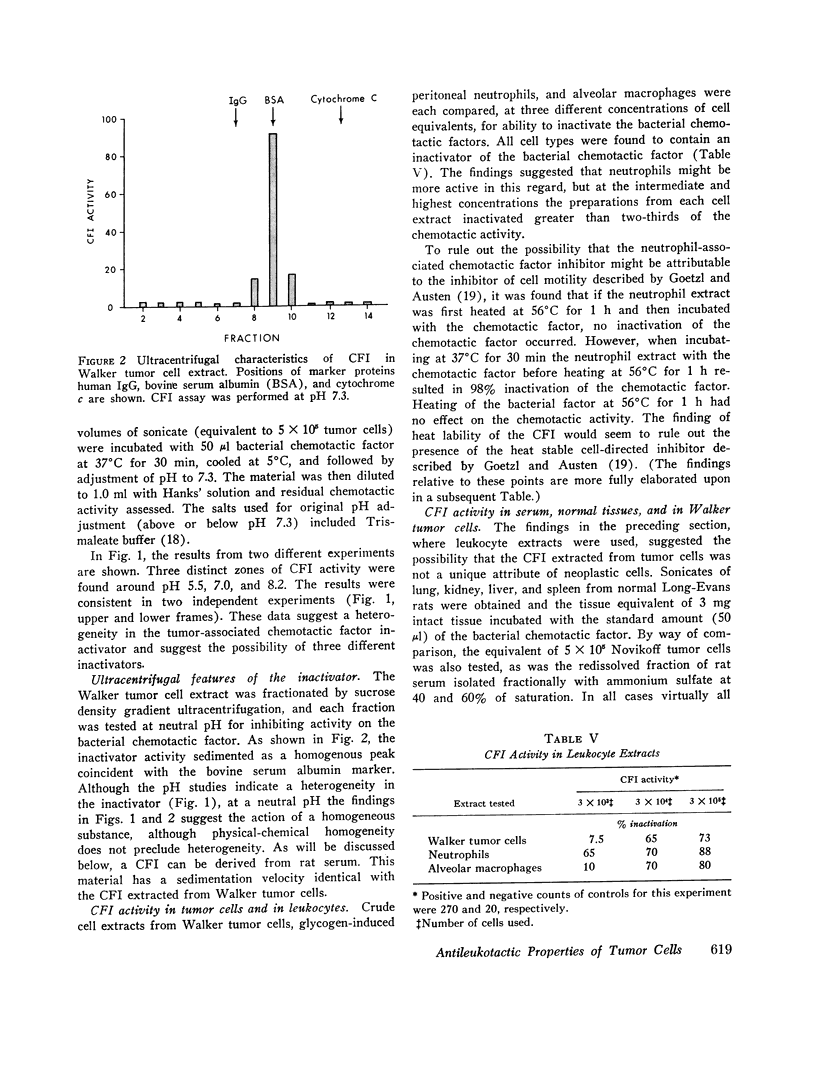
Abstract
A chemotactic factor inactivator (CFI) has been found in extracts of Walker and Novikoff tumor cells maintained in rats. The CFI directly inactivates the bacterial chemotactic factor as well as the leukotactic activity (fro both neutrophils and monocytes) associated with C3 and C5 fragments and with culture fluids of lectin-stimulated lymphoid cells. The inactivation of the bacterial chemotactic factor is temperature and pH dependent. Subcellular fractionation procedures indicate that CFI is largely associated with the microsomal and cytosol fractions of tumor cells. CFI activity is also found in rat neutrophils, alveolar macrophages, and in extracts of liver, spleen, and kidney from normal animals. CFI derived from normal tissues also directly inactivates the bacterial chemotactic factor and has the ability to inactivate chemotactic activity associated with C3 and C5 fragments. A feature of the tumor-associated CFI is its presence in ascitic fluids of animals bearing tumor cells and the relative absence of any CFI activity in acute inflammatory exudates. The finding of the tumor-associated CFI may explain, at least in part, the tendency of malignant tumor cells to suppress cellular inflammatory reactions.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERG J. W. Inflammation and prognosis in breast cancer; a search for host resistance. Cancer. 1959 Jul-Aug;12(4):714–720. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(195907/08)12:4<714::aid-cncr2820120414>3.0.co;2-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berenberg J. L., Ward P. A. Chemotactic factor inactivator in normal human serum. J Clin Invest. 1973 May;52(5):1200–1206. doi: 10.1172/JCI107287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokisch V. A., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Anaphylatoxin inactivator of human plasma: its isolation and characterization as a carboxypeptidase. J Clin Invest. 1970 Dec;49(12):2427–2436. doi: 10.1172/JCI106462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Duve C. The separation and characterization of subcellular particles. Harvey Lect. 1965;59:49–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Duve C. Tissue fractionation. Past and present. J Cell Biol. 1971 Jul;50(1):20d–55d. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilber F. R., Morton D. L. Impaired immunologic reactivity and recurrence following cancer surgery. Cancer. 1970 Feb;25(2):362–367. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197002)25:2<362::aid-cncr2820250213>3.0.co;2-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauve R. M., Hevin B., Jacob H., Gaillard J. A., Jacob F. Antiinflammatory effects of murine malignant cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4052–4056. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetzl E. J., Austen K. F. A neutrophil-immobilizing factor derived from human leukocytes. I. Generation and partial characterization. J Exp Med. 1972 Dec 1;136(6):1564–1580. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.6.1564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLMBERG B. Inhibition of cellular adhesion and pseudopodia formation by a dialysable factor from tumour fluids. Nature. 