Abstract
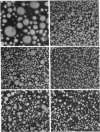
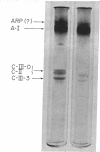
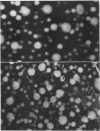
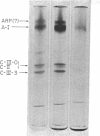
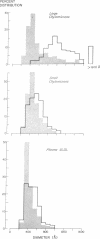
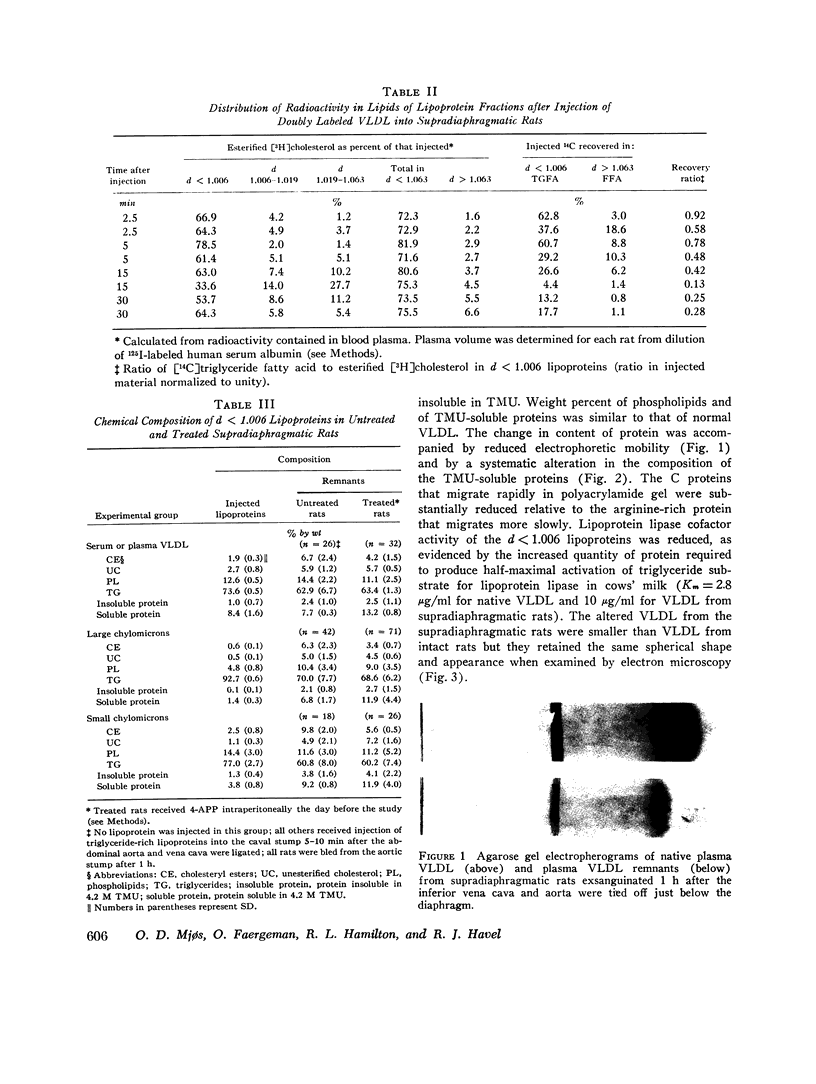
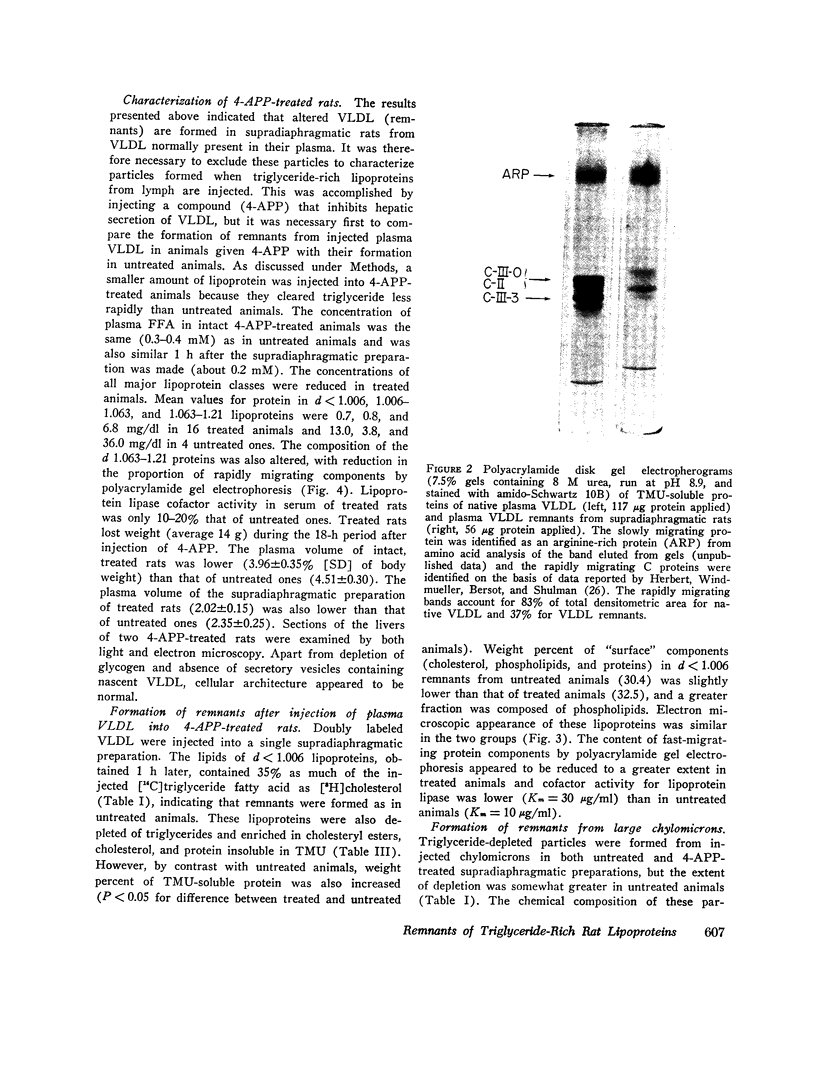
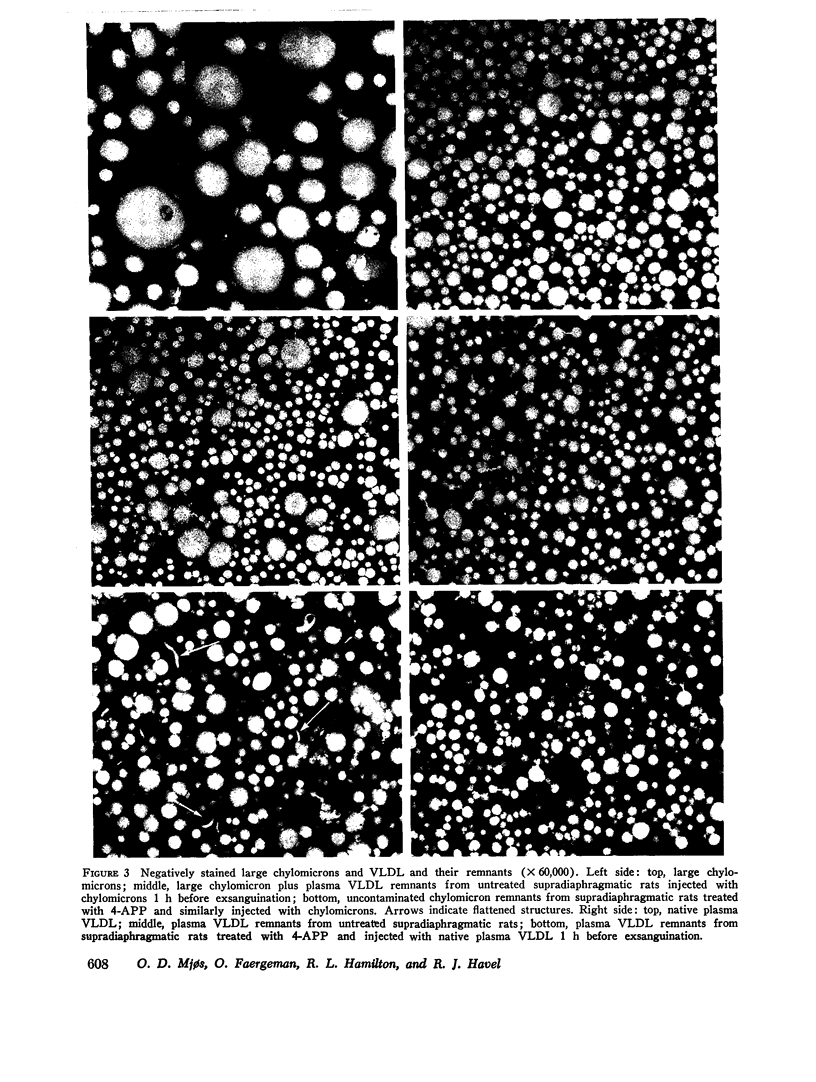
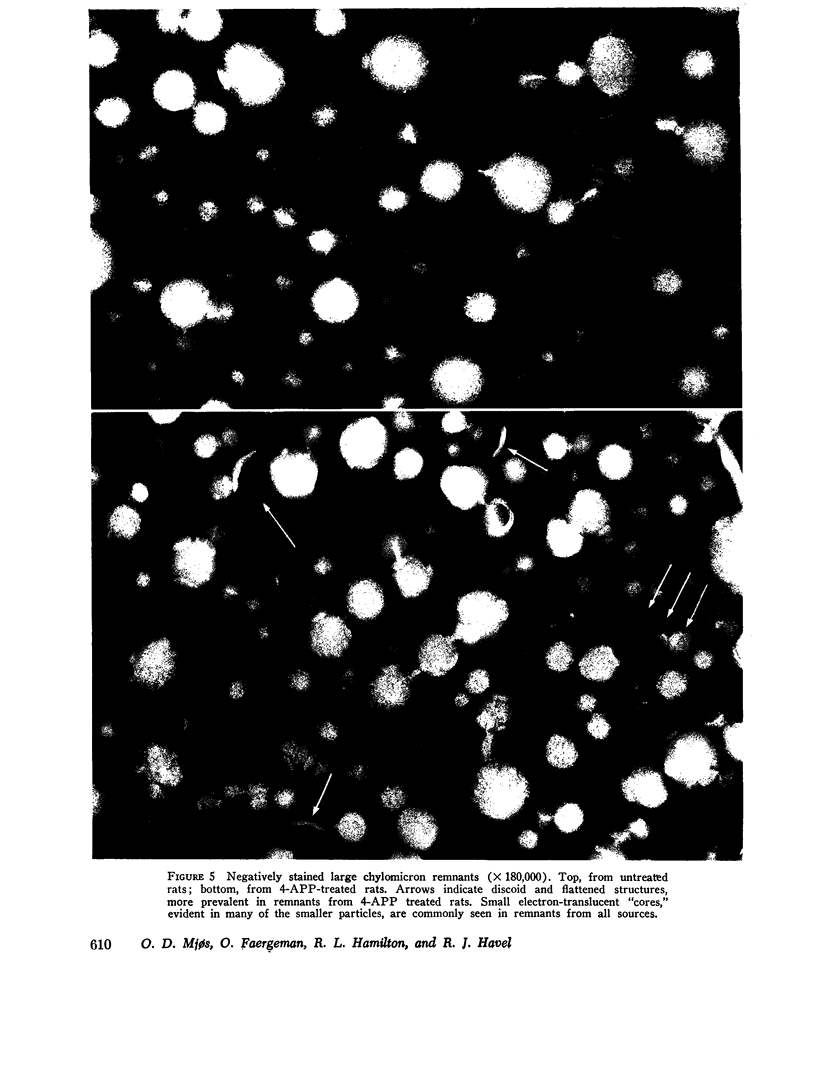
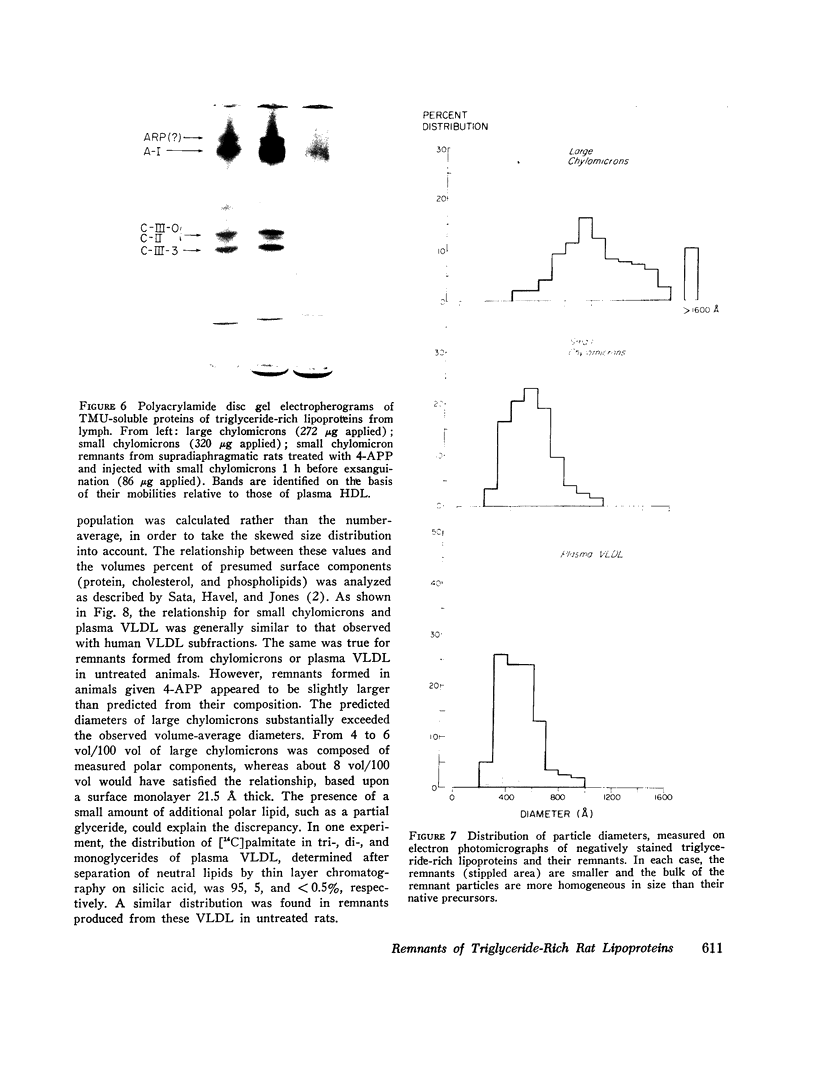
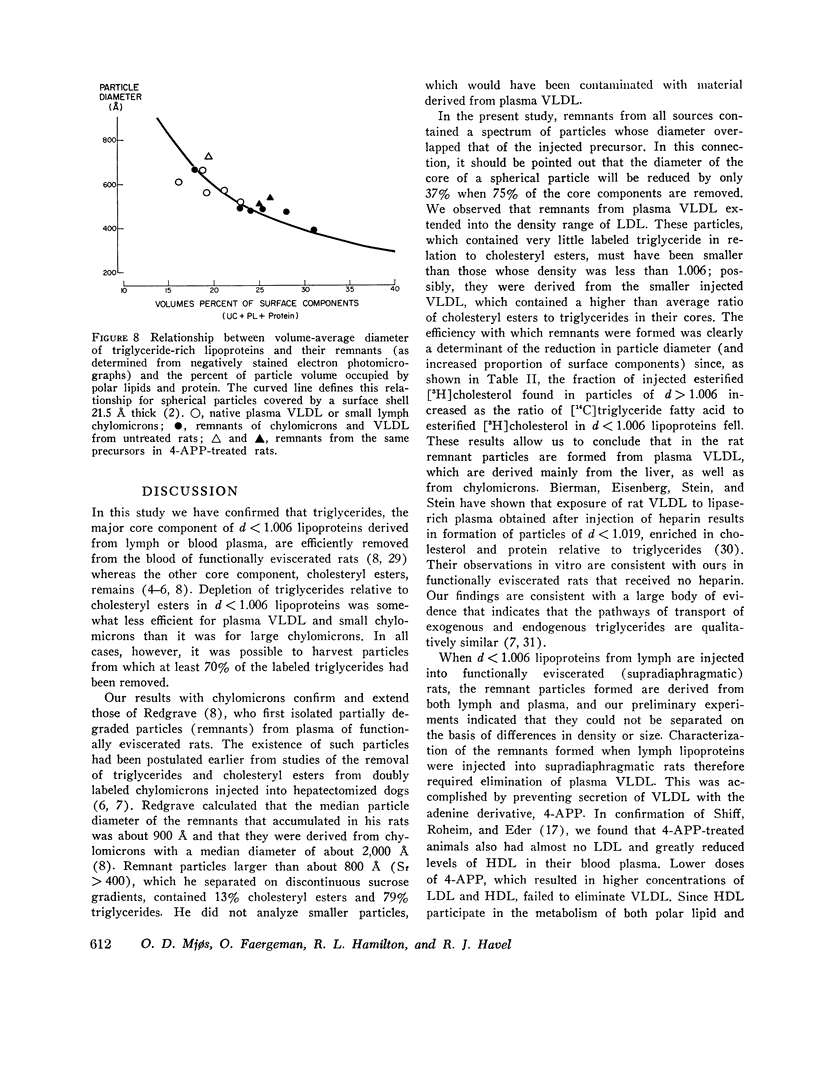
The metabolism of intravenously injected large and small chylomicrons from intestinal lymph and of very low density lipoproteins from blood plasma was studied in functionally eviscerated "supradiaphragmetic" rats. For studies with lymph lipoproteins, recipient animals were injected with 4-amino-pyrazolopyrimidine 18 h before injection of lipoprotein to prevent secretion of very low density lipoproteins into their blood plasma. In all cases, most of the triglycerides (labeled with 14C) were rapidly metabolized, whereas cholesteryl esters (labeled with 3H) persisted in the blood. Most of the cholesteryl esters remained in smaller "remnant" lipoproteins, less dense that 1.006, which retained an apparently spherical shape, as determined by electron microscopy of negatively stained preparations. Whereas the diameters and chemical compositions of large chylomicrons were substantially different from those of small chylomicrons and very low density lipoproteins, all remnants were similar in these respects. Average remnant diameters were 400-600 A and remnants were enriched in cholesteryl esters and in protein insoluble in tetramethylurea. In addition to triglycerides, remnants were depleted of phospholiarticle