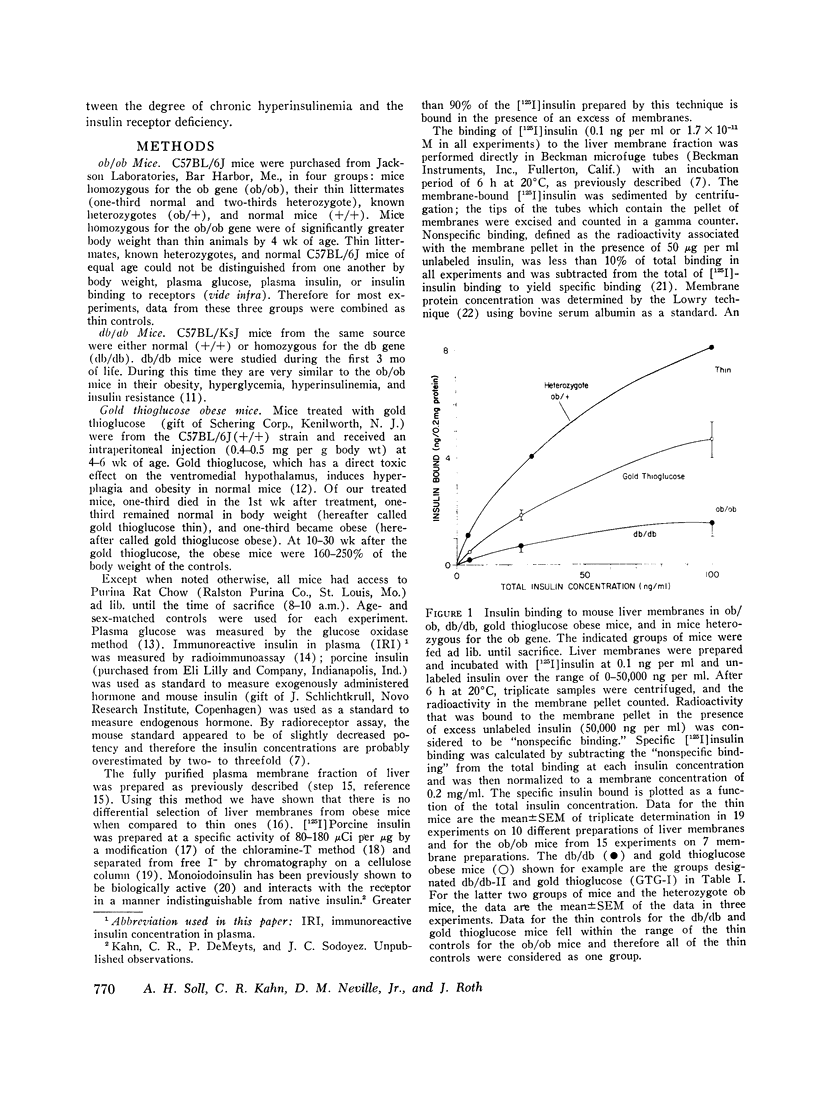
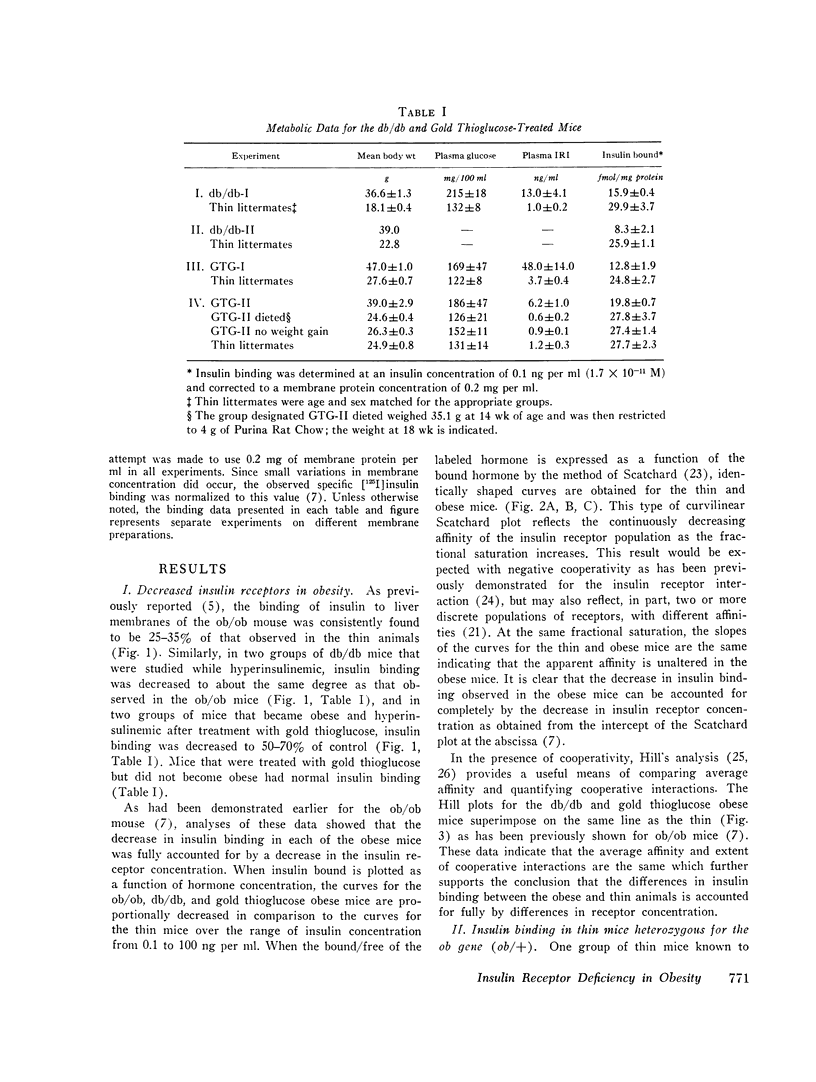
Abstract
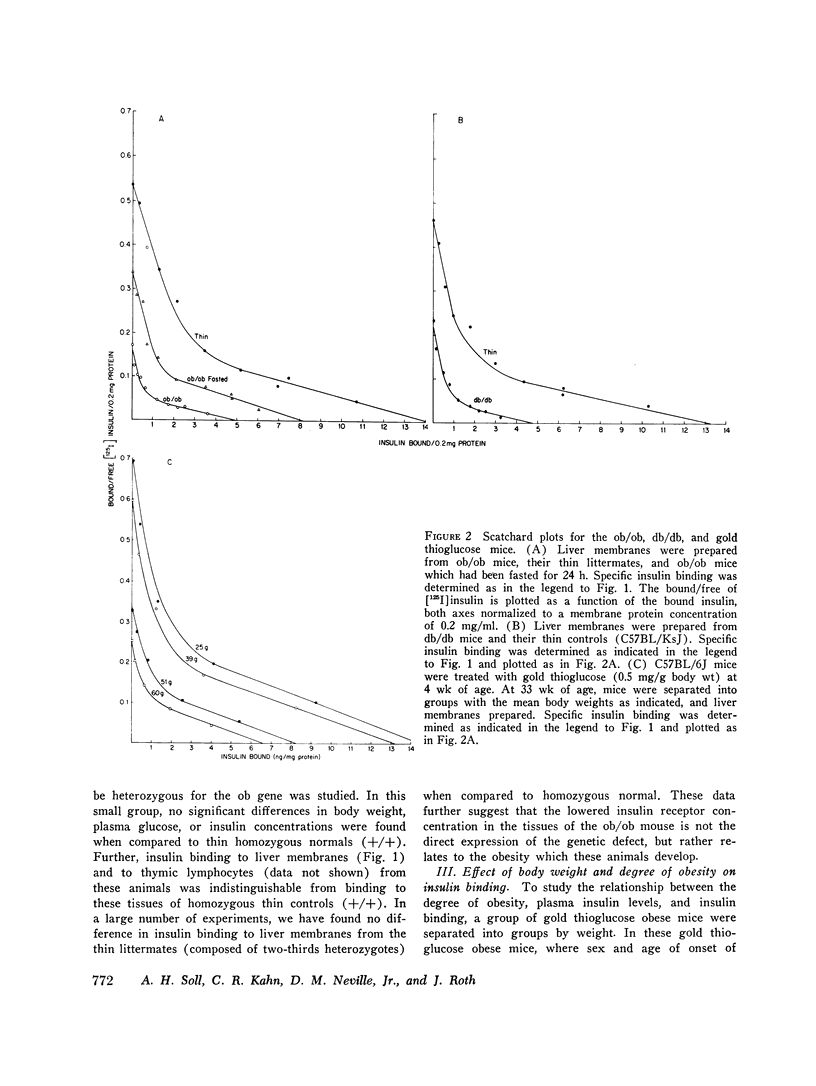
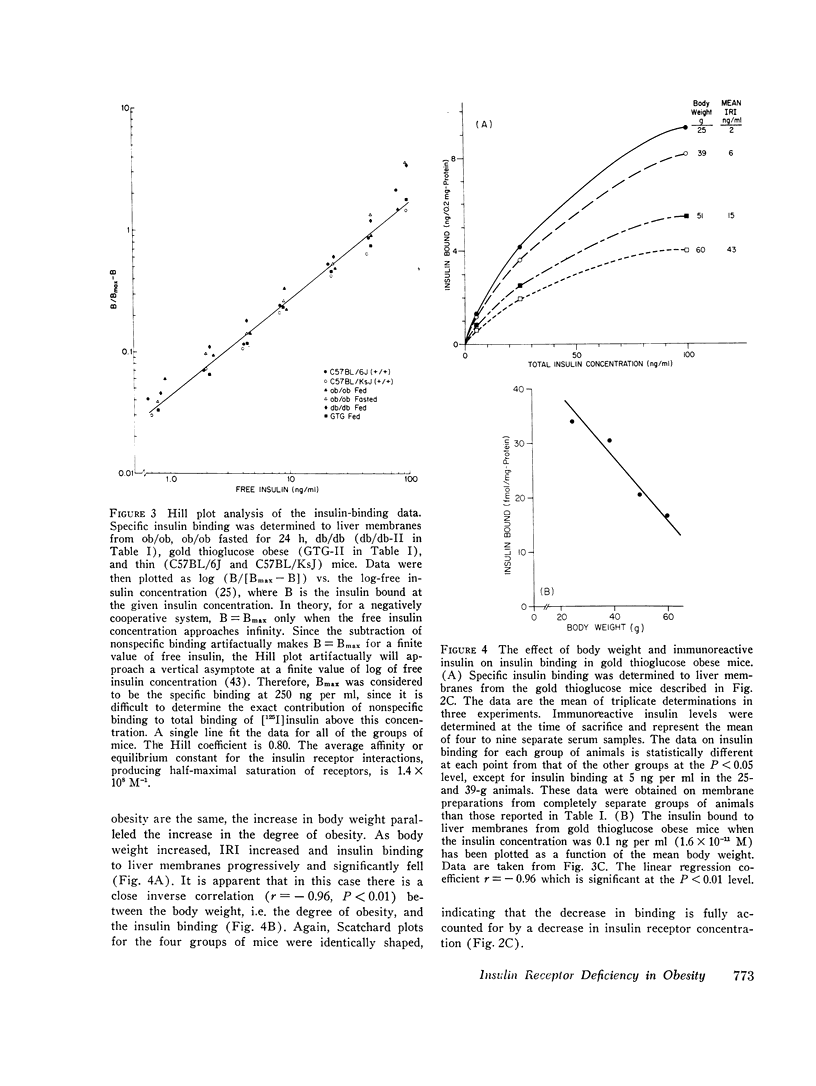
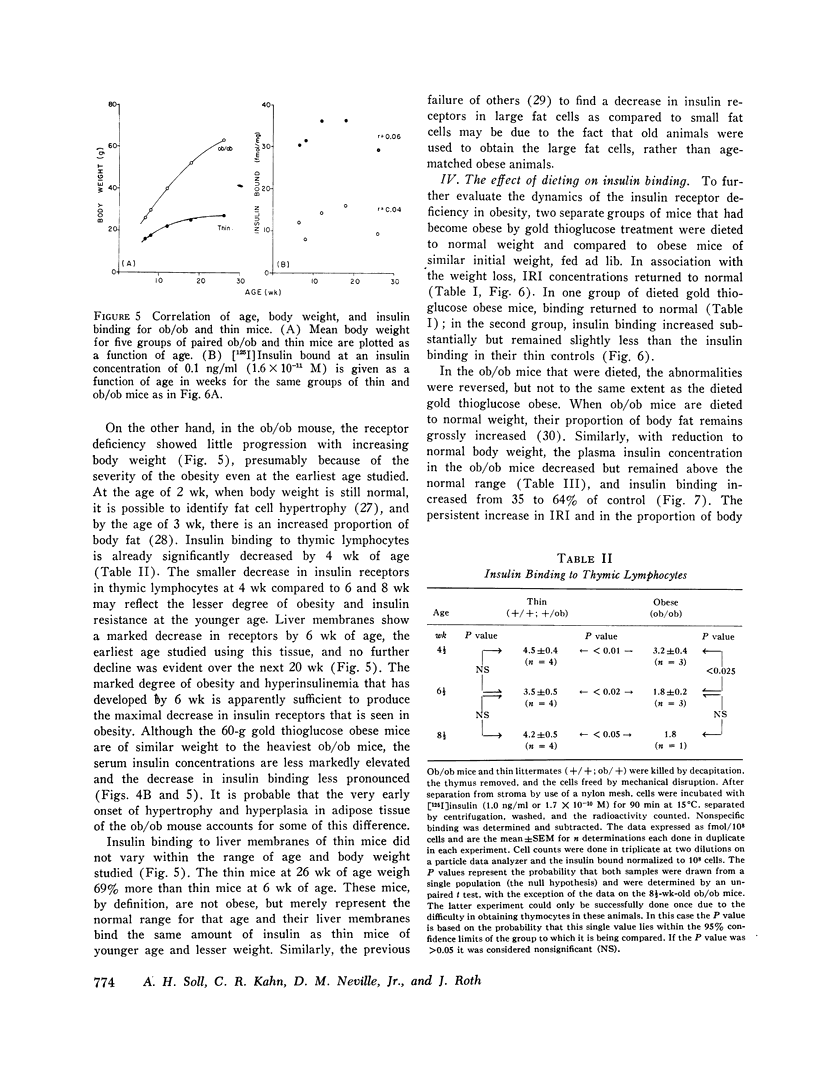
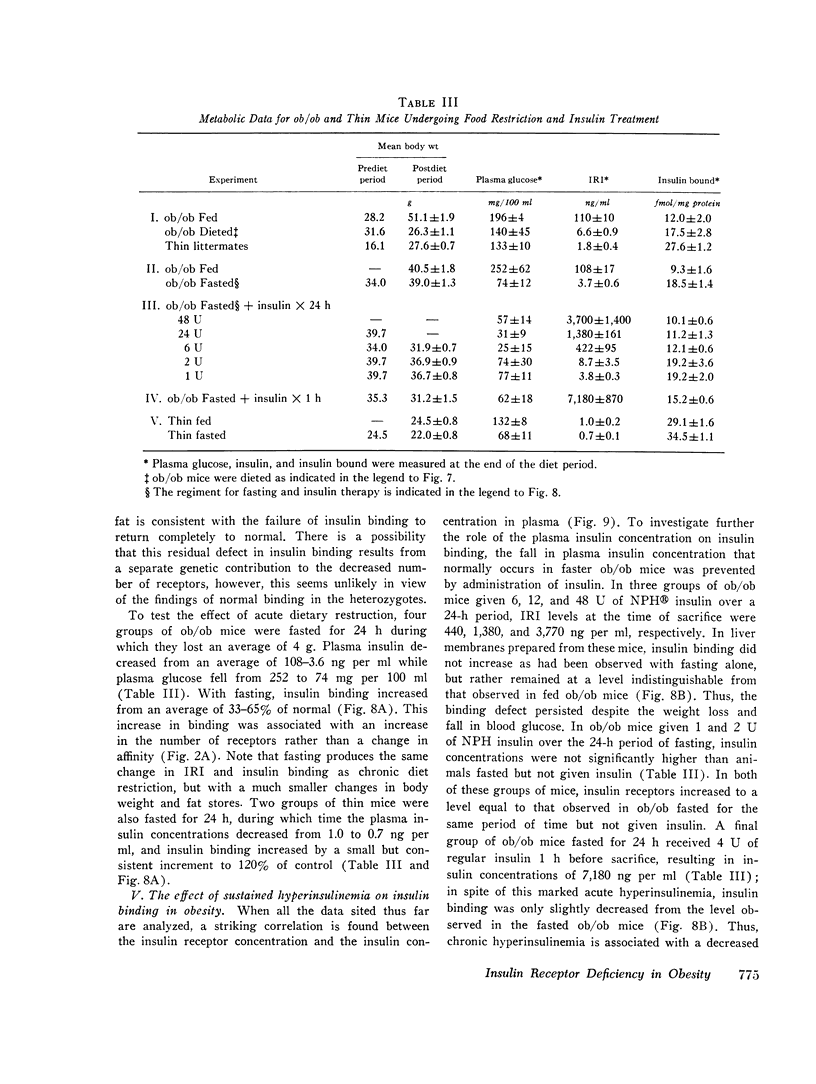
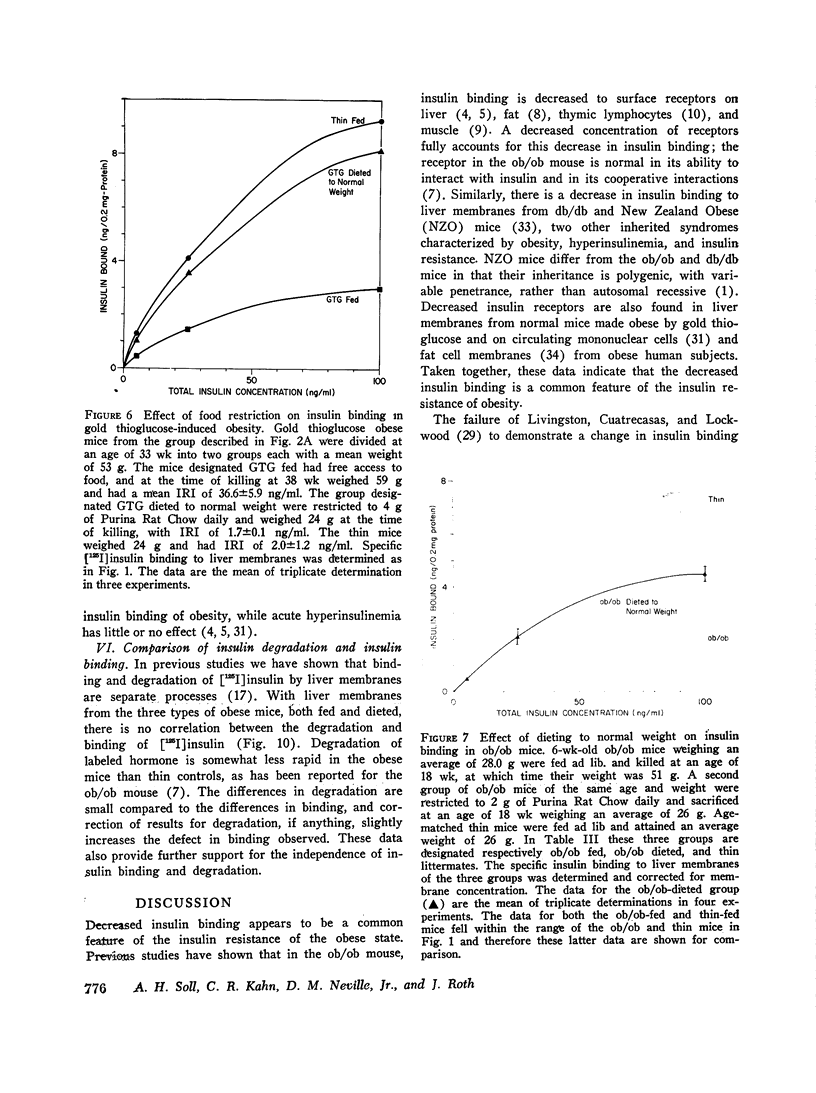
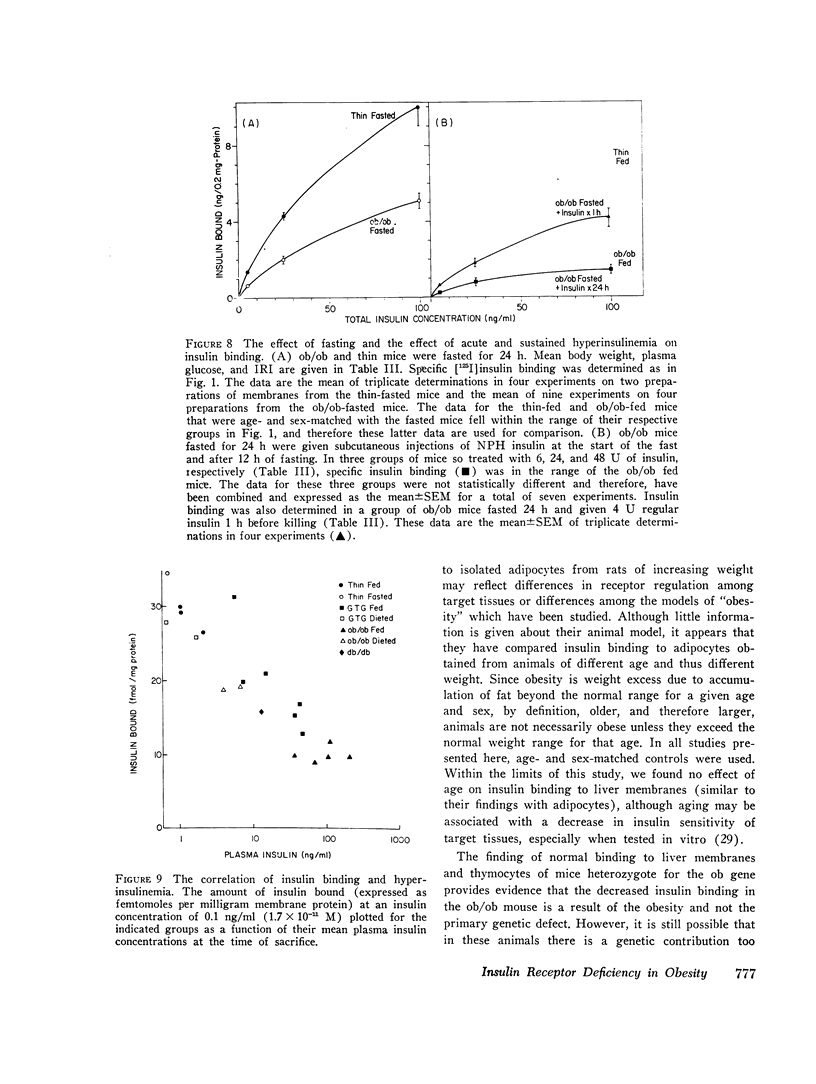
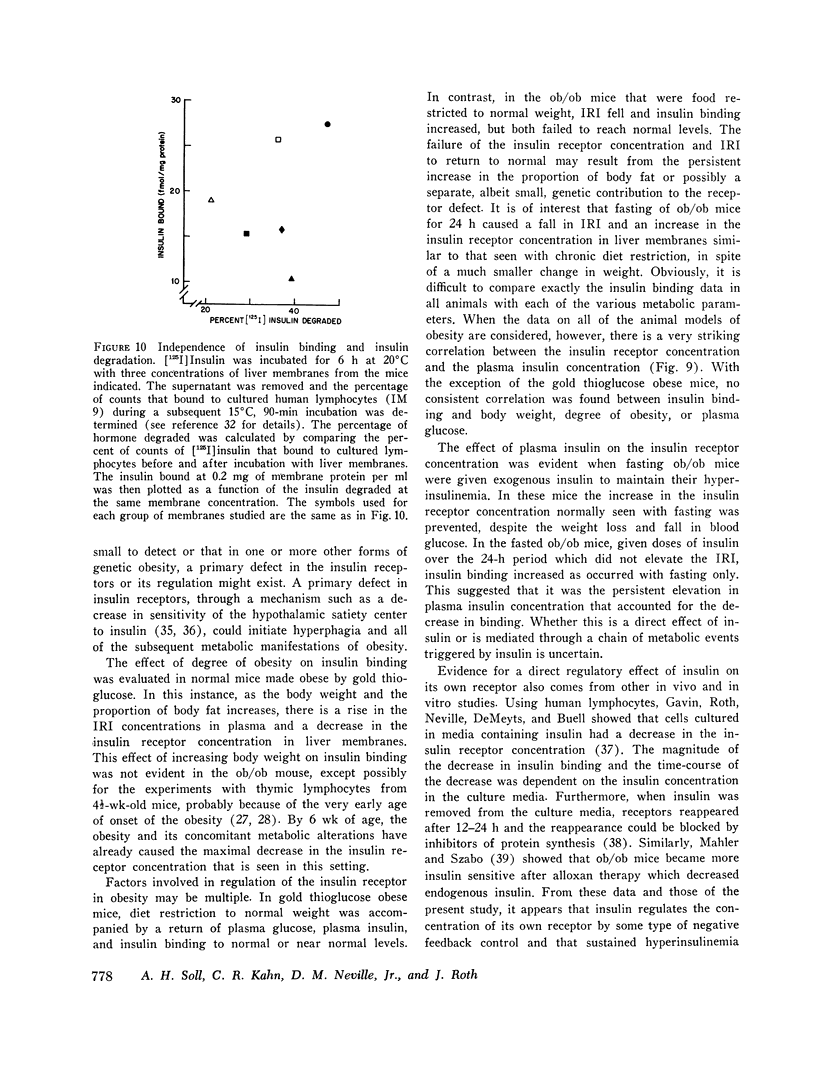
We have previously shown that in the insulin-resistant obese hyperglycemic mouse (ob/ob) there is a deficiency in the number of insulin receptor sites on hepatocytes, adipocytes, and thymic lymphocytes. We now find that concentration of insulin receptors on liver plasma membranes is decreased in the db/db mouse, another form of inherited obesity, and in normal mice that became obese after treatment with gold thioglucose, while thin mice, heterozygous for the ob mutation (ob/+), have normal insulin binding. With acute and chronic food restriction of the ob/ob and gold thioglucose obese mice, there is reduction in hyperinsulinemia and an associated increase in the insulin receptor concentration toward normal. In contrast, when fasting ob/ob mice were given exogenous insulin to maintain