1962 Jul 7;195:45–47. doi: 10.1038/195045a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill J. H., Ward P. A. C3 leukotactic factors produced by a tissue protease. J Exp Med. 1969 Sep 1;130(3):505–518. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.3.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes L. E., Mackay W. D. Suppression of the tuberculin response in malignant disease. Br Med J. 1965 Dec 4;2(5474):1346–1348. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5474.1346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. J., Ward P. A. Acute immunologic pulmonary alveolitis. J Clin Invest. 1974 Aug;54(2):349–357. doi: 10.1172/JCI107770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. W., Maibach H. I., Salmon S. E. Skin reactivity in patients with cancer. Impaired delayed hypersensitivity or faulty inflammatory response? N Engl J Med. 1971 Jun 3;284(22):1255–1257. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197106032842210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAMB D., PILNEY F., KELLY W. D., GOOD R. A. A comparative study of the incidence of anergy in patients with carcinoma, leukemia, hodgkin's disease and other lymphomas. J Immunol. 1962 Oct;89:555–558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVIN A. G., MCDONOUGH E. F., Jr, MILLER D. G., SOUTHAM C. M. DELAYED HYPERSENSITIVITY RESPONSE TO DNFB IN SICK AND HEALTHY PERSONS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Nov 30;120:400–409. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb34739.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAHONEY M. J., LEIGHTON J. The inflammatory response to a foreign body within transplantable tumors. Cancer Res. 1962 Apr;22:334–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwin R. P., Richters A. Pathobiology of lymphocyte interactions. Pathol Annu. 1973;8:379–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Till G., Ward P. A. Two distinct chemotactic factor inactivators in human serum. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 2):843–847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARD P. A., COCHRANE C. G., MUELLER-EBERHARD H. J. THE ROLE OF SERUM COMPLEMENT IN CHEMOTAXIS OF LEUKOCYTES IN VITRO. J Exp Med. 1965 Aug 1;122:327–346. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Berenberg J. L. Defective regulation of inflammatory mediators in Hodgkin's disease. Supernormal levels of chemotactic-factor inactivator. N Engl J Med. 1974 Jan 10;290(2):76–80. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197401102900203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A. Chemotaxis of polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1968 Mar;(Suppl):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(68)90297-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Lepow I. H., Newman L. J. Bacterial factors chemotactic for polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Am J Pathol. 1968 Apr;52(4):725–736. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolberg W. H. Inhibition of migration of human autogenous and allogeneic leukocytes by extracts of patients' cancers. Cancer Res. 1971 Jun;31(6):798–802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]