Abstract
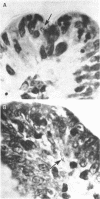
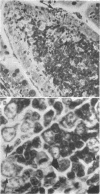
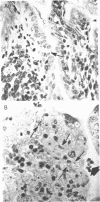
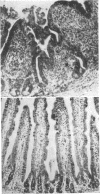
Strains of Salmonella typhimurium were studied in the ligated rabbit ileal loop model to gain insight into the mechanisms whereby bacteria which invade the gastrointestinal mucosa evoke fluid exsorption. The organisms employed differed in various biologic attributes including the ability to invade the ileal epithelium, multiply within the mucosa, elicit an acute inflammatory reaction, and disseminate across the intestinal wall. Some strains provoked small intestinal fluid exsorption although these did not elaborate enterotoxin. Only those strains which invaded the mucosa were accompanied by either mucosal inflammation or fluid exsorption. Noninvasive strains produced neither histologic abnormalities nor fluid secretion. While strains which invaded the mucosa caused an acute inflammatory reaction, not all such strains evoked fluid secretion. Furthermore, there was no correlation in ability of invasive organisms to evoke fluid secretion or in the intensity of mucosal inflammation, number of intramucosal salmonellae, or in ability to disseminate from the rabbit ileum.
These observations suggest that, as is the case in shigellosis, mucosal invasion may be a necessary factor for the intestinal fluid loss in salmonellosis. A bacterial property or factor, in addition to invasion of the gastrointestinal mucosa, seems to be responsible for fluid exsorptin. However, it is unlikely that a salmonella enterotoxin comparable to that elaborated by Vibrio cholerae, toxigenic Escherichia coli, or Shigella dysenteriae 1 is related to fluid secretion in salmonellosis.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABRAMS G. D., SCHNEIDER H., FORMAL S. B., SPRINZ H. CELLULAR RENEWAL AND MUCOSAL MORPHOLOGY IN EXPERIMENTAL ENTERITIS. INFECTION WITH SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM IN THE MOUSE. Lab Invest. 1963 Dec;12:1241–1248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ARM H. G., FLOYD T. M., FABER J. E., HAYES J. R. USE OF LIGATED SEGMENTS OF RABBIT SMALL INTESTINE IN EXPERIMENTAL SHIGELLOSIS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Mar;89:803–809. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.3.803-809.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Al-Awqati Q., Wallace C. K., Greenough W. B., 3rd Stimulation of intestinal secretion in vitro by culture filtrates of Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1972 Mar;125(3):300–303. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.3.300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrows W., Musteikis G. M. Cholera infection and toxin in the rabbit ileal loop. J Infect Dis. 1966 Apr;116(2):183–190. doi: 10.1093/infdis/116.2.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane C. G. Immunologic tissue injury mediated by neutrophilic leukocytes. Adv Immunol. 1968;9:97–162. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60442-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE S. N., BHATTACHARYA K., SARKAR J. K. A study of the pathogenicity of strains of Bacterium coli from acute and chronic enteritis. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1956 Jan;71(1):201–209. doi: 10.1002/path.1700710126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE S. N., CHATTERJE D. N. An experimental study of the mechanism of action of Vibriod cholerae on the intestinal mucous membrane. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1953 Oct;66(2):559–562. doi: 10.1002/path.1700660228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuPont H. L., Formal S. B., Hornick R. B., Snyder M. J., Libonati J. P., Sheahan D. G., LaBrec E. H., Kalas J. P. Pathogenesis of Escherichia coli diarrhea. N Engl J Med. 1971 Jul 1;285(1):1–9. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197107012850101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORMAL S. B., DAMMIN G. J., LABREC E. H., SCHNEIDER H. Experimental Shigella infections: characteristics of a fatal infection produced in guinea pigs. J Bacteriol. 1958 May;75(5):604–610. doi: 10.1128/jb.75.5.604-610.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORMAL S. B., KUNDEL D., SCHNEIDER H., KUNEVN, SPRINZ H. Studies with Vibrio cholerae in the ligated loop of the rabbit intestine. Br J Exp Pathol. 1961 Oct;42:504–510. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M: Intestinal secretion: effect of cyclic AMP and its role in cholera. N Engl J Med. 1971 May 20;284(20):1137–1144. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197105202842008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M., Fromm D., al-Awqati Q., Greenough W. B., 3rd Effect of cholera enterotoxin on ion transport across isolated ileal mucosa. J Clin Invest. 1972 Apr;51(4):796–804. doi: 10.1172/JCI106874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemski P., Jr, Stocker B. A. Transduction by bacteriophage P22 in nonsmooth mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1967 May;93(5):1588–1597. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.5.1588-1597.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemski P., Jr, Takeuchi A., Washington O., Formal S. B. Shigellosis due to Shigella dysenteriae. 1. Relative importance of mucosal invasion versus toxin production in pathogenesis. J Infect Dis. 1972 Nov;126(5):523–530. