Abstract
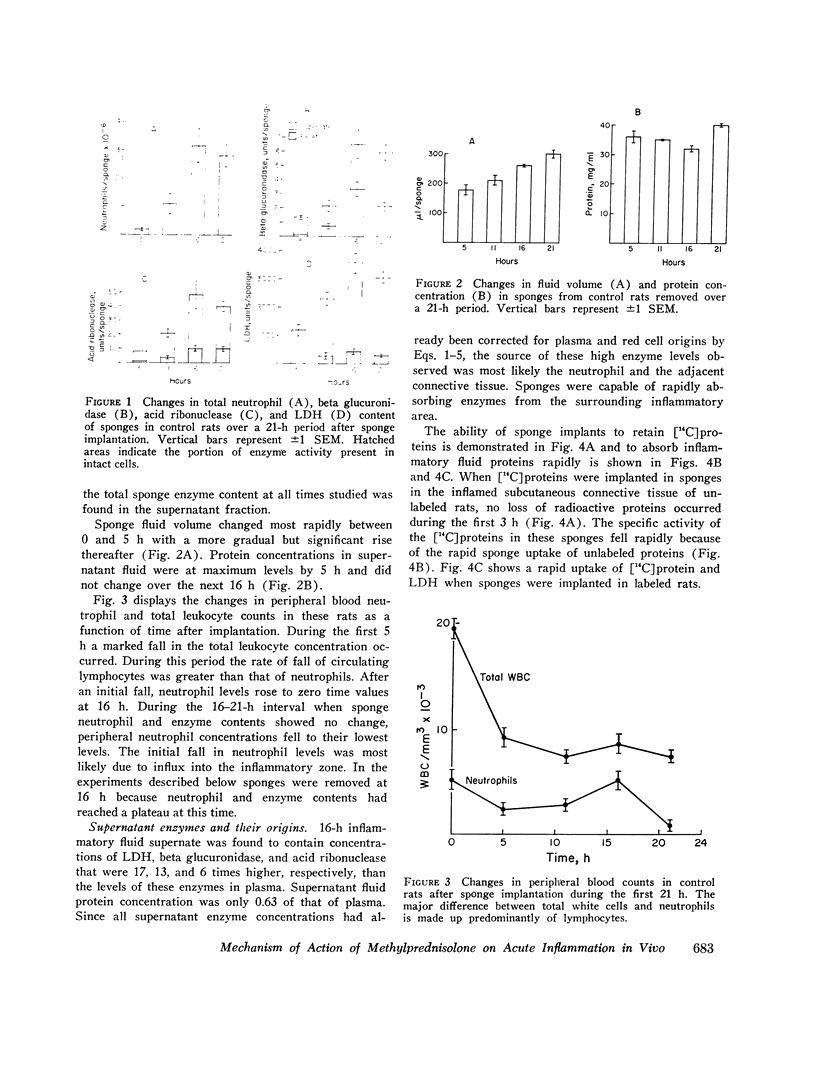
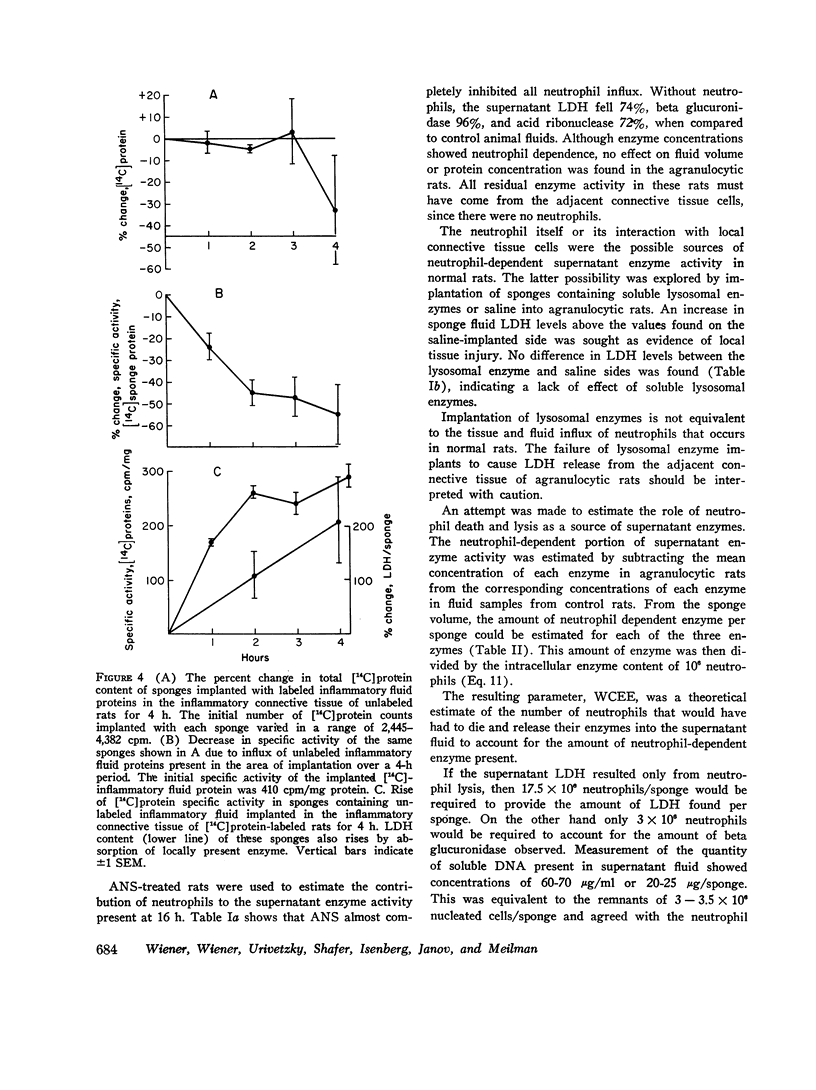
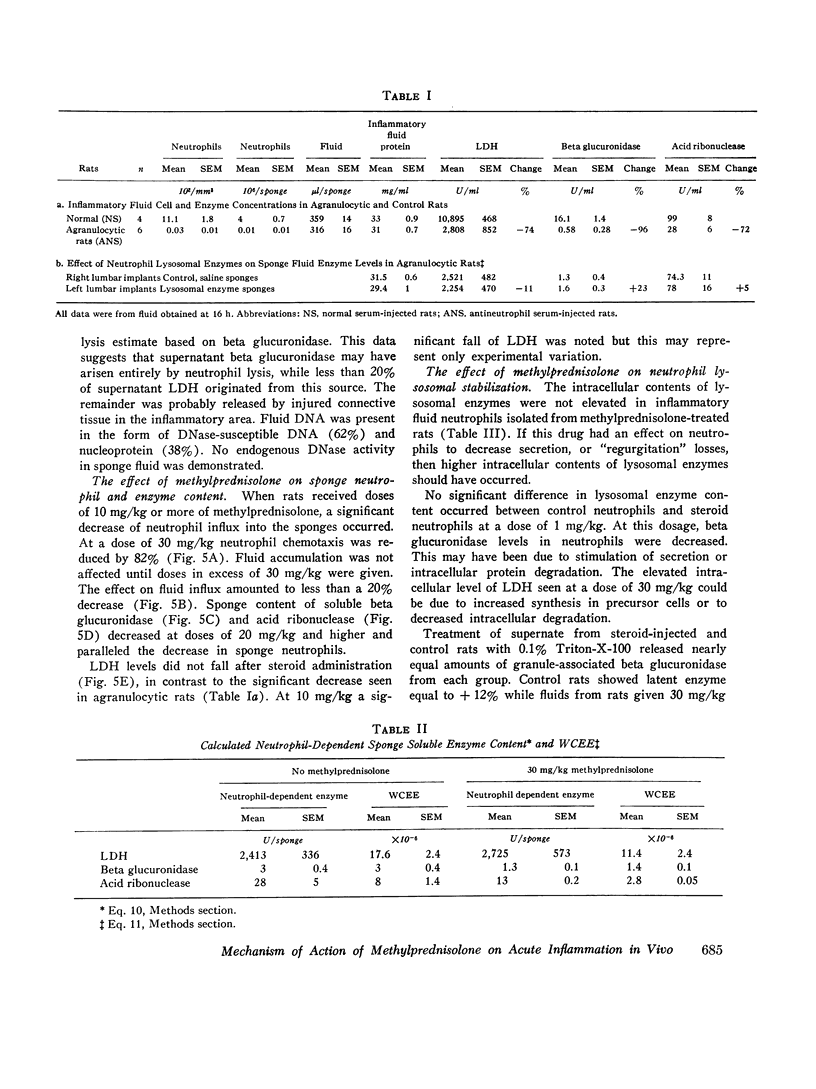
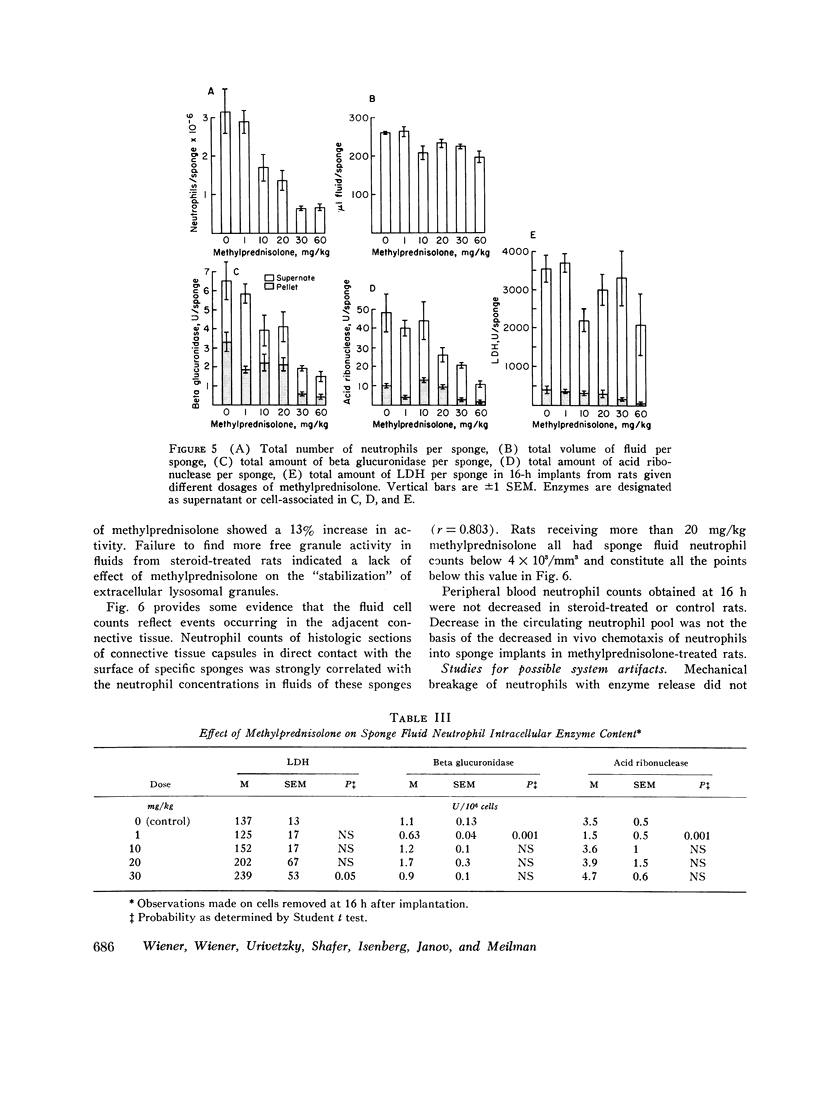
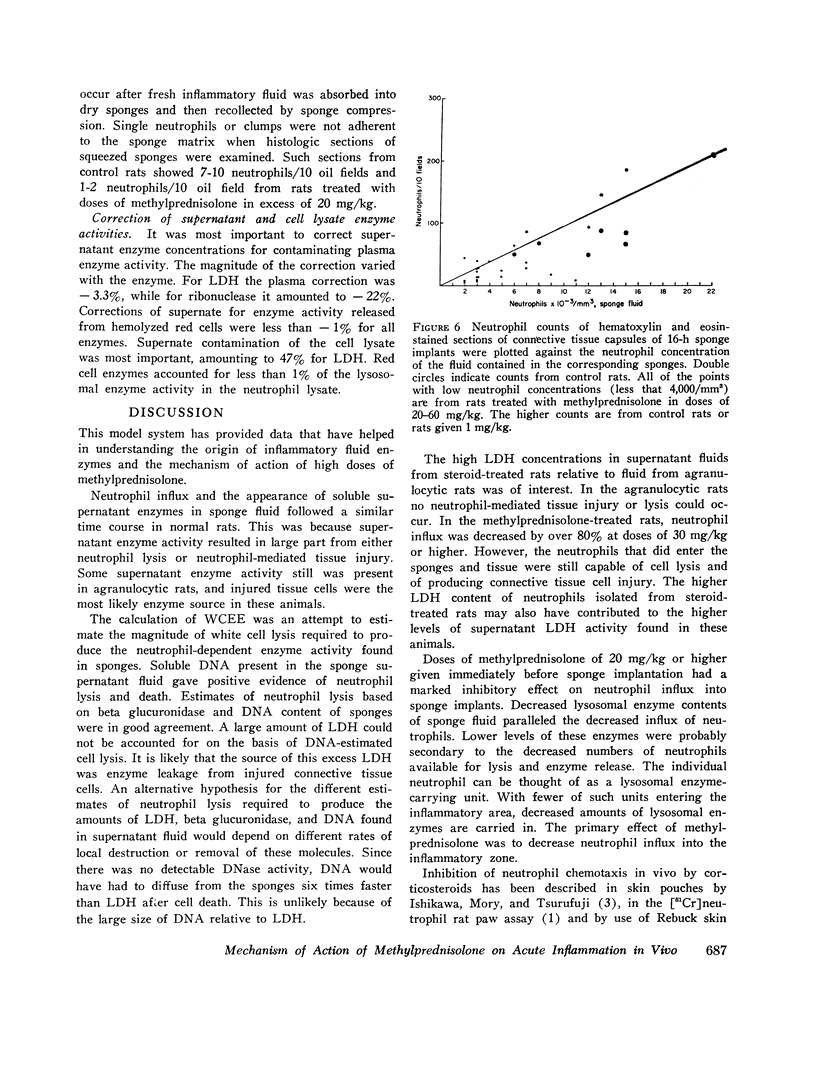
A model system for the study of inflammation in vivo has been developed using the 16-h polyvinyl sponge implant in the rat. This system allows for simultaneous measurement of in vivo chemotaxis, volume of fluid influx, and fluid concentrations of lysosomal and lactic dehydrogenase (LDH) enzymes. In addition, the enzyme content of inflammatory fluid neutrophils may also be determined. A parallel time course of neutrophil and lysosomal enzyme influx into sponge implants was observed. This was characterized by an initial lag phase and a rapid increase between 5 and 16 h. The origin of supernatant LDH and lysosomal enzymes was studied with anti-neutrophil serum to produce agranulocytic rats. Inflammatory fluid in these rats was almost acellular and contained decreased concentrations of beta glucuronidase (-96%) and LDH (-74%). In control rats all of the supernatant beta glucuronidase could be accounted for by cell death and lysis, as estimated from measurements of soluble DNA. Only 15-20% of the LDH activity could be accounted for on the basis of cell lysis. The remainder was derived from neutrophil-mediated injury to connective tissue cells. Large intravascular doses of methylprednisolone markedly inhibited neutrophil influx into sponges and adjacent connective tissue. Secondary to decreased neutrophil influx, fewer neutrophils were available for lysis, and lysosomal enzyme levels in inflammatory fluid decreased. No evidence for intracellular or extracellular stabilization of neutrophil lysosomal granules by methylprenisolone was found.