Abstract
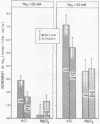
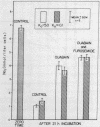
Others have concluded that a second Na “pump” (active Na outflux) exists in human erythrocytes. This second pump was said to be ouabain-insensitive, unlike the classic ouabain-sensitive Na-K pump. An alternative explanation is that “pump II” is Na exchange diffusion. These hypotheses were examined in the present experiments, utilizing 22Na influx and outflux measurements, net Na fluxes, and ATPase determinations. Ouabain-uninhibited Na outflux was reduced 0.58±0.05 mmol/liter cells per h when extracellular Na (Nao) was replaced by Mg. Ethacrynic acid or furosemide produced similar decrements of outflux (0.50 mmol) in the presence of ouabain and Nao. However, these diuretics had minimal inhibitory effects on outflux in the absence of Nao suggesting that they inhibited principally the Nao-dependent outflux. Whereas this ouabain-uninhibited portion of outflux was dependent on Nao, it was independent of Ko. Contrary to expectations, Na influx did not change when intracellular Na was altered. No uphill, net Na transport (ouabain-uninhibited) could be demonstrated under a variety of circumstances. Furosemide at high concentrations inhibited ATPase, reducing both ouabain-sensitive and ouabain-insensitive enzyme at 1.0 mM concentration while showing no effect on ATPase at 0.05-0.1 mM concentration. The effects of furosemide on ATPase and on Na flux were dissociable on a dose-response curve. Energy depletion for 22 h practically eliminated the Nao-dependent, diuretic-inhibited Na outflux. Activation energies and temperature coefficients for the diuretic-inhibited outflux were one-half the values for the classic ouabain-inhibited pump. These data are interpreted as evidence against a second Na pump. Exchange diffusion accounts adequately for most of these observations; however, the ouabain-insensitive fluxes may be complex and composed of several processes.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartlett G. R., Bucolo G. The metabolism of ribonucleoside by the human erythrocyte. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Mar 11;156(2):240–253. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(68)90253-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn M. J. Alterations of red blood cell sodium transport during malarial infection. J Clin Invest. 1969 Apr;48(4):674–684. doi: 10.1172/JCI106025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn M. J. Ouabain-uninhibited Na+ Transport in human erythrocytes: the effects of triflocin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 11;255(2):567–571. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90160-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn M. J. The effects of transport inhibitors on sodium outflux and influx in red blood cells: evidence for exchange diffusion. J Clin Invest. 1970 Oct;49(10):1804–1814. doi: 10.1172/JCI106398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Essig A. The "pump-leak" model and exchange diffusion. Biophys J. 1968 Jan;8(1):53–63. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(68)86474-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrahan P. J., Glynn I. M. The behaviour of the sodium pump in red cells in the absence of external potassium. J Physiol. 1967 Sep;192(1):159–174. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrahan P. J., Glynn I. M. The sensitivity of the sodium pump to external sodium. J Physiol. 1967 Sep;192(1):175–188. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunn R. B., Tosteson D. C. The effect of 2,4,6-trinitro-m-cresol on cation and anion transport in sheep red blood cells. J Gen Physiol. 1971 May;57(5):593–609. doi: 10.1085/jgp.57.5.593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman J. F., Kregenow F. M. The characterization of new energy dependent cation transport processes in red blood cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jul 14;137(2):566–576. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb50182.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman J. F. The red cell membrane and the transport of sodium and potassium. Am J Med. 1966 Nov;41(5):666–680. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(66)90029-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubowitz H. Exchange diffusion in human red blood cells. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 May;140(1):153–156. doi: 10.3181/00379727-140-36414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubowitz H., Whittam R. Ion movements in human red cells independent of the sodium pump. J Physiol. 1969 May;202(1):111–131. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maizels M. Effect of sodium content on sodium efflux from human red cells suspended in sodium-free media containing potassium, rubidium, caesium or lithium chloride. J Physiol. 1968 Apr;195(3):657–679. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post R. L., Albright C. D., Dayani K. Resolution of pump and leak components of sodium and potassium ion transport in human erythrocytes. J Gen Physiol. 1967 May;50(5):1201–1220. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.5.1201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poznansky M., Solomon A. K. Effect of cell volume on potassium transport in human red cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jul 3;274(1):111–118. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90286-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rettori O., Lenoir J. P. Ouabain-insensitive active socium transport in erythrocytes: effect of external cation. Am J Physiol. 1972 Apr;222(4):880–884. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.222.4.880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs J. R. Ouabain-insensitive sodium movements in the human red blood cell. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Mar;57(3):259–282. doi: 10.1085/jgp.57.3.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs J. R. Sodium movements in the human red blood cell. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Sep;56(3):322–341. doi: 10.1085/jgp.56.3.322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- USSING H. H. Transport of ions across cellular membranes. Physiol Rev. 1949 Apr;29(2):127–155. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1949.29.2.127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittam R., Wheeler K. P. Transport across cell membranes. Annu Rev Physiol. 1970;32:21–60. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.32.030170.000321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittembury G., Proverbio F. Two modes of Na extrusion in cells from guinea pig kidney cortex slices. Pflugers Arch. 1970;316(1):1–25. doi: 10.1007/BF00587893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley J. S. Co-ordinated increase of sodium leak and sodium pump in hereditary spherocytosis. Br J Haematol. 1972 May;22(5):529–542. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1972.tb05700.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]