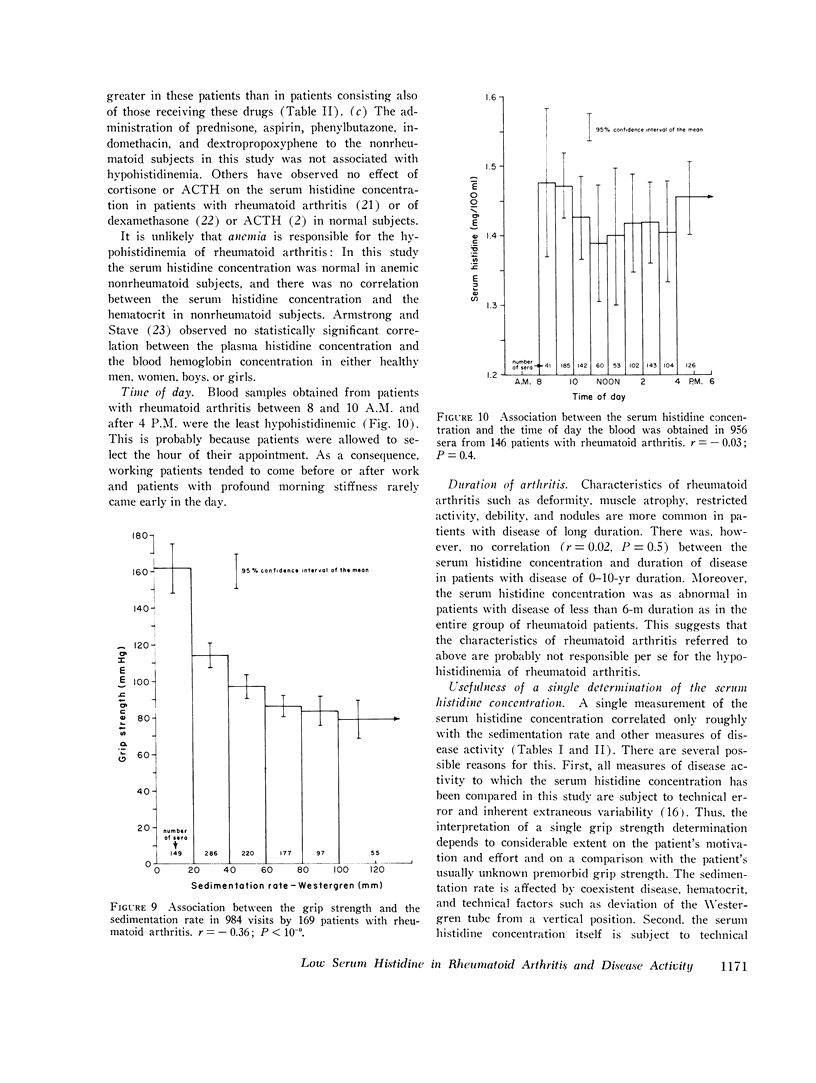
A study of sera from 285 patients with definite or classical rheumatoid arthritis (including 37 patients receiving no anti-inflammatory drugs) and sera from 67 healthy subjects has confirmed 10 published reports of a statistically significant decreased blood histidine concentration in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Contrastingly, in sera from 231 patients with a variety of acute and chronic illnesses other than rheumatoid arthritis, no statistically significant hypohistidinemia was observed either in the group as a whole or in association with the administration of aspirin, prednisone, indomethacin, phenylbutazone, or dextropropoxyphene. In the patients with rheumatoid arthritis there was a statistically significant correlation between the serum histidine concentration and the following: Westergren sedimentation rate (r=-0.33, P smaller than 10- minus 9), grip strength (r=0.26, P smaller than 10- minus 9), hematocrit (r=0.23, P smaller than 10- minus 9), duration of morning stiffness (r=-0.14, P=10- minus 5), walking time (r=-0.13, P=10- minus 4), latex titer of rheumatoid factor (r=-0.11, P=0.001), and the duration of arthritis (r=-0.06, P=0.05). There was no statistically significant association between the serum histidine concentration and the duration of rheumatoid arthritis in the 151 patients with disease of 0-10-yr duration (r=0.02, P=0.5), the sex of the patient, or the presence of antinuclear antibody (R=0.007, P=0.9). The serum histidine concentration was less in rheumatoid patients receiving steroids (P=0.00001), gold (P=0.009), and aspirin (P=0.15) than in rheumatoid patients not receiving these drugs. This study indicates that histidine determinations on properly preserved casual serum samples can be helpful in the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis and in the evaluation of the activity of the disease.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong M. D., Stave U. A study of plasma free amino acid levels. V. Correlations among the amino acids and between amino acids and some other blood constituents. Metabolism. 1973 Jun;22(6):827–833. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(73)90054-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BORDEN A. L., BRODIE E. C., WALLRAFF E. B., HOLBROOK W. P., HILL D. F., STEPHENS C. A. L., Jr, JOHNSON R. B., KEMMERER A. R. Amino acid studies and clinical findings in normal adults and rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with ACTH. J Clin Invest. 1952 Apr;31(4):375–379. doi: 10.1172/JCI102619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BORDEN A. L., WALLRAFF E. B., BRODIE E. C., HOLBROOK W. P., HILL D. F., STEPHENS C. A. L., Jr, KENT L. J., KEMMERER A. R. Plasma levels of free amino acids in normal subjects compared with patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1950 Oct;75(1):28–30. doi: 10.3181/00379727-75-18087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dormidontov E. N. Materialy k kharakteristike aminokislotnoso obmena pri razlichnykh variantakh infektsionnogo nespetsificheskogo poliartrita. Ter Arkh. 1971 Jan;43(1):52–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber D. A. Copper-catalyzed thermal aggregation of human gamma-globulin. Inhibition by histidine, gold thiomalate, and penicillamine. Arthritis Rheum. 