Abstract
A model which permits evaluation in molecular terms of the role of antibody and of complement in the immune destruction of erythrocytes was established in the guinea pig. IgM and IgG immunoglobulins were isolated from rabbit anti-guinea pig erythrocyte antisera and were used to sensitize 51Cr-labeled guinea pig erythrocytes. The average number of complement-fixing sites per erythrocyte formed by antibody was determined for each of the various preparations by the Cla fixation and transfer test. The rate of clearance and of organ localization was determined for cells sensitized with either IgM or IgG antibodies, and dose-response curves were established in normal guinea pigs and guinea pigs with a genetically controlled, complete absence of the fourth component of complement (C4).
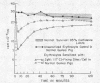
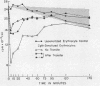
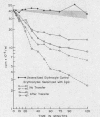
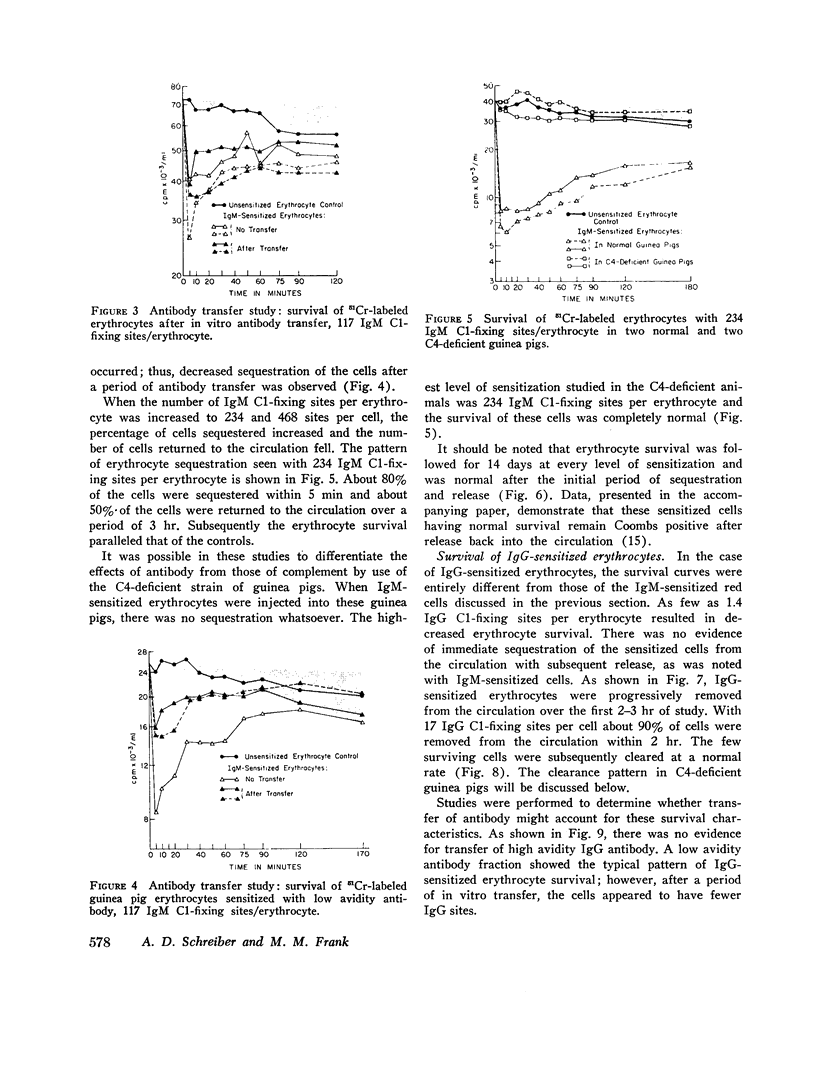
At least 60 complement-fixing sites per cell were required for accelerated clearance of IgM-sensitized erythrocytes. The bulk of cells with IgM sites were cleared by the liver within 5 min after injection and were then slowly returned to the circulation where they survived normally. There was no accelerated clearance whatsoever of IgM-sensitized erythrocytes in C4-deficient guinea pigs.
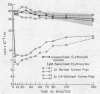
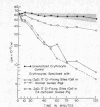
As few as 1.4 IgG complement-fixing sites per cell resulted in decreased erythrocyte survival. There was no evidence of immediate tissue sequestration and release. Progressive trapping and destruction of erythrocytes by the spleen was responsible for most of the clearance of IgG-sensitized cells. Clearance of IgG-sensitized cells was markedly impaired in guinea pigs with C4 deficiency; however, there was some decrease over normal survival.
The data indicate that IgG and IgM antibodies interact with complement in vivo by mechanisms which are qualitatively or quantitatively different and produce different biologic effects.
