Abstract
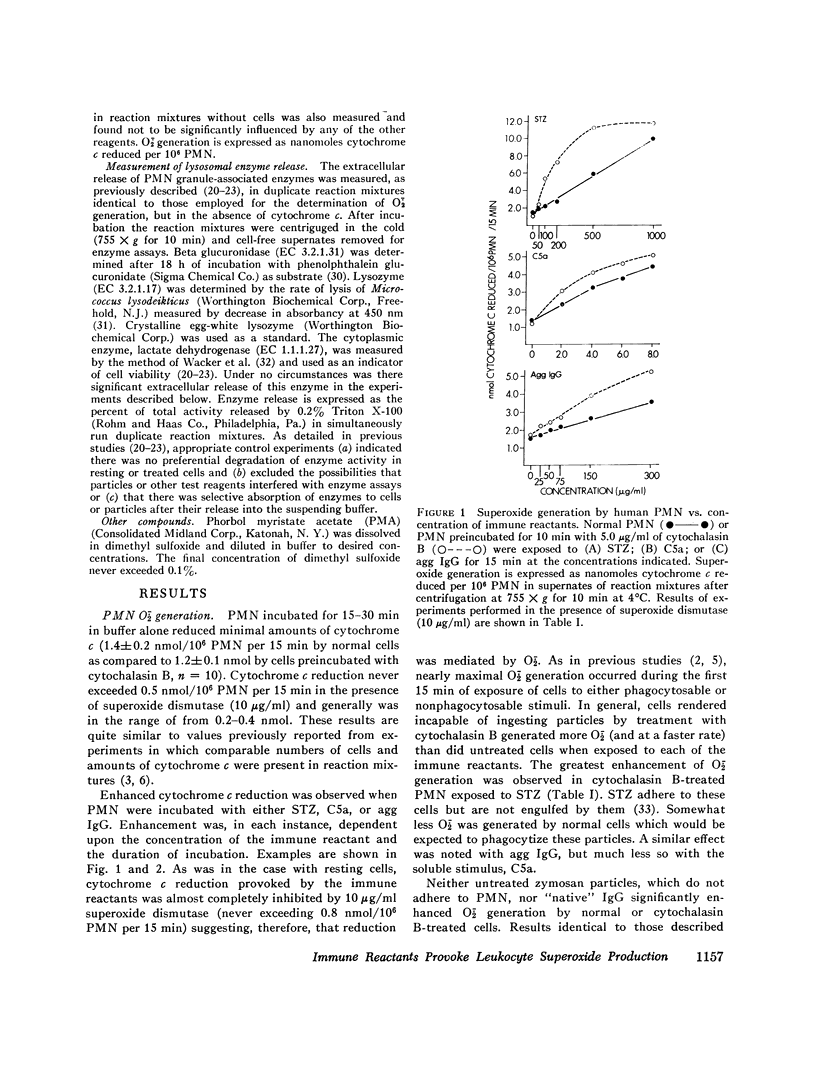
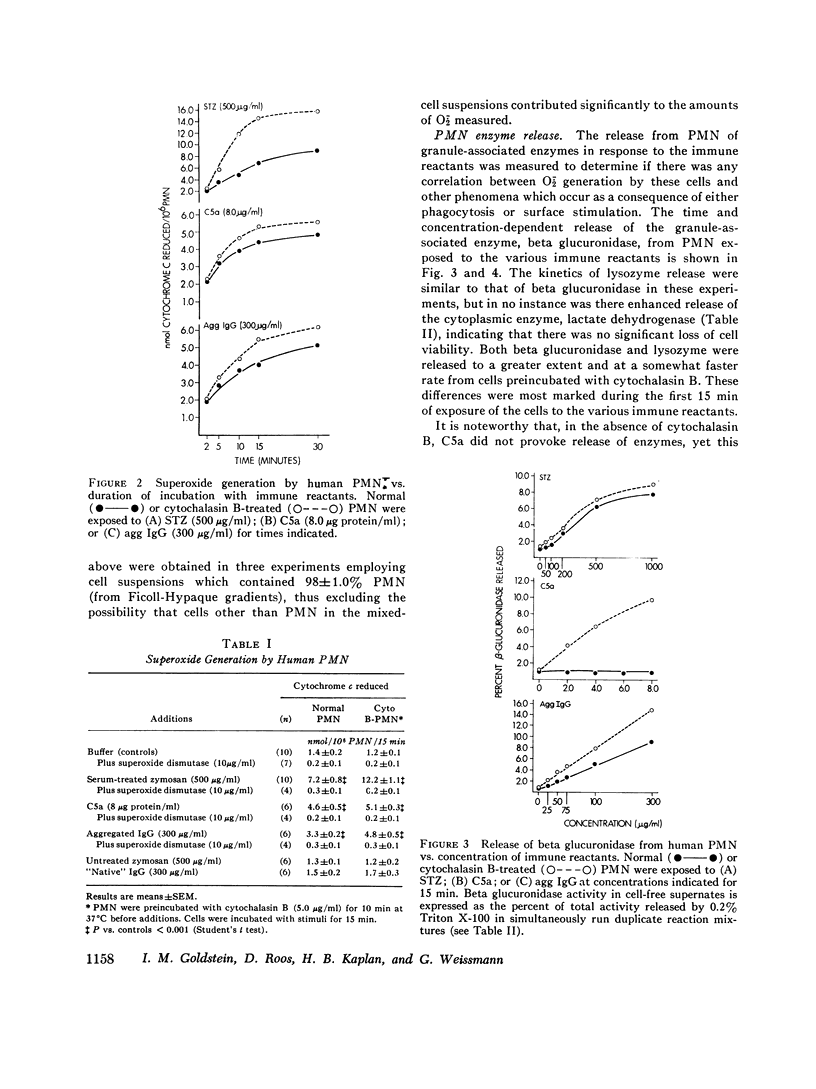
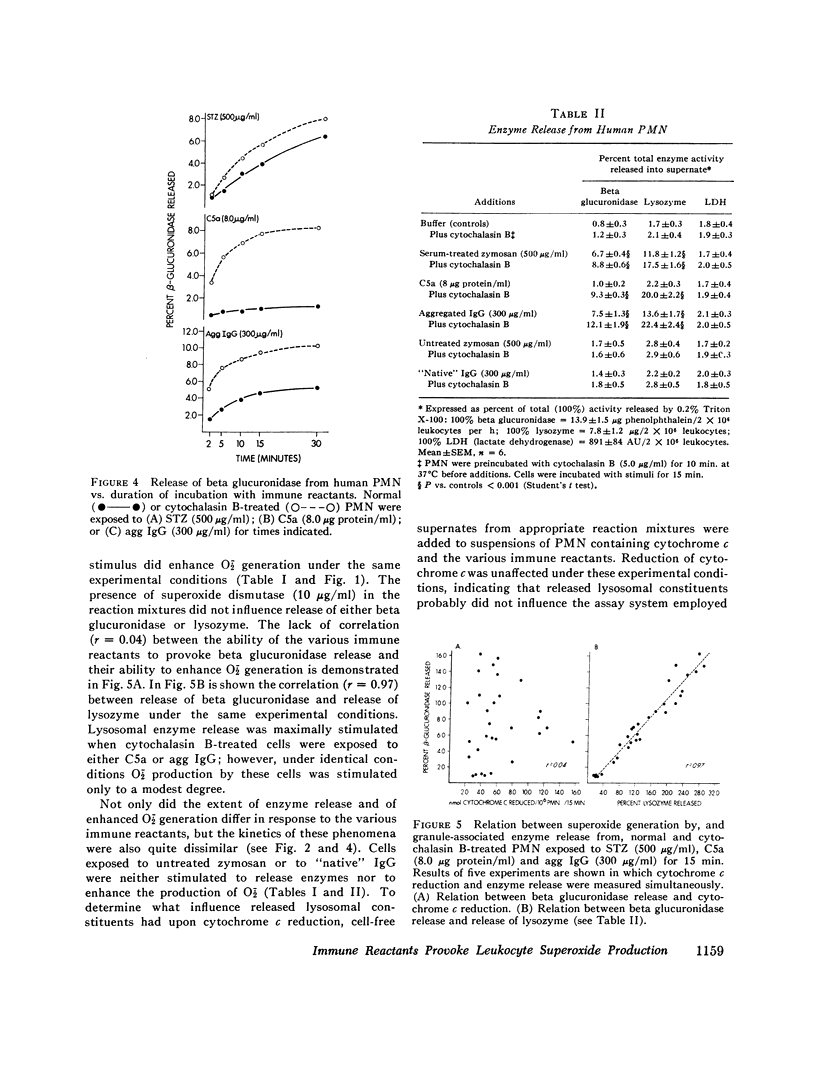
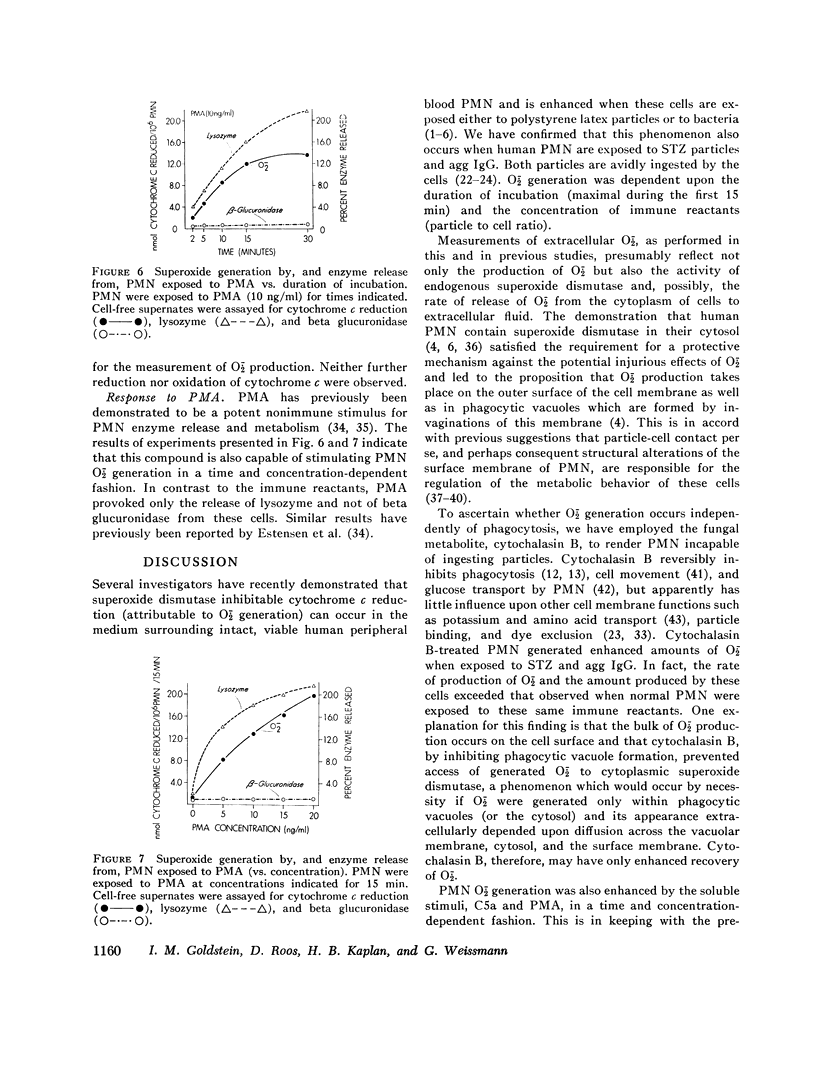
Human peripheral blood polymorphonuclear leukocytes, when exposed to appropriate stimuli, generate significant amounts of superoxide anion (O-.2), a highly reactive molecule which is possibly involved in bacterial killing. Since the subcellular localization and mechanism of activation of O-.2 generating systems are unknown, we have investigated superoxide dismutase-inhibitable cytochrome c reduction (attributable to O-.2) by, and lysosomal enzyme release from, normal polymorphonuclear leukocytes and cells rendered incapable of ingesting particles by treatment with cytochalasin B. Neither phagocytosis nor lysosomal degranulation were prerequisites for enhanced O-.2 generation. Cytochalasin B-treated cells exposed to (a) serum-treated zymosan, a C3b receptor stimulus; (b) heat aggregated human IgG, an Fc receptor stimulus; and (c) the complement component, C5a, generated enhanced amounts of O-.2 in a time and concentration-dependent fashion. These cells also responded by releasing lysosomal enzymes, but there was no correlation between the ability of any immune reactant to provoke enzyme release and its ability to stimulate O-.2 generation. The three stimuli also enhanced O-.2 generation by normal (untreated) polymorphonuclear leukocytes, but only serum-treated zymosan and aggregated IgG were capable of provoking lysosomal enzyme release from normal cells. Untreated zymosan and native IgG neither stimulated O-.2 production nor provoked lysomal enzyme release. Since enhanced O-.2 production was stimulated by immune reactants in the absence of phagocytosis, the O-.2 generating system is very likely associated with the external plasma membrane of the polymorphonuclear leukocyte. Leukocyte membrane receptors for complement and immunoglobulins may therefore not only serve in particle recognition but also may initiate biochemical events which accompany phagocytosis and killing.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAUMSTARK J. S., LAFFIN R. J., BARDAWIL W. A. A PREPARATIVE METHOD FOR THE SEPARATION OF 7S GAMMA GLOBULIN FROM HUMAN SERUM. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964 Dec;108:514–522. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(64)90436-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babior B. M., Curnutte J. T., Kipnes R. S. Biological defense mechanisms. Evidence for the participation of superoxide in bacterial killing by xanthine oxidase. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Feb;85(2):235–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babior B. M., Kipnes R. S., Curnutte J. T. Biological defense mechanisms. The production by leukocytes of superoxide, a potential bactericidal agent. J Clin Invest. 