Abstract
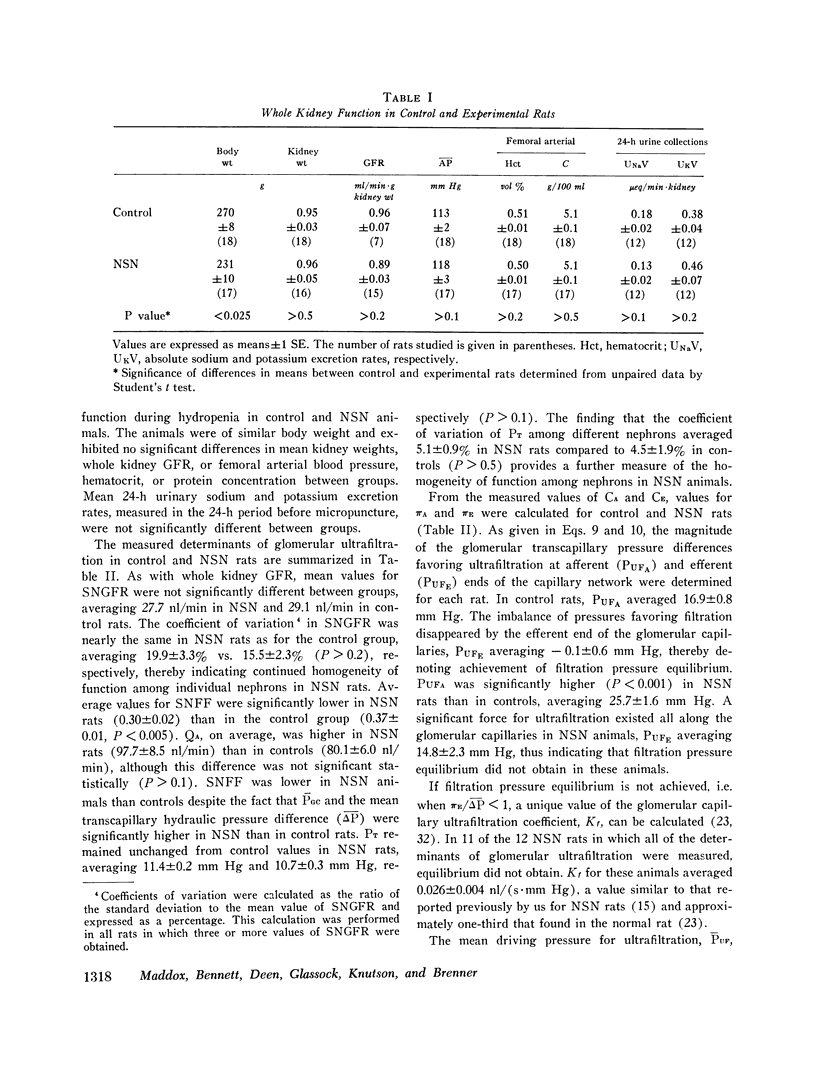
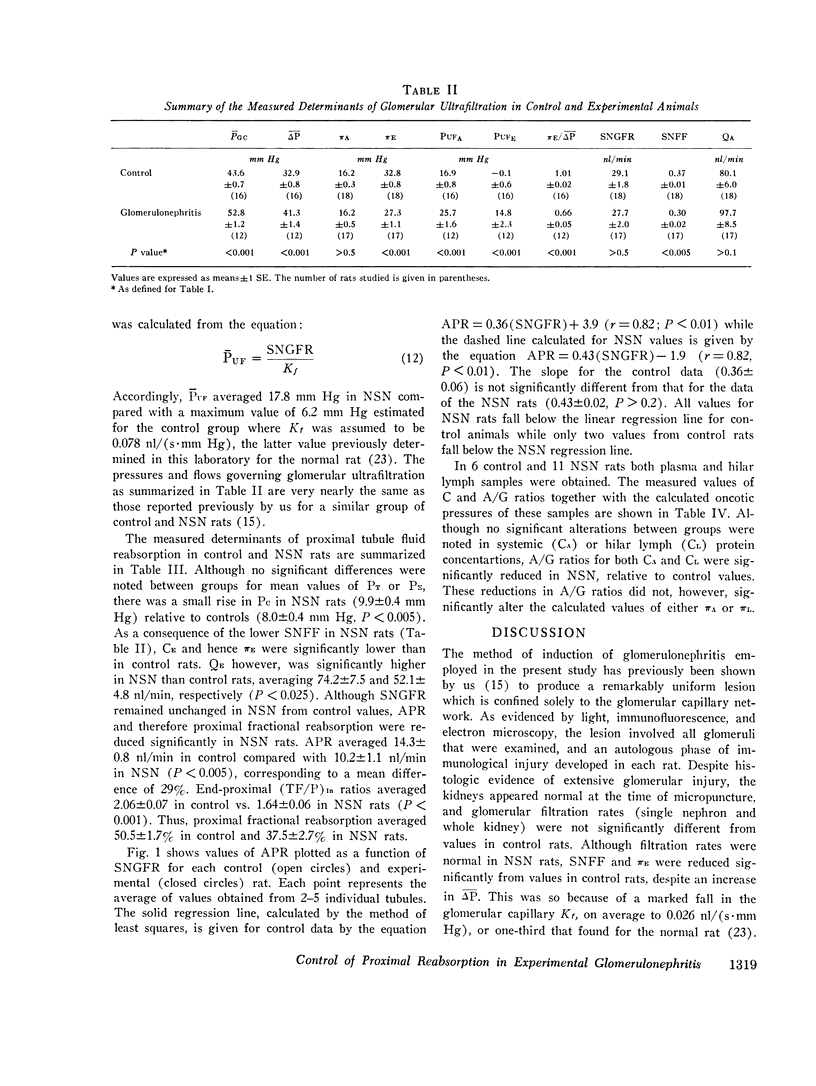
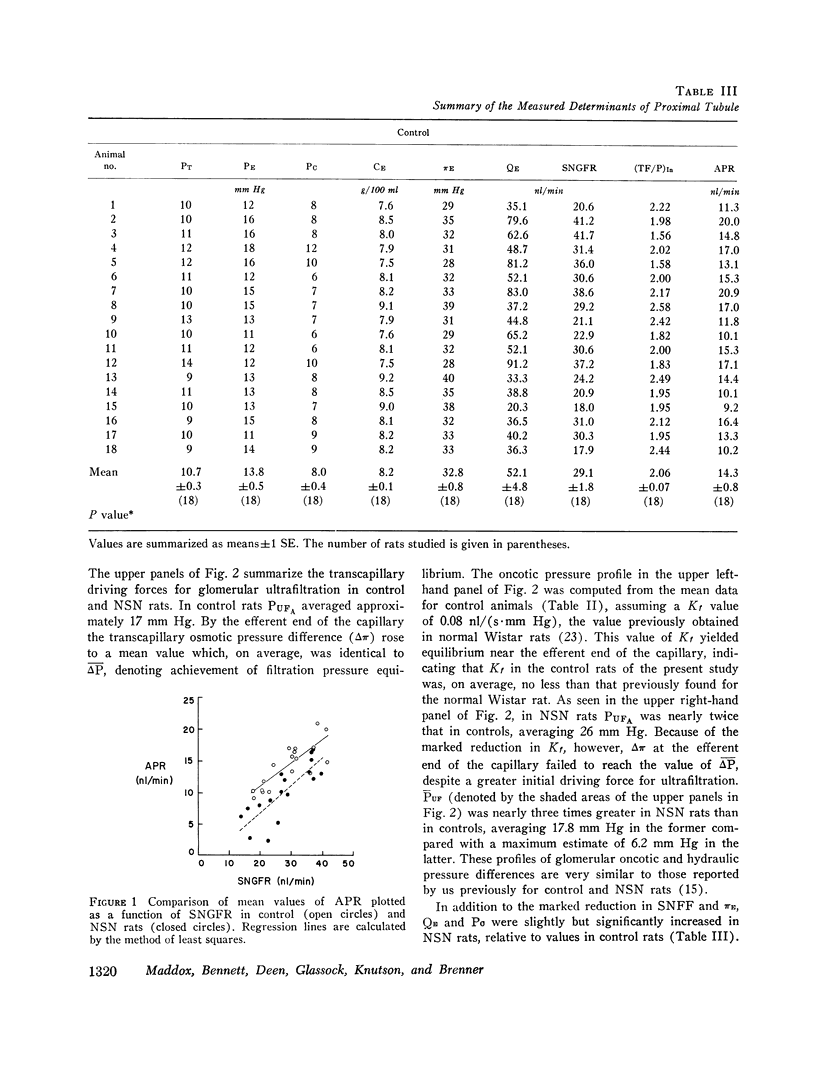
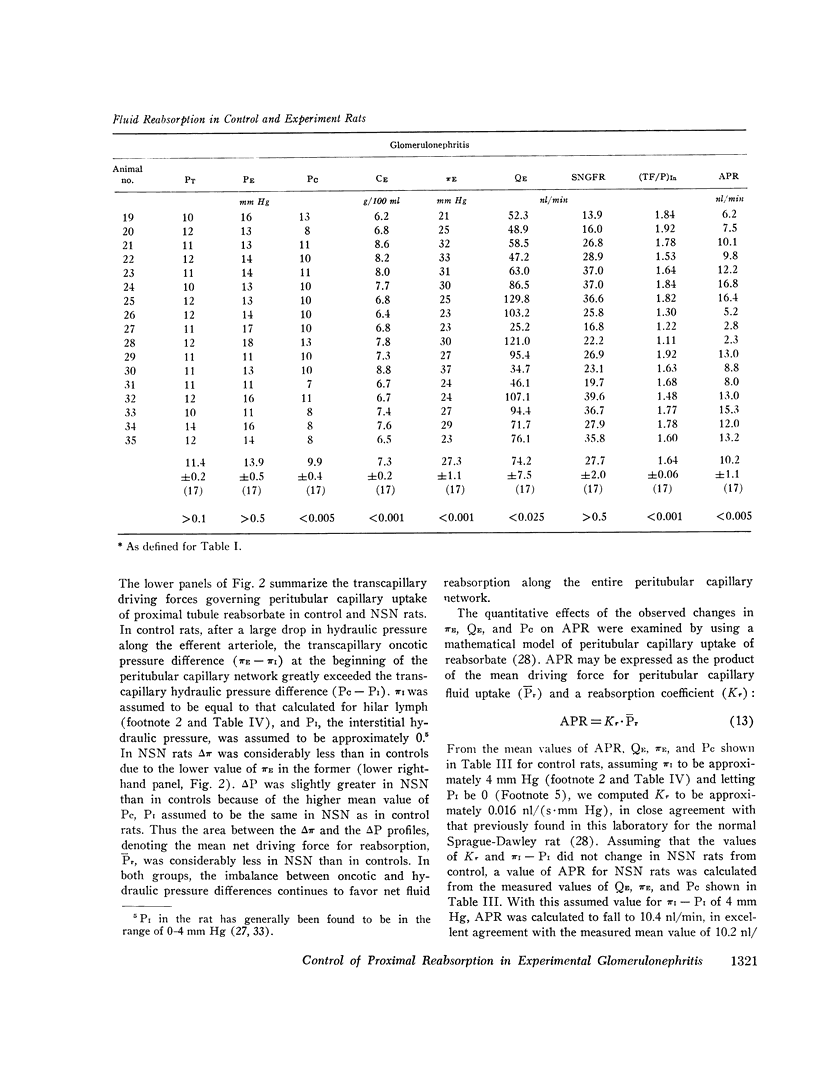
We have recently shown that in the early autologous phase of nephrotoxic serum nephritis (NSN) single nephron glomerular filtration rate is unchanged from values in normal hydropenic control rats, but that single nephron filtration fraction and efferent arteriolar oncotic pressure (piE) are reduced because of a marked reduction in the glomerular capillary ultrafiltration coefficient. The present study was undertaken to examine the influence of this decline in piE as well as the other known determinants of peritubular capillary fluid exchange on absolute proximal fluid reabsorption (APR) in NSN. The findings indicate that APR and proximal fractional reabsorption are reduced significantly in NSN, relative to values in a separate group of age and weight-matched normal hydropenic control rats studied concurrently. In addition to the measured decline in piE, efferent arteriolar plasma flow (Qe) and peritubular capillary hydraulic pressure (Pc) were found to increase significantly, while interstitial oncotic pressure, estimated from hilar lymph, was not significantly different from values in control rats. Using a mathematical model of peritubular capillary fluid uptake we found that, assuming that the capillary permeability-surface area product and interstitial hydraulic pressure are unchanged in NSN, the observed changes in piE and Pc are sufficient to offset the effect of the increase in QE, yielding a calculated reduction in APR of approximately 4 nl/min, in excellent agreement with the observed mean decline of 4.1 nl/min. These findings suggest that control of APR in NSN is mediated by the same factors that regulate APR under normal physiological conditions, namely, the imbalance of forces governing peritubular capillary uptake of isotonic reabsorbate.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison M. E., Wilson C. B., Gottschalk C. W. Pathophysiology of experimental glomerulonephritis in rats. J Clin Invest. 1974 May;53(5):1402–1423. doi: 10.1172/JCI107689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrizurieta-Muchnik E. E., Lassiter W. E., Lipham E. M., Gottschalk C. W. Micropuncture study of glomerulotubular balance in the rat kidney. Nephron. 1969;6(3):418–436. doi: 10.1159/000179743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. M., Bennett C. M., Berliner R. W. The relationship between glomerular filtration rate and sodium reabsorption by the proximal tubule of the rat nephron. J Clin Invest. 