Abstract
A 63-year-old female was presented to emergency room with an abdominal pain. The patient had moderate mitral valve stenosis and atrial fibrillation. Abdominal computed tomography revealed right renal infarction. Transthoracic echocardiography showed a large mobile mass in the left atrium. Transesophageal two-and three-dimensional echocardiography showed a large mobile ovoid mass with a narrow stalk attached to the left atrial septum. It was thought to be a myxoma rather than thrombus. Anticoagulation with heparin was continued. When the operation was performed, there was no mass in the left atrium. It must be a thrombus and melt away.
Keywords: Left atrium, Thrombus, Myxoma, Stalk, Atrial fibrillation
Introduction
Echocardiography plays a key role in establishing the diagnosis of patients with cardiac myxomas and thrombi. The differentiation between myxomas and thrombi is important because of the distinct treatment strategy. But it is often difficult to triage one from the other. In some cases, atrial thrombi may have stalk and can be misdiagnosed as myxoma.
Case
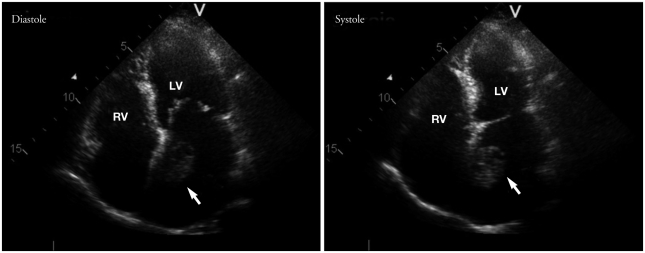
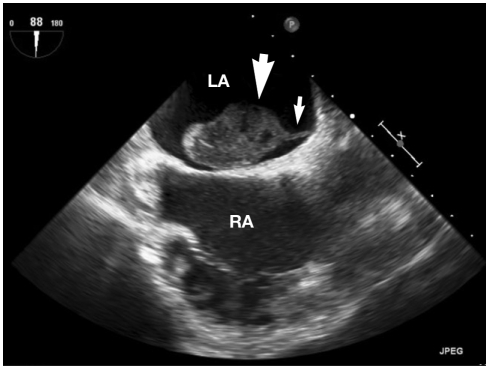
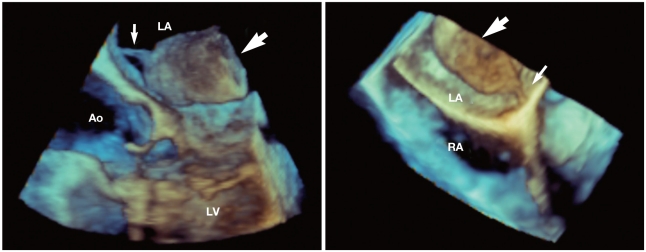
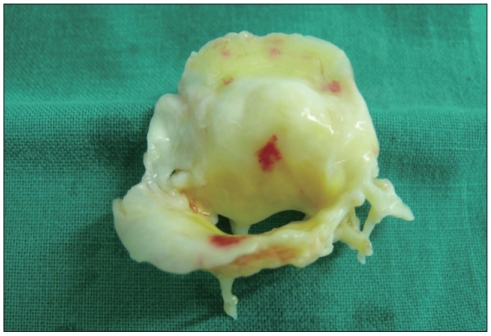
A 63-year-old female was presented to emergency room with an abdominal pain. The patient had moderate mitral valve stenosis and atrial fibrillation since one year ago. She has been treated with warfarin but she often skipped her medication. Blood pressure was 120/80 mmHg and pulse rate was 72 min. The 12-lead electrocardiogram revealed atrial fibrillation with normal ventricular response. Her international normalized ratio (INR) was 1.11. Abdominal computed tomography (CT) revealed right renal infarction. Two-dimensional transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) showed moderate mitral valve stenosis with valve area of 1.2 cm2 and an enlarged left atrium. A large mobile round mass (2-3 cm in size) was seen in the left atrium (Fig. 1). It was unclear whether the mass had any attachment to the interatrial septum. The mean pressure gradient across the mitral valve on Doppler was 6 mmHg. To confirm a diagnosis, a transesophageal two-and three-dimensional echocardiography (TEE) was performed. A large (4 cm × 2.5 cm), ovoid and heterogeneous mass was observed in the left atrium attached with a narrow stalk to the left atrial septum (Fig. 2). Three-dimensional TEE showed a more definite connection with a long stalk between the mass and atrial septum. It showed tumor-like movement with cardiac cycle (Fig. 3). There was no mass in the left atrial appendage. Because it was thought to be a myxoma rather than thrombus, surgery with mass removal and mitral valve replacement was planed. Anticoagulation with heparin was continued for 12 days because of delayed surgery. Follow-up echocardiogram could not be done before surgery. When the operation was performed, surprisingly, there was no mass in the left atrium. We concluded that the mass must be thrombus and melt away. There was no remnant structure in the left atrium. Mitral valve replacement was done (Fig. 4).
