Abstract
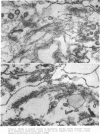
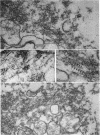
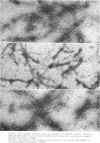
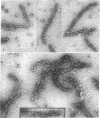
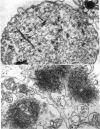
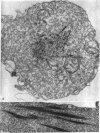
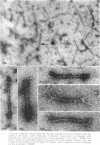
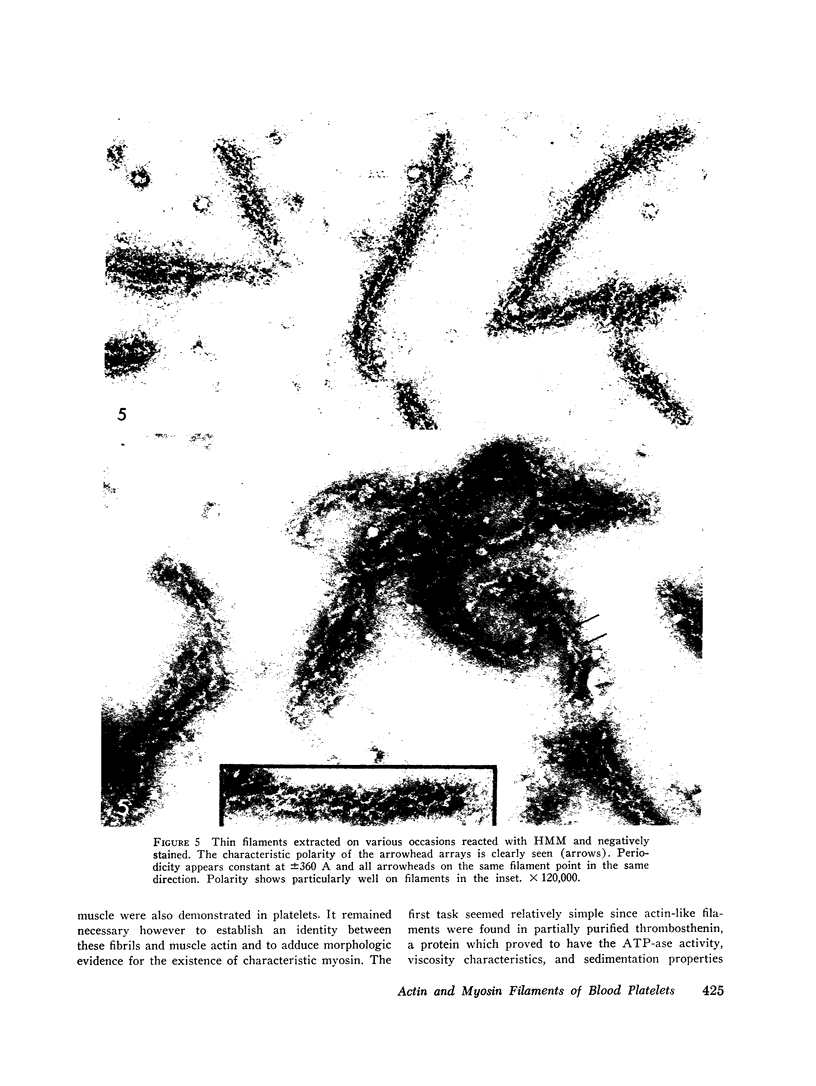
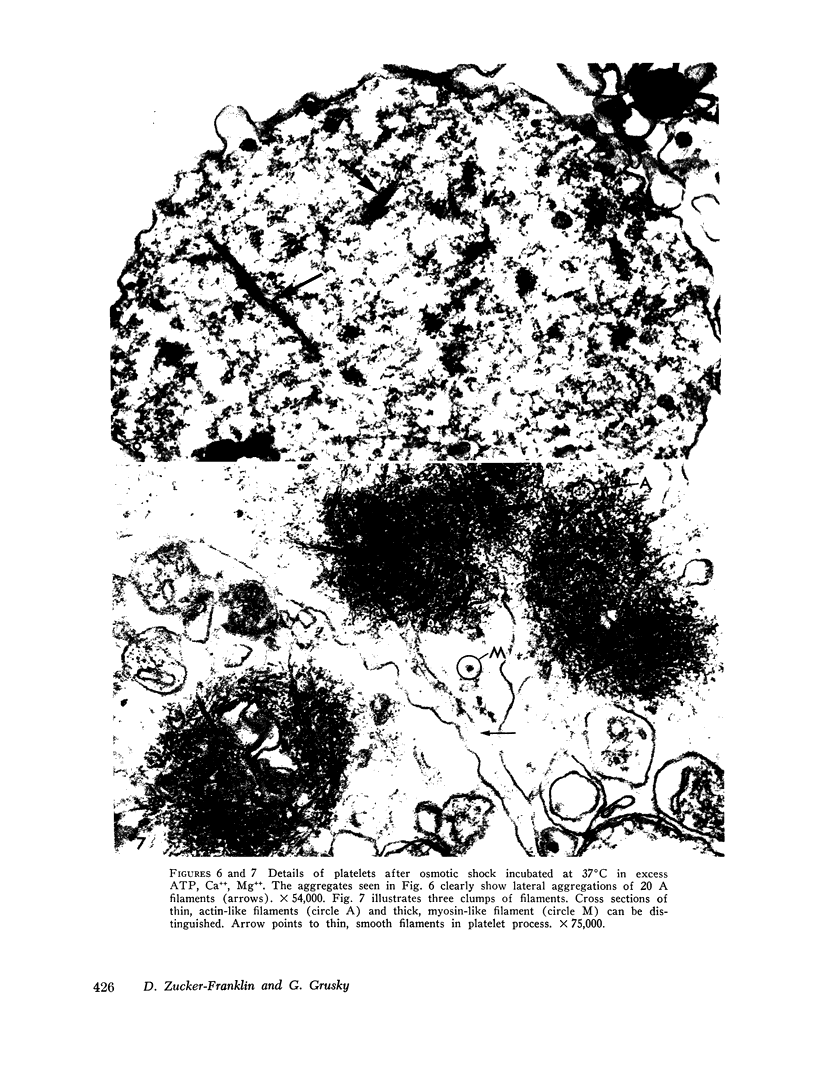
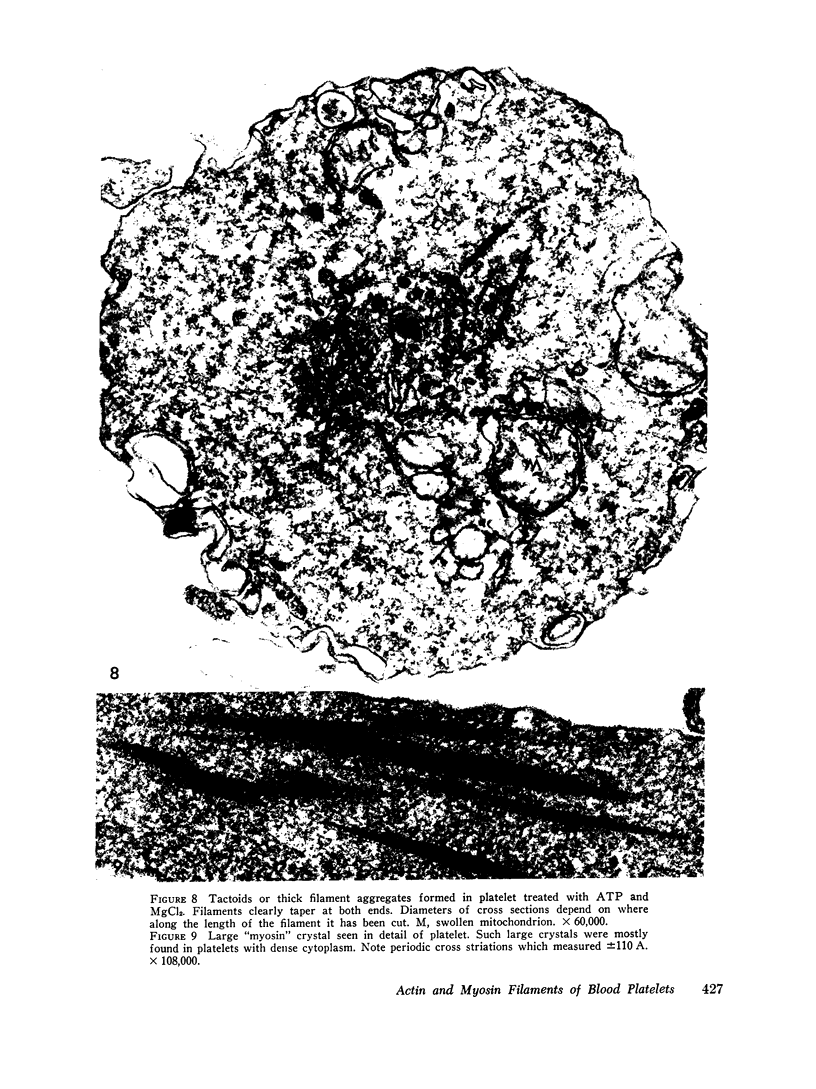
The contractility of platelets has been attributed to an actomyosin-like protein which has been well defined on a physicochemical basis. Moreover, platelets contain ±80 A filaments which resemble actin filaments in smooth muscle. Studies were undertaken on human and bovine platelets to better define the morphologic structures which may subserve this contractile function. In order to identify actin, the ability of the filaments to react with heavy meromyosin (HMM) was tested. Accordingly, platelets were glycerinated and treated with HMM. In addition, platelet actin was extracted, reacted with HMM, and examined by negative staining. In both instances typical arrowhead structures with clearly defined polarity and a periodicity of ±360 A formed. As is the case with purified muscle actin, the complexes were dissociable with Mg-ATP. The formation of myosin-like filaments was observed when osmotically shocked platelets were incubated with MgCl2 and excess ATP. These “thick” filaments measured 250-300 A in width, tapered at both ends and often occurred in clumps. They resembled aggregates of thick filaments described in contracted smooth muscle. Extraction of platelets by methods suitable for the demonstration of myosin showed filaments with an average length of 0.3 μ, a smooth shaft, and frayed or bulbous ends. These appeared identical to those seen in synthetically prepared myosin of striated muscle. It is suggested that the filaments described here represent the actin and myosin of platelets.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelstein R. S., Pollard T. D., Kuehl W. M. Isolation and characterization of myosin and two myosin fragments from human blood platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Nov;68(11):2703–2707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.11.2703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BETTEX-GALLAND M., LUESCHER E. F. Extraction of an actomyosin-like protein from human thrombocytes. Nature. 