Abstract
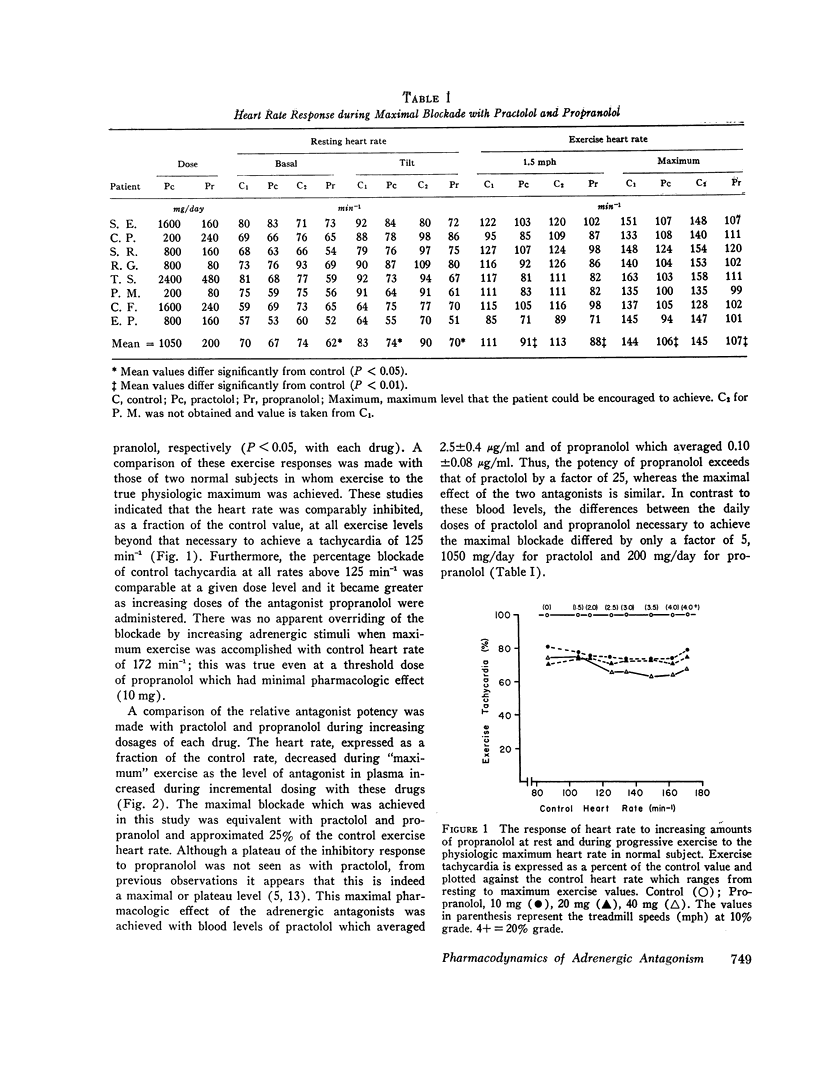
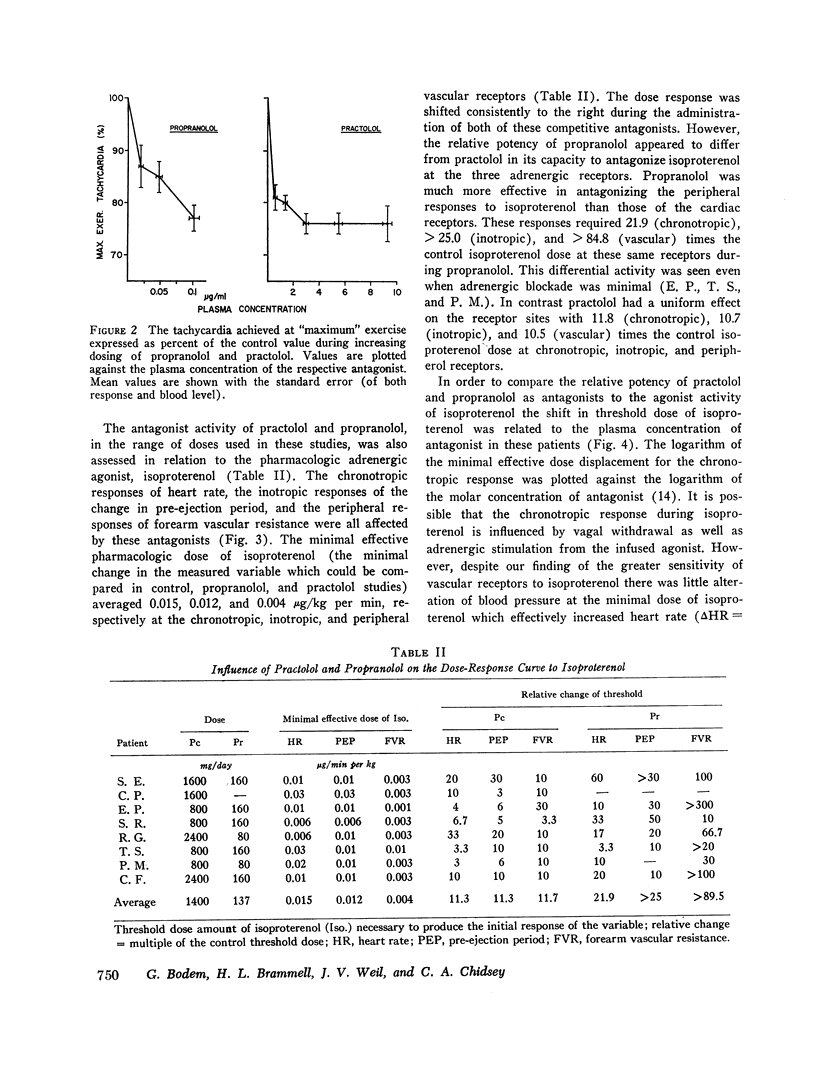
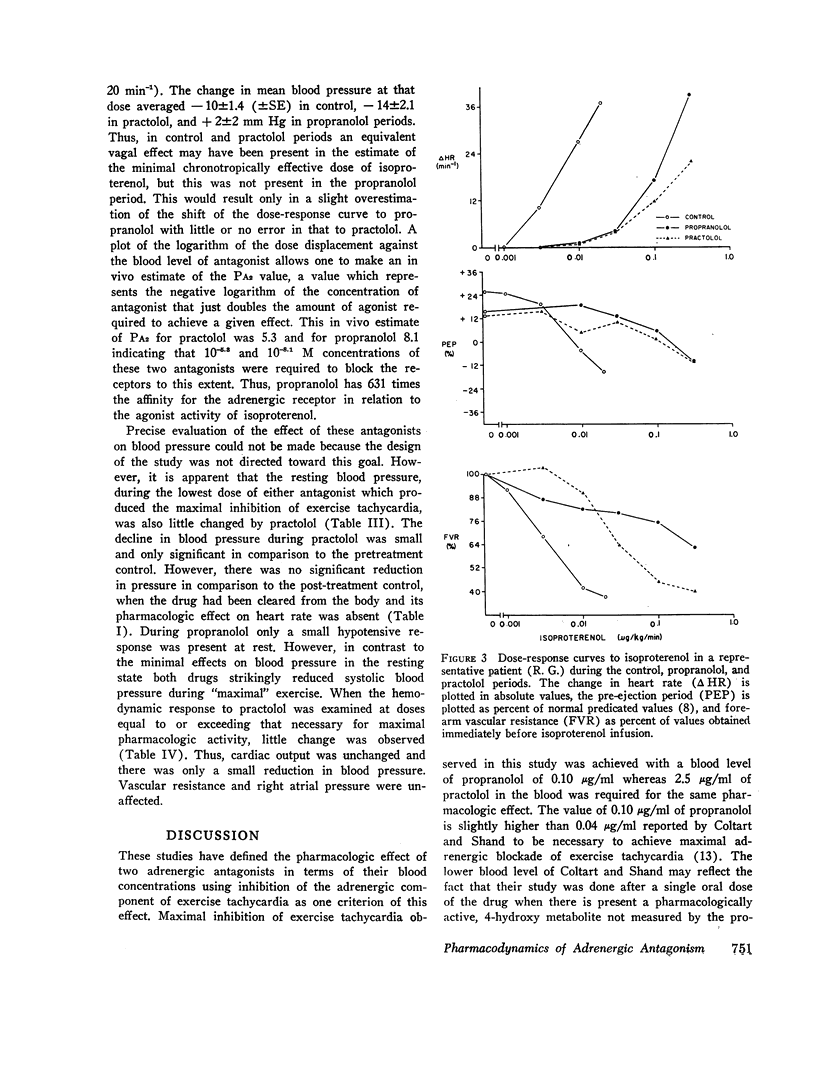
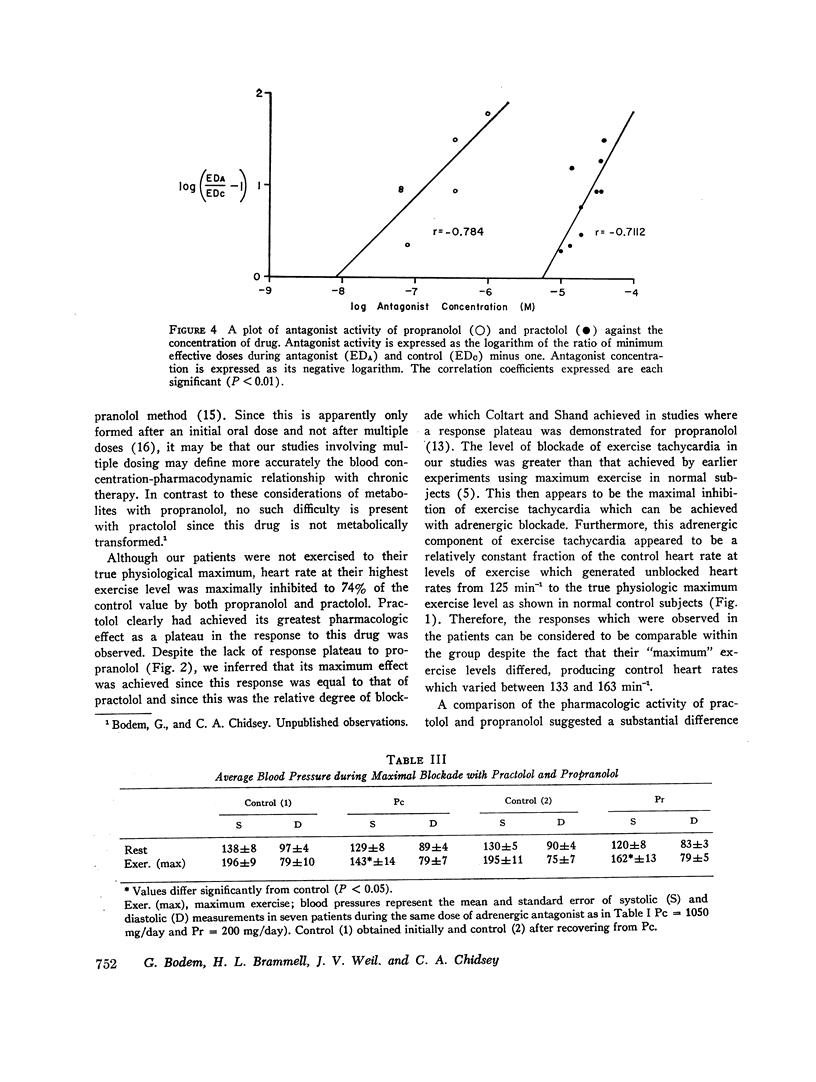
The pharmacodynamic activities of two beta adrenergic antagonists, propranolol and practolol, were compared in eight hypertensive patients. The activity of each antagonist was established in relation to its blood concentration at maximal and submaximal adrenergic blockade defined by inhibition of exercise tachycardia. Maximal inhibition of exercise tachycardia was comparable with both drugs and averaged 74±7% of the control value during drug treatment. This inhibition was achieved with a blood concentration of 2.5±0.4 μg/ml practolol and 0.10±0.08 μg/ml propranolol. The antagonist activities of these drugs against adrenergic stimulation with isoproterenol infusion indicated a much greater relative potency of propranolol against this stimulus, and in vivo estimates of PA2 values differed by more than 600-fold. Relative antagonist activity of practolol during isoproterenol stimulation was equivalent both at cardiac (inotropic and chronotropic) and at vascular adrenergic receptors, whereas greater antagonist activity of propranolol was observed at vascular receptors than at cardiac receptors. Thus, the activity of practolol was not limited to cardiac receptors as previously suggested. Practolol did not reduce cardiac output at any dose level and the effect on resting blood pressure was small. Both practolol and propranolol had much greater hypotensive activity during exercise. These studies have defined the differing pharmacodynamic activities on the cardiovascular system of two effective beta adrenergic receptor antagonists and have established the blood levels of these antagonists necessary to achieve effective adrenergic blockade.