1968 Jun;47(6):1358–1374. doi: 10.1172/JCI105828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. M., Daugharty T. M., Ueki I. F., Troy J. L. Quantitative assessment of proximal tubule function in single nephrons of the rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1971 Jun;220(6):2058–2067. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.6.2058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. M., Falchuk K. H., Keimowitz R. I., Berliner R. W. The relationship between peritubular capillary protein concentration and fluid reabsorption by the renal proximal tubule. J Clin Invest. 1969 Aug;48(8):1519–1531. doi: 10.1172/JCI106118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. M., Galla J. H. Influence of postglomerular hematocrit and protein concentration on rat nephron fluid transfer. Am J Physiol. 1971 Jan;220(1):148–161. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.1.148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. M., Troy J. L., Daugharty T. M., Deen W. M., Robertson C. R. Dynamics of glomerular ultrafiltration in the rat. II. Plasma-flow dependence of GFR. Am J Physiol. 1972 Nov;223(5):1184–1190. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.223.5.1184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. M., Troy J. L., Daugharty T. M., MacInnes R. M. Quantitative importance of changes in postglomerular colloid osmotic pressure in mediating glomerulotubular balance in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jan;52(1):190–197. doi: 10.1172/JCI107164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. M., Troy J. L., Daugharty T. M. On the mechanism of inhibition in fluid reabsorption by the renal proximal tubule of the volume-expanded rat. J Clin Invest. 1971 Aug;50(8):1596–1602. doi: 10.1172/JCI106647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. M., Troy J. L., Daugharty T. M. Pressures in cortical structures of the rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1972 Feb;222(2):246–251. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.222.2.246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. M., Troy J. L., Daugharty T. M. The dynamics of glomerular ultrafiltration in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1971 Aug;50(8):1776–1780. doi: 10.1172/JCI106667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. M., Troy J. L. Postglomerular vascular protein concentration: evidence for a causal role in governing fluid reabsorption and glomerulotublar balance by the renal proximal tubule. J Clin Invest. 