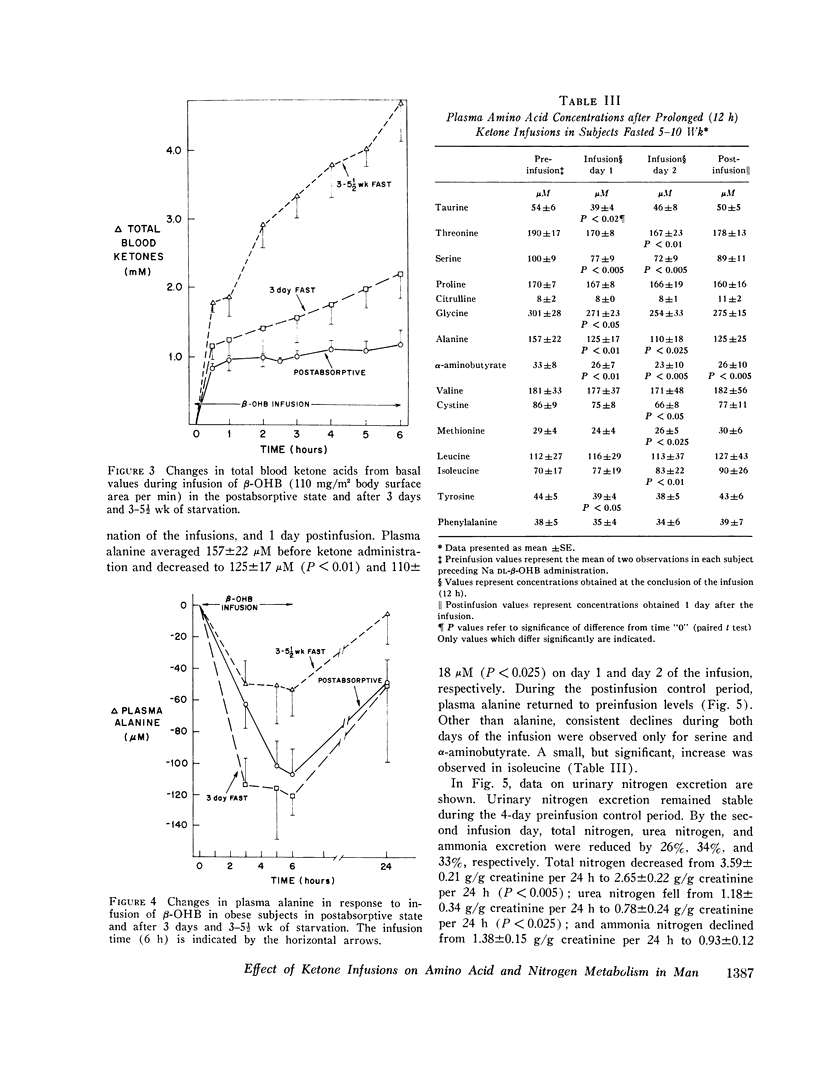
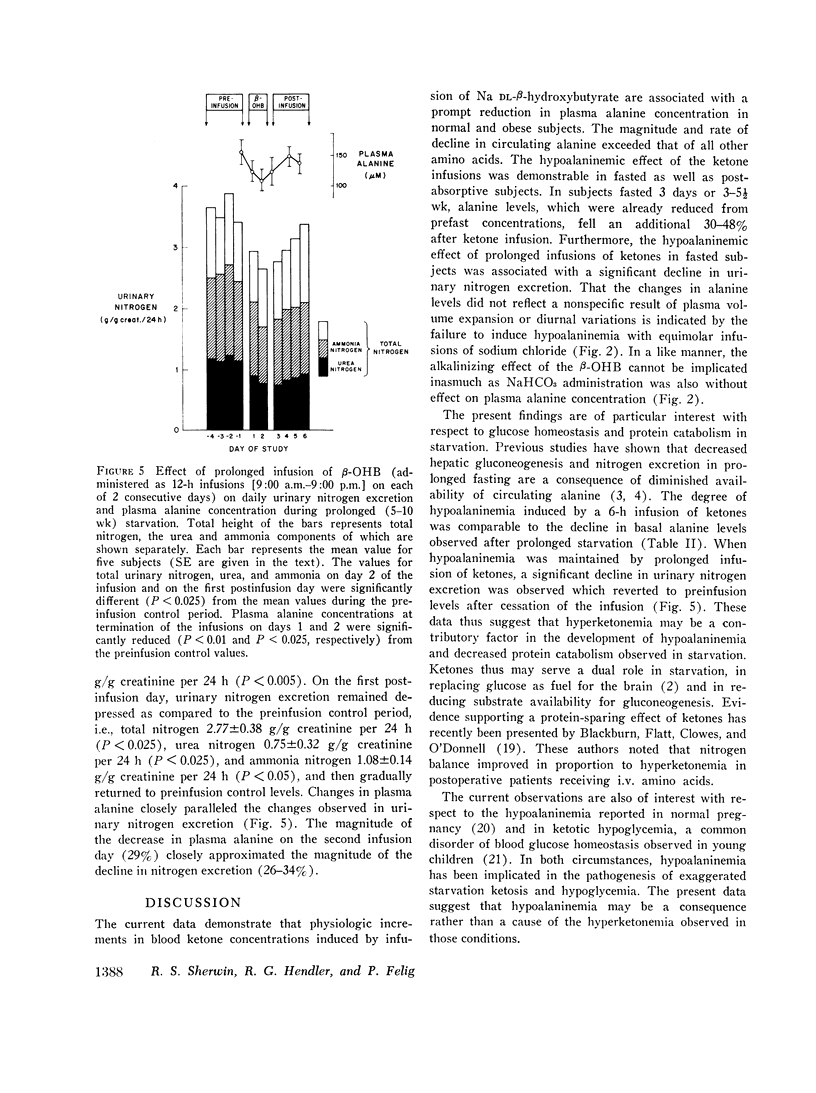
Abstract
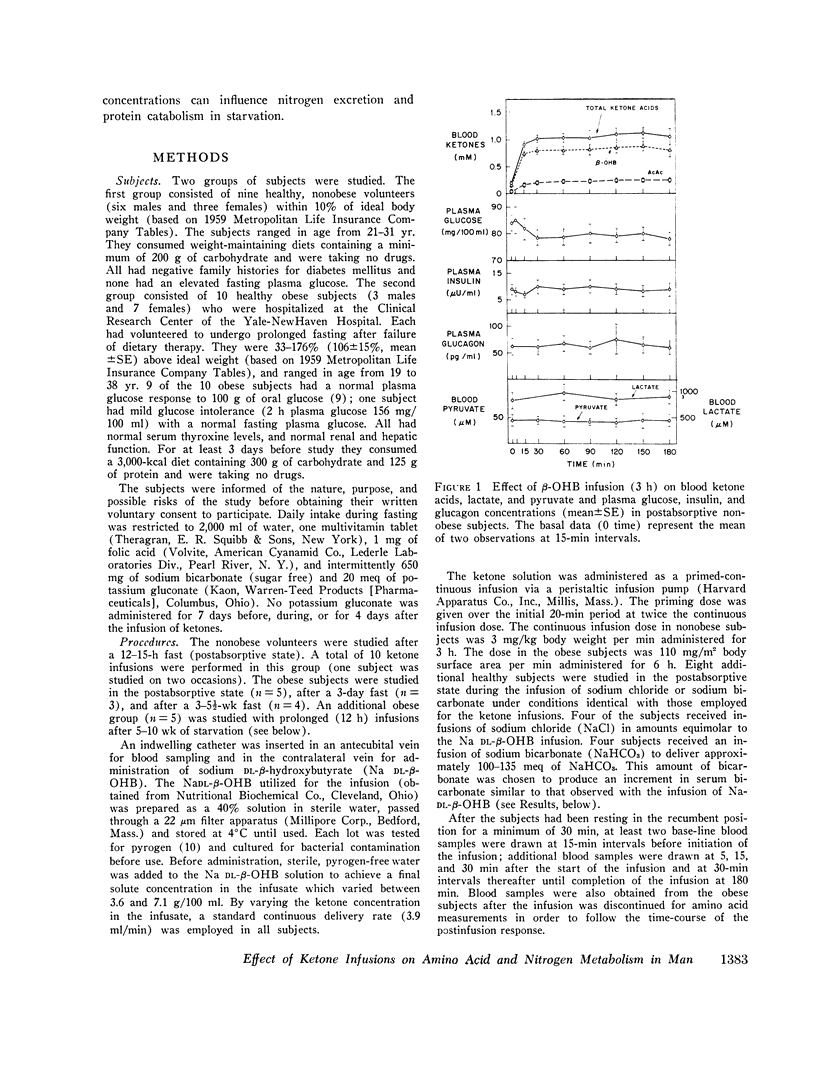
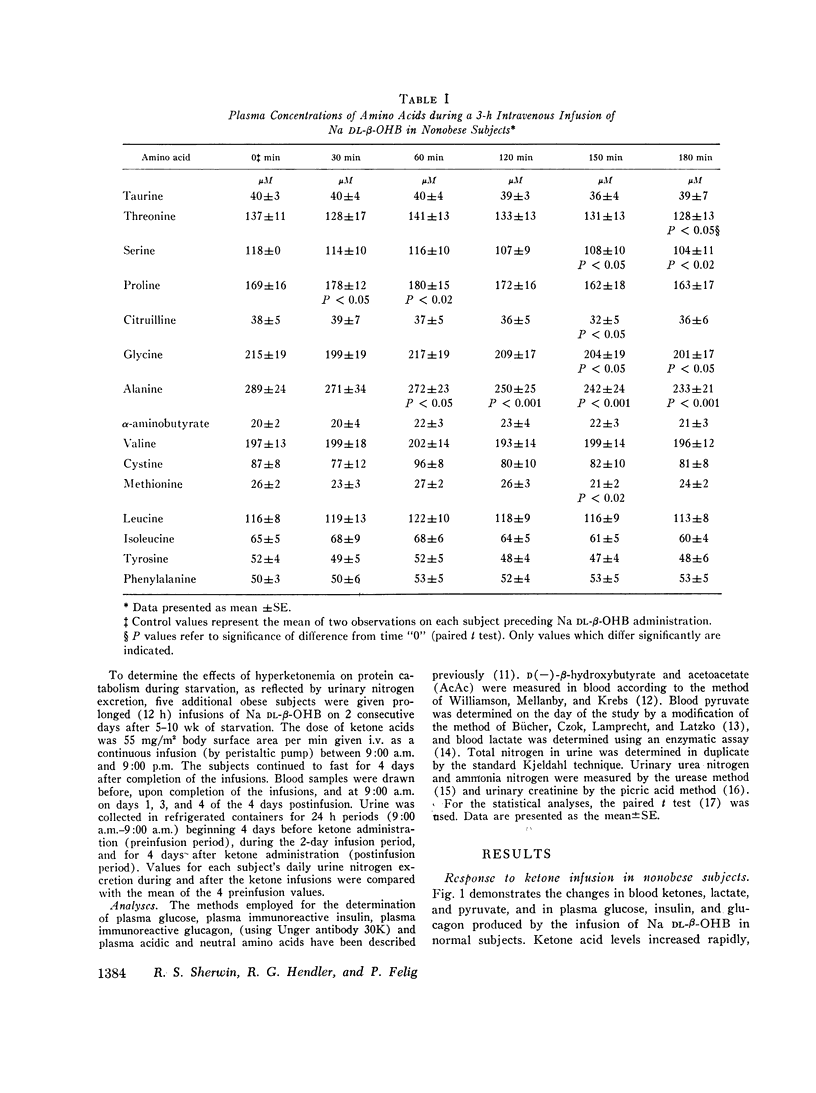
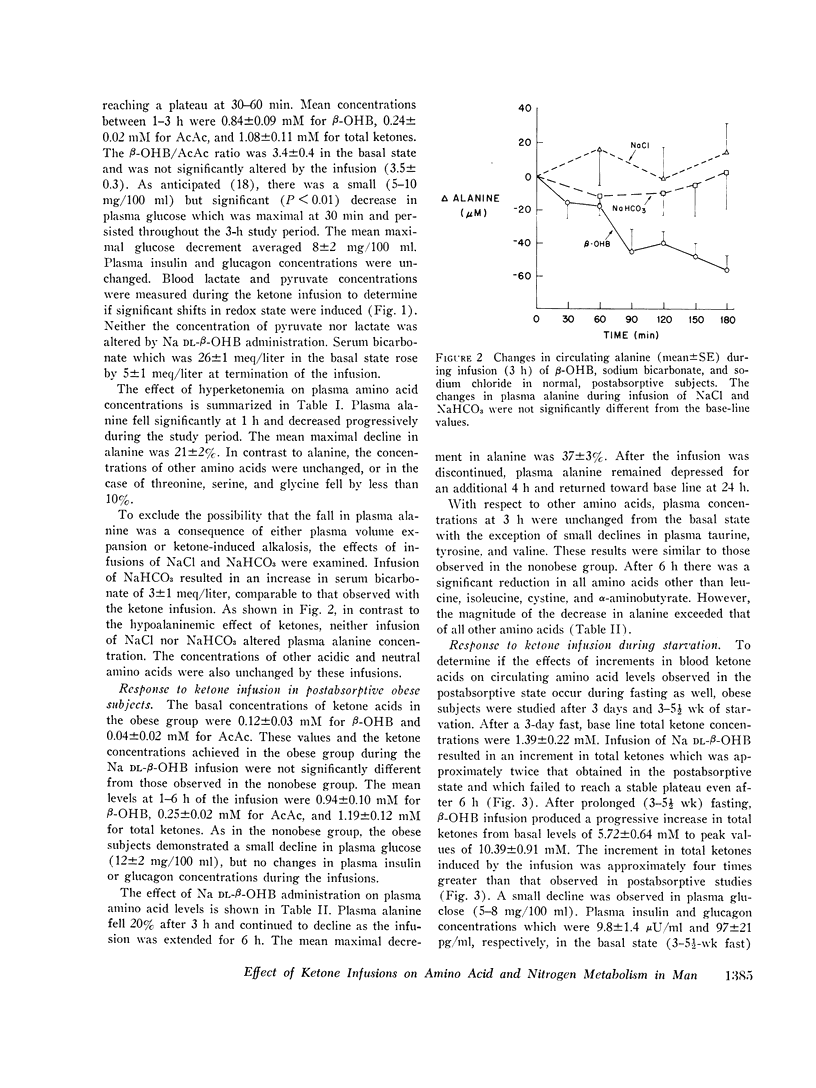
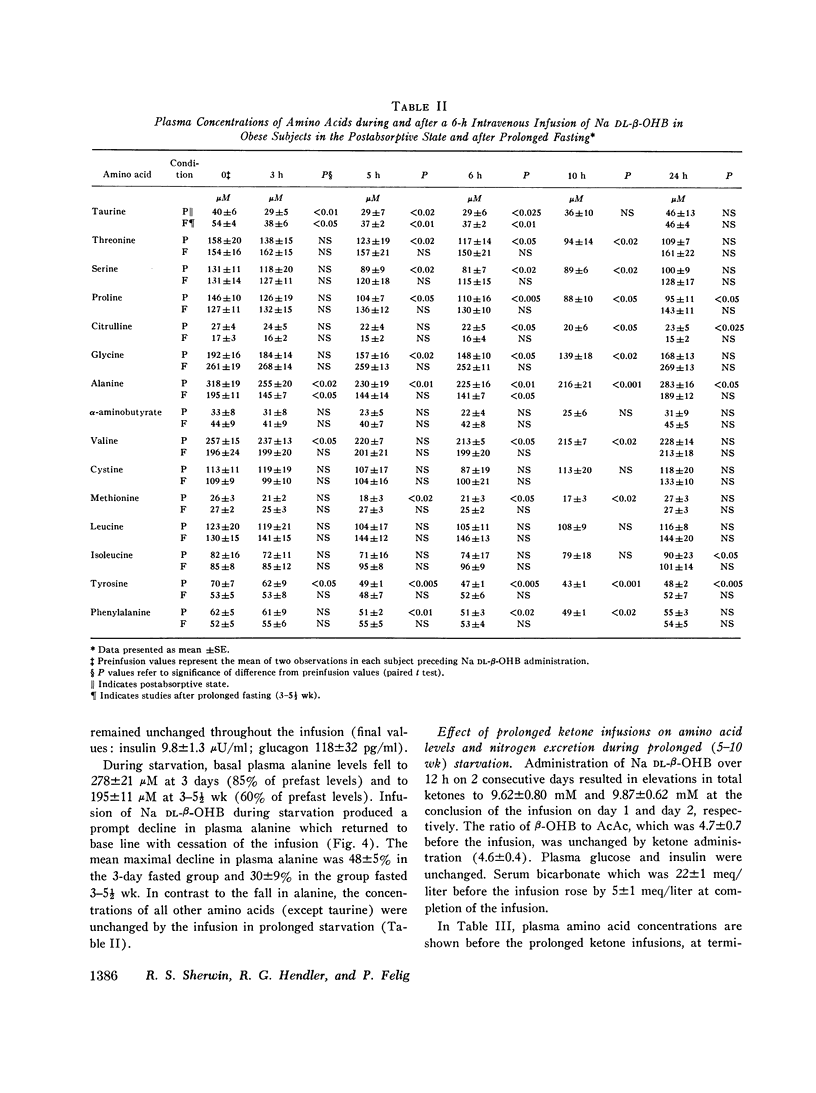
To evaluate the role of hyperketonemia in the hypoalaninemia and decreased protein catabolism of prolonged starvation, Na dl-beta-hydroxybutyrate was administered as a primed continuous 3-6-h infusion in nonobese subjects and in obese subjects in the postabsorptive state and after 3 days and 3-5 1/2 wk of starvation. An additional obese group received 12-h ketone infusions on 2 consecutive days after 5-10 wk of fasting. The ketone infusion in nonobese and obese subjects studied in the postabsorptive state resulted in total blood ketone acid levels of 1.1-1.2 mM, a 5-15 mg/100 ml decrease in plasma glucose, and unchanged levels of insulin, glucagon, lactate, and pyruvate. Plasma alanine fell by 21% (P smaller than 0.001) in 3 h. In contrast, other amino acids were stable or varied by less than 10%. Infusions lasting 6 h reduced plasma alanine by 37%, reaching levels comparable to those observed in prolonged starvation. Equimolar infusions of NaC1 and/or administration of NaHCO3 failed to alter plasma alanine levels. During prolonged fasting, plasma alanine, which had fallen by 40% below prefast levels, fell an additional 30% in response to the ketone infusion. In association with repeated prolonged (12 h) infusions in subjects fasted 5-10 wk, urinary nitrogen excretion fell by 