Abstract
Five families with inherited thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG) abnormalities were studied. On the basis of serum thyroxine (T4)- binding capacity of TBG in affected males, three family types were identified: TBG deficiency, low TBG, and high TBG capacity. In all families evidence for X-linked inheritance was obtained and in one family all criteria establishing this mode of inheritance were met. Only females were heterozygous, exhibiting values intermediate between affected males and normals. Overlap in heterozygotes was most commonly encountered in families with low TBG.
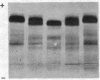
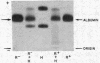
Quantitative variation in the serum concentration of functionally normal TBG was demonstrated by: (a) failure of serum from TBG-deficient subjects to react with anti-TBG antibodies; (b) normal kinetics of T4 and triiodothyronine-binding to TBG in sera from subjects with low TBG and high TBG capacity; (c) concordance of estimates of TBG concentration by T4 saturation and by immunological methods; and (d) normal rate of heat inactivation of TBG.
No abnormalities in serum transport of cortisol, testosterone, aldosterone, or thyroxine bound to prealbumin could be detected.
These observations suggest that all the TBG abnormalities thus far observed reflect mutations at a single X-linked locus involved in the control of TBG synthesis.
Full text
PDF



















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alper C. A., Propp R. P. Genetic polymorphism of the third component of human complement (C'3). J Clin Invest. 1968 Sep;47(9):2181–2191. doi: 10.1172/JCI105904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altland K., Goedde H. W. Variability of pseudocholinesterase. Humangenetik. 1970;9(3):241–244. doi: 10.1007/BF00279233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEIERWALTES W. H., CARR E. A., Jr, HUNTER R. L. Hereditary increase in the thyroxine-binding sites in the serum alpha globulin. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1961;74:170–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEIERWALTES W. H., ROBBINS J. Familial increase in the thyroxine-binding sites in serum alpha globulin. J Clin Invest. 1959 Oct;38:1683–1688. doi: 10.1172/JCI103946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEISEL W. R., ZAINAL H., HANE S., DIRAIMONDO V. C., FORSHAM P. H. Low thyroidal iodine uptake with euthyroidism associated with deficient thyroid-binding globulin but normal cortisol binding. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1962 Dec;22:1165–1170. doi: 10.1210/jcem-22-12-1165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEUTLER E., YEH M., FAIRBANKS V. F. The normal human female as a mosaic of X-chromosome activity: studies using the gene for C-6-PD-deficiency as a marker. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Jan 15;48:9–16. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayley T. A., Higgins H. P., Row V. V., James W., Vidal R. The metabolic significance of thyroxine-binding globulin. Studies in a family with decreased thyroxine-binding globulin. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1969 May;61(1):137–150. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0610137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellabarba D., Peterson R. E., Sterling K. An improved method for chromatography of iodothyronines. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1968 Feb;28(2):305–307. doi: 10.1210/jcem-28-2-305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARK F., HORN D. B. ASSESSMENT OF THYROID FUNCTION BY THE COMBINED USE OF THE SERUM PROTEIN-BOUND IODINE AND RESIN UPTAKE OF 131-I-TRIIODOTHYRONINE. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Jan;25:39–45. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-1-39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavalieri R. R., Searle G. L. The kinetics of distribution between plasma and liver of 131-I-labeled L-thyroxine in man: observations of subjects with normal and decreased serum thyroxine-binding globulin. J Clin Invest. 1966 Jun;45(6):939–949. doi: 10.1172/JCI105409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIGIULIO W. D., MICHALAK Z., WEINHOLD P. A., HAMILTON J. R., THOMA G. E. USE OF AGAR GEL ELECTROPHORESIS AND AUTORADIOGRAPHY TO MEASURE THYROXINE-BINDING PROTEIN CAPACITIES. J Lab Clin Med. 1964 Aug;64:349–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dern R. J., McCurdy P. R., Yoshida A. A new structural variant of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase with a high production rate (G6PD Hektoen). J Lab Clin Med. 1969 Feb;73(2):283–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELZINGA K. E., CARR E. A., Jr, BEIERWALTES W. H. Adaptation of the standard Durrum-type cell for reverse-flow paper electrophoresis. Am J Clin Pathol. 1961 Aug;36:125–131. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/36.2.125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLORSHEIM W. H., DOWLING J. T., MEISTER L., BODFISH R. E. Familial elevation of serum thyroxine-binding capacity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1962 Jul;22:735–740. doi: 10.1210/jcem-22-7-735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fang V. S., Selenkow H. A. Determination of free thyroxine in serum by low-temperature equilibrium dialysis. Clin Chem. 1970 Mar;16(3):185–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fialkow P. J., Giblett E. R., Musa B. Increased serum thyroxine-binding globulin capacity: inheritance and linkage relationships. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1970 Jan;30(1):66–70. doi: 10.1210/jcem-30-1-66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerversman A. P., Bottema J. K. Hereditair tekort aan thyroxine-bindende globuline. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 1968 Aug 3;112(31):1408–1409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinonen O. P., Lamberg B. A., Virtamo J. Inherited decrease of the binding capacity of thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG). Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1970 May;64(1):171–180. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0640171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hippe E. Hereditary ectodermal dysplasia of anhidrotic type with increased protein-bound serum thyroxine. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1967 Nov;56(6):687–692. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1967.tb15997.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INGBAR S. H. Observations concerning the binding of thyroid hormones by human serum prealbumin. J Clin Invest. 1963 Feb;42:143–160. doi: 10.1172/JCI104701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INGBAR S. H., WATERHOUSE C., CUSHMAN P. OBSERVATIONS ON THE NATURE OF THE UNDERLYING DISORDER AND THE OCCURRENCE OF ASSOCIATED PLASMA TRANSPORT ABNORMALITIES IN A PATIENT WITH AN IDIOPATHIC INCREASE IN THE PLASMA THYROXINE-BINDING GLOBULIN. J Clin Invest. 1964 Dec;43:2266–2271. doi: 10.1172/JCI105100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingbar S. H. CLINICAL AND PHYSIOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS IN A PATIENT WITH AN IDIOPATHIC DECREASE IN THE THYROXINE-BINDING GLOBULIN OF PLASMA. J Clin Invest. 1961 Nov;40(11):2053–2063. doi: 10.1172/JCI104431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JESPERSEN H. G. Hereditary ectodermal dysplasia of anhidrotic type. A report of three cases in boys aged 3-4 months. Acta Paediatr. 1962 Nov;51:712–720. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1962.tb06603.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. E., Seal U. S. X-chromosome linked inheritance of elevated thyroxine-binding globulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1967 Nov;27(11):1521–1528. doi: 10.1210/jcem-27-11-1521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraemer E., Wiswell J. G. Familial thyroxine-binding globulin deficiency. Metabolism. 1968 Mar;17(3):260–262. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(68)90128-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAURELL C. B. ANTIGEN-ANTIBODY CROSSED ELECTROPHORESIS. Anal Biochem. 1965 Feb;10:358–361. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B., Niléhn J. E. A new type of inherited serum albumin anomaly. J Clin Invest. 1966 Dec;45(12):1935–1945. doi: 10.1172/JCI105498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy R. P., Marshall J. S., Velayo N. L. Radioimmunoassay of human thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG). J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Mar;32(3):372–381. doi: 10.1210/jcem-32-3-372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCKUSICK V. A. On the X chromosome of man. Q Rev Biol. 1962 Jun;37:69–175. doi: 10.1086/403631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MULLER-EBERHARD H. J. A new supporting medium for preparative electrophoresis. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1960;12:33–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall J. S., Levy R. P., Steinberg A. G. Human thyroxine-binding globulin deficiency. A genetic study. N Engl J Med. 1966 Jun 30;274(26):1469–1473. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196606302742604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall J. S., Pensky J. Studies on human thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG). I. Purification of TBG and immunologic studies on the relationship between TBG from normal persons and those with TBG "deficiency". J Clin Invest. 1969 Mar;48(3):508–515. doi: 10.1172/JCI106008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moloshok R. E., Hsu L. Y., Seal U. S., Hirschhorn K. Partial thyroxine-binding globulin deficiency in a family. Pediatrics. 1969 Oct;44(4):518–525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NICOLOFF J. T., DOWLING J. T., PATTON D. D. INHERITANCE OF DECREASED THYROXINE-BINDING BY THE THYROXINE-BINDING GLOBULIN. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1964 Mar;24:294–298. doi: 10.1210/jcem-24-3-294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikolai T. F., Roberts R. C. Thyroxine binding globulin (TBG) deficiency. A problem in the diagnosis of thyroid disease. Arch Intern Med. 1969 Dec;124(6):691–694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikolai T. F., Seal U. S. X-chromosome linked familial decrease in thyroxine-binding globulin activity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1966 Aug;26(8):835–841. doi: 10.1210/jcem-26-8-835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikolai T. F., Seal U. S. X-chromosome linked inheritance of thyroxine-binding globulin deficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1967 Nov;27(11):1515–1520. doi: 10.1210/jcem-27-11-1515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikolai T. F. Thyroxine binding globulin deficiency. Constitutional growth retardation erroneously diagnosed as isolated thyrotropin deficiency. J Pediatr. 1969 Jul;75(1):130–132. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(69)80114-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OPPENHEIMER J. H., SQUEF R., SURKS M. I., HAUER H. BINDING OF THYROXINE BY SERUM PROTEINS EVALUATED BY EQUILIBRUM DIALYSIS AND ELECTROPHORETIC TECHNIQUES. ALTERATIONS IN NONTHYROIDAL ILLNESS. J Clin Invest. 1963 Nov;42:1769–1782. doi: 10.1172/JCI104862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBBINS J. Reverse-flow zone electrophoresis; a method for determining the thyroxine-binding capacity of serum protein. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1956 Aug;63(2):461–469. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(56)90062-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUSSELL L. B. ANOTHER LOOK AT THE SINGLE-ACTIVE-X HYPOTHESIS. Trans N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Apr;26:726–736. doi: 10.1111/j.2164-0947.1964.tb01939.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Refetoff S., Hagen S. R., Selenkow H. A. Estimation of the T 4 binding capacity of serum TBG and TBPA by a single T 4 load ion exchange resin method. J Nucl Med. 1972 Jan;13(1):2–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Refetoff S., Robin N. I., Fang V. S. Parameters of thyroid function in serum of 16 selected vertebrate species: a study of PBI, serum T4, free T4, and the pattern of T4 and T3 binding to serum proteins. Endocrinology. 1970 Apr;86(4):793–805. doi: 10.1210/endo-86-4-793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Refetoff S., Selenkow H. A. Familial thyroxine-binding globulin deficiency in a patient with Turner's syndrome (XO). Genetic study of a kindred. N Engl J Med. 1968 May 16;278(20):1081–1087. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196805162782002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. C., Nikolai T. F., Lohrenz F. N. A TBG-deficient family with a male exhibiting decreased but not zero TBG levels. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1970 Jan;30(1):131–133. doi: 10.1210/jcem-30-1-131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robin N. I., Hagen S. R., Collaço F., Refetoff S., Selenkow H. A. Serum tests for measurement of thyroid function. Hormones. 1971;2(5):266–279. doi: 10.1159/000178240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHEIDEGGER J. J. Une micro-méthode de l'immuno-electrophorèse. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1955;7(2):103–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siersbaek-Nielsen K., Hansen J. M., Hippe E. Familial elevation of serum thyroxine-binding globulin capacity. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1969 Jan;60(1):130–136. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0600130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TANAKA S., STARR P. Excessive circulating thyroxine in euthyroid, non-pregnant women with elevated thyroxine-binding serum globulin. Metabolism. 1959 Jul 1;8(4 Pt 1):441–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torkington P., Harrison R. J., Maclagan N. F., Burston D. Familial thyroxine-binding globulin deficiency. Br Med J. 1970 Jul 4;3(5713):27–29. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5713.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windhorst D. B., Holmes B., Good R. A. A newly defined X-linked trait in man with demonstration of the Lyon effect in carrier females. Lancet. 1967 Apr 8;1(7493):737–739. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)91360-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida A. Amino acid substitution (histidine to tyrosine) in a glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase variant (G6PD Hektoen) associated with over-production. J Mol Biol. 1970 Sep 28;52(3):483–490. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90414-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida A., Motulsky A. G. A pseudocholinesterase variant (E Cynthiana) associated with elevated plasma enzyme activity. Am J Hum Genet. 1969 Sep;21(5):486–498. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]