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agarwal D. S. Subcutaneous staphylococcal infection in mice. 3. Effect of active and passive immunization and anti-inflammatory drugs. Br J Exp Pathol. 1967 Oct;48(5):483–500. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson A. J. Lysosomal enzyme activity in rats with adjuvant-induced arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1970 May;29(3):307–313. doi: 10.1136/ard.29.3.307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrigoni-Martelli E., Restelli A. Release of lysosomal enzymes in experimental inflammations: effects of anti-inflammatory drugs. Eur J Pharmacol. 1972 Aug;19(2):191–198. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(72)90008-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop C. R., Athens J. W., Boggs D. R., Warner H. R., Cartwright G. E., Wintrobe M. M. Leukokinetic studies. 13. A non-steady-state kinetic evaluation of the mechanism of cortisone-induced granulocytosis. J Clin Invest. 1968 Feb;47(2):249–260. doi: 10.1172/JCI105721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borel J. F. Effect of some drugs on the chemotaxis of rabbit neutrophils in vitro. Experientia. 1973 Jun 15;29(6):676–678. doi: 10.1007/BF01944767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brittinger G., Hirschhorn R., Douglas S. D., Weissmann G. Studies on lysosomes. XI. Characterization of a hydrolase-rich fraction from human lymphocytes. J Cell Biol. 1968 May;37(2):394–411. doi: 10.1083/jcb.37.2.394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CERIOTTI G. A microchemical determination of desoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1952 Sep;198(1):297–303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROSBY W. H., FURTH F. W. A modification of the benzidine method for measurement of hemoglobin in plasma and urine. Blood. 