30%, returning to base line after cessation of theinfusions and paralleling the changes in plasma alanine. Ketone infusins resulted in two- to fourfold greater increments in blood ketone acids in fasted as compared to postabsorptive subjects. It is concluded that increased blood ketone acid levels induced by infusions of Na DL-beta-hydroxybutyrate result in hypoalaninemia and in nitrogen conservation in starvation. These data suggest that hyperketonemia may be a contributory factor in the decreased availability or circulating alanine and reduction in protein catabolism characteristic of prolonged fastings9
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoki T. T., Müller W. A., Cahill G. F., Jr Hormonal regulation of glutamine metabolism in fasting man. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1972;10:145–151. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(72)90011-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balasse E., Couturier E., Franckson J. R. Influence of sodium beta-hydroxybutyrate on glucose and free fatty acid metabolism in normal dogs. Diabetologia. 1967 Dec;3(6):488–493. doi: 10.1007/BF01213566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balasse E., Ooms H. A. Changes in the concentrations of glucose, free fatty acids, insulin and ketone bodies in the blood during sodium beta-hydroxybutyrate infusions in man. Diabetologia. 1968 Jun;4(3):133–135. doi: 10.1007/BF01219433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn G. L., Flatt J. P., Clowes G. H., O'Donnell T. E. Peripheral intravenous feeding with isotonic amino acid solutions. Am J Surg. 1973 Apr;125(4):447–454. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(73)90080-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buse M. G., Biggers J. F., Friderici K. H., Buse J. F. Oxidation of branched chain amino acids by isolated hearts and diaphragms of the rat. The effect of fatty acids, glucose, and pyruvate respiration. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 25;247(24):8085–8096. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANEY A. L., MARBACH E. P. Modified reagents for determination of urea and ammonia. Clin Chem. 1962 Apr;8:130–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahill G. F., Jr, Herrera M. G., Morgan A. P., Soeldner J. S., Steinke J., Levy P. L., Reichard G. A., Jr, Kipnis D. M. Hormone-fuel interrelationships during fasting. J Clin Invest. 1966 Nov;45(11):1751–1769. doi: 10.1172/JCI105481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DARE J. G., MOGEY G. A. Rabbit responses to human threshold doses of a bacterial pyrogen. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1954 May;6(5):325–332. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1954.tb10954.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAJANS S. S., FLOYD J. C., Jr, KNOPF R. F., CONN J. W. A COMPARISON OF LEUCINE- AND ACETOACETATE-INDUCED HYPOGLYCEMIA IN MAN. J Clin Invest. 1964 Oct;43:2003–2008. doi: 10.1172/JCI105074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felig P., Kim Y. J., Lynch V., Hendler R. Amino acid metabolism during starvation in human pregnancy. J Clin Invest. 