Abstract
Interaction of washed pig, rabbit, or human platelets with fibrinogen was studied during its transition to fibrin using photometric, isotopic, and electron microscopic techniques. Untreated fibrinogen and fully polymerized fibrin had no detectable effect on platelets. Fibrinogen, incubated with low concentrations of reptilase or thrombin, formed intermediate products which readily became associated with platelets and caused their aggregation. Neutralization of the thrombin did not prevent this interaction. In the absence of fibrinogen, reptilase did not affect platelets.
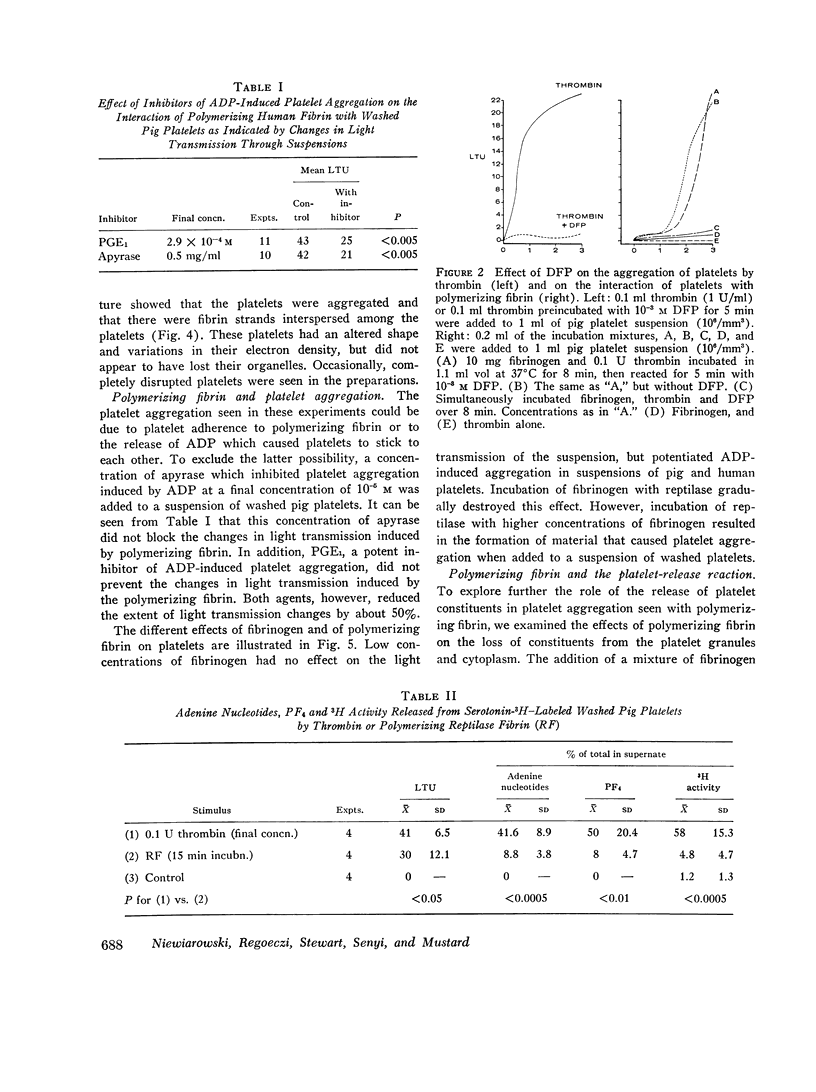
The interaction of polymerizing fibrin with platelets was accompanied by small losses of platelet constituents (serotonin, adenine nucleotides, platelet factor 4, and lactic dehydrogenase). This loss did not appear to be the result of the platelet release reaction. Inhibitors of the release reaction or of adenosine diphosphate (ADP)-induced aggregation did not prevent the interaction of platelets with polymerizing fibrin. Apyrase or prostaglandin E1 (PGE1) reduced the extent of platelet aggregation by polymerizing fibrin, but the amount of protein associated with platelets was slightly increased.