size, the composition of remnants, like that of their precursors, was consistent with the "pseudomicellar" model of lipoproteins, in which a core of nonpolar lipids is covered by a monolayer of polar lipids and protein. These results domonstrate the fundamental similarity of the initial step in the metabolism of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins from intestinal mucosa and liver and show that loss of triglycerides from the core of the particles is accompanied by removal of polar components from the surface.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOBERG J., CARLSON L. A. DETERMINATION OF HEPARIN-INDUCED LIPOPROTEIN LIPASE ACTIVITY IN HUMAN PLASMA. Clin Chim Acta. 1964 Nov;10:420–427. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(64)90171-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergman E. N., Havel R. J., Wolfe B. M., Bohmer T. Quantitative studies of the metabolism of chylomicron triglycerides and cholesterol by liver and extrahepatic tissues of sheep and dogs. J Clin Invest. 1971 Sep;50(9):1831–1839. doi: 10.1172/JCI106674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bier D. M., Havel R. J. Activation of lipoprotein lipase by lipoprotein fractions of human serum. J Lipid Res. 1970 Nov;11(6):565–570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bierman E. L., Eisenberg S., Stein O., Stein Y. Very low density lipoprotein "remnant" particles: uptake by aortic smooth muscle cells in culture. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Nov 2;329(1):163–169. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(73)90021-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOLE V. P. A relation between non-esterified fatty acids in plasma and the metabolism of glucose. J Clin Invest. 