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blinks J. R. Evaluation of the cardiac effects of several beta adrenergic blocking agents. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Feb 10;139(3):673–685. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb41237.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodem G., Chidsey C. A. Simple fluorometric method for estimating practolol (1-(4-aminophenoxy)-3-isopropylaminopropan-2-0l) in blood and urine. Clin Chem. 1972 Apr;18(4):363–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHIDSEY C. A., HARRISON D. C., BRAUNWALD E. Augmentation of the plasma nor-epinephrine response to exercise in patients with congestive heart failure. N Engl J Med. 1962 Sep 27;267:650–654. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196209272671305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleaveland C. R., Shand D. G. Effect of route of administration on the relationship between -adrenergic blockade and plasma propranolol level. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1972 Mar-Apr;13(2):181–185. doi: 10.1002/cpt1972132181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coltart D. J., Shand D. G. Plasma propranolol levels in the quaniitative assessment of beta-adrenergic blockade in man. Br Med J. 1970 Sep 26;3(5725):731–734. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5725.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlop D., Shanks R. G. Selective blockade of adrenoceptive beta receptors in the heart. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1968 Jan;32(1):201–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1968.tb00444.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein S., Robinson B. F., Kahler R. L., Braunwald E. Effects of beta-adrenergic blockade on the cardiac response to maximal and submaximal exercise in man. J Clin Invest. 1965 Nov;44(11):1745–1753. doi: 10.1172/JCI105282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohlich E. D., Tarazi R. C., Dustan H. P., Page I. H. The paradox of beta-adrenergic blockade in hypertension. Circulation. 1968 Mar;37(3):417–423. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.37.3.417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore E., Weil J., Chidsey C. Treatment of essential hypertension with a new vasodilator in combination with beta-adrenergic blockade. N Engl J Med. 1970 Mar 5;282(10):521–527. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197003052821001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison D. C., Griffin J. R. Metabolic and circulatory responses to selective adrenergic stimulation and blockade. Circulation. 1966 Aug;34(2):218–225. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.34.2.218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lands A. M., Arnold A., McAuliff J. P., Luduena F. P., Brown T. G., Jr Differentiation of receptor systems activated by sympathomimetic amines. Nature. 1967 May 6;214(5088):597–598. doi: 10.1038/214597a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leon D. F., Thompson M. E., Shaver J. A., McDonald R. H., Jr Hemodynamic effects of practolol at rest and during exercise. Circulation. 1972 Jan;45(1):46–54. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.45.1.46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy B. A comparison of the adrenergic receptor blocking properties of 1-(4'-methylphenyl)-2-isopropylamino-propanol-HCl and propranolol. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1967 Jun;156(3):452–462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prichard B. N., Gillam P. M. Treatment of hypertension with propranolol. Br Med J. 1969 Jan 4;1(5635):7–16. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5635.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shand D. G., Nuckolls E. M., Oates J. A. Plasma propranolol levels in adults with observations in four children. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1970 Jan-Feb;11(1):112–120. doi: 10.1002/cpt1970111112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VENDSALU A. Studies on adrenaline and noradrenaline in human plasma. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1960;49(173):1–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissler A. M., Harris W. S., Schoenfeld C. D. Bedside technics for the evaluation of ventricular function in man. Am J Cardiol. 1969 Apr;23(4):577–583. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(69)90012-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winer N., Chokshi D. S., Yoon M. S., Freedman A. D. Adrenergic receptor mediation of renin secretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1969 Sep;29(9):1168–1175. doi: 10.1210/jcem-29-9-1168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