1971 Feb;50(2):336–349. doi: 10.1172/JCI106501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. M., Ueki I. F., Daugharty T. M. On estimating colloid osmotic pressure in pre- and postglomerular plasma in the rat. Kidney Int. 1972 Jul;2(1):51–53. doi: 10.1038/ki.1972.68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buentig W. E., Earley L. E. Demonstration of independent roles of proximal tubular reabsorption and intratubular load in the phenomenon of glomerulotubular balance during aortic constriction in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jan;50(1):77–89. doi: 10.1172/JCI106486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burg M. B., Orloff J. Control of fluid absorption in the renal proximal tubule. J Clin Invest. 1968 Sep;47(9):2016–2024. doi: 10.1172/JCI105888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daugharty T. M., Ueki I. F., Nicholas D. P., Brenner B. M. Comparative renal effects of isoncotic and colloid-free volume expansion in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1972 Jan;222(1):225–235. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.222.1.225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deen W. M., Robertson C. R., Brenner B. M. A model of glomerular ultrafiltration in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1972 Nov;223(5):1178–1183. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.223.5.1178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deen W. M., Robertson C. R., Brenner B. M. A model of peritubular capillary control of isotonic fluid reabsorption by the renal proximal tubule. Biophys J. 1973 Apr;13(4):340–358. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(73)85989-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deen W. M., Robertson C. R., Brenner B. M. Glomerular ultrafiltration. Fed Proc. 1974 Jan;33(1):14–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deen W. M., Troy J. L., Robertson C. R., Brenner B. M. Dynamics of glomerular ultrafiltration in the rat. IV. Determination of the ultrafiltration coefficient. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jun;52(6):1500–1508. doi: 10.1172/JCI107324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUHR J., KACZMARCZYK J., KRUTTGEN C. D. Eine einfache colorimetrische Methode zur Inulinbestimmung für Nieren-Clearance-Untersuchungen bei Stoffwechselgesunden und Diabetikern. Klin Wochenschr. 