1956 Feb;35(2):150–154. doi: 10.1172/JCI103259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S., Bilheimer D. W., Levy R. I., Lindgren F. T. On the metabolic conversion of human plasma very low density lipoprotein to low density lipoprotein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Dec 20;326(3):361–377. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(73)90138-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S., Rachmilewitz D. Metabolism of rat plasma very low density lipoprotein. I. Fate in circulation of the whole lipoprotein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Dec 20;326(3):378–390. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(73)90139-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S., Rachmilewitz D. Metabolism of rat plasma very low density lipoprotein. II. Fate in circulation of apoprotein subunits. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Dec 20;326(3):391–405. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(73)90140-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faergeman O., Havel R. J. Metabolism of cholesteryl esters of rat very low density lipoproteins. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jun;55(6):1210–1218. doi: 10.1172/JCI108039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODMAN D. S. The metabolism of chylomicron cholesterol ester in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1962 Oct;41:1886–1896. doi: 10.1172/JCI104645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glomset J. A., Norum K. R. The metabolic role of lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase: perspectives form pathology. Adv Lipid Res. 1973;11:1–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., EDER H. A., BRAGDON J. H. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1345–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI103182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton R. L., Havel R. J., Kane J. P., Blaurock A. E., Sata T. Cholestasis: lamellar structure of the abnormal human serum lipoprotein. Science. 1971 Apr 30;172(3982):475–478. doi: 10.1126/science.172.3982.475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havel R. J., Kane J. P., Kashyap M. L. Interchange of apolipoproteins between chylomicrons and high density lipoproteins during alimentary lipemia in man. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jan;52(1):32–38. doi: 10.1172/JCI107171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havel R. J., Kane J. P. Primary dysbetalipoproteinemia: predominance of a specific apoprotein species in triglyceride-rich lipoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):2015–2019. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.2015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazzard W. R., Porte D., Jr, Bierman E. L. Abnormal lipid composition of chylomicrons in broad-beta disease (type 3hyperlipoproteinemia). J Clin Invest. 1970 Oct;49(10):1853–1858. doi: 10.1172/JCI106403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert P. N., Windmueller H. G., Bersot T. P., Shulman R. S. Characterization of the rat apolipoproteins. I. The low molecular weight proteins of rat plasma high density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 25;249(18):5718–5724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. L., Havel R. J. Metabolism of free fatty acids and chylomicron triglycerides during exercise in rats. Am J Physiol. 