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.5.523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannella R. A., Broitman S. A., Zamcheck N. Salmonella enteritis. I. Role of reduced gastric secretion in pathogenesis. Am J Dig Dis. 1971 Nov;16(11):1000–1006. doi: 10.1007/BF02235012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannella R. A., Broitman S. A., Zamcheck N. Salmonella enteritis. II. Fulminant diarrhea in and effects on the small intestine. Am J Dig Dis. 1971 Nov;16(11):1007–1013. doi: 10.1007/BF02235013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbach S. L. Intestinal microflora. Gastroenterology. 1971 Jun;60(6):1110–1129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grady G. F., Keusch G. T. Pathogenesis of bacterial diarrheas (second of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1971 Oct 14;285(16):891–900. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197110142851605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hersh E. M., Bodey G. P. Leukocytic mechanisms in inflammation. Annu Rev Med. 1970;21:105–132. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.21.020170.000541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENKIN C. R., ROWLEY D. BASIS FOR IMMUNITY TO TYPHOID IN MICE AND THE QUESTION OF "CELLULAR IMMUNITY". Bacteriol Rev. 1963 Dec;27:391–404. doi: 10.1128/br.27.4.391-404.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent T. H., Formal S. B., Labrec E. H. Acute enteritis due to Salmonella typhimurium in opium-treated guinea pigs. Arch Pathol. 1966 Jun;81(6):501–508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent T. H., Formal S. B., Labrec E. H. Salmonella gastroenteritis in rhesus monkeys. Arch Pathol. 1966 Sep;82(3):272–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keusch G. T., Grady G. F., Mata L. J., McIver J. The pathogenesis of Shigella diarrhea. I. Enterotoxin production by Shigella dysenteriae I. J Clin Invest. 1972 May;51(5):1212–1218. doi: 10.1172/JCI106915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimberg D. V., Field M., Johnson J., Henderson A., Gershon E. Stimulation of intestinal mucosal adenyl cyclase by cholera enterotoxin and prostaglandins. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jun;50(6):1218–1230. doi: 10.1172/JCI106599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labrec E. H., Schneider H., Magnani T. J., Formal S. B. EPITHELIAL CELL PENETRATION AS AN ESSENTIAL STEP IN THE PATHOGENESIS OF BACILLARY DYSENTERY. J Bacteriol. 1964 Nov;88(5):1503–1518. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.5.1503-1518.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low-Beer T. S., Read A. E. Diarrhoea: mechanisms and treatment. Gut. 1971 Dec;12(12):1021–1036. doi: 10.1136/gut.12.12.1021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maenza R. M., Powell D. W., Plotkin G. R., Formal S. B., Jervis H. R., Sprinz H. Experimental diarrhea: salmonella enterocolitis inthe rat. J Infect Dis. 1970 May;121(5):475–485. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.5.475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa H., Nakamura A., Sakazaki R. Pathogenic properties of "enteropathogenic" Escherichia coli from diarrheal children and adults. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1968 Oct;21(5):333–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell D. W., Plotkin G. R., Maenza R. M., Solberg L. I., Catlin D. H., Formal S. B. Experimental diarrhea. I. Intestinal water and electrolyte transport in rat salmonella enterocolitis. Gastroenterology. 1971 Jun;60(6):1053–1064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp G. W., Hynie S. Stimulation of intestinal adenyl cyclase by cholera toxin. Nature. 1971 Jan 22;229(5282):266–269. doi: 10.1038/229266a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR J., MALTBY M. P., PAYNE J. M. Factors influencing the response of ligated rabbit-gut segments to injected Escherichia coli. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1958 Oct;76(2):491–499. doi: 10.1002/path.1700760218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRIER J. S. STUDIES ON SMALL INTESTINAL CRYPT EPITHELIUM. II. EVIDENCE FOR THE MECHANISMS OF SECRETORY ACTIVITY BY UNDIFFERENTIATED CRYPT CELLS OF THE HUMAN SMALL INTESTINE. Gastroenterology. 1964 Nov;47:480–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi A. Electron microscope studies of experimental Salmonella infection. I. Penetration into the intestinal epithelium by Salmonella typhimurium. Am J Pathol. 1967 Jan;50(1):109–136. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi A., Formal S. B., Sprinz H. Exerimental acute colitis in the Rhesus monkey following peroral infection with Shigella flexneri. An electron microscope study. Am J Pathol. 1968 Mar;52(3):503–529. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi A., Sprinz H. Electron-Microscope Studies of Experimental Salmonella Infection in the Preconditioned Guinea Pig: II. Response of the Intestinal Mucosa to the Invasion by Salmonella typhimurium. Am J Pathol. 1967 Jul;51(1):137–161. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN HEYNINGEN W. E., GLADSTONE G. P. The neurotoxin of Shigella shigae. I. Production, purification and properties of the toxin. Br J Exp Pathol. 1953 Apr;34(2):202–216. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Lepow I. H., Newman L. J. Bacterial factors chemotactic for polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Am J Pathol. 1968 Apr;52(4):725–736. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]