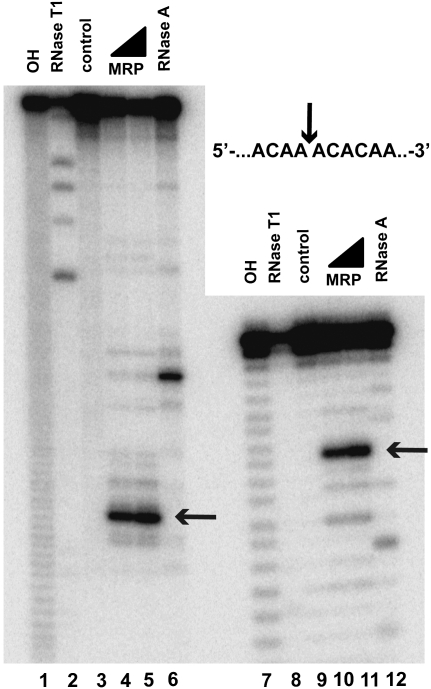
FIGURE 7.
A putative hairpin located 5′ to the A3 site in the internal transcribed spacer 1 of pre-rRNA (Fig. 1C) is not essential for RNase MRP cleavage. (Lanes 1–6) RNase MRP cleavage of an ITS1 fragment encompassing nucleotides −81 to 66 from the A3 site. (Lanes 7–12) RNase MRP cleavage of a short ITS1 fragment encompassing nucleotides −47 to 7 from the A3 site with the putative hairpin (nucleotides −39 to −7) removed. (Lanes 1,7) Alkaline hydrolysis (markers); (lanes 2,8) RNase T1 digests (markers); (lanes 3,9) untreated RNA substrates; (lanes 4,5,10,11) RNase MRP digests; (lanes 6,12) RNase A digests (markers). The mobilities of the short products of RNase MRP digestion differ slightly from those of the products of alkaline hydrolysis due to the presence of additional terminal phosphates in the latter; RNase A digest markers (lanes 6,12) were treated with T4 polynucleotide kinase to eliminate this effect (Brown and Bevilacqua 2005). All substrates were 5′-end-labeled with 32P and separated on a 6% denaturing polyacrylamide gel.