1974 Jan-Feb;17(1):85–91. doi: 10.1002/art.1780170113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber D. A. Determination of histidine in serum with o-phthaldialdehyde. Anal Biochem. 1970 Apr;34(2):500–504. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90135-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber D. A. Sulfhydryl-dependent thermal aggregation of human gamma globulin: augmentation by hyaluronic acid. Arthritis Rheum. 1975 Jan-Feb;18(1):59–66. doi: 10.1002/art.1780180112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmaeva M. E., Zotov A. A., Rosin I. V. Materialy kompleksnogo izucheniia obmena nekotorykh vitaminov, svobodnykh aminokislot i biogennykh aminov u bol'nykh infektsionnym nespetsificheskim (revmatoidnym) poliartritom. Ter Arkh. 1971 Nov;43(11):98–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NETTELBLADT E., SANDELL B. M. AMINO-ACID CONTENT OF SERUM IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS. Ann Rheum Dis. 1963 Jul;22:269–272. doi: 10.1136/ard.22.4.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PLOTZ C. M., SINGER J. M. The latex fixation test. I. Application to the serologic diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Med. 1956 Dec;21(6):888–892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux H., Aquaron R., Laurent B., Veron L., Recordier A. M. Les acides aminès basiques du sérum au cours de la polyarthrite rhumatoïde. Rev Rhum Mal Osteoartic. 1972 Nov;39(11):677–680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEPHENS C. A. L., Jr, WALLRAFF E. B., BORDEN A. L., BRODIE E. C., HOLBROOK W. P., HILL D. F., KENT L. J., KEMMERER A. R. Apparent free histidine plasma and urine values in rheumatoid arthritis treated with cortisone and ACTH. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1950 Jun;74(2):275–279. doi: 10.3181/00379727-74-17876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuhlsatz H. W., Plagemann L., Greiling H. Die freien Aminosäuren in Synovialflüssigkeit und Serum bei der rheumatoiden Arthritis. Z Rheumaforsch. 1973 Sep-Oct;32(9):388–393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRNAVSKA Z., SITAJ S. [The changes of free amino acids in the serum and urine of patients with primary chronic poly-arthritis]. Z Rheumaforsch. 1960 Apr;19:125–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zischka R., Orti E., Castells S. Effects of short-term administration of dexamethasone on urinary and plasma free amino acids in children. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1970 Jul;31(1):95–97. doi: 10.1210/jcem-31-1-95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



