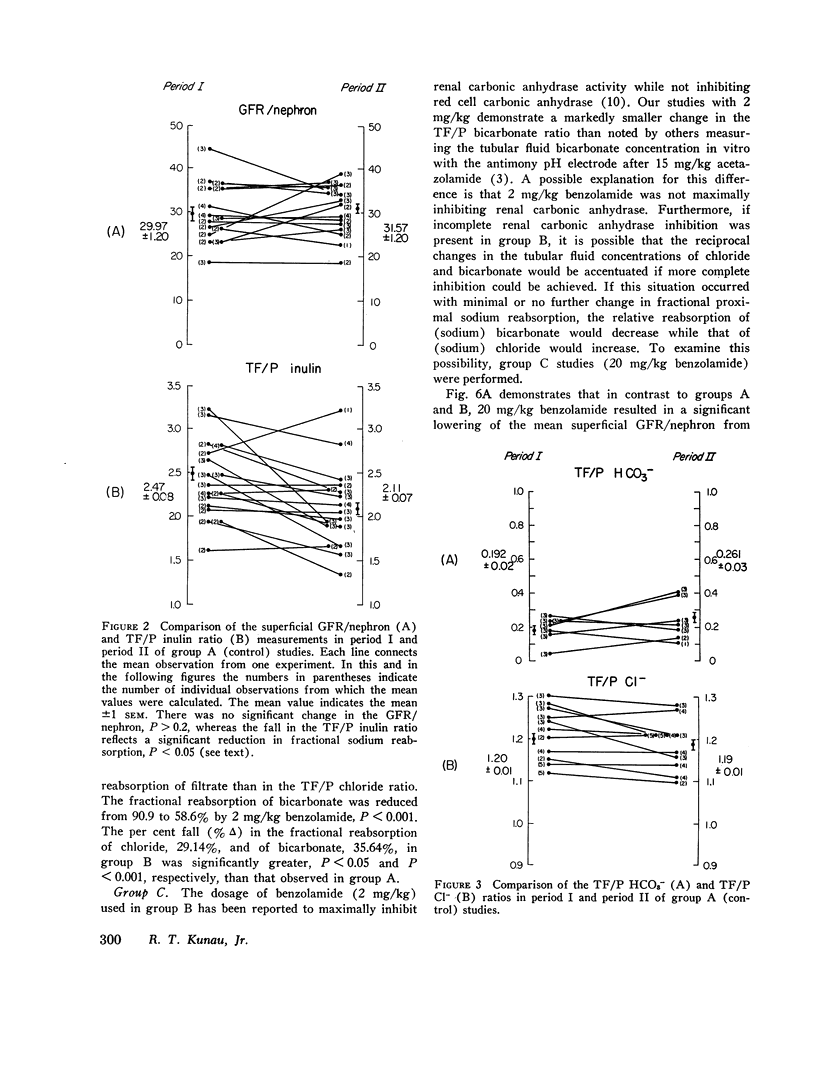
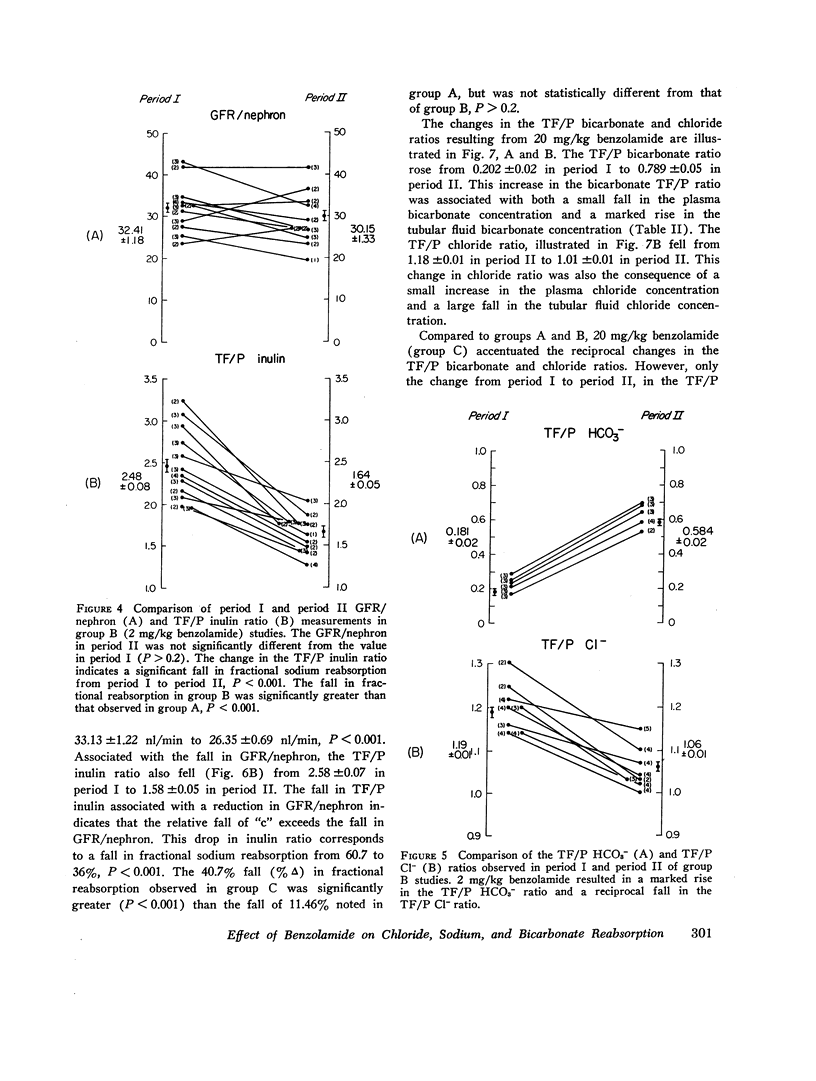
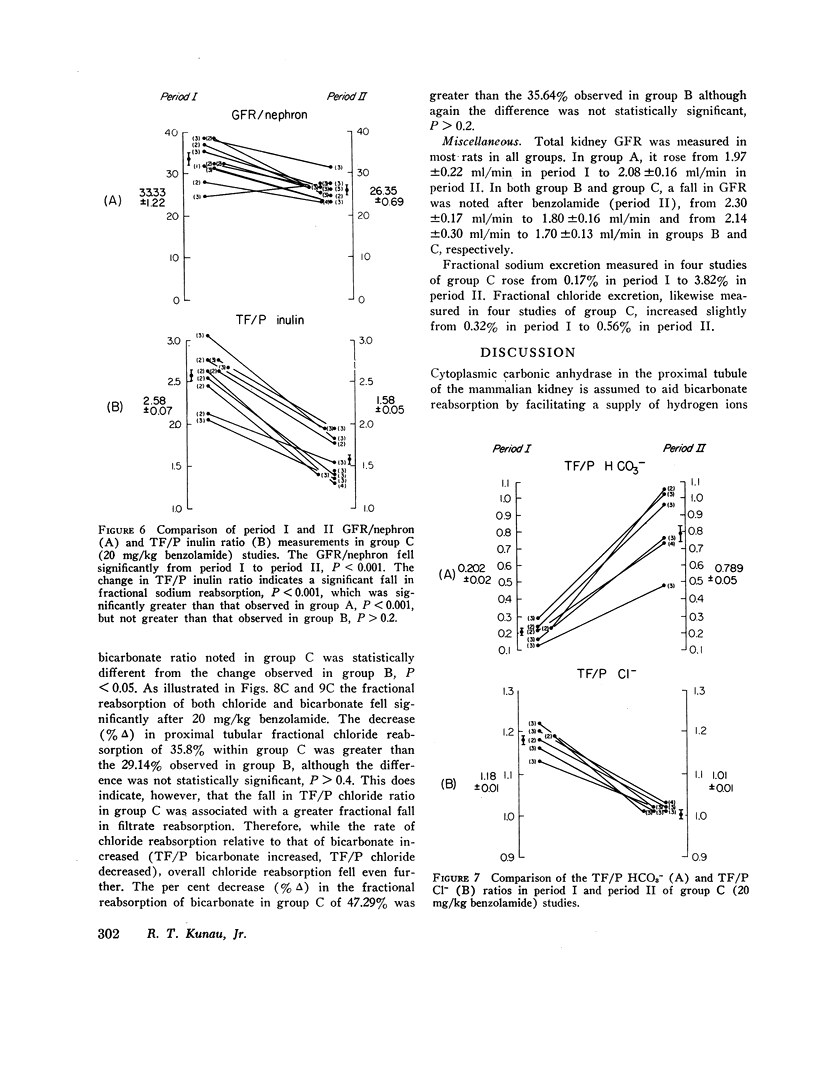
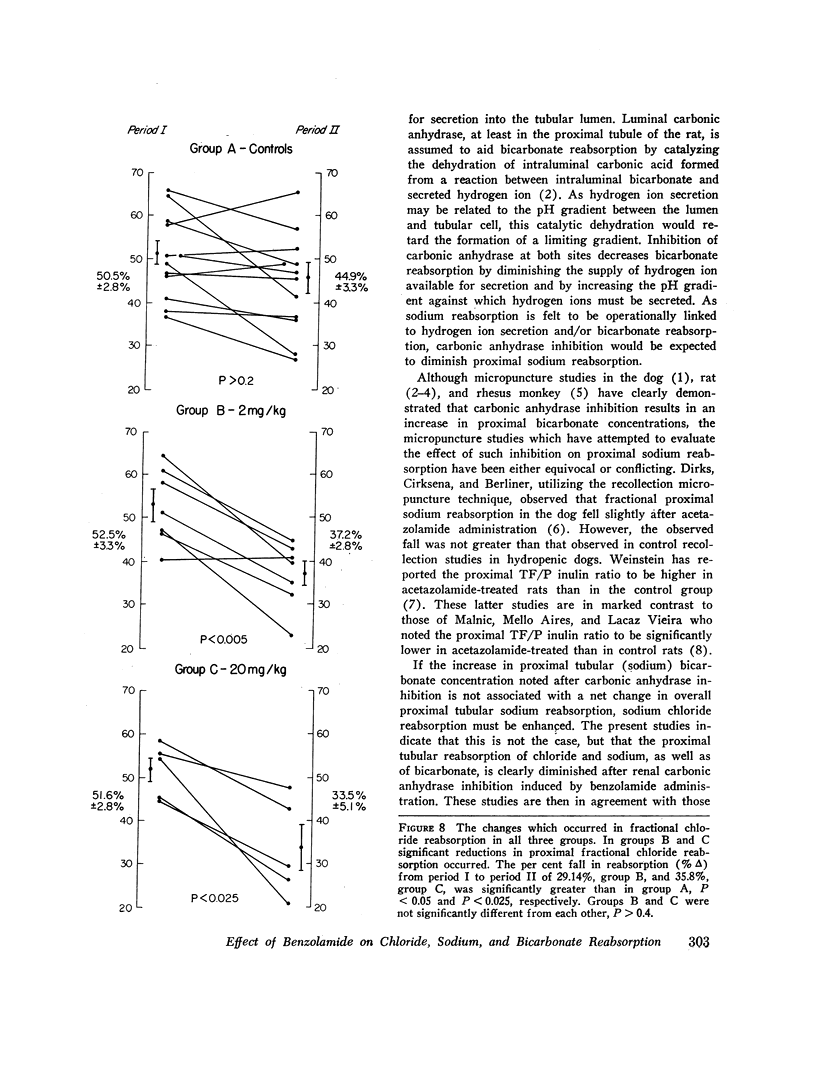
Abstract
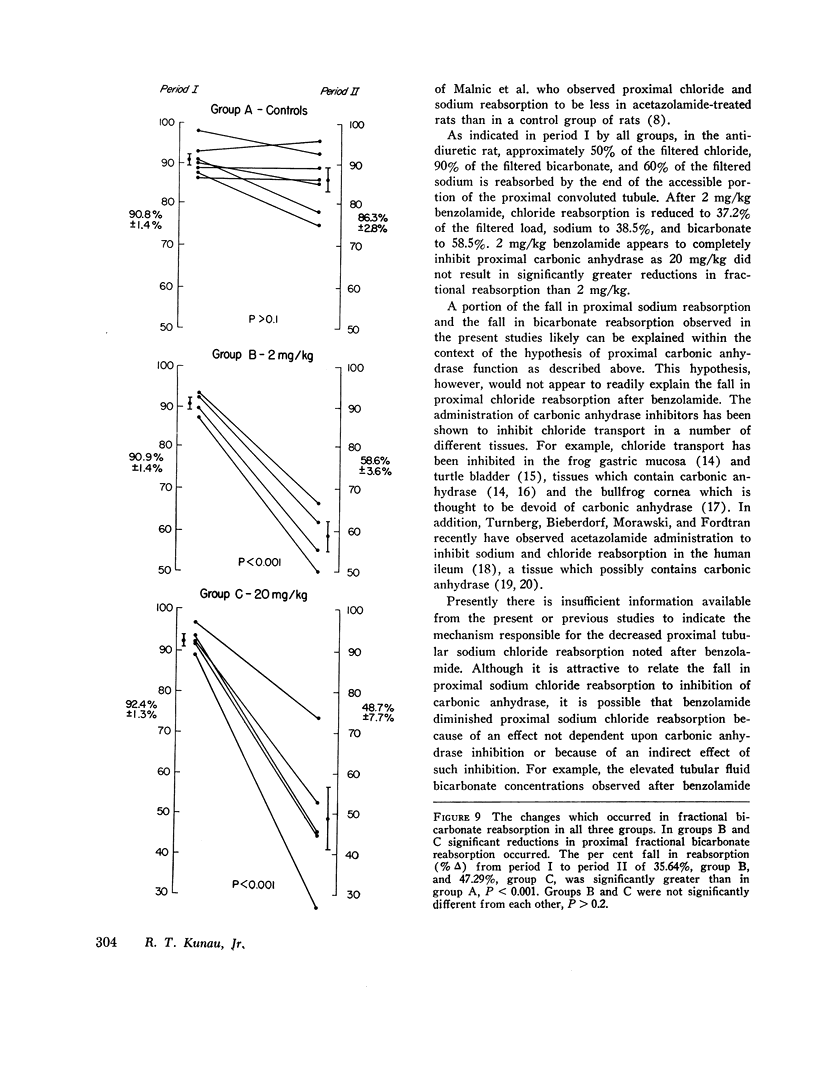
Benzolamide (CL-11,366), a potent carbonic anhydrase inhibitor, was used to examine the influence of carbonic anhydrase inhibition on the reabsorption of chloride, sodium, and bicarbonate in the rat proximal convoluted tubule. Administration of 2 mg/kg benzolamide was associated with a decrease in the tubular fluid/plasma (TF/P) chloride ratio from 1.19±0.10 (SEM) to 1.06±0.01, and an increase in the TF/P bicarbonate ratio from 0.181±0.02 to 0.584±0.02. This dose of benzolamide significantly reduced proximal fractional reabsorption of chloride by 29.14%, of sodium by 34.3%, and of bicarbonate by 35.64%. These results indicate that benzolamide administration inhibits the reabsorption of all three electrolytes in the proximal convoluted tubule. Although 20 mg/kg benzolamide accentuated the changes in fractional reabsorption, the differences between 2 and 20 mg/kg were not statistically significant.
