Abstract
We assessed CD4 count at initial presentation for HIV care among ≥50-year-olds from 1997-2007 in 13 US and Canadian clinical cohorts and compared to <50-year-olds. 44,491 HIV-infected individuals in the North American AIDS Cohort Collaboration on Research and Design (NA-ACCORD) were included in our study. Trends in mean CD4 count (measured as cells/mm3) and 95% confidence intervals ([,]) were determined using linear regression stratified by age category and adjusted for gender, race/ethnicity, HIV transmission risk and cohort. From 1997-2007, the proportion of individuals presenting for HIV care who were ≥50-years-old increased from 17% to 27% (p-value < 0.01). The median CD4 count among ≥50 year-olds was consistently lower than younger adults. The interaction of age group and calendar year was significant (p-value <0.01) with both age groups experiencing modest annual improvements over time (< 50-year-olds: 5 [4 , 6] cells/mm3; ≥50-year-olds: 7 [5 , 9] cells/mm3), after adjusting for sex, race/ethnicity, HIV transmission risk group and cohort; however, increases in the two groups were similar after 2000. A greater proportion of older individuals had an AIDS-defining diagnosis at, or within three months prior to, first presentation for HIV care compared to younger individuals (13% vs. 10%, respectively). Due to the increasing proportion, consistently lower CD4 counts, and more advanced HIV disease in adults ≥50-year-old at first presentation for HIV care, renewed HIV testing efforts are needed.
Findings
We recently reported that the median CD4 count at first presentation for HIV care in the US and Canada increased from 256 (IQR: 96-455) to 317 (IQR: 135-517) from 1997 to 2007, yet remained below 350 cells/mm3 - the current cut-off for initiating highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) [1,2]. Over the study period, there was an increase in the median age at first presentation for HIV care (from 40 to 43 years in 1997 to 2007, p < 0.01) [1]. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) 10% of the total incident HIV infections occurring in the US in 2006 were among adults ≥50-years-old [3]. Further, the prevalence of HIV infection in individuals ≥50 years of age is rapidly increasing [4,5], yet there is evidence that this older age group may not be as aware of HIV infection and the need for preventive measures and less likely to be tested and seek care early [6-9]. As this is the largest cohort collaboration of HIV-infected individuals in North America, we have conducted a new analysis that focuses on CD4 at first presentation for HIV care among patients ≥50-years-old.
We briefly describe study population and analytical methods; more details are provided in Althoff et al. [1].
All patients were enrollees in clinical care cohorts contributing to the North American Cohort Collaboration on Research and Design (NA-ACCORD) [10], a regional group of the International Epidemiological Databases to Evaluate AIDS (IeDEA) project. Each cohort's participation in NA-ACCORD was approved by the respective local institutional review boards. All 14 NA-ACCORD clinical cohorts agreed to participate in this study although one was excluded because their study population enrollment criteria restricted to those in later stages of HIV disease. These 13 clinical cohorts have clinical sites in 17 US states, Washington DC, and 3 Canadian provinces. Our primary focus was on HIV-infected adults who were ≥50 years of age and who first presented for clinical care between January 1997 and December 2007, as compared to individuals presenting at younger ages. First presentation for HIV clinical care was defined as the date (month and year) at which the first CD4 count was reported.
The first measured CD4 was our outcome of interest. The month and year in which the CD4 was measured were recorded. If there was more than one CD4 measurement in the first month at presentation for HIV care, we calculated the mean CD4 count for the month. Other information obtained at first presentation for care included self-reported year of birth, gender, race/ethnicity (as black, white, Latino and other/unknown) and HIV transmission risk group (male-to-male sex (MSM), injection drug use (IDU) including MSM/IDU, heterosexual contact and other/unknown).
Statistical comparisons of demographic and clinical characteristics across calendar dates were made using the Cochran-Armitage trend test for categorical variables or the Cuzick trend test for continuous variables. We determined the median absolute CD4 count and interquartile range (IQR) at first presentation for HIV clinical care annually from 1997 through 2007, by age group. Multivariate linear regression models were used to describe the annual trends in estimated mean CD4 count using a linear variable for year, stratified by age group and adjusting for cohort demographic and risk characteristics; 95% confidence intervals ([,]) were also estimated using these models. Sensitivity analyses were conducted by omitting participants from the Veterans Aging Cohort Study (VACS) and the HIV Research Network (HIVRN) as these two cohorts contribute ≈50% of the participants in the NA-ACCORD and the median age in the VACS was slightly older. Results with a two-sided p-value of <0.05 were considered statistically significant. Analyses were conducted using SAS, version 9.