Fig. 1.
Transthoracic echocardiographic image in the apical 4-chamber view showing left atrial mass indicated by arrow. LV: left ventricle, RV: right ventricle.
Fig. 2.
Two-dimensional transesophageal echocardiographic image showing a large (4 cm×2.5 cm), ovoid and heterogeneous mass (large arrow) in left atrium attached with a long narrow stalk (small arrow) to the anteroseptal wall of the left atrium. LA: left atrium, RA: right atrium.
Fig. 3.
Three-dimensional transesophageal echocardiographic image showing a more definite connection via a long stalk (small arrow) between the mass (large arrow) and left atrial wall. LA: left atrium, LV: left ventricle, RA: right atrium, Ao: aorta.
Fig. 4.
Gross pathologic specimen of stenotic mitral valve. There was no mass or thrombus in the left atrium.
Discussion
TTE and TEE are the procedures of choice for the diagnosis of cardiac mass involving the left atrium. TEE has been shown to be a superior method in defining the characteristics of a mass in the left atrium.1) An echocardiographic procedure should be able to characterize the mass by morphologic shape and appearance, site of attachment, types of margin, and presence or absence in the left atrial appendage.2)
Cardiac myxomas are the most common benign primary tumor of the heart.3) On echocardiogram cardiac myxomas typically appear as a mobile mass attached to the endocardial surface by a stalk, usually arising from the fossa ovalis. Myxomas with this appearance can be confidently diagnosed by echocardiography and further imaging is not necessary. If the narrow stalk is not visible, the diagnosis cannot be made by echocardiography and require further imaging, including magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or CT. However, the imaging appearance of myxomas sometimes mimics thrombus.4),5) Once diagnosis has been established, surgery should be performed promptly because of the possibility of embolic complications. Even acute myocardial infarction can be caused by coronary myxoemboli.6)
Cardiac thrombi, which appear more frequently than cardiac myxomas7) are typically located in the atrium, more often in the left, and generally occur in patients with organic heart disease.8) In some cases, atrial thrombi may have stalk and can be diagnosed as myxomas, which can lead to an unnecessary surgical resection.9),10) Rarely, thrombus can be entrapped in patent foramen ovale and it may be confused with myxoma.11)
Potential errors in diagnosis can be made, however, if the characteristics are not well defined, especially if the tumor size is very small or smooth in contour, or attachment site is illdefined.12) Left atrial thrombi are classically found in an atrial appendage, but can also be found in the body of the left atrium.13) A mass located in the left atrium can be defined as thrombus if it is associated with the presence of atrial fibrillation, enlarged atrial chamber, prosthetic mitral and tricuspid valves, stenotic mitral and tricuspid valves, low cardiac output state, and spontaneous atrial contrast echoes.12),13) However, in case of left atrial myxoma with mitral stenosis, it is very difficult to differentiate a thrombus from a myxoma.
