Abstract
Phenobarbital, by inducing liver microsomal enzymes, may affect bile acid synthesis from cholesterol and thus alter the secretion of biliary lipids and the composition of bile. We, therefore, determined the effects of phenobarbital on bile flow, biliary lipid secretion, bile acid synthesis, and bile-acid pool size. Using an experimental preparation that allows controlled interruption of the enterohepatic circulation (1), we administered 5 mg/kg per day of phenobarbital to healthy Rhesus monkeys for 1-2 wk to achieve steady-state conditions. Three animals were studied with an intact enterohepatic circulation and three with a total bile fistula, each animal served as its own control. Total bile flow and secretion of bile salt, phospholipid, and cholesterol were measured every 24 h during steady-state conditions. Further, under conditions of an intact enterohepatic circulation bile-acid synthetic rate was measured in three animals and pool size estimated in two animals during both control and drug treatment periods.
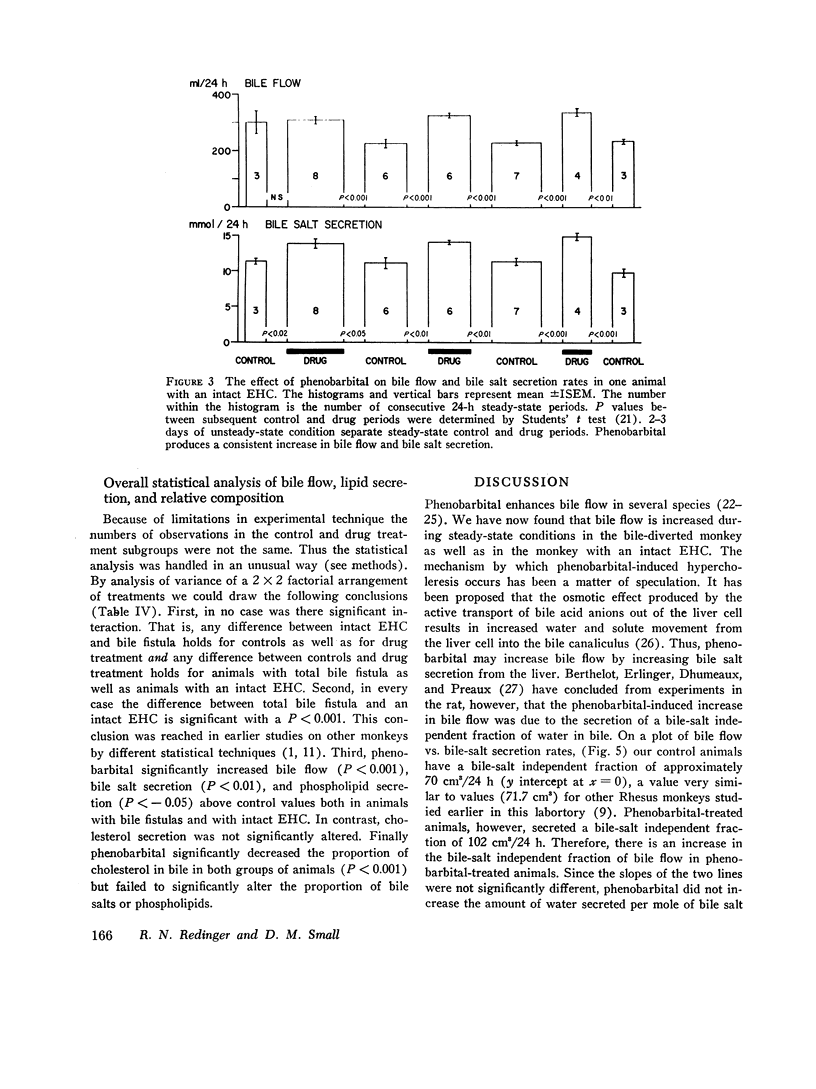
Phenobarbital at doses of 5 mg/kg per day increased bile flow 30-50% in all animals (P < 0.001). The increased bile flow resulted from both an increased “bile-salt independent fraction” and an increased bile-salt secretion rate. Phenobarbital significantly increased bile salt (P < 0.01) and phospholipid secretion (P < 0.05) by about 30% but cholesterol secretion was not significantly changed. Consequently, the concentration of cholesterol relative to bile salt and phospholipid was decreased (P < 0.001). Phenobarbital significantly enhanced the maximal rate of bile acid synthesis 25-30% in all three monkeys with total bile fistulas (P < 0.05) and also augmented bile acid synthesis and pool size in animals with intact enterohepatic circulations despite the fact that the rates of bile salt returning to the liver in these animals would have inhibited bile acid synthesis in control animals. Thus, phenobarbital not only increases the maximal rate of bile acid synthesis but also alters the normal control mechanisms by which bile salts returning to the liver inhibit bile salt synthesis. The fact that phenobarbital treatment results in increased synthesis of bile salt and unchanged secretion of cholesterol is consistant with the view that the drug augments conversion of hepatic cholesterol to bile salt. The resulting decrease in relative cholesterol content in bile may have therapeutic implications for cholesterol gallstone therapy.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Admirand W. H., Small D. M. The physicochemical basis of cholesterol gallstone formation in man. J Clin Invest. 1968 May;47(5):1043–1052. doi: 10.1172/JCI105794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Back P., Hamprecht B., Lynen F. Regulation of cholesterol biosynthesis in rat liver: diurnal changes of activity and influence of bile acids. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Aug;133(1):11–21. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90482-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger J., Redinger R., Small D. M. Instrument for sampling and measuring bile flow. Med Biol Eng. 1970 Jan;8(1):19–24. doi: 10.1007/BF02551745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berthelot P., Erlinger S., Dhumeaux D., Preaux A. M. Mechanism of phenobarbital-induced hypercholeresis in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1970 Sep;219(3):809–813. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.219.3.809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowling R. H., Mack E., Picott J., Berger J., Small D. M. Experimental model for the study of the enterohepatic circulation of bile in rhesus monkeys. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 Jul;72(1):169–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowling R. H., Mack E., Small D. M. Biliary lipid secretion and bile composition after acute and chronic interruption of the enterohepatic circulation in the Rhesus monkey. IV. Primate biliary physiology. J Clin Invest. 1971 Sep;50(9):1917–1926. doi: 10.1172/JCI106684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowling R. H., Mack E., Small D. M. Effects of controlled interruption of the enterohepatic circulation of bile salts by biliary diversion and by ileal resection on bile salt secretion, synthesis, and pool size in the rhesus monkey. J Clin Invest. 1970 Feb;49(2):232–242. doi: 10.1172/JCI106232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERIKSSON S. Biliary excretion of bile acids and cholesterol in bile fistula rats; bile acids and steroids. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1957 Mar;94(3):578–582. doi: 10.3181/00379727-94-23018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ESTABROOK R. W., COOPER D. Y., ROSENTHAL O. THE LIGHT REVERSIBLE CARBON MONOXIDE INHIBITION OF THE STEROID C21-HYDROXYLASE SYSTEM OF THE ADRENAL CORTEX. Biochem Z. 1963;338:741–755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einarsson K., Johansson G. Effect of phenobarbital on the conversion of cholesterol to taurocholic acid. Bile acids and steroids 204. Eur J Biochem. 1968 Nov;6(2):293–298. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1968.tb00448.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eneroth P., Hellström K., Sjövall J. A method for quantitative determination of bile acids in human feces. Bile acids and steroids 195. Acta Chem Scand. 1968;22(6):1729–1744. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.22-1729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evrard E., Janssen G. Gas-liquid chromatographic determination of human fecal bile acids. J Lipid Res. 1968 Mar;9(2):226–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart L. G., Guarino A. M., Adamson R. H. Effects of phenobarbital on biliary excretion of organic acids in male and female rats. Am J Physiol. 1969 Jul;217(1):46–52. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.217.1.46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones A. L., Armstrong D. T. Increased cholesterol biosynthesis following phenobarbital induced hypertrophy of agranular endoplasmic reticulum in liver. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Aug-Sep;119(4):1136–1139. doi: 10.3181/00379727-119-30396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato R. Possible role of P-450 in the oxidation of drugs in liver microsomes. J Biochem. 1966 Jun;59(6):574–583. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaassen C. D. Biliary flow after microsomal enzyme induction. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1969 Aug;168(2):218–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MYASNIKOV A. L. Influence of some factors on development of experimental cholesterol atherosclerosis. Circulation. 1958 Jan;17(1):99–113. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.17.1.99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manes J. D., Schneider D. L. Extraction of bile acids from rat feces containing cholestyramine. J Lipid Res. 1971 May;12(3):376–377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omura T., Sato R., Cooper D. Y., Rosenthal O., Estabrook R. W. Function of cytochrome P-450 of microsomes. Fed Proc. 1965 Sep-Oct;24(5):1181–1189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orrenius S., Dallner G., Ernster L. Inhibition of the TPNH-linked lipid peroxidation of liver microsomes by drugs undergoing oxidative demethylation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1964;14:329–334. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(64)80005-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orrenius S., Ericsson J. L., Ernster L. Phenobarbital-induced synthesis of the microsomal drug-metabolizing enzyme system and its relationship to the proliferation of endoplasmic membranes. A morphological and biochemical study. J Cell Biol. 1965 Jun;25(3):627–639. doi: 10.1083/jcb.25.3.627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orrenius S., Ernster L. Phenobarbital-induced synthesis of the oxidative demethylating enzymes of rat liver microsomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1964 May 22;16(1):60–65. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(64)90211-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. J., Plaa G. L. Effect of phenobarbital on the excretion of an exogenous bilirubin load. Biochem Pharmacol. 1967 May;16(5):827–835. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(67)90055-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson S. H. Increased bilirubin conjugation in heterozygous Gunn rats treated with phenobarbital. Nature. 1969 Jun 7;222(5197):990–991. doi: 10.1038/222990a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANDBERG D. H., SJOEVALL J., SJOEVALL K., TURNER D. A. MEASUREMENT OF HUMAN SERUM BILE ACIDS BY GAS-LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY. J Lipid Res. 1965 Apr;6:182–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIPERSTEIN M. D., CHAIKOFF I. L. C14-Cholesterol. III. Excretion of carbons 4 and 26 in feces, urine, and bile. J Biol Chem. 1952 Sep;198(1):93–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIPERSTEIN M. D., JAYKO M. E., CHAIKOFF I. L., DAUBEN W. G. Nature of the metabolic products of C14-cholesterol excreted in bile and feces. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1952 Dec;81(3):720–724. doi: 10.3181/00379727-81-19999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPERBER I. Secretion of organic anions in the formation of urine and bile. Pharmacol Rev. 1959 Mar;11(1):109–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampliner R. E., Bennett P. H., Comess L. J., Rose F. A., Burch T. A. Gallbladder disease in pima indians. Demonstration of high prevalence and early onset by cholecystography. N Engl J Med. 1970 Dec 17;283(25):1358–1364. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197012172832502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shefer S., Hauser S., Bekersky I., Mosbach E. H. Biochemical site of regulation of bile acid biosynthesis in the rat. J Lipid Res. 1970 Sep;11(5):404–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shefer S., Hauser S., Bekersky I., Mosbach E. H. Feedback regulation of bile acid biosynthesis in the rat. J Lipid Res. 1969 Nov;10(6):646–655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shefer S., Hauser S., Mosbach E. H. Stimulation of cholesterol 7 -hydroxylase by phenobarbital in two strains of rats. J Lipid Res. 1972 Jan;13(1):69–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small D. M. The formation of gallstones. Adv Intern Med. 1970;16:243–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TALALAY P. Enzymic analysis of steroid hormones. Methods Biochem Anal. 1960;8:119–143. doi: 10.1002/9780470110249.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada F., Hirata K., Nakao K., Sakamoto Y. Participation of P-450 in 7 alpha-hydroxylation of cholesterol. J Biochem. 1968 Sep;64(3):415–417. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weis H. J., Dietschy J. M. Failure of bile acids to control hepatic cholesterogenesis: evidence for endogenous cholesterol feedback. J Clin Invest. 1969 Dec;48(12):2398–2408. doi: 10.1172/JCI106206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D. L., Powell G., McMillan W. O. Phenobarbital-induced alterations in phosphatidylcholine and triglyceride synthesis in hepatic endoplasmic reticulum. J Lipid Res. 1971 Jan;12(1):1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