1973 Mar;52(3):741–744. doi: 10.1172/JCI107236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brittinger G., Hirschhorn R., Douglas S. D., Weissmann G. Studies on lysosomes. XI. Characterization of a hydrolase-rich fraction from human lymphocytes. J Cell Biol. 1968 May;37(2):394–411. doi: 10.1083/jcb.37.2.394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curnutte J. T., Babior B. M. Biological defense mechanisms. The effect of bacteria and serum on superoxide production by granulocytes. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jun;53(6):1662–1672. doi: 10.1172/JCI107717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curnutte J. T., Whitten D. M., Babior B. M. Defective superoxide production by granulocytes from patients with chronic granulomatous disease. N Engl J Med. 1974 Mar 14;290(11):593–597. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197403142901104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis A. T., Estensen R., Quie P. G. Cytochalasin B. 3. Inhibition of human polymorphonuclear leukocyte phagocytosis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 May;137(1):161–164. doi: 10.3181/00379727-137-35535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeChatelet L. R., McCall C. E., McPhail L. C., Johnston R. B., Jr Superoxide dismutase activity in leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1974 Apr;53(4):1197–1201. doi: 10.1172/JCI107659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drath D. B., Karnovsky M. L. Superoxide production by phagocytic leukocytes. J Exp Med. 1975 Jan 1;141(1):257–262. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.1.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estensen R. D., White J. G., Holmes B. Specific degranulation of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Nature. 1974 Mar 22;248(446):347–348. doi: 10.1038/248347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong K. L., McCay P. B., Poyer J. L., Keele B. B., Misra H. Evidence that peroxidation of lysosomal membranes is initiated by hydroxyl free radicals produced during flavin enzyme activity. J Biol Chem. 1973 Nov 25;248(22):7792–7797. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I. M., Brai M., Osler A. G., Weissmann G. Lysosomal enzyme release from human leukocytes: mediation by the alternate pathway of complement activation. J Immunol. 1973 Jul;111(1):33–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I. M., Feit F., Weissmann G. Enhancement of nitroblue tetrazolium dye reduction by leukocytes exposed to a component of complement in the absence of phagocytosis. J Immunol. 