Left atrial myxomas and thrombi can be differentiated using CT by assessing the distinguishing features of size, origin, shape, mobility, and prolapse. Myxomas are larger, frequently found in the left atrium and usually originate from fossa ovalis compared to thrombi which most originate from the appendage.14)
In this case, three-dimensional TEE could clearly identify the attachment of the left atrial mass to the anteroseptal atrial surface by a narrow stalk. In addition, mobility with cardiac cycle and the absence of any additional masses in the left atrial appendage favor the diagnosis of cardiac myxoma. But, the presence of stenotic mitral valve together with atrial fibrillation favor the diagnosis of atrial thrombus.
This case suggests that: (1) in a left atrial mass with stalk, differential diagnosis between thrombus and myxoma may be difficult; (2) when the differential diagnosis is difficult and thrombus is a possibility, a trial of anticoagulation may be advised.
References
- 1.Alam M, Sun I. Transesophageal echocardiographic evaluation of left atrial mass lesions. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 1991;4:323–330. doi: 10.1016/s0894-7317(14)80442-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Feinglass NG, Reeder GS, Finck SJ, Shine TS, Maniu CV. Myxoma of the left atrial appendage mimicking thrombus during aortic valve replacement. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 1998;11:677–679. doi: 10.1016/s0894-7317(98)70046-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Araoz PA, Mulvagh SL, Tazelaar HD, Julsrud PR, Breen JF. CT and MR imaging of benign primary cardiac neoplasms with echocardiographic correlation. Radiographics. 2000;20:1303–1319. doi: 10.1148/radiographics.20.5.g00se121303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Fang YM, Dean R, Figueroa R. Right atrial myxoma mimicking an atrial thrombus in the third trimester of pregnancy. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2007;20:77–78. doi: 10.1080/14767050601131229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Feinglass NG, Reeder GS, Finck SJ, Shine TS, Maniu CV. Myxoma of the left atrial appendage mimicking thrombus during aortic valve replacement. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 1998;11:677–679. doi: 10.1016/s0894-7317(98)70046-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Park HS, Park JH, Jeong JO. Intracoronary catheter aspirarion can be an adequate option in patient with acute myocardial infarction caused by left atrial myxoma. J Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2009;17:145–147. doi: 10.4250/jcu.2009.17.4.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Burke A, Jeudy J, Jr, Virmani R. Cardiac tumours: an update: Cardiac tumours. Heart. 2008;94:117–123. doi: 10.1136/hrt.2005.078576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Restrepo CS, Largoza A, Lemos DF, Diethelm L, Koshy P, Castillo P, Gomez R, Moncada R, Pandit M. CT and MR imaging findings of benign cardiac tumors. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2005;34:12–21. doi: 10.1067/j.cpradiol.2004.10.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hesse B, Murphy RT, Myles J, Huang J, Sabik EM. Images in cardiovascular medicine. A left atrial appendage thrombus mimicking atrial myxoma. Circulation. 2006;113:e456–e457. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.565903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Heitner JF, Klem I, Alexander K, Thomson L, Meine TJ, Patel MR, Haq SA, Shah DJ, Kim RJ. The case of the disappearing myxoma. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2005;7:841–843. doi: 10.1080/10976640500288156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kim SE, Park DG. Tentatively diagnosed as myxoma: Transit thrombus entrapped in patent foramen ovale. J Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2007;15:19–22. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Alam M. Pitfalls in the echocardiographic diagnosis of intracardiac and extracardiac masses. Echocardiography. 1993;10:181–191. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8175.1993.tb00029.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Sim EK, Lim YT, Ng WL, Goh JJ, Reebye S. Co-existing left atrial thrombus and myxoma in mitral stenosis--a diagnostic challenge. Singapore Med J. 1999;40:46–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Scheffel H, Baumueller S, Stolzmann P, Leschka S, Plass A, Alkadhi H, Schertler T. Atrial myxomas and thrombi: comparison of imaging features on CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009;192:639–645. doi: 10.2214/AJR.08.1694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]