Abstract
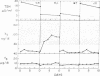
The role of liver in the peripheral conversion of thyroxine (T4) to triiodothyronine (T3) was studied in normal subjects and patients with alcoholic liver disease by measurement of thyrotrophin (TSH) and total and free T4 and T3 in randomand serial serum samples. Also, T4 to T3 conversion rates and T3 disposal rates were compared by noncompartmental analysis. While the mean total serum T4 values were similar for the two groups, 8.6 and 8.1 mug/kl, the mean free T4 value was significantly higher in the cirrhotic patients (3.3 ng/dl) than in the normal subjects (2.1 ng/dl, P less than 0.001). The mean serum T3 value, 85 ng/dl, was significantly reduced in the hepatic patients as compared to a mean serum T3 value of 126 ng/dl in the normal subjects (P less than 0.001), while the free T3 value was 0.28 ng/dl in both groups. The reduction of the serum total and free T3 values were closely correlated with the degree of liver damage, as indicated by elevation of serum bilirubin (r equal -0.547) and reduction of serum albumin (r equal 0.471). The mean serum TSH level was 3.1 muU/ml in the normals and 7.1 muU/ml in the cirrhotic aptients ( less than 0.001). 15% of the hepatic patients had serum TSH values above 10 muU/ml, which, however, did not correlate with any of the four liver function tests studied. Serial blood sampling from two convalescing patients with alcoholic hepatitis showed a gradual normalization of serum TSH and T3 levels as the liver function improved. After oral T4 administration, 0.25 mg/day for 10 days, three of four cirrhotic patients studied failed to raise their serum T3 values. The mean T4 to T3 conversion rate of seven normal subjects was 35.7%. The mean T4 to T3 conversion rate of four cirrhotic patients studied was significantly reduced to 15.6% (P less than 0.001). The mean disposal rates of T4 and T3 of the normal subjects were 114 and 34 mug/day, respectively. The ratio of T4 disposal to T3 disposal was 3.5. In contrast, the mean T4 disposal rate, 82 mug/day, and the mean T3 disposal rate, 10 mug/day, were both reduced in the cirrhotic patients. Their ratio of T4 disposal to T3 disposal was 7.9. These findings suggest that impairment of T4 conversion in patients with advanced hepatic cirrhosis may lead to reduced T3 production and lowered serum T3 level. Therefore, the liver is one of the major sites of T4 conversion to T3.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALBRIGHT E. C., LARSON F. C., TUST R. H. In vitro conversion of thyroxin to triiodothyronine by kidney slices. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1954 May;86(1):137–140. doi: 10.3181/00379727-86-21031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BECKER D. V., PRUDDEN J. F. The metabolism of I 131-labeled thyroxine, triiodothyronine and diiodotyrosine by an isolated perfused rabbit liver. Endocrinology. 1959 Jan;64(1):136–148. doi: 10.1210/endo-64-1-136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein G., Artz S. A., Hasen J., Oppenheimer J. H. Hepatic accumulation of 125I-thyroxine in the rat: augmentation by phenobarbital and chlordane. Endocrinology. 1968 Feb;82(2):406–409. doi: 10.1210/endo-82-2-406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braverman L. E., Ingbar S. H., Sterling K. Conversion of thyroxine (T4) to triiodothyronine (T3) in athyreotic human subjects. J Clin Invest. 1970 May;49(5):855–864. doi: 10.1172/JCI106304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter J. N., Eastman C. J., Corcoran J. M., Lazarus L. Effect of severe, chronic illness on thyroid function. Lancet. 1974 Oct 26;2(7887):971–974. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92070-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavalieri R. R., Searle G. L. The kinetics of distribution between plasma and liver of 131-I-labeled L-thyroxine in man: observations of subjects with normal and decreased serum thyroxine-binding globulin. J Clin Invest. 1966 Jun;45(6):939–949. doi: 10.1172/JCI105409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I. J. A radioimmunoassay for measurement of thyroxine in unextracted serum. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1972 Jun;34(6):938–947. doi: 10.1210/jcem-34-6-938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I. J., Fisher D. A., Solomon D. H., Beall G. N. Thyroxine and triiodothyronine in the human thyroid. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1973 Feb;36(2):311–316. doi: 10.1210/jcem-36-2-311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I. J., Solomon D. H., Beall G. N. Radioimmunoassay for measurement of triiodothyronine in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1971 Oct;50(10):2033–2041. doi: 10.1172/JCI106696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I. J., Solomon D. H., Chopra U., Young R. T., Chua Teco G. N. Alterations in circulating thyroid hormones and thyrotropin in hepatic cirrhosis: evidence for euthyroidism despite subnormal serum triiodothyronine. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 Sep;39(3):501–511. doi: 10.1210/jcem-39-3-501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIIS T. Thyroxine metabolism in man estimated by means of I 131-labelled L-thyroxine. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1958 Dec;29(4):587–601. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0290587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher D. A., Chopra I. J., Dussault J. H. Extrathyroidal conversion of thyroxine to triiodothyronine in sheep. Endocrinology. 1972 Oct;91(4):1141–1144. doi: 10.1210/endo-91-4-1141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRINBERG R., VOLPERT E. M., WERNER S. C. In vivo deiodination of labeled L-thyroxine to L-3,5,3'-triiodothyronine in mouse and human pituitaries. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1963 Feb;23:140–142. doi: 10.1210/jcem-23-2-140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inada M., Sterling K. Thyroxine Turnover and Transport in Laennec's Cirrhosis of the Liver. J Clin Invest. 1967 Aug;46(8):1275–1282. doi: 10.1172/JCI105620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LENNON E. J., ENGBRING N. H., ENGSTROM W. W. Studies of the rate of disappearance of labeled thyroxine from the intravascular compartment. J Clin Invest. 1961 Jun;40:996–1005. doi: 10.1172/JCI104339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieber C. S. Liver adaptation and injury in alcoholism. N Engl J Med. 1973 Feb 15;288(7):356–362. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197302152880710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConnon J., Row V. V., Volpé R. The influence of liver damage in man on the distribution and disposal rates of thyroxine and triiodothyronine. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1972 Jan;34(1):144–151. doi: 10.1210/jcem-34-1-144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer J. H., Bernstein G., Surks M. I. Increased thyroxine turnover and thyroidal function after stimulation of hepatocellular binding of thyroxine by phenobarbital. J Clin Invest. 1968 Jun;47(6):1399–1406. doi: 10.1172/JCI105831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman C. S., Chambers J. B., Jr, Read V. H. The extrathyroidal conversion rate of thyroxine to triiodothyronine in normal man. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jun;50(6):1187–1196. doi: 10.1172/JCI106596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnay G. I., O'Brian J. T., Bush J., Vagenakis A. G., Azizi F., Arky R. A., Ingbar S. H., Braverman L. E. The effect of starvation on the concentration and binding of thyroxine and triiodothyronine in serum and on the response to TRH. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 Jul;39(1):191–194. doi: 10.1210/jcem-39-1-191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RALL J. E., RAWSON R. W., TATA J. R. Metabolism of L-thyroxine and L-3:5:3'-triiodothyronine by brain tissue preparations. Endocrinology. 1957 Jan;60(1):83–98. doi: 10.1210/endo-60-1-83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinowitz J. L., Hercker E. S. Thyroxine: convesion to triiodothyronine by isolated perfused rat heart. Science. 1971 Sep 24;173(4003):1242–1243. doi: 10.1126/science.173.4003.1242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Refetoff S., Matalon R., Bigazzi M. Metabolism of L-thyroxine (T4) and L-triiodothyronine (T3) by human fibroblasts in tissue culture: evidence for cellular binding proteins and conversion of T4 to T3. Endocrinology. 1972 Oct;91(4):934–947. doi: 10.1210/endo-91-4-934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz H. L., Surks M. I., Oppenheimer J. H. Quantitation of extrathyroidal conversion of L-thyroxine to 3,5,3'-triiodo-L-thyronine in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1971 May;50(5):1124–1130. doi: 10.1172/JCI106584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterling K., Brenner M. A. Free thyroxine in human serum: simplified measurement with the aid of magnesium precipitation. J Clin Invest. 1966 Jan;45(1):153–163. doi: 10.1172/JCI105320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterling K., Brenner M. A., Newman E. S. Conversion of thyroxine to triiodothyronine in normal human subjects. Science. 1970 Sep 11;169(3950):1099–1100. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3950.1099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterling K., Brenner M. A., Saldanha V. F. Conversion of thyroxine to triiodothyronine by cultured human cells. Science. 1973 Mar 9;179(4077):1000–1001. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4077.1000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surks M. I., Schadlow A. R., Stock J. M., Oppenheimer J. H. Determination of iodothyronine absorption and conversion of L-thyroxine (T 4 ) to L-triiodothyronine (T 3 ) using turnover rate techniques. J Clin Invest. 1973 Apr;52(4):805–811. doi: 10.1172/JCI107244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAIT J. F. REVIEW: THE USE OF ISOTOPIC STEROIDS FOR THE MEASUREMENT OF PRODUCTION RATES IN VIVO. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1963 Dec;23:1285–1297. doi: 10.1210/jcem-23-12-1285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VANNOTTI A., BERAUD T. Functional relationships between the liver, the thyroxine-binding protein of serum, and the thyroid. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1959 Apr;19(4):466–477. doi: 10.1210/jcem-19-4-466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]