After excluded individuals contributing data during the first year that the cohort contributed data to the NA-ACCORD to remove individuals who may have been previously in care, a total of 67,961 adults received HIV clinical care at one of the participating NA-ACCORD sites between 1997 and 2007 and had complete date and CD4 measurement information. Of these, 21,983 (32%) had a prior history of antiretroviral therapy or HIV-1 RNA results and 1,487 (2%) had an AIDS-defining diagnosis recorded more than 3 months prior to the first recorded CD4 count. These individuals were excluded as they were likely to have been previously in care. Our study population consisted of 44,491 HIV-infected individuals.
The proportions of individuals who were < and ≥50-years-old who first presented for HIV care each year are shown in Table 1; additional characteristics of the study population can be found in Althoff et al. [1]. From 1997-2007, the proportion of individuals presenting for HIV care who were aged ≥50 years increased from 17% to 27% (p-value < 0.01). The increase over time in median CD4 count at first presentation for care was similar in absolute magnitude in both age groups (67 cells/mm3 and 63 cells/mm3 from 1997 to 2007 among <50-year-olds and ≥50-year-olds, respectively). However, the ≥50-year-olds had a median CD4 count of 266 cells/mm3, compared to 336 cells/mm3 among <50-year-olds, in 2007.
Table 1.
Characteristics of N = 44,491 participating patients, by year at first presentation
| Total | 1997 | 1998 | 1999 | 2000 | 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | p-value‡ | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N = 44,491 | N = 4,479 | N = 4,412 | N = 4,857 | N = 5,262 | N = 4,258 | N = 4,063 | N = 3,688 | N = 3,773 | N = 3,486 | N = 3,354 | N = 2,859 | ||||||||||||||
| Age (years) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 18-< 50 | 35,093 | 79% | 3,698 | 83% | 3,624 | 82% | 3,953 | 81% | 4,244 | 81% | 3,344 | 79% | 3,158 | 78% | 2,855 | 77% | 2,912 | 77% | 2,709 | 78% | 2,516 | 75% | 2,080 | 73% | < 0.01 |
| ≥50 | 9,398 | 21% | 781 | 17% | 788 | 18% | 904 | 19% | 1,018 | 19% | 914 | 21% | 905 | 22% | 833 | 23% | 861 | 23% | 777 | 22% | 838 | 25% | 779 | 27% | < 0.01 |
| AIDS-defining illness | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 18-< 50 | 3,390 | 10% | 417 | 11% | 385 | 11% | 362 | 9% | 370 | 9% | 344 | 10% | 331 | 10% | 277 | 10% | 270 | 9% | 251 | 9% | 208 | 8% | 175 | 8% | < 0.01 |
| ≥50 | 1,242 | 13% | 142 | 18% | 127 | 16% | 119 | 13% | 121 | 12% | 133 | 15% | 119 | 13% | 105 | 13% | 105 | 12% | 102 | 13% | 95 | 11% | 74 | 9% | < 0.01 |
| CD4+ T-cell Count (cells/mm3) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 18-< 50 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Median | 298 | 269 | 277 | 275 | 284 | 293 | 313 | 296 | 312 | 323 | 333 | 336 | < 0.01 | ||||||||||||
| IQR | 112-493 | 100-467 | 96-481 | 99-464 | 104-494 | 100-494 | 124-501 | 114-504 | 127-499 | 134-500 | 141-512 | 152-522 | |||||||||||||
| ≥50 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Median | 251 | 203 | 211 | 246 | 261 | 234 | 272 | 274 | 261 | 272 | 273 | 266 | < 0.01 | ||||||||||||
| IQR | 90-457 | 80-390 | 65-403 | 88-440 | 102-464 | 88-443 | 111-457 | 92-475 | 83-487 | 81-511 | 107-491 | 111-494 | |||||||||||||
‡P-values calculated using Cochran-Armitage test for categorical variables or Cuzick's test for continuous variables.