1959 Jul 25;184(Suppl 5):276–277. doi: 10.1038/184276b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BETTEX-GALLAND M., PORTZEHL H., LUSCHER E. F. Dissociation of thrombosthenin into two components comparable with actin and myosin. Nature. 1962 Feb 24;193:777–778. doi: 10.1038/193777a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behnke O., Kristensen B. I., Nielsen L. E. Electron microscopical observations on actinoid and myosinoid filaments in blood platelets. J Ultrastruct Res. 1971 Nov;37(3):351–369. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(71)80129-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behnke O. Morphological changes in the hyalomere of rat blood platelets in experimental venous thrombi. Scand J Haematol. 1966;3(2):136–148. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1966.tb01434.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bettex-Galland M., Lüscher E. F., Weibel E. R. Thrombosthenin--electron microscopical studies on its localization in human blood platelets and some properties of its subunits. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1969 Dec 31;22(3):431–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRETTE K. Relaxing factor in extracts of blood platelets and its function in the cells. Nature. 1963 May 4;198:488–489. doi: 10.1038/198488a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa H., Bischoff R., Holtzer H. Formation of arrowhead complexes with heavy meromyosin in a variety of cell types. J Cell Biol. 1969 Nov;43(2):312–328. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaminer B. Synthetic myosin filaments from vertebrate smooth muscle. J Mol Biol. 1969 Jan;39(2):257–264. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90315-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R. E., Rice R. V. Ultrastructural studies on the contractile mechanism of smooth muscle. J Cell Biol. 1969 Sep;42(3):683–694. doi: 10.1083/jcb.42.3.683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane B. P. Alterations in the cytologic detail of intestinal smooth muscle cells in various stages of contraction. J Cell Biol. 1965 Oct;27(1):199–213. doi: 10.1083/jcb.27.1.199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus A. J., Zucker-Franklin D., Safier L. B., Ullman H. L. Studies on human platelet granules and membranes. J Clin Invest. 