1955 Aug 1;33(29-30):729–730. doi: 10.1007/BF01473295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falchuk K. H., Berliner R. W. Hydrostatic pressures in peritubular capillaries and tubules in the rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1971 May;220(5):1422–1426. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.5.1422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falchuk K. H., Brenner B. M., Tadokoro M., Berliner R. W. Oncotic and hydrostatic pressures in peritubular capillaries and fluid reabsorption by proximal tubule. Am J Physiol. 1971 May;220(5):1427–1433. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.5.1427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Källskog O., Wolgast M. Driving forces over the peritubular capillary membrane in the rat kidney during antidiuresis and saline expansion. Acta Physiol Scand. 1973 Sep;89(1):116–125. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1973.tb05502.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewy J. E., Windhager E. E. Peritubular control of proximal tubular fluid reabsorption in the rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1968 May;214(5):943–954. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.214.5.943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubowitz H., Mazumdar D. C., Kawamura J., Crosson J. T., Weisser F., Rolf D., Bricker N. S. Experimental glomerulonephritis in the rat: structural and functional observations. Kidney Int. 1974 May;5(5):356–364. doi: 10.1038/ki.1974.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martino J. A., Earley L. E. Demonstraton of a role of physical factors as determinants of the natriuretic response to volume expansion. J Clin Invest. 1967 Dec;46(12):1963–1978. doi: 10.1172/JCI105686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel F., Murayama Y. Simultaneous measurement of undirectional and net sodium fluxes in microperfused rat proximal tubules. Pflugers Arch. 1970;320(1):1–23. doi: 10.1007/BF00588454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan T., Berliner R. W. A study by continuous microperfusion of water and electrolyte movements in the loop of Henle and distal tubule of the rat. Nephron. 1969;6(3):388–405. doi: 10.1159/000179741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan T., Berliner R. W. In vivo perfusion of proximal tubules of the rat: glomerulotubular balance. Am J Physiol. 1969 Oct;217(4):992–997. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.217.4.992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radtke H. W., Rumrich G., Klöss S., Ullrich K. J. Influence of luminal diameter and flow velocity on the isotonic fluid absorption and 36Cl permeability of the proximal convolution of the rat kidney. Pflugers Arch. 1971;324(4):288–296. doi: 10.1007/BF00592457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson C. R., Deen W. M., Troy J. L., Brenner B. M. Dynamics of glomerular ultrafiltration in the rat. 3. Hemodynamics and autoregulation. Am J Physiol. 1972 Nov;223(5):1191–1200. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.223.5.1191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocha A., Marcondes M., Malnic G. Micropuncture study in rats with experimental glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 1973 Jan;3(1):14–23. doi: 10.1038/ki.1973.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodicio J., Herrera-Acosta J., Sellman J. C., Rector F. C., Jr, Seldin D. W. Studies on glomerulotubular balance during aortic constriction, ureteral obstruction and venous occlusion in hydropenic and saline-loaded rats. Nephron. 1969;6(3):437–456. doi: 10.1159/000179744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnermann J., Levine D. Z., Horster M. A direct evaluation of the Gertz hypothesis on single rat proximal tubules in vivo: failure of the tubular volume to be the sole determinant of the reabsorptive rate. Pflugers Arch. 1969;308(2):149–165. doi: 10.1007/BF00587022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitzer A., Windhager E. E. Effect of peritubular oncotic pressure changes on proximal tubular fluid reabsorption. Am J Physiol. 1970 Apr;218(4):1188–1193. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.218.4.1188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIEDERHIELM C. A., WOODBURY J. W., KIRK S., RUSHMER R. F. PULSATILE PRESSURES IN THE MICROCIRCULATION OF FROG'S MESENTERY. Am J Physiol. 1964 Jul;207:173–176. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.207.1.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolgast M., Persson E., Schnermann J., Ulfendahl H., Wunderlich P. Colloid osmotic pressure of the subcapsular interstitial fluid of rat kidneys during hydropenia and volume expansion. Pflugers Arch. 1973 May 18;340(2):123–131. doi: 10.1007/BF00588171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wunderlich P., Persson E., Schnermann J., Ulfendahl H., Wolgast M. Hydrostatic pressure in the subcapsular interstitial space of rat and dog kidneys. Pflugers Arch. 1971;328(4):307–319. doi: 10.1007/BF00586833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