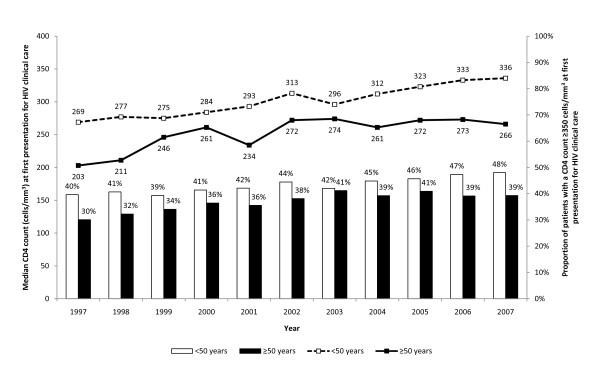
The median CD4 count was consistently lower in the ≥50-year-olds compared to the <50-year-olds from 1997 to 2007 (Figure 1). The proportion of individuals at first presentation for HIV care who had a CD4 count ≥350 cells/mm3 was lower in the ≥50-year-olds compared to the <50-year-olds; this proportion increased over time for both age groups.
Figure 1.
Median CD4 count, and the proportion of individuals who have a CD4 count ≥350 cells/mm3, at first presentation for HIV clinical care.
In the multivariate analyses, the estimated annual change in CD4 count from 1997 to 2007 was higher among ≥50-year-olds years (7 [5 , 9] cells/mm 3) compared to <50-year-olds (5 [4 , 6] cells/mm3) adjusting for sex, race and ethnicity, HIV transmission risk group and cohort. Findings were similar in sensitivity analyses. The interaction of age group and calendar year was statistically significant (p-value <0.01). After restriction to the years 2000-2007 in the ≥50-year-olds, the estimated annual change in CD4 count was 4 [1, 7] cells/mm3, similar to the change in the <50-year-olds from 1997-2007 (5 [4, 6] cells/mm3).
Overall, the proportion of individuals who had an AIDS-defining diagnosis recorded at, or 3 months prior to, the first CD4 measurement was highest among those aged ≥50 years (< 50-year-olds: 10%; ≥50-year-olds: 13%; p-value < 0.01); in sensitivity analyses, these proportions increased (< 50-year-olds: 12%; ≥50-year-olds: 18%; p-value < 0.01). The proportions who had an AIDS-defining diagnosis at first presentation for care decreased from 1997 to 2007 in both age groups (Table 1). Older individuals had a greater proportion with an AIDS-defining diagnosis in all years, however this disparity decreased over time (Table 1); in sensitivity analyses the decreases were of less magnitude (≥50-year-olds: 20% in 1997 to 15% in 2007, p-value < 0.01; <50-year-olds: 13% in 1997 to 12% in 2007, p-value < 0.01). Finally, among individuals who had an AIDS-defining diagnosis at first presentation for care, the proportion of older individuals who had ≥2 AIDS-defining diagnosis was similar to that of younger individuals (18% vs. 19%, p = 0.19).
Our study has three important findings: 1) the proportion of individuals at first presentation for care who are aged ≥50 years has increased over the past 11 years; 2) older individuals at first presentation of care consistently had a lower median CD4 count compared to younger individuals; and 3) a greater proportion of older individuals have an AIDS-defining diagnosis at, or within three months prior to, first presentation for HIV care compared to younger individuals.
The increase in the proportion of individuals who were ≥50 years at first presentation for care has implications for effective HIV management and survival for older infected individuals. Older individuals initiating HAART have a decreased immune response [11-18] and mortality increases with lower CD4 counts at HAART initiation [19]. In addition, older individuals at first presentation for care may have existing co-morbid conditions that may complicate HIV treatment decisions. From a public health perspective, a delay in presentation for treatment increases the risk for ongoing transmission [20-23]. These data suggest improved screening by health providers may help detect HIV infection earlier and at younger ages.
The estimated mean annual increase in CD4 count for individuals aged < and ≥50 years is small and likely of little clinical relevance as the within-patient variation in CD4 counts is ~25%. More importantly, the annual median CD4 count is still well below the CD4 recommended for initiation of HAART [24]. The proportion of individuals presenting with a CD4 ≥350 cell/smm3 increased in all age groups, however, the proportion was approximately 10% lower among ≥50-year-olds. This suggests the potential for greater HIV treatment initiation guideline adherence if effective testing and treatment interventions target older individuals.