Inhibition of proximal tubular cytoplasmic and luminal carbonic anhydrase could well explain the diminished bicarbonate reabsorption and a fraction of the diminished sodium reabsorption noted in these studies. The fall in chloride reabsorption, and a portion of the fall in sodium reabsorption, however, may be a direct or indirect consequence of carbonic anhydrase inhibition or of an influence of benzolamide on a transport mechanism not dependent upon carbonic anhydrase.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARTELS H., WRBITZKY R. [Determination of carbon dioxide absorption coefficients between 15 and 38 degrees C. in water and plasma]. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1960;271:162–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett C. M., Brenner B. M., Berliner R. W. Micropuncture study of nephron function in the rhesus monkey. J Clin Invest. 1968 Jan;47(1):203–216. doi: 10.1172/JCI105710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein B. A., Clapp J. R. Micropuncture study of bicarbonate reabsorption by the dog nephron. Am J Physiol. 1968 Feb;214(2):251–257. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.214.2.251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLAPP J. R., WATSON J. F., BERLINER R. W. EFFECT OF CARBONIC ANHYDRASE INHIBITION ON PROXIMAL TUBULAR BICARBONATE REABSORPTION. Am J Physiol. 1963 Oct;205:693–696. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1963.205.4.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter M. J., Parsons D. S. Carbonic anhydrase activity of mucosa of small intestine and colon. Nature. 1968 Jul 13;219(5150):176–177. doi: 10.1038/219176a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dirks J. H., Cirksena W. J., Berliner R. W. Micropuncture study of the effect of various diuretics on sodium reabsorption by the proximal tubules of the dog. J Clin Invest. 1966 Dec;45(12):1875–1885. doi: 10.1172/JCI105492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez C. F. Inhibitory effect of acetazolamide on the active chloride and bicarbonate transport mechanisms across short-circuited turtle bladders. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Oct 14;193(1):146–158. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90068-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitahara S., Fox K. R., Hogben C. A. Depression of chloride transport by carbonic anhydrase inhibitors in the absence of carbonic anhydrase. Nature. 1967 May 20;214(5090):836–837. doi: 10.1038/214836a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunau R. T., Jr, Frick A., Rector F. C., Jr, Seldin D. W. Micropuncture study of the proximal tubular factors responsible for the maintenance of alkalosis during potassium deficiency in the rat. Clin Sci. 1968 Apr;34(2):223–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANERY J. F. Water and electrolyte metabolism. Physiol Rev. 1954 Apr;34(2):334–417. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1954.34.2.334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maren T. H. Carbonic anhydrase: chemistry, physiology, and inhibition. Physiol Rev. 1967 Oct;47(4):595–781. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1967.47.4.595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RECTOR F. C., Jr, CARTER N. W., SELDIN D. W. THE MECHANISM OF BICARBONATE REABSORPTION IN THE PROXIMAL AND DISTAL TUBULES OF THE KIDNEY. J Clin Invest. 1965 Feb;44:278–290. doi: 10.1172/JCI105142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosin J. M., Katz M. A., Rector F. C., Jr, Seldin D. W. Acetazolamide in studying sodium reabsorption in diluting segment. Am J Physiol. 1970 Dec;219(6):1731–1738. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.219.6.1731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott W. N., Shamoo Y. E., Brodsky W. A. Carbonic anhydrase content of turtle urinary bladder mucosal cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970;219(1):248–250. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(70)90084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRAVIS D. M., WILEY C., NECHAY B. R., MAREN T. H. SELECTIVE RENAL CARBONIC ANHYDRASE INHIBITION WITHOUT RESPIRATORY EFFECT: PHARMACOLOGY OF 2-BENZENESULFONAMIDO-1,3, 4-THIADIAZOLE-5-SULFONAMIDE (CL 11,366). J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1964 Mar;143:383–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnberg L. A., Bieberdorf F. A., Morawski S. G., Fordtran J. S. Interrelationships of chloride, bicarbonate, sodium, and hydrogen transport in the human ileum. J Clin Invest. 1970 Mar;49(3):557–567. doi: 10.1172/JCI106266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira F. L., Malnic G. Hydrogen ion secretion by rat renal cortical tubules as studied by an antimony microelectrode. Am J Physiol. 1968 Apr;214(4):710–718. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.214.4.710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein S. W. Micropuncture studies of the effects of acetazolamide on nephron function in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1968 Feb;214(2):222–227. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.214.2.222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