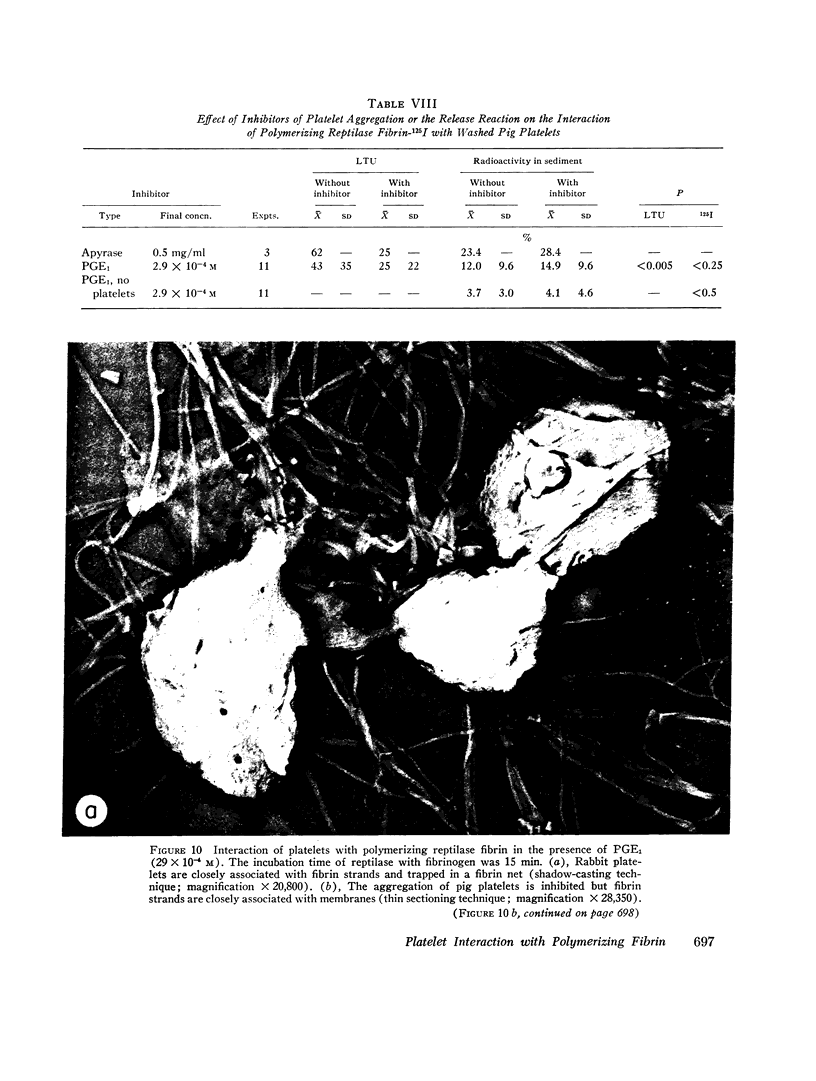
The interaction of polymerizing fibrin with platelets was completely inhibited by ethylenediaminetetraacetate (EDTA) or ethylene glycol bis (β-aminoethyl ether) N, N,N′,N′-tetraacetic acid (EGTA).