1972 May;51(5):1195–1202. doi: 10.1172/JCI106913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felig P., Marliss E. B., Cahill G. F., Jr Metabolic response to human growth hormone during prolonged starvation. J Clin Invest. 1971 Feb;50(2):411–421. doi: 10.1172/JCI106508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felig P., Marliss E., Owen O. E., Cahill G. F., Jr Blood glucose and cluconeogenesis in fasting man. Arch Intern Med. 1969 Mar;123(3):293–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felig P., Owen O. E., Wahren J., Cahill G. F., Jr Amino acid metabolism during prolonged starvation. J Clin Invest. 1969 Mar;48(3):584–594. doi: 10.1172/JCI106017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felig P., Pozefsky T., Marliss E., Cahill G. F., Jr Alanine: key role in gluconeogenesis. Science. 1970 Feb 13;167(3920):1003–1004. doi: 10.1126/science.167.3920.1003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felig P. The glucose-alanine cycle. Metabolism. 1973 Feb;22(2):179–207. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(73)90269-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felig P., Wahren J. Amino acid metabolism in exercising man. J Clin Invest. 1971 Dec;50(12):2703–2714. doi: 10.1172/JCI106771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulks R. M., Li J. B., Goldberg A. L. Effects of insulin, glucose, and amino acids on protein turnover in rat diaphragm. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 10;250(1):290–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber A. J., Menzel P. H., Boden G., Owen O. E. Hepatic ketogenesis and gluconeogenesis in humans. J Clin Invest. 1974 Oct;54(4):981–989. doi: 10.1172/JCI107839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCANN W. P. The oxidation of ketone bodies by mitochondria from liver and peripheral tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):15–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marliss E. B., Aoki T. T., Unger R. H., Soeldner J. S., Cahill G. F., Jr Glucagon levels and metabolic effects in fasting man. J Clin Invest. 1970 Dec;49(12):2256–2270. doi: 10.1172/JCI106445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odessey R., Khairallah E. A., Goldberg A. L. Origin and possible significance of alanine production by skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 10;249(23):7623–7629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen O. E., Felig P., Morgan A. P., Wahren J., Cahill G. F., Jr Liver and kidney metabolism during prolonged starvation. J Clin Invest. 1969 Mar;48(3):574–583. doi: 10.1172/JCI106016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen O. E., Morgan A. P., Kemp H. G., Sullivan J. M., Herrera M. G., Cahill G. F., Jr Brain metabolism during fasting. J Clin Invest. 1967 Oct;46(10):1589–1595. doi: 10.1172/JCI105650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen O. E., Reichard G. A., Jr Human forearm metabolism during progressive starvation. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jul;50(7):1536–1545. doi: 10.1172/JCI106639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen O. E., Reichard G. A., Jr, Markus H., Boden G., Mozzoli M. A., Shuman C. R. Rapid intravenous sodium acetoacetate infusion in man. Metabolic and kinetic responses. J Clin Invest. 1973 Oct;52(10):2606–2616. doi: 10.1172/JCI107453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PITTS R. F. RENAL PRODUCTION AND EXCRETION OF AMMONIA. Am J Med. 1964 May;36:720–742. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(64)90182-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagliara A. S., Kari I. E., De Vivo D. C., Feigin R. D., Kipnis D. M. Hypoalaninemia: a concomitant of ketotic hypoglycemia. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jun;51(6):1440–1449. doi: 10.1172/JCI106940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior B., Loridan L. Direct regulatory effect of ketones on lipolysis and on glucose concentrations in man. Nature. 1968 Jul 6;219(5149):83–84. doi: 10.1038/219083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMSON D. H., MELLANBY J., KREBS H. A. Enzymic determination of D(-)-beta-hydroxybutyric acid and acetoacetic acid in blood. Biochem J. 1962 Jan;82:90–96. doi: 10.1042/bj0820090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise J. K., Hendler R., Felig P. Influence of glucocorticoids on glucagon secretion and plasma amino acid concentrations in man. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2774–2782. doi: 10.1172/JCI107473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