1956 Apr;11(4):380–383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chodirker W. B., Bock G. N., Vaughan J. H. Isolation of human PMN leukocytes and granules: observations on early blood diluion and on heparin. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 Jan;71(1):9–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale D. C., Fauci A. S., Wolff S. M. Alternate-day prednisone. Leukocyte kinetics and susceptibility to infections. N Engl J Med. 1974 Nov 28;291(22):1154–1158. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197411282912203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EBERT R. H., BARCLAY W. R. [Changes in connective tissue reaction induced by cortisone]. Ann Intern Med. 1952 Sep;37(3):506–518. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-37-3-506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I. M. Effect of steroids on lysosomes. Transplant Proc. 1975 Mar;7(1):21–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyttel J., Jorgensen A. Studies on lysosome stabilization by antirheumatic drugs. Eur J Pharmacol. 1970;11(3):383–387. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(70)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J., Colombo C. Enzyme release from guinea-pig polymorphonuclear leucocyte lysosomes inhibited in vitro by anti-inflammatory drugs. Nat New Biol. 1972 Oct 4;239(92):155–157. doi: 10.1038/newbio239155a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J. Lysosome membrane stabilization in vivo: effects of steroidal and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on the integrity of rat liver lysosomes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1972 Jul;182(1):179–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa H., Mori Y., Tsurufuji S. The characteristic feature of glucocorticoids after local application with reference to leucocyte migration and protein exudation. Eur J Pharmacol. 1969 Aug;7(2):201–205. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(69)90011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KALNITSKY G., HUMMEL J. P., DIERKS C. [Some factors which affect the enzymatic digestion of ribonucleic acid]. J Biol Chem. 1959 Jun;234(6):1512–1516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KETCHEL M. M., FAVOUR C. B., STURGIS S. H. The in vitro action of hydrocortisone on leucocyte migration. J Exp Med. 1958 Feb 1;107(2):211–218. doi: 10.1084/jem.107.2.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G. L., Wilson J. E. A study of variables in the assay of cytotoxic antisera. J Immunol. 1968 Nov;101(5):1068–1073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEACOCK A. C., BUNTING S. L., QUEEN K. G. SERUM PROTEIN ELECTROPHORESIS IN ACRYLAMIDE GEL: PATTERNS FROM NORMAL HUMAN SUBJECTS. Science. 1965 Mar 19;147(3664):1451–1453. doi: 10.1126/science.147.3664.1451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perper R. J., Sanda M., Chinea G., Oronsky A. L. Leukocyte chemotaxis in vivo. II. Analysis of the selective inhibition of neutrophil or mononuclear cell accumulation. J Lab Clin Med. 1974 Sep;84(3):394–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persellin R. H., Ku L. C. Effects of steroid hormones on human polymorphonuclear leukocyte lysosomes. J Clin Invest. 