Full text
PDF


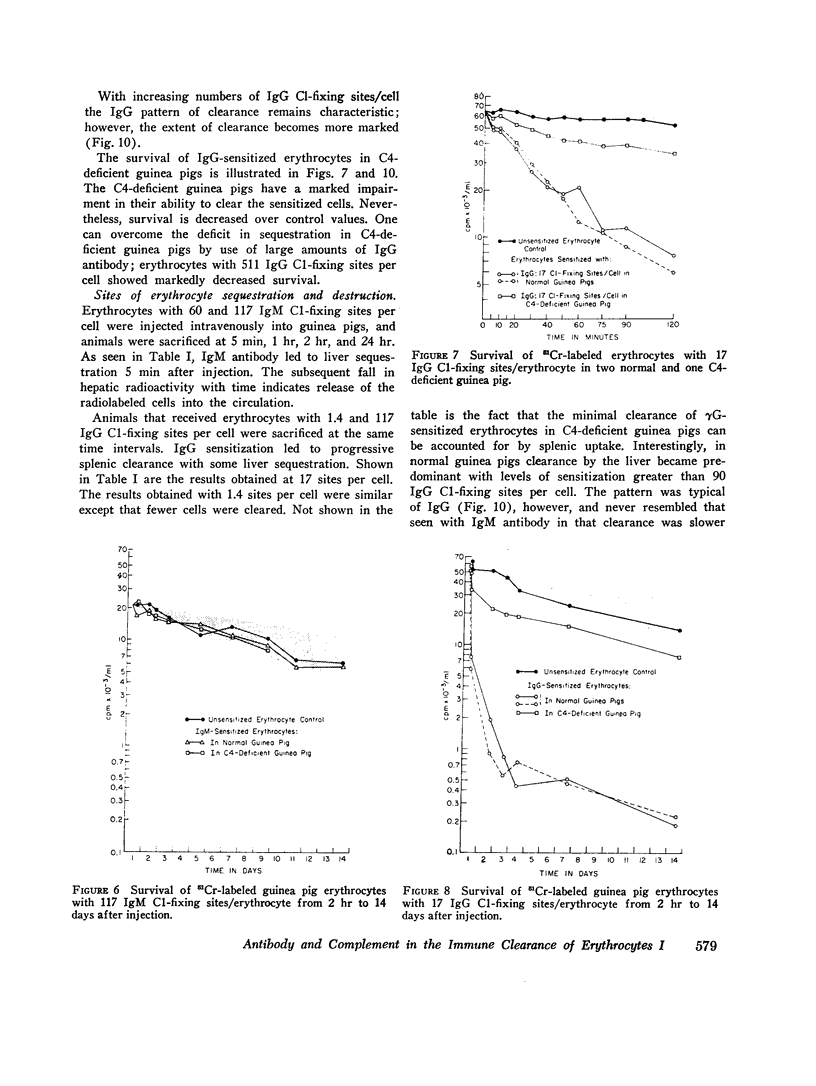
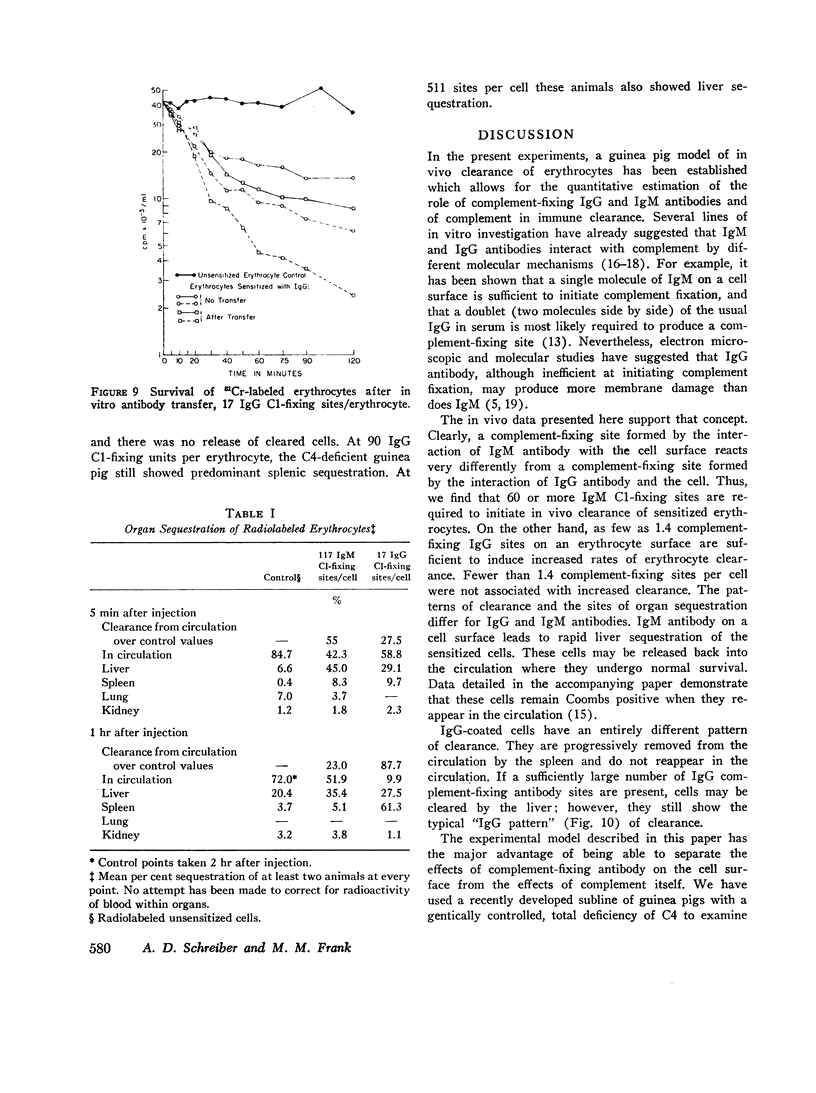
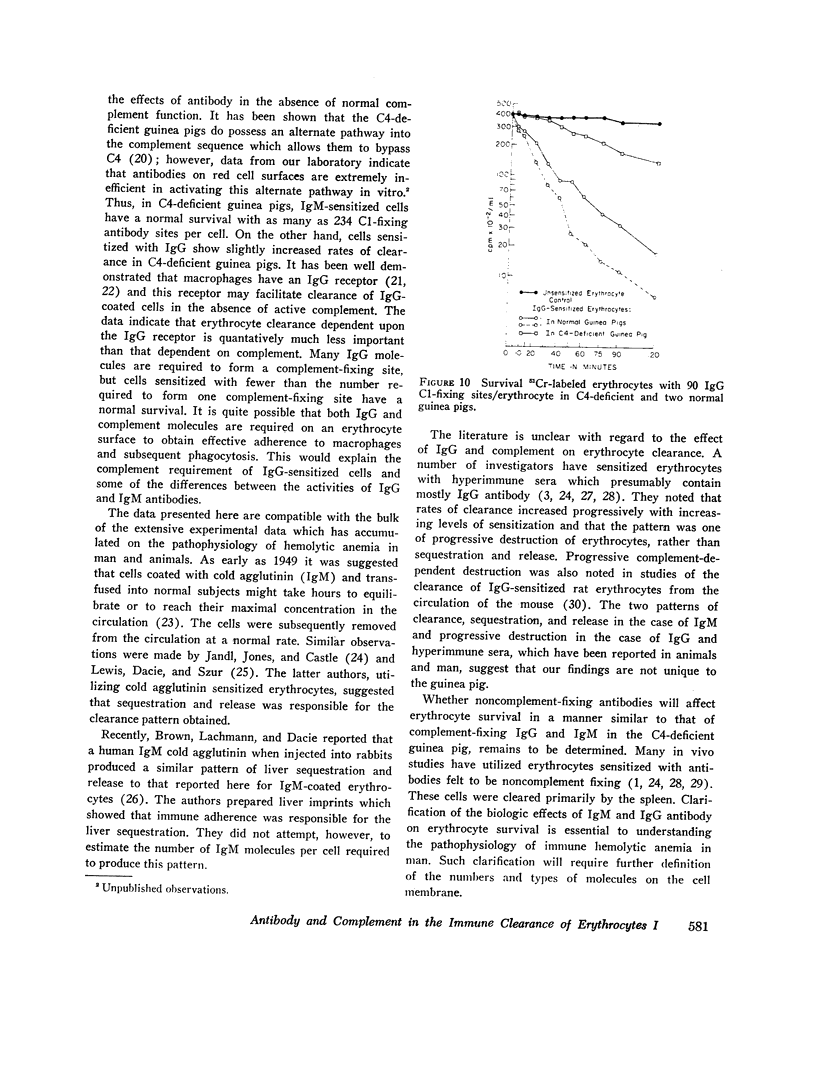

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borsos T., Colten H. R., Spalter J. S., Rogentine N., Rapp H. J. The C'la fixation and transfer test: examples of its applicability to the detection and enumeration of antigens and antibodies at cell surfaces. J Immunol. 1968 Sep;101(3):392–398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borsos T., Rapp H. J. Complement fixation on cell surfaces by 19S and 7S antibodies. Science. 1965 Oct 22;150(3695):505–506. doi: 10.1126/science.150.3695.505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borsos T., Rapp H. J. Hemolysin titration based on fixation of the activated first component of complement: evidence that one molecule of hemolysin suffices to sensitize an erythrocyte. J Immunol. 1965 Sep;95(3):559–566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borsos T., Rapp H. J. Immune hemolysis: a simplified method for the preparation of EAC'4 with guinea pig or with human complement. J Immunol. 1967 Aug;99(2):263–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. L., Lachmann P. J., Dacie J. V. The in vivo behaviour of complement-coated red cells: studies in C6-deficient, C3-depleted and normal rabbits. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Sep;7(3):401–421. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colten H. R., Borsos T., Rapp H. J. Reversible loss of activity of the first component of complement (C'1) as a function of ionic strength. J Immunol. 1968 Apr;100(4):799–807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dacie J. V. Autoimmune haemolytic anaemias. Br Med J. 1970 May 16;2(5706):381–386. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5706.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank M. M., Dourmashkin R. R., Humphrey J. H. Observations on the mechanism of immune hemolysis: importance of immunoglobulin class and source of complement on the extent of damage. J Immunol. 1970 Jun;104(6):1502–1510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank M. M., Gaither T. Evidence that rabbit gamma G haemolysin in capable of utilizing guinea-pig complement more efficiently than rabbit gamma M haemolysin. Immunology. 