1966 Jan;45(1):14–28. doi: 10.1172/JCI105318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki-Noumura T., Oosawa F. An actin-like protein of the sea urchin eggs. I. Its interaction with myosin from rabbit striated muscle. Exp Cell Res. 1969 Aug;56(2):224–232. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(69)90006-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachman R. L., Ferris B. Studies on human platelet protease activity. J Clin Invest. 1969 Nov;47(11):2530–2540. doi: 10.1172/JCI105935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachman R. L., Marcus A. J., Safier L. B. Platelet thrombosthenin: subcellular localization and function. J Clin Invest. 1967 Aug;46(8):1380–1389. doi: 10.1172/JCI105630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachmias V. T., Huxley H. E. Electron microscope observations on actomyosin and actin preparations from Physarum polycephalum, and on their interaction with heavy meromyosin subfragment I from muscle myosin. J Mol Biol. 1970 May 28;50(1):83–90. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90105-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D., Shelton E., Weihing R. R., Korn E. D. Ultrastructural characterization of F-actin isolated from Acanthamoeba castellanii and identification of cytoplasmic filaments as F-actin by reaction with rabbit heavy meromyosin. J Mol Biol. 1970 May 28;50(1):91–97. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90106-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice R. V., McManus G. M., Devine O. F., Somlyo A. P. Regular organization of thick filaments in mammalian smooth muscle. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 23;231(25):242–243. doi: 10.1038/newbio231242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbluth J. Myosin-like aggregates in trypsin-treated smooth muscle cells. J Cell Biol. 1971 Jan;48(1):174–188. doi: 10.1083/jcb.48.1.174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbluth J. Myosin-like tactoids in trypsin-treated blood platelets. J Cell Biol. 1971 Sep;50(3):900–904. doi: 10.1083/jcb.50.3.900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SABATINI D. D., BENSCH K., BARRNETT R. J. Cytochemistry and electron microscopy. The preservation of cellular ultrastructure and enzymatic activity by aldehyde fixation. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:19–58. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somlyo A. P., Somlyo A. V., Devine C. E., Rice R. V. Aggregation of thick filaments into ribbons in mammalian smooth muscle. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 23;231(25):243–246. doi: 10.1038/newbio231243a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tice L. W., Smith D. S. The localization of myofibrillar ATPase activity in the flight muscles of the blowfly, Calliphora erythrocephala. J Cell Biol. 1965 Jun;25(3 Suppl):121–135. doi: 10.1083/jcb.25.3.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATSON M. L. Staining of tissue sections for electron microscopy with heavy metals. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 Jul 25;4(4):475–478. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.4.475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weihing R. R., Korn E. D. Ameba actin: the presence of 3-methylhistidine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Jun 27;35(6):906–912. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90710-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker-Franklin D. Microfibrils of blood platelets: their relationship TO MICROTUBULES AND THE CONTRACTILE PROTEIN. J Clin Invest. 1969 Jan;48(1):165–175. doi: 10.1172/JCI105965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker-Franklin D., Nachman R. L., Marcus A. J. Ultrastructure of thrombosthenin, the contractile protein of human blood platelets. Science. 1967 Aug 25;157(3791):945–946. doi: 10.1126/science.157.3791.945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker-Franklin D. The submembranous fibrils of human blood platelets. J Cell Biol. 1970 Oct;47(1):293–299. doi: 10.1083/jcb.47.1.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]