Finally, our data suggest older individuals are entering into care with advanced HIV disease. The CDC recently reported an increase in the proportion of ≥50-year-olds in the US who had a first HIV diagnosis within a year before AIDS diagnosis compared to 30-< 50-year-olds [25]; the Public Health Agency of Canada has noted the increase among ≥50 year-olds [26,27]. Data from New York City showed the proportion of new HIV diagnoses that are concurrent with an AIDS diagnoses increased with older age [28].
There are limitations to our study, including our lack of data regarding time since seroconversion. We chose to stratify the data using a cut-off of 50 years. Although there were more than enough individuals for additional stratification at younger ages, additional stratification at older ages was not possible.
While all age groups are experiencing modest improvements in CD4 count at presentation over time, older individuals have not "caught up." These data suggest that targeted renewed prevention and testing strategies are needed in all age groups, including those ≥50-years-old.
Competing interests
Dr. Gebo reports receiving consulting fees from Tibotec and grant support from Johns Hopkins University Richard Ross Award, and Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; Dr. Klein reports receiving consulting fees from GlaxoSmithKline, Abbott, Pfizer, and Merck, lecture fees from Abbott, Gilead, Tibotec, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and GlaxoSmithKline and research support from Canadian Institutes of Health Research/Fonds de la recherche en santé du Québec, Canadian HIV Trials Network, Ontario HIV Treatment Network, and Schering Plough Canada; Dr. Hogg reports receiving payment from a commercial entity that sponsored his study and grant support from Merck; Dr. Horberg reports receiving grant support from Pfizer, Merck, and Kaiser Permanente Community Benefits; Dr. Saag reports receiving consulting fees from Ardea Biosciences, Avexa, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead Sciences, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, Monogram Biosciences, Pain Therapeutics, Pfizer, Progenics, Tibotec, Tobira Therapeutics, and Vicro and research support from Avexa, Achillion Pharmaceuticals, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Merck, Pfizer, Progenics, and Tibotec; Dr. Kitahata has served as a consultant to Gilead Sciences; Dr. Eron reports receiving consulting fees from Tibotec, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Merck, GlaxoSmithKline, Avexa, Tobira and Virco Labs, lecture fees from Roche, Bristol-Myers Squibb Virco Labs, and grant support from GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, and TaiMed; Dr. Gill reports receiving consulting fees from GlaxoSmithKline, Gilead, Abbott, Merck, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Thera, Tibotec, and Pfizer and grant support from GlaxoSmithKline, Abbott, Canadian Institutes of Health Research, Gilead, Tibotec, and Pfizer; Dr. Rodriguez reports receiving consulting fees from Gilead and Bristol-Myers Squibb, lecture fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb, and grant support from STERIS; Dr. Sterling reports receiving grant support from Pfizer; Dr. Deeks reports receiving grant support from Merck, Gilead, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Pfizer; Dr. Collier reports receiving consulting fees from Merck, Pfizer, and GlaxoSmithKline, equity ownership/stock options in Bristol-Myers Squibb and Abbott, and grant support from Schering-Plough, Tibotec-Virco, Gilead, Boeringer-Ingelheim and Merck; Dr. Benson reports receiving consulting fees from GlaxoSmithKline, Pfizer, Merck, and Achillion, and grant support from Gilead; Dr. Silverberg reports receiving grant support from Pfizer and Merck; Dr. Rachlis reports receiving honoraria and research support from Bristol Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, Pfizer, Gilead, Tibotec, Schering-Plough, Merck, Theratechnologies, Abbott and the Ontario HIV Treatment Network; and Dr. Moore reports receiving consulting fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb and GlaxoSmithKline, lecture fees from Gilead, and grant support from Pfizer, Merck, Gilead, and Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.
Drs. Althoff, Gange, Brooks, Rourke, Bosch, Martin, Jacobson, Kirk, Napravnik, Goedert, Buchacz, Thorne, McKaig and Justice declare they have no conflict of interest.