1975 Jan;114(1 Pt 2):516–518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I., Hoffstein S., Gallin J., Weissmann G. Mechanisms of lysosomal enzyme release from human leukocytes: microtubule assembly and membrane fusion induced by a component of complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2916–2920. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson P. M., Johnson H. B., Spiegelberg H. L. The release of granule enzymes from human neutrophils stimulated by aggregated immunoglobulins of different classes and subclasses. J Immunol. 1972 Dec;109(6):1182–1192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson P. M. The adherence of leucocytes and platelets induced by fixed IgG antibody or complement. Immunology. 1969 Jan;16(1):107–121. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson P. M. The immunologic release of constituents from neutrophil leukocytes. I. The role of antibody and complement on nonphagocytosable surfaces or phagocytosable particles. J Immunol. 1971 Dec;107(6):1535–1546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston R. B., Jr, Keele B. B., Jr, Misra H. P., Lehmeyer J. E., Webb L. S., Baehner R. L., RaJagopalan K. V. The role of superoxide anion generation in phagocytic bactericidal activity. Studies with normal and chronic granulomatous disease leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jun;55(6):1357–1372. doi: 10.1172/JCI108055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston R. B., Jr, Newman S. L., Struth A. G. An abnormality of the alternate pathway of complement activation in sickle-cell disease. N Engl J Med. 1973 Apr 19;288(16):803–808. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197304192881601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan S. S., Finch S. C., Basford R. E. Polymorphonuclear leukocyte activation: effects of phospholipase C. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Jun;140(2):540–543. doi: 10.3181/00379727-140-36498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J., Hamon C. B. Role of myeloperoxidase-mediated antimicrobial systems in intact leukocytes. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1972 Aug;12(2):170–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J. Role of the superoxide anion in the myeloperoxidase-mediated antimicrobial system. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 25;249(12):3724–3728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krinsky N. I. Singlet excited oxygen as a mediator of the antibacterial action of leukocytes. Science. 1974 Oct 25;186(4161):363–365. doi: 10.1126/science.186.4161.363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lay W. H., Nussenzweig V. Receptors for complement of leukocytes. J Exp Med. 1968 Nov 1;128(5):991–1009. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.5.991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malawista S. E., Gee J. B., Bensch K. G. Cytochalasin B reversibly inhibits phagocytosis: functional, metabolic, and ultrastructural effects in human blood leukocytes and rabbit alveolar macrophages. Yale J Biol Med. 1971 Dec;44(3):286–300. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandell G. L. Influence of type of ingested particle on human leukocyte metabolism. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Sep;137(4):1228–1230. doi: 10.3181/00379727-137-35761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire J., Moellmann G. Cytochalasin B: effects on microfilaments and movement of melanin granules within melanocytes. Science. 1972 Feb 11;175(4022):642–644. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4022.642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messner R. P., Jelinek J. Receptors for human gamma G globulin on human neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1970 Dec;49(12):2165–2171. doi: 10.1172/JCI106435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton D. J., Moran J. F., Stjernholmrl Carbohydte metabolism in leukocytes. XI. Stimulation of eosinophils and neutrophils. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1969 Oct-Dec;6(5):525–535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repine J. E., White J. G., Clawson C. C., Holmes B. M. Effects of phorbol myristate acetate on the metabolism and ultrastructure of neutrophils in chronic granulomatous disease. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jul;54(1):83–90. doi: 10.1172/JCI107752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repine J. E., White J. G., Clawson C. C., Holmes B. M. The influence of phorbol myristate acetate on oxygen consumption by polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Lab Clin Med. 1974 Jun;83(6):911–920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi F., Zatti M., Patriarca P., Cramer R. Effect of specific antibodies on the metabolism of guinea pig polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1971 Jan;9(1):67–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sajnani A. N., Ranadive N. S., Movat H. Z. The visualization of receptors for the Fc portion of the IgG molecule on human neutrophil leukocytes. Life Sci. 1974 Jun 16;14(12):2427–2430. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(74)90138-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salin M. L., McCord J. M. Superoxide dismutases in polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1974 Oct;54(4):1005–1009. doi: 10.1172/JCI107816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ULMER D. D., VALLEE B. L., WACKER W. E. Metalloenzymes and myocardial infarction. II. Malic and lactic dehydrogenase activities and zinc concentrations in serum. N Engl J Med. 1956 Sep 6;255(10):450–456. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195609062551001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallota E. H., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Formation of C3a and C5a anaphylatoxins in whole human serum after inhibition of the anaphylatoxin inactivator. J Exp Med. 1973 May 1;137(5):1109–1123. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.5.1109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weening R. S., Wever R., Roos D. Quantitative aspects of the production of superoxide radicals by phagocytizing human granulocytes. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Feb;85(2):245–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissmann G., Brand A., Franklin E. C. Interaction of immunoglobulins with liposomes. J Clin Invest. 1974 Feb;53(2):536–543. doi: 10.1172/JCI107587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissmann G., Zurier R. B., Spieler P. J., Goldstein I. M. Mechanisms of lysosomal enzyme release from leukocytes exposed to immune complexes and other particles. J Exp Med. 1971 Sep 1;134(3 Pt 2):149s–165s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessells N. K., Spooner B. S., Ash J. F., Bradley M. O., Luduena M. A., Taylor E. L., Wrenn J. T., Yamada K. Microfilaments in cellular and developmental processes. Science. 1971 Jan 15;171(3967):135–143. doi: 10.1126/science.171.3967.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G., Estensen R. D. Selective labilization of specific granules in polymorphonuclear leukocytes by phorbol myristate acetate. Am J Pathol. 1974 Apr;75(1):45–60. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zigmond S. H., Hirsch J. G. Effects of cytochalasin B on polymorphonuclear leucocyte locomotion, phagocytosis and glycolysis. Exp Cell Res. 1972 Aug;73(2):383–393. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(72)90062-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurier R. B., Hoffstein S., Weissmann G. Cytochalasin B: effect on lysosomal enzyme release from human leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):844–848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurier R. B., Weissmann G., Hoffstein S., Kammerman S., Tai H. H. Mechanisms of lysosomal enzyme release from human leukocytes. II. Effects of cAMP and cGMP, autonomic agonists, and agents which affect microtubule function. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jan;53(1):297–309. doi: 10.1172/JCI107550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van GELDER B., SLATER E. C. The extinction coefficient of cytochrome c. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Apr 23;58:593–595. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90073-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