1967 Oct;213(4):824–828. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.213.4.824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLEY T. F. IMPROVED METHOD FOR MICROTITRATION OF FATTY ACIDS. Anal Chem. 1965 Jul;37:1078–1079. doi: 10.1021/ac60227a044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane J. P. A rapid electrophoretic technique for identification of subunit species of apoproteins in serum lipoproteins. Anal Biochem. 1973 Jun;53(2):350–364. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90081-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NESTEL P. J., HAVEL R. J., BEZMAN A. METABOLISM OF CONSTITUENT LIPIDS OF DOG CHYLOMICRONS. J Clin Invest. 1963 Aug;42:1313–1321. doi: 10.1172/JCI104815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble R. P. Electrophoretic separation of plasma lipoproteins in agarose gel. J Lipid Res. 1968 Nov;9(6):693–700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quarfordt S., Levy R. I., Fredrickson D. S. On thelipoprotein abnormality in type 3 hyperlipoproteinemia. J Clin Invest. 1971 Apr;50(4):754–761. doi: 10.1172/JCI106546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redgrave T. G. Cholesterol feeding alters the metabolism of thoracic-duct lymph lipoprotein cholesterol in rabbits but not in rats. Biochem J. 1973 Sep;136(1):109–113. doi: 10.1042/bj1360109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redgrave T. G. Formation of cholesteryl ester-rich particulate lipid during metabolism of chylomicrons. J Clin Invest. 