Authors' contributions
KNA, KAG, SJG, RDM, and ACJ designed the study, interpreted the data, and drafted the manuscript; KNA also conducted the analysis. MBK, JTB, RSH, RJB, MAH made substantial contributions to the design of the study, interpretation of the data, and revised the manuscript critically for important intellectual content. MSS, MMK, JJE, SN, SBR, MJG, BR, TRS, SGD, JNM, LPJ, SDK, ACC, CAB, MJS, JJG, RGM, JT, AR oversee acquisition of data and revised the manuscript critically for important intellectual content. All authors approved the final manuscript.
Contributor Information
Keri N Althoff, Email: kalthoff@jhsph.edu.
Kelly A Gebo, Email: kgebo1@jhsph.edu.
Stephen J Gange, Email: sgange@jhsph.edu.
Marina B Klein, Email: marina.klein@mcgill.ca.
John T Brooks, Email: zud4@cdc.gov.
Robert S Hogg, Email: bobhogg@cfenet.ubc.ca.
Ronald J Bosch, Email: ronbosch@sdac.harvard.edu.
Michael A Horberg, Email: Michael.Horberg@kp.org.
Michael S Saag, Email: msaag@uab.edu.
Mari M Kitahata, Email: kitahata@U.WASHINGTON.EDU.
Joseph J Eron, Email: joseph_eron@med.unc.edu.
Sonia Napravnik, Email: napravs@med.unc.edu.
Sean B Rourke, Email: sean.rourke@utoronto.ca.
M John Gill, Email: john.gill@calgaryhealthregion.ca.
Benigno Rodriguez, Email: rodriguez.benigno@clevelandactu.org.
Timothy R Sterling, Email: timothy.sterling@Vanderbilt.Edu.
Steven G Deeks, Email: SDeeks@php.ucsf.edu.
Jeffrey N Martin, Email: martin@psg.ucsf.edu.
Lisa P Jacobson, Email: ljacobso@jhsph.edu.
Gregory D Kirk, Email: gkirk@jhsph.edu.
Ann C Collier, Email: acollier@u.washington.edu.
Constance A Benson, Email: cbenson@ucsd.edu.
Michael J Silverberg, Email: Michael.J.Silverberg@kp.org.
James J Goedert, Email: goedertj@mail.nih.gov.
Rosemary G McKaig, Email: Rosemary.McKaig@nih.hhs.gov.
Jennifer Thorne, Email: jthorne@jhmi.edu.
Anita Rachlis, Email: a.rachlis@utoronto.ca.
Richard D Moore, Email: rdmoore@jhmi.edu.
Amy C Justice, Email: amy.justice2@med.va.gov.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to all patients, physicians, investigators, and staff involved in the NA-ACCORD. This work was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health: U01-AI069918, U01-AA013566, U01-AI31834, U01-AI34989, U01-AI34993, U01-AI34994, U01-AI35004, U01-AI35039, U01-AI35040, U01-AI35041, U01-AI35042, U01-AI35043, U01-AI37613, U01-AI37984, U01-AI38855, U01-AI38858, U01-AI42590, U01-AI68634, U01-AI68636, U01-HD32632, M01-RR00071, M01-RR00079, M01-RR00083, M01-RR00722, P30-AI27757, P30-AI27767, P30-AI50410, P30-AI54999, R01-DA04334, R01-DA12568, R01-MH54907, R24-AI067039, Z01-CP010176, AHQ290-01-0012, N02-CP55504, R01-DA11602, AI-69432, K01-AI071754, R01-AA16893, K24-00432, K23-AI-61-0320. This work was also supported by the Centers for Disease Control (CDC200-2006-18797), the Canadian Institutes for Health Research (CIHR: TGF-96118; HCP-97105; CBR-86906; CBR-94036; KRS-86251; 169621) and the Canadian Trials Network (project number 242).