the hyperinsulinemia, insulin receptors failed to increase. Thus, in all cases, there was a consistent relationship between the degree of hyperinsulinemia and of insulin receptor loss. These findings suggest that decreased insulin binding is a characteristic feature of the insulin resistance of obesity, and that sustained hyperinsulinemia is a major factor in the control of the concentration of insulin receptors on target cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALONSO L. G., MAREN T. H. Effect of food restriction on body composition of hereditary obese mice. Am J Physiol. 1955 Nov;183(2):284–290. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1955.183.2.284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abraham R. R., Beloff-Chain A. Hormonal control of intermediary metabolism in obese hyperglycemic mice. I. The sensitivity and response to insulin in adipose tissue and muscle in vitro. Diabetes. 1971 Aug;20(8):522–534. doi: 10.2337/diab.20.8.522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archer J. A., Gorden P., Roth J. Defect in insulin binding to receptors in obese man. Amelioration with calorie restriction. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jan;55(1):166–174. doi: 10.1172/JCI107907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baile C. A., Herrera M. G., Mayer J. Ventromedial hypothalamus and hyperphagia in hyperglycemic obese mice. Am J Physiol. 1970 Mar;218(3):857–863. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.218.3.857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chlouverakis C., White P. A. Obesity and insulin resistance in the obese-hyperglycemic mouse (obob). Metabolism. 1969 Dec;18(12):998–1006. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(69)90016-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman D. L., Hummel K. P. Studies with the mutation, diabetes, in the mouse. Diabetologia. 1967 Apr;3(2):238–248. doi: 10.1007/BF01222201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debons A. F., Krimsky I., From A., Cloutier R. J. Rapid effects of insulin on the hypothalamic satiety center. Am J Physiol. 1969 Oct;217(4):1114–1118. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.217.4.1114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P., Kahn R., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Insulin interactions with liver plasma membranes. Independence of binding of the hormone and its degradation. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3953–3961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P., Laudat M. H., Laudat P., Rosselin G., Kahn C. R., Gorden P., Roth J. Impairment of insulin binding to the fat cell plasma membrane in the obese hyperglycemic mouse. FEBS Lett. 1972 Sep 15;25(2):339–342. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80519-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Monoiodoinsulin: demonstration of its biological activity and binding to fat cells and liver membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Apr 16;43(2):400–408. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90767-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavin J. R., 3rd, Roth J., Jen P., Freychet P. Insulin receptors in human circulating cells and fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):747–751. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavin J. R., 3rd, Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr, de Meyts P., Buell D. N. Insulin-dependent regulation of insulin receptor concentrations: a direct demonstration in cell culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):84–88. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill A. V. The Combinations of Haemoglobin with Oxygen and with Carbon Monoxide. I. Biochem J. 1913 Oct;7(5):471–480. doi: 10.1042/bj0070471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Freychet P., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Quantitative aspects of the insulin-receptor interaction in liver plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 10;249(7):2249–2257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Neville D. M., Jr, Gorden P., Freychet P., Roth J. Insulin receptor defect in insulin resistance: studies in the obese-hyperglycimic mouse. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jul 11;48(1):135–142. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90354-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Neville D. M., Jr, Roth J. Insulin-receptor interaction in the obese-hyperglycemic mouse. A model of insulin resistance. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 10;248(1):244–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARSHALL N. B., BARRNETT R. J., MAYER J. Hypothalamic lesions in goldthioglucose injected mice. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1955 Oct;90(1):240–244. doi: 10.3181/00379727-90-21995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahler R. J., Szabo O. Amelioration of insulin resistance in obese mice. Am J Physiol. 1971 Oct;221(4):980–983. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.4.980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neville D. M., Jr Isolation of an organ specific protein antigen from cell-surface membrane of rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Apr 9;154(3):540–552. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(68)90014-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinowitz D. Some endocrine and metabolic aspects of obesity. Annu Rev Med. 1970;21:241–258. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.21.020170.001325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J., Gorden P., Pastan I. "Big insulin": a new component of plasma insulin detected by immunoassay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Sep;61(1):138–145. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.1.138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J. Peptide hormone binding to receptors: a review of direct studies in vitro. Metabolism. 1973 Aug;22(8):1059–1073. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(73)90225-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soll A. H., Goldfine I. D., Roth J., Kahn C. R. Thymic lymphocytes in obese (ob-ob) mice. A mirror of the insulin receptor defect in liver and fat. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4127–4131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soll A. H., Kahn C. R., Neville D. M., Jr Insulin binding to liver plasm membranes in the obese hyperglycemic (ob/ob) mouse. Demonstration of a decreased number of functionally normal receptors. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 25;250(12):4702–4707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stauffacher W., Orci L., Cameron D. P., Burr I. M., Renold A. E. Spontaneous hyperglycemia and-or obesity in laboratory rodents: an example of the possible usefulness of animal disease models with both genetic and environmental components. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1971;27:41–95. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571127-2.50026-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WASHKO M. E., RICE E. W. Determination of glucose by an improved enzymatic procedure. Clin Chem. 1961 Oct;7:542–545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead E. The regulation of enzyme activity and allosteric transition. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1970;21:321–397. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(70)90028-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YALOW R. S., BERSON S. A. Immunoassay of endogenous plasma insulin in man. J Clin Invest. 1960 Jul;39:1157–1175. doi: 10.1172/JCI104130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Meyts P., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr, Gavin J. R., 3rd, Lesniak M. A. Insulin interactions with its receptors: experimental evidence for negative cooperativity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Nov 1;55(1):154–161. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(73)80072-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]