1970 Mar;49(3):465–471. doi: 10.1172/JCI106255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sata T., Estrich D. L., Wood P. D., Kinsell L. W. Evaluation of gel chromatography for plasma lipoprotein fractionation. J Lipid Res. 1970 Jul;11(4):331–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sata T., Havel R. J., Jones A. L. Characterization of subfractions of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins separated by gel chromatography from blood plasma of normolipemic and hyperlipemic humans. J Lipid Res. 1972 Nov;13(6):757–768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiff T. S., Roheim P. S., Eder H. A. Effects of high sucrose diets and 4-aminopyrazolopyrimidine on serum lipids and lipoproteins in the rat. J Lipid Res. 1971 Sep;12(5):596–603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swaney J. B., Reese H., Eder H. A. Polypeptide composition of rat high density lipoprotein: characterization by SDS-gel electrophoresis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Jul 24;59(2):513–519. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80010-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windmueller H. G., Herbert P. N., Levy R. I. Biosynthesis of lymph and plasma lipoprotein apoproteins by isolated perfused rat liver and intestine. J Lipid Res. 1973 Mar;14(2):215–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilversmit D. B. The composition and structure of lymph chylomicrons in dog, rat, and man. J Clin Invest. 1965 Oct;44(10):1610–1622. doi: 10.1172/JCI105267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]