NA-ACCORD Participating cohorts (representatives):
• AIDS Link to the IntraVenous Experience (Gregory D.Kirk)
• Adult AIDS Clinical Trials Group Longitudinal Linked Randomized Trials (Constance A. Benson, Ronald J. Bosch, Ann C. Collier)
• HAART Observational Medical Evaluation and Research (Robert S. Hogg, Richard Harrigan, Julio Montaner)
• HIV Outpatient Study (John T. Brooks, Kate Buchacz)
• HIV Research Network (Kelly A. Gebo)
• Johns Hopkins HIV Clinical Cohort (Richard D. Moore)
• John T. Carey Special Immunology Unit Patient Care and Research Database, Case Western Reserve University (Benigno Rodriguez)
• Kaiser Permanente Northern California (Michael A. Horberg, Michael J. Silverberg)
• Longitudinal Study of Ocular complications of AIDS (Jennifer E. Thorne)
• Multicenter Hemophilia Cohort Study-II (James J. Goedert)
• Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study (Lisa P. Jacobson)
• Montreal Chest Institute Immunodeficiency Service Cohort (Marina B. Klein)
• Ontario HIV Treatment Network Cohort Study (Sean B. Rourke, Anita R. Rachlis)
• Southern Alberta Clinic Cohort (M. John Gill)
• Studies of the Consequences of the Protease Inhibitor Era (Steven G, Deeks, Jeffery N. Martin)
• University of Alabama at Birmingham 1917 Clinic Cohort (Michael S. Saag, Michael Mugavero, James Willig)
• University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill HIV Clinic Cohort (Joseph J. Eron, Sonia Napravnik)
• University of Washington HIV Cohort (Mari M. Kitahata and Heidi M. Crane)
• Veterans Aging Cohort Study (Amy C. Justice, David Fiellin)
• Vanderbilt-Meharry CFAR Cohort (Timothy R. Sterling, Sam Stinette, Peter Rebeiro, David Haas)
• Women's Interagency HIV Study (Stephen J. Gange, Kathryn Anastos)
Executive Committee: Richard D. Moore, Michael S. Saag, Stephen J. Gange, Mari M. Kitahata, Rosemary G. McKaig, Aimee Freeman
Epidemiology/Biostatistics Core: Stephen J. Gange, Alison G. Abraham, Bryan Lau, Keri N. Althoff, Jinbing Zhang
Data Management Core: Mari M. Kitahata, Stephen E. Van Rompaey, Heidi M. Crane, Eric Webster, Liz Morton, Brenda Simon
References
- Althoff KN, Gange SJ, Klein MB, Brooks JT, Hogg RS, Bosch RJ. et al. Late presentation for human immunodeficiency virus care in the United States and Canada. Clin Infect Dis. 2010;50:1512–1520. doi: 10.1086/652650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panel on Antiretroviral Guidelines for Adults and Adolescents. Guidelines for the use of antiretroviral agents in HIV-1-infected adults and adolescents. US Department of Health and Human Services. 2008. pp. 1–139.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Estimated percentage of new HIV infections by age - United States, 2006. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. 2009.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. HIV/AIDS Surveillance Report, 2006. Atlanta, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2008;18 [Google Scholar]
- Luther VP, Wilkin AM. HIV infection in older adults. Clin Geriatr Med. 2007;23:567–83. doi: 10.1016/j.cger.2007.02.004. vii. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stall R, Catania J. AIDS risk behaviors among late middle-aged and elderly Americans. The National AIDS Behavioral Surveys. Arch Intern Med. 1994;154:57–63. doi: 10.1001/archinte.154.1.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Sadr W, Gettler J. Unrecognized human immunodeficiency virus infection in the elderly. Arch Intern Med. 1995;155:184–186. doi: 10.1001/archinte.155.2.184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abel T, Werner M. HIV risk behaviour of older persons. Eur J Public Health. 2003;13:350–352. doi: 10.1093/eurpub/13.4.350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winningham A, Corwin S, Moore C, Richter D, Sargent R, Gore-Felton C. The changing age of HIV: sexual risk among older African American women living in rural communities. Prev Med. 2004;39:809–814. doi: 10.1016/j.ypmed.2004.03.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gange SJ, Kitahata MM, Saag MS, Bangsberg DR, Bosch RJ, Brooks JT. et al. Cohort profile: the North American AIDS Cohort Collaboration on Research and Design (NA-ACCORD) Int J Epidemiol. 2007;36:294–301. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyl286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manfredi R, Calza L, Cocchi D, Chiodo F. Antiretroviral treatment and advanced age: epidemiologic, laboratory, and clinical features in the elderly. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2003;33:112–114. doi: 10.1097/00126334-200305010-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viard JP, Mocroft A, Chiesi A, Kirk O, Roge B, Panos G. et al. Influence of age on CD4 cell recovery in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients receiving highly active antiretroviral therapy: evidence from the EuroSIDA study. J Infect Dis. 2001;183:1290–1294. doi: 10.1086/319678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knobel H, Guelar A, Valldecillo G, Carmona A, Gonzalez A, Lopez-Colomes JL. et al. Response to highly active antiretroviral therapy in HIV-infected patients aged 60 years or older after 24 months follow-up. AIDS. 2001;15:1591–1593. doi: 10.1097/00002030-200108170-00025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalayjian RC, Landay A, Pollard RB, Taub DD, Gross BH, Francis IR. et al. Age-related immune dysfunction in health and in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) disease: association of age and HIV infection with naive CD8+ cell depletion, reduced expression of CD28 on CD8+ cells, and reduced thymic volumes. J Infect Dis. 2003;187:1924–1933. doi: 10.1086/375372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabar S, Kousignian I, Sobel A, Le BP, Gasnault J, Enel P. et al. Immunologic and clinical responses to highly active antiretroviral therapy over 50 years of age. Results from the French Hospital Database on HIV. AIDS. 2004;18:2029–2038. doi: 10.1097/00002030-200410210-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverberg MJ, Leyden W, Horberg MA, DeLorenze GN, Klein D, Quesenberry CP Jr. Older age and the response to and tolerability of antiretroviral therapy. Arch Intern Med. 2007;167:684–691. doi: 10.1001/archinte.167.7.684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuzin L, Delpierre C, Gerard S, Massip P, Marchou B. Immunologic and clinical responses to highly active antiretroviral therapy in patients with HIV infection aged >50 years. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;45:654–657. doi: 10.1086/520652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collaboration of Observational HIV Epidemiologic Research Europe (COHERE) Study Group. Response to combination antiretroviral therapy: variation by age. AIDS. 2008;22:1463–1473. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e3282f88d02. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitahata MM, Gange SJ, Abraham AG, Merriman B, Saag MS, Justice AC. et al. Effect of early versus deferred antiretroviral therapy for HIV on survival. N Engl J Med. 2009;360:1815–1826. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0807252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia PM, Kalish LA, Pitt J, Minkoff H, Quinn TC, Burchett SK. et al. Maternal levels of plasma human immunodeficiency virus type 1 RNA and the risk of perinatal transmission. Women and Infants Transmission Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:394–402. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199908053410602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn TC, Wawer MJ, Sewankambo N, Serwadda D, Li C, Wabwire-Mangen F. et al. Viral load and heterosexual transmission of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Rakai Project Study Group. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:921–929. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200003303421303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modjarrad K, Chamot E, Vermund SH. Impact of small reductions in plasma HIV RNA levels on the risk of heterosexual transmission and disease progression. AIDS. 2008;22:2179–2185. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e328312c756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks G, Crepaz N, Senterfitt JW, Janssen RS. Meta-analysis of high-risk sexual behavior in persons aware and unaware they are infected with HIV in the United States: implications for HIV prevention programs. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2005;39:446–453. doi: 10.1097/01.qai.0000151079.33935.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes MD, Stein DS, Gundacker HM, Valentine FT, Phair JP, Volberding PA. Within-subject variation in CD4 lymphocyte count in asymptomatic human immunodeficiency virus infection: implications for patient monitoring. J Infect Dis. 1994;169:28–36. doi: 10.1093/infdis/169.1.28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall HI, Geduld J, Boulos D, Rhodes P, An Q, Mastro TD. et al. Epidemiology of HIV in the United States and Canada: current status and ongoing challenges. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2009;51(Suppl 1):S13–S20. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0b013e3181a2639e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Public Health Agency of Canada. HIV and AIDS in Canada: Surveillance Report to December 31, 2006. Surveillance and Risk Assessment Division, Centre for Infectious Disease Prevention and Control. 2007.
- Public Health Agency of Canada. HIV/AIDS Epi Updates, November 2007. Surveillance and Risk Assessment Division, Centre for Infectious Disease Prevention and Control, Public Health Agency of Canada, 1-140. 2007.
- Torian L, Wiewel E. Risk factors for concurrent diagnosis fo HIV/AIDS in New York City, 2004: The role of age, transmission risk, and country of birth. 14th Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections, Los Angeles, California. 2007.