1974 Oct;54(4):919–925. doi: 10.1172/JCI107832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters W. P., Holland J. F., Senn H., Rhomberg W., Banerjee T. Corticosteroid administration and localized leukocyte mobilization in man. N Engl J Med. 1972 Feb 17;286(7):342–345. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197202172860703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson D. M., Ross R. Effects of heterologous antineutrophil serum in guinea pigs. Hematologic and ultrastructural observations. Am J Pathol. 1971 Oct;65(1):79–102. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson D. M., Ross R. The neutrophilic leukocyte in wound repair a study with antineutrophil serum. J Clin Invest. 1972 Aug;51(8):2009–2023. doi: 10.1172/JCI107007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WROBLEWSKI F., LADUE J. S. Lactic dehydrogenase activity in blood. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1955 Oct;90(1):210–213. doi: 10.3181/00379727-90-21985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A. The chemosuppression of chemotaxis. J Exp Med. 1966 Aug 1;124(2):209–226. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.2.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiener S. L., Wiener R., Janov C., Darmstadt R., Upmanis S., Urivetzky M., Meilman E. Kinetic study of neutrophil and inflammatory fluid beta glucuronidase. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1975 Mar;10(3):491–499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiener S., Lendvai S., Rogers B., Urivetzky M., Meilman E. Nonimmune chemotaxis in vivo: inhibition by complement depletion with cobra factor. Am J Pathol. 1973 Dec;73(3):807–816. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]