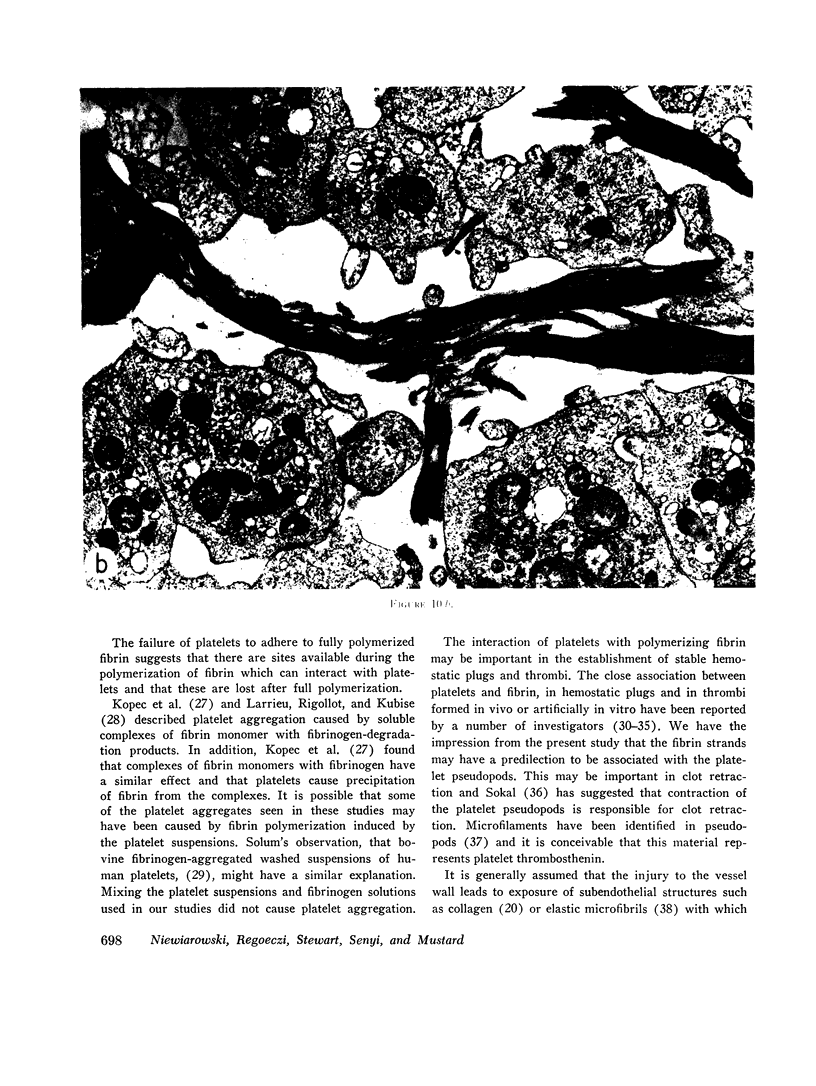
Fibers formed in solutions of polymerizing fibrin were larger in the presence than in the absence of washed platelets, suggesting that platelets affect fibrin polymerization. The adherence of platelets to polymerizing fibrin may be responsible for the establishment of links between platelets and fibrin in hemostatic plugs and thrombi.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ardlie N. G., Packham M. A., Mustard J. F. Adenosine diphosphate-induced platelet aggregation in suspensions of washed rabbit platelets. Br J Haematol. 1970 Jul;19(1):7–17. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1970.tb01596.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ardlie N. G., Perry D. W., Packham M. A., Mustard J. F. Influence of apyrase on stability of suspensions of washed rabbit platelets. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Apr;136(4):1021–1023. doi: 10.3181/00379727-136-35419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong P. W., Gold H. K., Daggett W. M., Austen W. G., Sanders C. A. Hemodynamic evaluation of glucagon in symptomatic heart disease. Circulation. 1971 Jul;44(1):67–73. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.44.1.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashford T. P., Freiman D. G. Platelet aggregation at sites of minimal endothelial injury. An electron microscopic study. Am J Pathol. 1968 Oct;53(4):599–607. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRINKHOUS K. M., READ M. S., MASON R. G. PLASMA THROMBOCYTE-AGGLUTINATING ACTIVITY AND FIBRINOGEN. SYNERGISM WITH ADENOSINE DIPHOSPHATE. Lab Invest. 1965 Apr;14:335–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumgartner H. R., Stemerman M. B., Spaet T. H. Adhesion of blood platelets to subendothelial surface: distinct from adhesion to collagen. Experientia. 1971 Mar 15;27(3):283–285. doi: 10.1007/BF02138148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROSS M. J. EFFECT OF FIBRINOGEN ON THE AGGREGATION OF PLATELETS BY ADENOSINE DIPHOSPHATE. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1964 Dec 31;12:524–527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovig T., Jorgensen L., Packham M. A., Mustard J. F. Platelet adherence to fibrin and collagen. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 Jan;71(1):29–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inceman S., Caen J., Bernard J. Aggregation, adhesion, and viscous metamorphosis of platelets in congenital fibrinogen deficiencies. J Lab Clin Med. 1966 Jul;68(1):21–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen L., Rowsell H. C., Hovig T., Mustard J. F. Resolution and organization of platelet-rich mural thrombi in carotid arteries of swine. Am J Pathol. 1967 Nov;51(5):681–719. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kattlove H. E., Spaet T. H. The effect of chromium on platelet function in vitro. Blood. 1970 May;35(5):659–668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopéc M., Budzyński A., Stachurska J., Wegrzynowicz Z., Kowalski E. Studies on the mechanism of interference by fibrinogen degradation products (FDP) with the platelet function role of fibrinogen in the platelet atmosphere. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1966 May 15;15(3):476–490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larrieu M. J., Rigollot C., Kubisz P. Platelet aggregation induced by soluble fibrin monomer complexes. Life Sci II. 1970 Oct 8;9(19):1111–1115. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(70)90262-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARR J., BARBORIAK J. J., JOHNSON S. A. RELATIONSHIP OF APPEARANCE OF ADENOSINE DIPHOSPHATE, FIBRIN FORMATION AND PLATELET AGGREGATION IN THE HAEMOSTATIC PLUG IN VIVO. Nature. 1965 Jan 16;205:259–262. doi: 10.1038/205259a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUSTARD J. F., HEGARDT B., ROWSELL H. C., MACMILLAN R. L. EFFECT OF ADENOSINE NUCLEOTIDES ON PLATELET AGGREGATION AND CLOTTING TIME. J Lab Clin Med. 1964 Oct;64:548–559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Movat H. Z., Weiser W. J., Glynn M. F., Mustard J. F. Platelet phagocytosis and aggregation. J Cell Biol. 1965 Dec;27(3):531–543. doi: 10.1083/jcb.27.3.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niewiarowski S., Thomas D. P. Platelet factor 4 and adenosine diphosphate release during human platelet aggregation. Nature. 1969 Jun 28;222(5200):1269–1270. doi: 10.1038/2221269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoeczi E., Stannard B. A. In vivo behaviour of frozen and freeze-dried fibrinogen and of that prepared from out-dated blood. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 May;181(1):287–294. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(69)90251-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodman N. F., Mason R. G. Platelet-platelet interaction: relationship to hemostasis and thrombosis. Fed Proc. 1967 Jan-Feb;26(1):95–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPAET T. H., ZUCKER M. B. MECHANISM OF PLATELET PLUG FORMATION AND ROLE OF ADENOSINE DIPHOSPHATE. Am J Physiol. 1964 Jun;206:1267–1274. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.206.6.1267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solum N. O. Aggregation of human platelets by bovine platelet fibrinogen. Scand J Haematol. 1968;5(6):474–485. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1968.tb00868.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solum N. O. Platelet aggregation during fibrin polymerization. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1966;18(6):577–587. doi: 10.3109/00365516609049041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart G. J. A fixation-shadowing technique for electron microscopic visualization of platelets, subcellular material, and fibrin. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1970 May 31;23(2):228–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren B. A., Davey M. G. Electron microscopy of human platelet aggregates formed in vitro with and without fibrin production. Angiologica. 1970;7(2):84–103. doi: 10.1159/000157823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker-Franklin D. Microfibrils of blood platelets: their relationship TO MICROTUBULES AND THE CONTRACTILE PROTEIN. J Clin Invest. 1969 Jan;48(1):165–175. doi: 10.1172/JCI105965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]