1970 Dec;19(6):975–981. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank M. M., Gaither T. The effect of temperature on the reactivity of guinea-pig complement with gamma G and gamma M haemolytic antibodies. Immunology. 1970 Dec;19(6):967–974. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank M. M., Humphrey J. H. The subunits in rabbit anti-Forssman IgM antibody. J Exp Med. 1968 May 1;127(5):967–982. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.5.967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank M. M., May J., Gaither T., Ellman L. In vitro studies of complement function in sera of C4-deficient guinea pigs. J Exp Med. 1971 Jul 1;134(1):176–187. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.1.176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber H., Fudenberg H. H. Receptor sites of human monocytes for IgG. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1968;34(1):18–31. doi: 10.1159/000230091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JANDL J. H., JONES A. R., CASTLE W. B. The destruction of red cells by antibodies in man. I. Observations of the sequestration and lysis of red cells altered by immune mechanisms. J Clin Invest. 1957 Oct;36(10):1428–1459. doi: 10.1172/JCI103542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JANDL J. H., KAPLAN M. E. The destruction of red cells by antibodies in man. III. Quantitative factors influencing the patterns of hemolysis in vivo. J Clin Invest. 1960 Jul;39:1145–1156. doi: 10.1172/JCI104129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linscott W. D. The effects of ionic strength, temperature, and antibody class and avidity on fixation and transfer of the first component of complement. J Immunol. 1969 Apr;102(4):993–1001. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LoBuglio A. F., Cotran R. S., Jandl J. H. Red cells coated with immunoglobulin G: binding and sphering by mononuclear cells in man. Science. 1967 Dec 22;158(3808):1582–1585. doi: 10.1126/science.158.3808.1582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOLLISON P. L. Blood-group antibodies and red-cell destruction. Br Med J. 1959 Nov 21;2(5159):1035–1041. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5159.1035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOLLISON P. L., CROME P., HUGHES-JONES N. C., ROCHNA E. RATE OF REMOVAL FROM THE CIRCULATION OF RED CELLS SENSITIZED WITH DIFFERENT AMOUNTS OF ANTIBODY. Br J Haematol. 1965 Jul;11:461–470. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1965.tb06609.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollison P. L. The role of complement in antibody-mediated red-cell destruction. Br J Haematol. 1970 Mar;18(3):249–255. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1970.tb01440.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp H. J., Borsos T. Forssman antigen and antibody: preparation of water soluble antigen and measurement of antibody concentration by precipitin analysis, by C'1a fixation and by hemolytic activity. J Immunol. 1966 Jun;96(6):913–919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPIEGELBERG H. L., MIESCHER P. A., BENACERRAF B. STUDIES ON THE ROLE OF COMPLEMENT IN THE IMMUNE CLEARANCE OF ESCHERICHIA COLI AND RAT ERYTHROCYTES BY THE RETICULOENDOTHELIAL SYSTEM IN MICE. J Immunol. 1963 May;90:751–759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber A. D., Frank M. M. Role of antibody and complement in the immune clearance and destruction of erythrocytes. II. Molecular nature of IgG and IgM complement-fixing sites and effects of their interaction with serum. J Clin Invest. 1972 Mar;51(3):583–589. doi: 10.1172/JCI106847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selwyn J. G., Hackett W. E. Acquired Haemolytic Anaemia: Survival of Transfused Erythrocytes in Patients and Normal Recipients. J Clin Pathol. 1949 May;2(2):114–120. doi: 10.1136/jcp.2.2.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitale B., Kaplan M. E., Rosenfield R. E., Kochwa S. Immune mechanisms for destruction of erythrocytes in vivo. I. The effect of IgG rabbit antibodies on rat erythrocytes. Transfusion. 1967 Jul-Aug;7(4):249–260. doi: 10.1111/j.1537-2995.1967.tb05513.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]